|
|
|
| Metallogenic prediction based on the deep interest evolution network: A case study of supergenetic calcrete-hosted uranium deposits in Western Australia |
ZHANG Chang-Jiang1,2( ), HE Jian-Feng1,2,3( ), HE Jian-Feng1,2,3( ), NIE Feng-Jun1,2, XIA Fei1,2, LI Wei-Dong1,2, WANG Xue-Yuan1,2,3, ZHANG Xin1,2, ZHONG Guo-Yun1,2,3 ), NIE Feng-Jun1,2, XIA Fei1,2, LI Wei-Dong1,2, WANG Xue-Yuan1,2,3, ZHANG Xin1,2, ZHONG Guo-Yun1,2,3 |
1. Jiangxi Engineering Technology Research Center of Nuclear Geoscience Data Science and System, East China University of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China
2. School of Information Engineering, East China University of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China
3. Jiangxi Engineering Laboratory on Radioactive Geoscience and Big Data Technology, East China University of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Recommendation system algorithms, having recently garnered significant attention in the field of digital Earth science, are expected to be widely applied in metallogenic prediction. Traditional metallogenic prediction studies fail to fully mine the various types of semantic information in massive geoscience data. The deep interest evolution network (DIEN), as a recommendation system algorithm, can fully mine semantic information to predict user preferences. Therefore, this study employed the DIEN model as the prediction model and the semantic information extracted from bedrock interpretation as the ore-controlling elements according to the database provided by the Western Australian government. The model was trained to perform metallogenic prediction for the study area. The prediction results indicate that 92.95% of uranium ore occurrences fell within the medium-high probability zone in the prediction map, with some unknown zones also showing high prediction probabilities. After removing known uranium ore occurrences in some zones, the retrained model still yielded medium-high prediction probabilities in these zones. The results suggest that the DIEN can effectively mine semantic information in metallogenic prediction studies, and the DIEN model exhibits strong predictive capacity for the study area, providing a novel approach for metallogenic prediction studies.
|
|
Received: 23 September 2024
Published: 22 April 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
15])
">
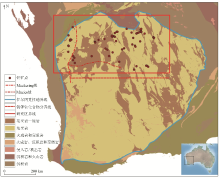
|
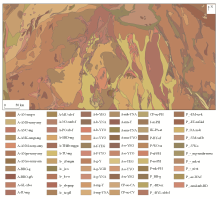
Regional of Yilgarn Craton geology(modified from GSWA[15])
|
22],2019)
">
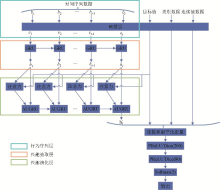
|
DIEN model architecture(modified from Zhou, et al.[22],2019)
|
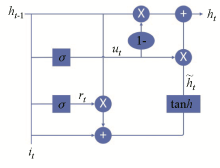
|
GRU structure
|

