|
|
|
| Petrophysical modeling of tight sandstones of the Lianggaoshan Formation,Southeast Sichuan |
ZHANG Zheng-Yu-Cheng( ), SU Jian-Long ), SU Jian-Long |
| Exploration Company,SINOPEC,Chengdu 610041,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The exploration and exploitation practices in the Sichuan Basin in recent years indicate that breakthroughs have been achieved in the Jurassic continental tight sandstones.Nevertheless,due to the low porosity and permeability of tight sandstone,conventional post-stack inversion frequently exhibits limited resolution,failing to meet the accuracy requirements for the prediction of actual exploration reservoirs.This necessitates pre-stack inversion for detailed characterization of tight sandstones,while S-wave velocity is crucial to pre-stack inversion.Based on continental exploration wells drilled in the southeastern Sichuan Basin in recent years,this study developed a petrophysical modeling technique for dense sandstones in this region.Specifically,given the low permeability of tight sandstones and the uneven mixing of fluids in the pore space,the Domenico model was preferentially employed to calculate the pore fluid modulus.Although fluid modulus and density are inevitably variable under the actual subsurface conditions,previous studies typically use constant values to conduct petrophysical modeling for tight sandstones.In this study,depth-dependent values were applied.Tight sandstones in the southeastern Sichuan Basin generally exhibit a porosity of less than 10%.Therefore,calculations using the Nur and the Krief models will yield high errors.Given this,this study preferred using the Lee-Pride model to calculate the skeleton modulus and controlled the relationship between the rock matrix and the skeleton by introducing the value of the cementation parameter.The application of the established petrophysical model of tight sandstone to an actual survey area indicates high agreement with data from actual wells.Additionally,based on log statistics,Poisson's ratio,the most sensitive parameter is used for high-precision pre-stack inversion in the proposed technique,enabling detailed characterization and prediction of the internal structure of channel sandstones.
|
|
Received: 09 September 2024
Published: 22 April 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
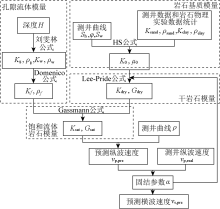
|
Flowchart for petrophysical modeling
|
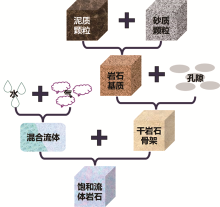
|
Schematic of petrophysical modeling
|

| 类型 | 体积模量/GPa | 剪切模量/GPa | 密度/(g·cm-3) | | 石英 | 52 | 31 | 2.72 | | 黏土 | 23 | 7 | 2.54 | | 气 | 0.001 5 | 0 | 0.002 | | 水 | 2.2 | 0 | 1.1 |
|
Bulk modulus, shear modulus and density of quartz, clay and fluids
|

| 参数 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | | 孔隙度/% | 2.00 | 12.57 | 4.24 | | 含水饱和度/% | 3.21 | 100 | 52.10 | | 泥质含量/% | 1.06 | 62.19 | 21.90 |
|
Maximum, minimum and average values of porosity, water saturation and mud content in logging data
|
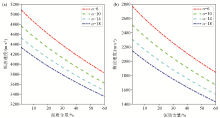
|
Variation of longitudinal(a) and transverse(b) wave velocity with mud content and consolidation parameter α
|
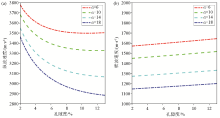
|
Variation of longitudinal(a) and transverse(b) wave velocity with porosity and consolidation parameter α
|
|
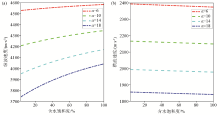
Variation of longitudinal(a) and transverse(b) wave velocity with water saturation and consolidation parameter α
|
|
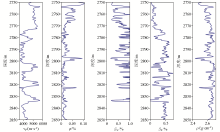
Logging data from well A is required for the petrophysical modeling process
|
|
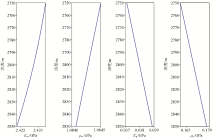
