|
|
|
| Distribution and origin of heavy metals in deep topsoil of the Zhangye Basin in the 1990s |
HE Gan-Di1( ), HE Jin-Zhong1( ), HE Jin-Zhong1( ), NIU Hong-Bing2, ZHANG Zhong-Ping1 ), NIU Hong-Bing2, ZHANG Zhong-Ping1 |
1. Geological Survey of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730000, China
2. Gansu Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration & Development, Lanzhou 730000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Zhangye Basin in Gansu Province serves as a national modern agriculture demonstration area in China. The 1990s was the only period that witnessed both agricultural soil surveys and regional geochemical surveys in the area. This study aims to provide data support for investigating the evolution of the regional soil environment in the area. It gathered geochemical survey data of rocks, deep topsoil, and stream sediments, which were sampled by Gansu geophysical and geochemical exploration teams in the Zhangye Basin and its surrounding mountains in the 1990s. Using these data, this study calculated the background values of elements in various geological units as per the Pauta criterion and sampling media. Focusing on heavy metals, it compared their regional background values in deep topsoil with the nationalsoil background values and the coetaneous averages of farming soil elements surveyed by the agricultural sector, as well as the soil background values of Quaternary sediments with the regional background values. Moreover, it combined geochemical hybrid models with geographical factors. Finally, it explored the distribution characteristics and material sources of heavy metals in deep topsoil of the Zhangye Basin in the 1990s. Compared to the national soil background values, the deep topsoil was enriched in Cu and Cd but depleted in Zn. Contrasting with contemporaneous farming soil, the deep topsoil was significantly enriched in Cr but prominently depleted in Cu, Zn, Pb, and As. In terms of sources, heavy metals Zn, Cd, and As were principally derived from the northern Qilian Mountains, Pb originated from the Longshou Mountains, and Hg and Cr might be primarily associated with human activities. The abnormal H3 potential ecological risk index of the deep topsoil resulted from the combined effect of northwest and southeast winds. The enrichment of heavy metals in deep topsoil was positively correlated with human activity intensity but negatively correlated with neotectonic movement intensity.
|
|
Received: 01 September 2023
Published: 21 October 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
