|
|
|
| Investigation and application of closely spaced linear dense arrays in detecting urban underground spaces |
JIANG Wei-Long1( ), YIN Qi-Feng2( ), YIN Qi-Feng2( ), YU Sen-Lin3, ZHANG Hua1, QIU Xiu-Quan1, HUANG Wei-Hong1, BAO Xing-Yue1, DING Ming-Yan4 ), YU Sen-Lin3, ZHANG Hua1, QIU Xiu-Quan1, HUANG Wei-Hong1, BAO Xing-Yue1, DING Ming-Yan4 |
1. National Key Laboratory of Uranium Resource Exploration-Mining and Nuclear Remote Sensing,East China University of Technology,Nanchang 330013,China
2. College of Transportation Engineering,Nanjing University of Technology,Nanjing 211816,China
3. Nanjing Surveying and Mapping Institute Co.,Ltd.,Nanjing 210019,China
4. Xinjiang Oilfield Company,PetroChina Company Limited,Karamay 834000,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Rapid,convenient,and reliable acquisition of shallow urban underground structures in densely populated areas with intense anthropogenic noise is significant for promoting the digital transparency and safe development of urban underground spaces.With the advancement of nodal seismometers,passive-source seismic imaging methods have been widely applied to image underground structures at various scales,successfully demonstrating the detection of shallow underground structures in urban underground spaces.Under the constraints imposed by urban roads and narrow spaces,linear dense arrays show high adaptability among various passive-source array deployment patterns.In a test area with known underground pipeline anomalies,this study designed three linear array arrangement patterns with spacings of 1 m,3 m,and 5 m for 1 h continuous observation of noise data.This study employed the extended spatial autocorrelation(ESPAC) method to extract surface-wave frequency dispersion data for shear-wave velocity inversion.Moreover,by comprehensively analyzing the raw data,frequency dispersion curves,and the shear-wave velocity profile obtained through inversion,this study provided a scientific understanding and basis for the parameter selection of the closely spaced linear dense array observation system for passive-source seismic detection of urban underground spaces.Finally,based on the experimental results,this study selected a scientifically reasonable observation system for detection in a real-world urban underground space construction and exploration project,revealing the complete stratigraphic structure and water-conducting structures like fracture zones at the construction area.Therefore,closely spaced linear dense arrays can yield higher resolution and accuracy in detecting urban underground spaces,showing higher adaptability in areas with severe anthropogenic interference.
|
|
Received: 21 December 2024
Published: 22 July 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
Overview map of the experimental area
|

|
Three seismic profiles
|

| 线号 | 道间距/m | 仪器数量 | 测线总长度/m | | L1 | 1 | 60 | 59 | | L2 | 3 | 36 | 105 | | L3 | 5 | 29 | 140 |
|
Line information
|
|
Small-scale array layout diagram
|
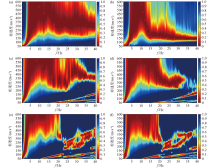
|
Dispersion spectra from different instruments along three survey lines
a、c、e—dispersion spectra of Lines L1,L2,and L3 at 15 m depth respectively;b、d、f—dispersion spectra of Lines L1,L2,and L3 at 30 m depth respectively
|
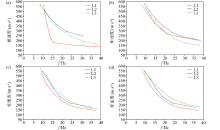
|
Dispersion curve plots of the micro-tremor array
a—dispersion curves for survey lines L1 to L3 at 15 meters depth;b—dispersion curves for survey lines L1 to L3 at 30 meters depth;c—dispersion curves for survey lines L1 to L3 at 45 meters depth;d—dispersion curves for survey lines L1 to L3 at 50 meters depth
|
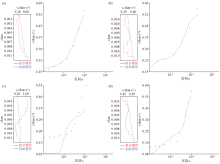
|
Initial,fitted model,and fitted curve
a、b、c—theoretical models and fitting curves for survey lines L1,L2,and L3 at 33 m depth;d—theoretical models and fitting curves for survey lines L3 at 25 m depth
|
|
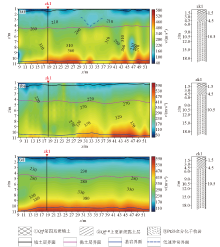
Shear wave velocity profile and borehole map
a、b、c—S-wave velocity profiles for survey lines L1,L2,and L3
|
|
Diagram of array layout and rolling arrangement methods
|
|
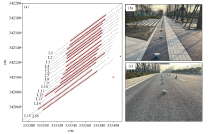
Currently completed layout map of passive source seismic imaging survey lines
|
|
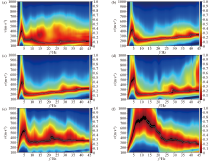
Typical frequency spectrum diagram for profiles
|
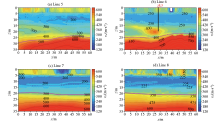
|
Cross-sectional transverse wave velocity profile for survey lines L5~L8
|
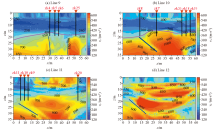
|
Cross-sectional transverse wave velocity profile for survey lines L9~L12
|
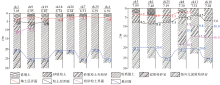
|
Borehole profile map
|
| [1] |
程光华, 苏晶文, 李采, 等. 城市地下空间探测与安全利用战略构想[J]. 华东地质, 2019, 40(3):226-233.