Bulk modulus and density of water and gas in pores during petrophysical modeling
|
|
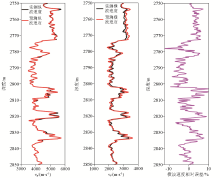
Relative error between measured and predicted longitudinal and transverse wave results and between measured and predicted transverse wave results for well A
|
|
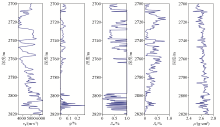
The petrophysical modeling process requires the number of logs in well B
|
|
Measured and predicted longitudinal wave velocities and predicted transverse wave velocities in well B
|
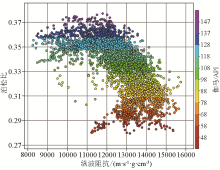
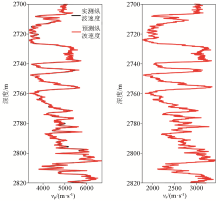
|
Poisson’s ratio and longitudinal wave impedance rendezvous plot for well A
|
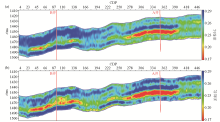
|
Comparison of Poisson’s ratio inversions obtained using well A(a) and also using well A and B(b)
|
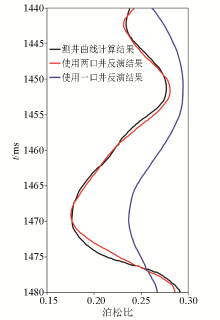
|
Comparison chart of original Poisson’s ratio logging curve and two Poisson’s ratio inversion result curves
|
| [1] |
Ruiz F, Cheng A. A rock physics model for tight gas sand[J]. Leading Edge, 2010, 29(12):1484-1489.
|
| [2] |
Avseth P, Johansen T A, Bakhorji A, et al. Rock-physics modeling guided by depositional and burial history in low-to-intermediate-porosity sandstones[J]. Geophysics, 2014, 79(2):D115-D121.
|
| [3] |
未晛, 杨志芳, 晏信飞, 等. 改进型随机斑块饱和模型及其在致密气层检测中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2018, 53(6):1227-1234.
|
| [3] |
Wei S, Yang Z F, Yan X F, et al. Modified continuous random patchy-saturation model in tight gas detection[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2018, 53 (6):1227-1234.
|
| [4] |
乔汉青, 方慧, 杜炳锐, 等. 基于改进Xu-White模型的富有机质页岩横波预测方法研究[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2023, 45(4):411-419.
|
| [4] |
Qiao H Q, Fang H, Du B R, et al. Research on transverse wave prediction method of organic-rich shale based on improved Xu-White model[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 45(4):411-419.
|
| [5] |
Castagna J P, Batzle M L, Eastwood R L. Relationships between compressional-wave and shear-wave velocities in clastic silicate rocks[J]. Geophysics, 1985, 50(4):571-581.
|
| [6] |
Han D H, Nur A, Morgan D. Effects of porosity and clay content on wave velocities in sandstones[J]. Geophysics, 1986, 51(11):2093-2107.
|
| [7] |
Greenberg M L, Castagna J P. Shear-wave velocity estimation in porous rocks:Theoretical formulation,preliminary verification and applications[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 1992, 40(2):195-209.
|
| [8] |
Rajabi M, Bohloli B, Ahangar E G. Intelligent approaches for prediction of compressional,shear and Stoneley wave velocities from conventional well log data:A case study from the Sarvak carbonate reservoir in the Abadan Plain(Southwestern Iran)[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2010, 36(5):647-664.
|
| [9] |
王晓光. 自适应BP神经网络在横波速度预测中的应用[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2013, 25(5):86-88.
|
| [9] |
Wang X G. Application of self-adaptive BP neural network to the prediction of shear wave velocity[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2013, 25(5):86-88.
|
| [10] |
Zhang Y, Zhong H R, Wu Z Y, et al. Improvement of petrophysical workflow for shear wave velocity prediction based on machine learning methods for complex carbonate reservoirs[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 192:107234.
|
| [11] |
Xu S, White R E. A new velocity model for clay-sand mixtu res[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 1995, 43(1):91-118.
|
| [12] |
Xu S, Payne M A. Modeling elastic properties in carbonate rocks[J]. Leading Edge, 2009, 28(1):66-74.