|
Uranium point assignment diagram
|
|
Raster data set
|
|
Bedrock type
|

|
Rock type
|

|
Initial stratigraphic map
|

|
Termination stratigraphic
|

|
Initial geological age
|

|
Termination geologic age
|
|
Loss curve
|
|
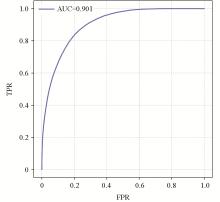
ROC curve
|
|
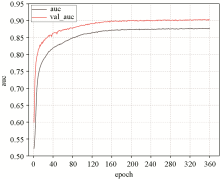
AUC curve
|
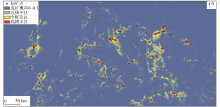
|
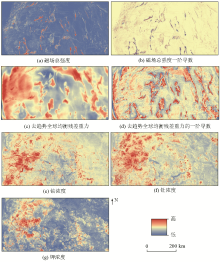
Study area prediction
|
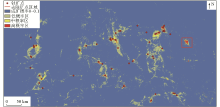
|
Study area prediction (selected uranium sites with some areas removed)
|
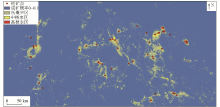
|
Study area prediction (30% of selected uranium deposits are removed)
|
| [1] |
The OECD Nuclear Energy Agency. Uranium 2022:Resources,production and demand[M]. Paris: OECD Publishing: 2023.
|
| [2] |
张士红, 林子瑜. 大数据时代(铀)成矿预测技术方法变革[J]. 铀矿地质, 2021, 37(5):913-919.
|
| [2] |
Zhang S H, Lin Z Y. Technological and methodological changes of (uranium) mineral resources prediction in big data era[J]. Uranium Geology, 2021, 37(5):913-919.
|
| [3] |
Needham S. Yeelirrie uranium deposit in Western Australia[R]. Australia: Department of Parliamentary Services, 2009.
|
| [4] |
左仁广. 基于深度学习的深层次矿化信息挖掘与集成[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2019, 38(1):53-60,203.
|
| [4] |
Zuo R G. Deep learning-based mining and integration of deep-level mineralization information[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2019, 38(1):53-60,203.
|
| [5] |
黄立威, 江碧涛, 吕守业, 等. 基于深度学习的推荐系统研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(7):1619-1647.
|
| [5] |
Huang L W, Jiang B T, Lyu S Y, et al. Survey on deep learning-based recommender systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(7):1619-1647.
|
| [6] |
路英川, 李鹏, 王浩, 等. 大数据时代矿床学研究发展状况综述[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2021, 38(3):295-310.
|
| [6] |
Lu Y C, Li P, Wang H, et al. A review on the development of mineral deposit science in the era of big data[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2021, 38(3):295-310.
|
| [7] |
周永章, 左仁广, 刘刚, 等. 数学地球科学跨越发展的十年:大数据、人工智能算法正在改变地质学[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2021, 40(3):556-573.
|
| [7] |
Zhou Y Z, Zuo R G, Liu G, et al. The great-leap-forward development of mathematical geoscience during 2010-2019:Big data and artificial intelligence algorithm are changing mathematical geoscience[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(3):556-573.
|
| [8] |
郭永志. 西澳大利亚太古代伊尔岗地块的地质情况简介[J]. 国外前寒武纪地质, 1978, 1(4):45-63.
|
| [8] |
Guo Y Z. Brief introduction to the geological situation of Archean Yilgam block in Western Australia[J]. North China Geology, 1978, 1(4):45-63.
|
| [9] |
地矿部赴西澳考察组. 赴西澳考察综合报告[J]. 国外地质勘探技术, 1989(5):46-50,9.
|
| [9] |
Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources Delegation to Western Australia for Inspection and Study. A comprehensive report on the investigation in western Australia[J]. Foreign Geoexploration Technology, 1989(5):46-50,9.
|
| [10] |
李艾银, 齐立平, 孔红杰, 等. 西澳大利亚中西铁矿区地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(S1):228-237.
|
| [10] |
Li A Y, Qi L P, Kong H J, et al. Geological features and exploration indicators of the Midwest iron ore district in western Australia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(S1):228-237.
|
| [11] |
陈秀法, 张振芳. 澳大利亚铀矿资源现状与勘查开发建议[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(S1):902-903.
|
| [11] |
Chen X F, Zhang Z F. Present situation of uranium resources in Australia and suggestions for exploration and development[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(S1):902-903.
|
| [12] |
Anand R R, Paine M. Regolith geology of the Yilgarn Craton,Western Australia:implications for exploration[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2002, 49(1):3-16.
|
| [13] |
Anand R R, Butt C R M. A guide for mineral exploration through the regolith in the Yilgarn Craton,Western Australia[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2010, 57(8):1015-1114.
|
| [14] |
Butt C R M, Horwitz R C, and Mann A W. Uranium occurrences in calcrete and associated sediments in Western Australia[R]. CSIRO,Division of Mineralogy,Minerals Research Laboratories,Report FP16.
|
| [15] |
Geological Survey of Western AustraliaGSWA. Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Reasearch Organization,1997. GSWA 2009 extended abstracts:Promoting the prospectivity of Western Australia[R]. Western Australia: Geological Survey of Western Australia, 2009.
|
| [16] |
Rakel A, Mcconchie D, 张兴余. 澳大利亚内陆古水系中钙结岩和膏结岩岩相的分类和成因及其与钒钾铀矿矿化的关系[J]. 国外铀矿地质, 1985, 2(1):6-15.
|
| [16] |
Arakel A, Mcconchie D, Zhang X Y. Classification and genesis of calcareous and gypsum lithofacies in the ancient inland water system of Australia and their relationship with the mineralization of vanadium-potassium-uranium deposits[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 1985, 2(1):6-15.
|
| [17] |
Briot P, 王智儒. 西澳伊利里含铀钙结岩水文地质环境[J]. 国外铀矿地质, 1984, 1(3):44-52.
|
| [17] |
Briot P, Wang Z R. Hydrogeological environment of uranium-bearing calcium nodules in Yili,western Australia[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 1984, 1(3):44-52.
|
| [18] |
Joly A, Porwal A, McCuaig T C, et al. Mineral systems approach applied to GIS-based 2D-prospectivity modelling of geological regions:Insights from Western Australia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 71:673-702.
|
| [19] |
Porwal A, Das R D, Chaudhary B, et al. Fuzzy inference systems for prospectivity modeling of mineral systems and a case-study for prospectivity mapping of surficial Uranium in Yeelirrie Area,Western Australia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 71:839-852.
|
| [20] |
张云龙. 西澳伊尔加恩地区多元地学信息GIS集成与钙结岩型铀矿成矿预测[D]. 抚州: 东华理工大学, 2014.
|
| [20] |
Zhang Y L. GIS integration of multi-geo-information and mineralization prediction of calcareous uranium deposits in ilgaen,western Australia[D]. Fuzhou: East China Institute of Technology, 2014.
|
| [21] |
Chudasama B, Porwal A, González-Álvarez I, et al. Calcrete-hosted surficial uranium systems in Western Australia:Prospectivity modeling and quantitative estimates of resources.Part 1-Origin of calcrete uranium deposits in surficial environments:A review[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 102:906-936.
|
| [22] |
Zhou G R, Mou N, Fan Y, et al. Deep interest evolution network for click-through rate prediction[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1):5941-5948.
|
| [1] |
LU Wen-Dong, SUN Bin, LI Guang-Jie, WEI Wei, XIA Xiao-Xing, PAN Bing-Lei, SHA Qing, LYU Xiao-Hong, LI Yuan-Chun, QIAO Na. Application of factor analysis in geochemical zoning and its implications: A case study of 1:50,000 stream sediment survey in the Juxian-Wulian area, Shandong Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(2): 411-421. |
| [2] |
TAI Wen-Xing, YANG Cheng-Fu, JIN Xiao-Ye, SHAO Yun-Bin, LIU Guang-Fu, ZHAO Ping, WANG Ze-Peng, TAN Li-Jin. Application of the multi-dimensional study of geochemical anomalies in deep metallogenic prediction of the Zhexiang gold deposit in southwestern Guizhou, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 856-867. |
|
|
|
|