|
| [1] |
Cheng G H, Su J W, Li C, et al. Strategic thinking of urban underground space exploration and safe utilization[J]. East China Geology, 2019, 40(3):226-233.
|
| [2] |
陈颙, 陈棋福, 黄静, 等. 减轻地震灾害[J]. 地震学报, 2003, 25(6):621-629,675.
|
| [2] |
Chen Y, Chen Q F, Huang J, et al. Reduction of earthquake disasters[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 2003, 25(6):621-629,675.
|
| [3] |
王栎, 陈颙, 于大勇, 等. 未来城市地下空间探测的关键技术——大陆气枪震源[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(12):4750-4759.
|
| [3] |
Wang L, Chen Y, Yu D Y, et al. Seismic airgun the key technology of future urban underground space exploration[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(12):4750-4759.
|
| [4] |
何继善, 李帝铨, 胡艳芳, 等. 城市强干扰环境地下空间探测技术与应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2022, 19(5):559-567.
|
| [4] |
He J S, Li D Q, Hu Y F, et al. Geophysical exploration methods for strong interference urban underground space[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2022, 19(5):559-567.
|
| [5] |
王成善, 周成虎, 彭建兵, 等. 论新时代我国城市地下空间高质量开发和可持续利用[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(3):1-8.
|
| [5] |
Wang C S, Zhou C H, Peng J B, et al. A discussion on high-quality development and sustainable utilization of China’s urban underground space in the new era[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(3):1-8.
|
| [6] |
杨文采, 瞿辰, 任浩然, 等. 青藏高原地壳地震纵波速度的层析成像[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(1):2-14.
|
| [6] |
Yang W C, Qu C, Ren H R, et al. Crustal P-wave seismic tomography of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) plateau[J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(1):2-14.
|
| [7] |
刘铁华, 刘铁, 程光华, 等. 复杂城市环境下地球物理勘探技术研究进展[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2020, 17(6):711-720.
|
| [7] |
Liu T H, Liu T, Cheng G H, et al. Research progress of geophysical exploration technology in complex urban environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2020, 17(6):711-720.
|
| [8] |
葛如冰. 高密度电阻率法在城市地下目的物探测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2011, 35(1):136-139.
|
| [8] |
Ge R B. The application of high-density resistivity to detecting urban underground objects[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 35(1):136-139.
|
| [9] |
李巧灵, 雷晓东, 李晨, 等. 微动测深法探测厚覆盖层结构——以北京城市副中心为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(4):1635-1643.
|
| [9] |
Li Q L, Lei X D, Li C, et al. Exploring thick overburden structure by microtremor survey:A case study in the subsidiary administrative center[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(4):1635-1643.
|
| [10] |
梁锋, 高磊, 王志辉, 等. 利用背景噪声层析成像研究济南浅层横波速度结构[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(3):129-139.
|
| [10] |
Liang F, Gao L, Wang Z H, et al. Study of the shear wave velocity structure of underground shallow layer of Jinan by ambient noise tomography[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(3):129-139.
|
| [11] |
王爽, 孙新蕾, 秦加岭, 等. 利用密集地震台网高频环境噪声研究广东新丰江库区浅层地下结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(2):593-603.
|
| [11] |
Wang S, Sun X L, Qin J L, et al. Fine fault structure of Xinfengjiang water reservoir area from high-frequency ambient noise tomography[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(2):593-603.
|
| [12] |
Mordret A, Roux P, Boué P, et al. Shallow three-dimensional structure of the San Jacinto fault zone revealed from ambient noise imaging with a dense seismic array[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2019, 216(2):896-905.
|
| [13] |
Gu N, Wang K D, Gao J, et al. Shallow crustal structure of the tanlu fault zone near Chao Lake in Eastern China by direct surface wave tomography from local dense array ambient noise analysis[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2019, 176(3):1193-1206.
|
| [14] |
刘国峰, 刘语, 孟小红, 等. 被动源面波和体波成像在内蒙古浅覆盖区勘探应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(3):937-948.
|
| [14] |
Liu G F, Liu Y, Meng X H, et al. Surface wave and body wave imaging of passive seismic exploration in shallow coverage area application of Inner Mongolia[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(3):937-948.
|
| [15] |
曾求, 储日升, 盛敏汉, 等. 基于地震背景噪声的四川威远地区浅层速度结构成像研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63(3):944-955.
|
| [15] |
Zeng Q, Chu R S, Sheng M H, et al. Seismic ambient noise tomography for shallow velocity structures beneath Weiyuan,Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(3):944-955.
|
| [16] |
田原, 瞿辰, 王伟涛, 等. 四川盐源盆地短周期密集台阵背景噪声分布特征分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63(6):2248-2261.