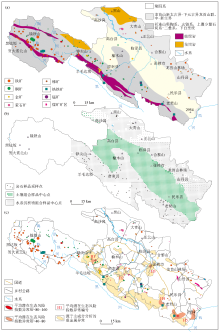
The geological background of Zhanye Basin (a),and its location of deep topsoil samples (b) and heavy metal anomalies(c) in 1990s
|

| 介质 | 地质
单元 | 代码 | 样数 | Cu | Zn | Mo | Cr | Hg | Cd | Pb | As | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Na2O | CaO | MgO | Fe2O3 | Mn | K2O | 岩石
(R) | 大青山
花岗岩 | DGR | 10 | 51.46 | 63.57 | 0.11 | 18.94 | 35.52 | 73.09 | 11.65 | 1.96 | 15.72 | 61.67 | 3.09 | 5.67 | 3.09 | 4.95 | 945.00 | 1.63 | | 龙首山 | LSS | 8 | 18.72 | 69.92 | 0.48 | 17.87 | 19.62 | 65.52 | 18.91 | 2.14 | 14.84 | 63.65 | 3.20 | 4.54 | 2.39 | 4.84 | 887.28 | 2.05 | | 北祁连 | NQL | 56 | 43.46 | 59.44 | 0.33 | 63.17 | 31.80 | 95.09 | 19.42 | 8.79 | 9.44 | 57.48 | 1.02 | 3.64 | 2.59 | 4.97 | 859.58 | 1.40 | 北祁连
蛇绿岩 | NQO | 11 | 21.95 | 50.09 | 0.36 | 55.54 | 34.68 | 76.40 | 25.15 | 8.79 | 10.59 | 65.24 | 1.19 | 2.53 | 2.16 | 4.06 | 585.05 | 1.83 | 土壤
(So) | 第四系 | Q | 1710 | 23.04 | 50.99 | 0.62 | 85.03 | 30.04 | 103.65 | 19.36 | 5.11 | 10.46 | 66.35 | 1.47 | 4.33 | 2.44 | 4.10 | 590.23 | 1.97 | 全国背
景值[39] | | 860 | 20.00 | 67.70 | 1.20 | 53.90 | 40.00 | 74.00 | 23.60 | 9.20 | 12.11 | | 3.61 | 0.99 | 1.04 | 3.90 | 482.00 | 2.16 | 1990耕
作层[6] | | | 35.03 | 89.99 | 15.47 | 50.13 | | | 105.10 | 326.50 | 4.31 | | 0.14 | 5.61 | 1.98 | 3.33 | 611.80 | 0.94 | 水系
沉积
物(St) | 大青山
花岗岩 | DGRS | 5 | 24.77 | 73.14 | 0.42 | 34.26 | 9.15 | 101.91 | 41.86 | 3.27 | 11.69 | 67.24 | 2.45 | 3.60 | 1.75 | 4.08 | 648.90 | 3.38 | | 龙首山 | LSSS | 560 | 12.36 | 33.93 | 0.58 | 35.98 | 16.60 | 73.81 | 22.83 | 1.38 | 9.53 | 69.44 | 1.54 | 3.37 | 1.54 | 2.56 | 470.46 | 2.40 | | 北祁连 | NQLS | 1482 | 27.55 | 62.91 | 0.64 | 83.49 | 28.71 | 107.22 | 20.82 | 11.05 | 12.41 | 63.90 | 1.44 | 3.03 | 2.18 | 4.86 | 646.96 | 2.32 | 北祁连
蛇绿岩 | NQOS | 153 | 36.46 | 69.73 | 0.78 | 153.84 | 31.93 | 136.77 | 19.74 | 15.83 | 11.80 | 62.90 | 1.22 | 3.47 | 3.44 | 5.59 | 765.5 | 1.91 | R/St
相对
偏差
RE/% | 大青山
花岗岩 | | | -70.03 | 14.01 | 115.31 | 57.60 | -118.10 | 32.94 | 112.93 | 50.08 | -29.38 | 8.65 | -23.02 | -44.72 | -55.16 | -19.26 | -37.15 | 70.02 | | 龙首山 | | | -40.91 | -69.31 | 19.73 | 67.25 | -16.65 | 11.90 | 18.78 | -43.16 | -43.58 | 8.69 | -69.90 | -29.61 | -43.50 | -61.73 | -61.40 | 15.33 | | 北祁连 | | | -44.80 | 5.67 | 63.50 | 27.72 | -10.20 | 12.00 | 6.97 | 22.78 | 27.20 | 10.57 | 34.42 | -18.39 | -17.06 | -2.36 | -28.23 | 49.89 | 北祁连
蛇绿岩 | | | 49.68 | 32.78 | 74.89 | 93.89 | -8.25 | 56.64 | -24.09 | 0.15 | 10.77 | -3.65 | 1.99 | 31.32 | 45.84 | 31.85 | 26.72 | 4.33 | | 介质 | 地质
单元 | 代码 | 样数数 | P | B | F | Sb | Ag | Co | La | Li | Nb | Ni | Sn | Sr | Th | Ti | Y | Zr | 岩石