|
| [13] |
Lee, Myung W. A simple method of predicting S-wave velocity[J]. Geophysics, 2006, 71(6):F161-F164.
|
| [14] |
张广智, 李呈呈, 印兴耀, 等. 基于修正Xu-White模型的碳酸盐岩横波速度估算方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2012, 47(5):717-722.
|
| [14] |
Zhang G Z, Li C C, Yin X Y, et al. A shear velocity estimation method for carbonate rocks based on the improved Xu-White model[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2012, 47(5):717-722.
|
| [15] |
张秉铭, 刘致水, 刘俊州, 等. 富有机质泥页岩岩石物理横波速度预测方法研究[J]. 石油物探, 2018, 57(5):658-667.
|
| [15] |
Zhang B M, Liu Z S, Liu J Z, et al. A new S-wave velocity estimation method for organic-enriched shale[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2018, 57(5):658-667.
|
| [16] |
王斌, 陈祥忠, 陈娟, 等. 四川盆地侏罗系致密砂岩弹性特征及岩石物理建模[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63 (12):4528-4539.
|
| [16] |
Wang B, Chen X Z, Chen J, et al. Elastic characteristics and petrophysical modeling of Jurassic tight sandstone in Sichuan Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63 (12):4528-4539.
|
| [17] |
张佳佳, 李宏兵, 张广智, 等. 基于多孔可变临界孔隙度模型的储层孔隙结构表征[C]// SPG/SEG北京2016国际地球物理会议, 2016.
|
| [17] |
Zhang J J, Li H B, Zhang G Z, et al. Characterization of reservoir pore structure based on porous variable critical porosity model[C]// SPG/SEG Beijing 2016 International Geophysical Conference, 2016.
|
| [18] |
Hashin Z, Shtrikman S. A variational approach to the theory of the elastic behaviour of multiphase materials[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1963, 11(2):127-140.
|
| [19] |
Hill R. The elastic behavior of crystalline aggregate[J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society:Section A, 1952, 65(5):349.
|
| [20] |
Domenico S N. Elastic properties of unconsolidated porous sand reservoirs[J]. Geophysics, 1977, 42(7):1339-1368.
|
| [21] |
贾凌云, 李琳, 王千遥, 等. 流体体积模量计算方法研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018, 33 (1):223-227.
|
| [21] |
Jia L Y, Li L, Wang Q Y, et al. Research on calculation methods of fluid bulk modulus[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 33 (1):223-227.
|
| [22] |
Wood A B, Lindsay R B. A textbook of sound[J]. Physics Today, 1956, 9(11):37-37.
|
| [23] |
刘雯林. 油气田开发地震技术[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1996.
|
| [23] |
Liu W L. Seismic technology for oil and gas field development[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1996.
|
| [24] |
Krief M, Garat J, Stellingwerff J, et al. A petrophysical interpretation using the velocities of P and S waves(full-waveform sonic)[J]. Log Analyst, 1990, 31:355-369.
|
| [25] |
Nur A. Critical porosity and the seismic velocities in rocks[J]. EOS, 1992, 73(1):43-66.
|
| [26] |
Pride S R. Relationships between seismic and hydrological properties[J]. Hydrogeophysics, 2005:217-255.
|
| [27] |
张佳佳, 李宏兵, 刘怀山, 等. 几种岩石骨架模型的适用性研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2010, 25(5):1697-1702.
|
| [27] |
Zhang J J, Li H B, Liu H S, et al. Accuracy of dry frame models in the study of rock physics[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2010, 25(5):1697-1702.
|
| [1] |
XU Feng, SI Zhao-Wei, LIANG Zhong-Kui, TIAN Chao-Guo, LUO Lan, GUO Yu-Hang. A method for quality classification of tight sandstone reservoirs in the Ordos Basin based on pore structures and multiphase seepage capacity[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(1): 138-147. |
| [2] |
HE Xiao-Long, ZHANG Bing, YANG Kai, HE Yi-Fan, LI Zhuo. A log-based lithofacies identification method based on random forest and sedimentary microfacies characteristics:A case study of tight sandstones in the second member of the Xujiahe Formation in the Xinchang area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1337-1347. |
|
|
|
|