|
| [16] |
Tian Y, Qu C, Wang W T, et al. Characteristics of the ambient noise distribution recorded by the dense seismic array in the Yanyuan Basin,Sichuan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(6):2248-2261.
|
| [17] |
Shao X H, Yao H J, et al. Shallow crustal velocity structures revealed by active source tomography and fault activities of the Mianning-Xichang segment of the Anninghe fault zone,SW China[J]. Earth and Planetary Physics, 2022,6.
|
| [18] |
Xu H R, Luo Y H, Chen C, et al. 3D shallow structures in the Baogutu area,Karamay,determined by eikonal tomography of short-period ambient noise surface waves[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2016,129:101-110.
|
| [19] |
Duvall T L Jr, Jeffferies S M, Harvey J W, et al. Time-distance helioseismology[J]. Nature, 1993, 362(6419):430-432.
|
| [20] |
Aki K. Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves,with special reference to microtremors[J]. Bulletin of the Earthquake Research Institute, 1957, 35(3):415-456.
|
| [21] |
Asten M W. On bias and noise in passive seismic data from finite circular array data processed using SPAC methods[J]. Geophysics, 2006, 71(6):V153-V162.
|
| [22] |
Ling S, Okada H. An extended use of the spatial autocorrelation method for the estimation of geological structures using microtremors[C]// Nagoya:Proceedings of the 89th SEGJ Conference, Society of Exploration Geophysicists of Japan,1993:44-48.
|
| [23] |
傅庆凯. 直线型台阵微动技术在隧道勘察中的应用研究[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2023, 45(6):757-765.
|
| [23] |
Fu Q K. Research and application of engineering geological microtremor survey technology in tunnel investigation[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 45(6):757-765.
|
| [24] |
高级, 张海江, 查华胜, 等. 台阵和噪声源分布对微动成像的影响及其在盐矿溶腔探测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2023, 66(6):2489-2506.
|
| [24] |
Gao J, Zhang H J, Zha H S, et al. The effect of different arrays and noise source distribution on microtremor imaging and its application in solute salt mine cavity detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2023, 66(6):2489-2506.
|
| [25] |
郭瑛霞, 张丽峰, 胡维云, 等. 地震背景噪声成像研究综述[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 2023, 44(2):18-26.
|
| [25] |
Guo Y X, Zhang L F, Hu W Y, et al. A review of ambient noise tomography[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research, 2023, 44(2):18-26.
|
| [26] |
敬嘉良, 陈国雄, 程飞, 等. 超短时线性台阵背景噪声成像技术在浅层地质结构探测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2024, 39(1):63-76.
|
| [26] |
Jing J L, Chen G X, Cheng F, et al. Application of ultra short time linear array ambient noise imaging technology to detect shallow geological structures[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2024, 39(1):63-76.
|
| [27] |
秦长春, 王国顺, 李婧. 主动源面波采集装置改进及在地铁施工勘察中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2024, 48(1):264-271.
|
| [27] |
Qin C C, Wang G S, Li J. Improvement in active-source surface wave acquisition device and its application in subway construction exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1):264-271.
|
| [28] |
李红星, 李涛, 章晨望, 等. 浅地表面波频散曲线组合勘探方法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(16):6343-6349.
|
| [28] |
Li H X, Li T, Zhang C W, et al. Exploration methods for subsurface wave by combined dispersion curves[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(16):6343-6349.
|
| [29] |
张泽奇, 高级, 刘梁, 等. 基于三角和线性台阵的煤矿背景噪声成像技术适用性研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(6):1528-1537.
|
| [29] |
Zhang Z Q, Gao J, Liu L, et al. Applicability of an imaging method for ambient noise in coal mines based on triangular and linear arrays[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6):1528-1537.
|
| [30] |
刘志清, 赵振国, 李添才, 等. 山区公路微动探测方法应用试验研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2023, 38(2):823-831.
|
| [30] |
Liu Z Q, Zhao Z G, Li T C, et al. Research for the application of microtremor survey method to high-way construction in mountainous areas[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2023, 38(2):823-831.
|
| [31] |
倪红玉, 郑海刚, 赵楠, 等. 基于密集线性台阵的背景噪声成像在明光市城市活断层调查中的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(7):2518-2531.
|
| [31] |
Ni H Y, Zheng H G, Zhao N, et al. Application of ambient noise tomography with a dense linear array in prospecting active faults in the Mingguang city[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(7):2518-2531.
|
| [1] |
DING Wei-Zhong, SUN Fu-Wen, LI Jian-Hua, ZHENG Cai-Jun, LIN Pin-Rong, QI Fang-Shuai. Development of multi-parameter parallel measuring high-density electrical system for urban underground space exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(6): 1448-1454. |
| [2] |
YONG Fan, LIU Zi-Long, JIANG Zheng-Zhong, LUO Shui-Yu, LIU Jian-Sheng. The key technology of shallow imaging in urban 3D seismic data processing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1266-1274. |
|
|
|
|