(R) | 大青山
花岗岩 | DGR | 10 | 645.92 | 20.92 | 480.93 | 0.30 | 39.75 | 17.37 | 29.47 | 10.05 | 9.23 | 15.83 | 1.71 | 405.92 | 7.50 | 4151.57 | 22.41 | 159.37 | | 龙首山 | LSS | 8 | 719.21 | 11.01 | 458.75 | 1.24 | 63.91 | 13.87 | 28.69 | 18.69 | 11.08 | 11.01 | 1.66 | 382.43 | 9.16 | 3932.44 | 21.01 | 146.00 | | 北祁连 | NQL | 56 | 268.86 | 23.83 | 487.02 | 2.24 | 78.49 | 13.34 | 16.63 | 16.32 | 10.25 | 35.20 | 2.12 | 140.00 | 9.09 | 2587.70 | 19.99 | 109.13 | 北祁连
蛇绿岩 | NQO | 11 | 363.37 | 18.42 | 368.63 | 5.12 | 83.10 | 11.18 | 24.27 | 13.71 | 9.68 | 22.94 | 1.79 | 122.87 | 9.14 | 2443.03 | 19.25 | 126.00 | 土壤
(So) | 第四系 | Q | 1710 | 541.90 | 37.21 | 471.51 | 0.83 | 58.29 | 11.27 | 34.47 | 21.23 | 11.98 | 33.42 | 2.35 | 160.10 | 9.10 | 3144.46 | 21.02 | 187.83 | 全国背
景值[39] | | 860 | 440.00 | 38.70 | 440.00 | 1.06 | 110.00 | 11.20 | 37.40 | 29.10 | | 23.40 | 2.30 | 121.00 | 12.80 | 3800.00 | 21.80 | 237.00 | 1990耕
作层[6] | | | 1413.00 | 88.29 | | | | 19.94 | | 38.65 | | 51.15 | 92.68 | | | | | | 水系
沉积
物(St) | 大青山
花岗岩 | DGRS | 5 | 656.10 | | 521.26 | 0.36 | 82.45 | 9.60 | 37.27 | 35.20 | 13.93 | 24.12 | 5.32 | 151.99 | 17.22 | 3473.82 | 26.30 | 183.21 | | 龙首山 | LSSS | 560 | 402.39 | | 448.11 | 0.47 | 48.01 | 6.35 | 37.15 | 12.40 | 11.19 | 11.06 | 2.20 | 170.83 | 8.48 | 2318.19 | 20.11 | 173.19 | | 北祁连 | NQLS | 1482 | 606.62 | | 518.04 | 0.98 | 61.65 | 13.75 | 35.81 | 25.89 | 12.72 | 36.73 | 2.50 | 145.35 | 11.38 | 3762.23 | 22.50 | 186.96 | 北祁连
蛇绿岩 | NQOS | 153 | 589.64 | | 594.70 | 1.30 | 72.34 | 16.83 | 35.06 | 28.37 | 12.99 | 76.11 | 2.30 | 118.17 | 11.31 | 4087.15 | 21.61 | 178.67 | R/St
相对
偏差
RE/% | 大青山
花岗岩 | | | 1.56 | | 8.05 | 18.63 | 69.88 | -57.64 | 23.39 | 111.19 | 40.64 | 41.49 | 102.80 | -91.03 | 78.69 | -17.78 | 15.97 | 13.92 | | 龙首山 | | | -56.49 | | -2.35 | -90.67 | -28.42 | -74.37 | 25.68 | -40.48 | 0.97 | 0.42 | 27.79 | -76.49 | -7.67 | -51.65 | -4.35 | 17.04 | | 北祁连 | | | 77.16 | | 6.17 | -78.81 | -24.04 | 3.03 | 73.16 | 45.38 | 21.53 | 4.24 | 16.43 | 3.74 | 22.40 | 36.99 | 11.81 | 52.57 | 北祁连
蛇绿岩 | | | 47.48 | | 46.93 | -118.97 | -13.84 | 40.31 | 36.36 | 69.68 | 29.15 | 107.38 | 24.85 | -3.89 | 21.19 | 50.35 | 11.53 | 34.58 |
|
Background values of heavy metals and other elements of Quaternary in Zhangye Basin and its adjacent geological units
|

| 地质单元 | 代码 | 样数 | Cu | Zn | Mo | Cr | Hg | Cu | Zn | Mo | Cr | Hg | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Na2O | CaO | MgO | Fe2O3 | | 第四系 | Q | 1710 | 23.04 | 50.99 | 0.62 | 85.03 | 30.04 | 23.04 | 50.99 | 0.62 | 85.03 | 30.04 | 10.46 | 66.35 | 1.47 | 4.33 | 2.44 | 4.10 | 下更新统玉
门组洪积层 | Qp1y | 4 | 19.87 | 48.04 | 0.46 | 93.73 | 39.44 | 19.87 | 48.04 | 0.46 | 93.73 | 39.44 | 10.95 | 69.67 | 1.57 | 3.51 | 2.58 | 3.91 | 中更新统酒
泉组洪积—
冰积层 | Qp2j | 17 | 20.64 | 47.80 | 0.60 | 66.97 | 30.57 | 20.64 | 47.80 | 0.60 | 66.97 | 30.57 | 11.57 | 67.22 | 1.30 | 3.62 | 2.12 | 4.21 | 上更新统近
河道洪积层 | | 119 | 15.81 | 44.03 | 1.00 | 43.70 | 17.59 | 15.81 | 44.03 | 1.00 | 43.70 | 17.59 | 10.79 | 64.69 | 1.29 | 4.87 | 2.83 | 3.35 | 上更新统河
道北砂砾层 | | 53 | 9.38 | 24.34 | 0.48 | 29.26 | 15.72 | 9.38 | 24.34 | 0.48 | 29.26 | 15.72 | 7.54 | 75.93 | 1.69 | 2.51 | 0.97 | 1.94 | 上更新统河
道南洪积层 | | 262 | 17.79 | 43.53 | 0.50 | 76.00 | 28.53 | 17.79 | 43.53 | 0.50 | 76.00 | 28.53 | 9.84 | 71.60 | 1.47 | 3.25 | 1.97 | 3.64 | 全新统河道
北冲洪积层 | Qhalpln | 7 | 9.75 | 26.60 | 0.23 | 23.19 | 16.26 | 9.75 | 26.60 | 0.23 | 23.19 | 16.26 | 10.02 | 73.28 | 2.11 | 2.98 | 1.20 | 1.96 | 全新统河道
南冲洪积层 | Qhalpls | 123 | 23.46 | 52.13 | 0.69 | 84.81 | 35.49 | 23.46 | 52.13 | 0.69 | 84.81 | 35.49 | 11.09 | 63.93 | 1.50 | 4.74 | 2.86 | 4.00 | 全新统河道
北坡残积层 | Qhdeln | 14 | 5.66 | 16.33 | 0.29 | 19.48 | 14.55 | 5.66 | 16.33 | 0.29 | 19.48 | 14.55 | 6.83 | 81.09 | 1.46 | 1.81 | 0.58 | 1.20 | 全新统河道
南坡残积层 | Qhdels | 10 | 12.76 | 34.03 | 0.48 | 54.89 | 24.93 | 12.76 | 34.03 | 0.48 | 54.89 | 24.93 | 8.74 | 76.04 | 1.48 | 2.57 | 1.28 | 2.87 | | 全新统风积层 | Qheol | 88 | 20.45 | 43.99 | 0.51 | 79.82 | 22.13 | 20.45 | 43.99 | 0.51 | 79.82 | 22.13 | 9.78 | 70.13 | 1.52 | 3.33 | 2.26 | 3.69 | 全新统湖
沼相堆积 | Qhl | 44 | 28.87 | 55.26 | 1.08 | 79.65 | 32.27 | 28.87 | 55.26 | 1.08 | 79.65 | 32.27 | 10.41 | 59.55 | 1.81 | 6.26 | 4.34 | 3.82 | 全新统河道
南洪积层 | Qhpls | 262 | 25.88 | 60.73 | 0.76 | 103.75 | 41.08 | 25.88 | 60.73 | 0.76 | 103.75 | 41.08 | 12.01 | 63.32 | 1.35 | 4.99 | 3.03 | 4.42 | | 全国背景值[39] | | 860 | 20.00 | 67.70 | 1.20 | 53.90 | 40.00 | 20.00 | 67.70 | 1.20 | 53.90 | 40.00 | 12.11 | | 3.61 | 0.99 | 1.04 | 3.90 | | 地质单元 | 代码 | 样数 | Cd | Pb | As | Sb | Ag | Co | La | Li | Nb | Ni | Sn | Sr | Th | Ti | Y | Zr | | 第四系 | Q | 1710 | 103.65 | 19.36 | 5.11 | 0.83 | 58.29 | 11.27 | 34.47 | 21.23 | 11.98 | 33.42 | 2.35 | 160.09 | 9.10 | 3144.46 | 21.02 | 187.83 | 下更新统玉
门组洪积层 | Qp1y | 4 | 87.82 | 14.09 | 1.19 | 0.57 | 58.66 | 11.10 | 36.66 | 15.19 | 10.89 | 30.50 | 1.85 | 149.04 | 6.85 | 3040.35 | 19.85 | 149.36 | 中更新统酒
泉组洪积—
冰积层 | Qp2j | 17 | 71.02 | 13.39 | 1.52 | 0.76 | 46.99 | 12.42 | 38.28 | 18.59 | 12.37 | 22.60 | 2.19 | 175.35 | 7.30 | 3259.46 | 20.67 | 157.68 | 上更新统近
河道洪积层 | | 119 | 67.50 | 17.66 | 1.46 | 0.67 | 39.24 | 8.80 | 43.18 | 14.58 | 14.75 | 16.49 | 2.08 | 183.66 | 8.26 | 2993.64 | 21.72 | 195.60 | 上更新统河
道北砂砾层 | | 53 | 60.82 | 26.76 | 1.25 | 0.35 | 50.27 | 4.55 | 29.50 | 9.65 | 8.44 | 7.58 | 2.08 | 166.94 | 7.83 | 1739.95 | 17.86 | 154.30 | 上更新统河
道南洪积层 | | 262 | 80.93 | 19.92 | 1.84 | 0.64 | 48.52 | 9.96 | 35.89 | 17.53 | 10.90 | 23.93 | 2.02 | 145.90 | 7.48 | 2772.55 | 19.32 | 156.04 | 全新统河道
北冲洪积层 | Qhalpln | 7 | 51.79 | 17.29 | 1.74 | 0.23 | 40.84 | 4.12 | 38.18 | 7.02 | 10.41 | 6.38 | 2.29 | 295.45 | 7.03 | 1540.52 | 17.99 | 139.54 | 全新统河道
南冲洪积层 | Qhalpls | 123 | 98.25 | 21.11 | 1.92 | 0.79 | 56.37 | 11.78 | 40.50 | 19.70 | 12.75 | 32.66 | 2.30 | 203.29 | 9.39 | 3225.36 | 21.66 | 179.09 | 全新统河道
北坡残积层 | Qhdeln | 14 | 60.79 | 25.76 | 1.06 | 0.25 | 44.25 | 2.63 | 29.62 | 7.78 | 7.85 | 4.57 | 1.85 | 150.15 | 6.47 | 1244.29 | 16.30 | 110.40 | 全新统河道
南坡残积层 | Qhdels | 10 | 80.66 | 22.05 | 1.43 | 0.61 | 58.44 | 7.15 | 33.88 | 13.17 | 9.33 | 12.86 | 1.99 | 138.50 | 7.66 | 2299.24 | 17.94 | 147.67 | | 全新统风积层 | Qheol | 88 | 84.84 | 19.09 | 2.06 | 0.63 | 52.26 | 10.29 | 36.33 | 17.81 | 10.81 | 24.02 | 2.27 | 160.61 | 8.60 | 2844.98 | 19.30 | 150.79 | 全新统湖
沼相堆积 | Qhl | 44 | 99.71 | 19.04 | 1.62 | 0.79 | 65.44 | 12.20 | 43.59 | 23.20 | 11.78 | 32.20 | 2.34 | 326.81 | 8.60 | 3213.38 | 21.06 | 177.54 | 全新统河道
南洪积层 | Qhpls | 262 | 106.65 | 22.23 | 2.03 | 0.85 | 60.45 | 13.64 | 42.35 | 22.47 | 13.54 | 41.54 | 2.35 | 193.43 | 8.53 | 3562.90 | 22.73 | 190.24 | | 全国背景值[39] | | 860 | 74.00 | 23.60 | 9.20 | 1.06 | 110.00 | 11.20 | 37.40 | 29.10 | | 23.40 | 2.30 | 121.00 | 12.80 | 3800.00 | 21.80 | 237.00 |
|
Background values of heavy metals and other elements of Quaternary sediments in Zhangye Basin
|

| 地质单元 | 代码 | 重金属 | 其他元素 | 平均潜在生态
风险指数( ) | | 富集 | 贫化 | 富集 | 贫化 | | 下更新统玉门组 | Qp1y | Cr、Cd | Cu、Zn | CaO、MgO、Fe2O3、P、Mn、F、Ni、Sr | K2O、Mo | 13.47~15.03 | | 中更新统酒泉组 | Qp2j | Cu、Cr | Zn | CaO、MgO、Fe2O3、P、Mn、Co、Sr | K2O、Mo | 5.63~34.37 | | 上更新统近河道洪积层 | | | Cu、Zn | CaO、MgO、K2O、P、Mn、F、La、Sr | Fe2O3、Mo | 5.63~30.48 | | 上更新统河道北砂砾层 | | Pb | Cu、Zn | CaO、K2O、Sr | MgO、Fe、P、Mn、Mo | 5.00~14.57 | | 上更新统河道南洪积层 | | Cr | Cu、Zn | CaO、MgO、Mn、Ni、Sr | Fe、K2O、P、Mo | 7.53~29.09 | | 全新统河道北冲洪积层 | Qhalpln | | Cu、Zn | CaO、MgO、K2O、Sr | Fe2O3、P、Mn、Mo | 7.18~11.38 | | 全新统河道南冲洪积层 | Qhalpls | Cu、Cr、Cd | Zn | CaO、MgO、Fe2O3、P、B、Mn、
Co、F、La、Ni、Sr | K2O、Mo | 13.98~49.89 | | 全新统河道北坡残积层 | Qhdeln | Pb | Cu、Zn | CaO、K2O、Sr、Mo | MgO、Fe2O3、P、Mn | 6.49~14.33 | | 全新统河道南坡残积层 | Qhdels | Cr、Cd | Cu、Zn | CaO、MgO、Sr、Mo | Fe2O3、K2O、P、Mn | 9.60~23.80 | | 全新统风积层 | Qheol | Cu、Cr、Cd | Zn | CaO、MgO、P、Mn、Ni、Sr、Mo | Fe2O3、K2O | 6.97~39.71 | | 全新统湖沼相堆积 | Qhl | Cu、Cr、Cd | Zn | CaO、MgO、P、B、Mn、Co、F、
La、Ni、Sn、Sr、Mo | Fe2O3、K2O | 0.91~1.13 | | 全新统河道南洪积层 | Qhpls | Cu、Cr、Hg、Cd | Zn | CaO、MgO、Fe2O3、K2O、P、B、
Mn、Co、F、La、Ni、Sn、Sr、Y、Mo | | 6.23~49.89 |
|
Rich state of elements in the Quaternary sediments
|

| 参数 | Zn | Pb | Ni | Hg | Cu | Cr | Cd | As | | | 样品数 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | | 平均值 | 69.75 | 20.87 | 58.20 | 109.50 | 32.15 | 131.12 | 148.33 | 3.22 | 45.80 | | 标准差 | 2.36 | 1.38 | 4.43 | 10.08 | 2.57 | 5.60 | 9.83 | 0.97 | 2.93 | | 最小值 | 65.70 | 20.10 | 49.80 | 103.00 | 27.60 | 119.70 | 130.00 | 1.50 | 43.91 | | 最大值 | 71.20 | 23.50 | 60.70 | 123.00 | 33.70 | 133.80 | 160.00 | 3.80 | 49.89 | | 偏度 | -0.75 | 1.06 | -1.02 | 0.54 | -0.82 | -1.36 | -0.80 | -0.83 | 0.55 | | 峰度 | 1.59 | 2.30 | 2.23 | 1.05 | 1.75 | 2.91 | 2.35 | 1.76 | 1.07 |
|
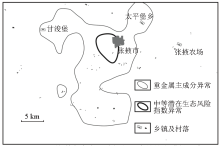
Statistics of the H3 anomaly of average potential ecological risk indexes
|
|
The princinpal component anomalies around H3 anomaly of average potential ecological risk indexes
|
Qp 3 p l m—diluvium layer of deep topsoil from upper Pleistocene near the river; —sand-gravel layer of deep topsoil from upper Pleistocenein in north side of river; —diluvium layer of deep topsoil from upper Pleistocene in south side of river; Qhalpln—alluvium-diluvium layer of deep topsoil from Holocene in north side of river; Qhalpls—alluvium-diluvium layer of deep topsoil from Holocene in south side of river; Qhdeln—eluvium-slope layer of deep topsoil from Holocene in north side of river; Qhdels—eluvium-slope layer of deep topsoil from Holocene in south side of river; Qheol—aeolian layer of deep topsoil from Holocene; Qhl—lacustrine-swamp layer of deep topsoil from Holocene; Qhpls—diluvium layer of deep topsoil from Holocene in south side of river
">
|
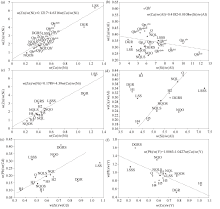
Geochemical diagrams for origins of deep subsoil and potential ecological risk index anomalies in Zhangye Basin
DGR—Daqing mountain granite rocks; LSS—Longshou mountain rocks; NQL—north Qilian rocks; NQO—north Qilian ophiolite rocks; DGRS—Daqing mountain granite stream sediment; LSSS—Longshou mountain drainage sediment; NQLS—north Qilian stream sediment; NQOS—north Qilian ophiolite stream sediment; Q—Quaternary deep topsoil; Qp1y—diluvium layer of deep topsoil from Yumen Formation; Qp2j—diluvium-glacial layer of deep topsoil from Jiuquan Formation; —diluvium layer of deep topsoil from upper Pleistocene near the river; —sand-gravel layer of deep topsoil from upper Pleistocenein in north side of river; —diluvium layer of deep topsoil from upper Pleistocene in south side of river; Qhalpln—alluvium-diluvium layer of deep topsoil from Holocene in north side of river; Qhalpls—alluvium-diluvium layer of deep topsoil from Holocene in south side of river; Qhdeln—eluvium-slope layer of deep topsoil from Holocene in north side of river; Qhdels—eluvium-slope layer of deep topsoil from Holocene in south side of river; Qheol—aeolian layer of deep topsoil from Holocene; Qhl—lacustrine-swamp layer of deep topsoil from Holocene; Qhpls—diluvium layer of deep topsoil from Holocene in south side of river
|
| [1] |
中国营养学会. 中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量(2013年修订版)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.
|
| [1] |
Chinese Nutrition Society. Chinese dietary reference intakes(2013 revision edition)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014.
|
| [2] |
生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB 15618—2018土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团, 2018.
|
| [2] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Repullic of China,State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 15618—2018 Soil environmental quality-risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land(for trial implementation)[S]. Beijing: China Enviromental Publishing Group, 2018.
|
| [3] |
汪春鹏, 尤建功, 孙浩, 等. 辽阳市土壤重金属含量特征及潜在风险评价[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(10):1680-1687.
|
| [3] |
Wang C P, You J G, Sun H, et al. Characteristics and potential risk assessment of heavy metal contents in urban soil,Liaoyang City[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(10):1680-1687.
|
| [4] |
孟飞, 刘敏, 史同广. 上海农田土壤重金属的环境质量评价[J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(2):428-433.
|
| [4] |
Meng F, Liu M, Shi T G. Evaluation on environmental quality of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Shanghai[J]. Environmental Science, 2008, 29(2):428-433.
|
| [5] |
燕鸿鹏. 微波消解—电感耦合等离子体质谱法同时测定垃圾渗滤液中8种生物毒性元素[J]. 化学分析计量, 2019, 28(6):35-38.
|
| [5] |
Yan H P. Simultaneous determination of 8 kinds of biotoxicity elements in landfill leachate by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with microwave digestion[J]. Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2019, 28(6):35-38.
|
| [6] |
侯格平. 张掖地区农田土壤农化性状测试结果与分析[J]. 甘肃农业科技, 1995(7):31-32.
|
| [6] |
Hou G P. Test results and analysis of agrochemical characteristics of farmland soil in Zhangye area[J]. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 1995(7):31-32.
|
| [7] |
甘肃地质矿产局物探队. 张掖幅(J-47-Ⅺ)、山丹幅(J-47-Ⅻ)地球化学图说明书[R]. 兰州: 甘肃省地矿局第二地质矿产勘查院,1990.
|
| [7] |
The Geophysical Exploration Team of Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Gansu Province. Direction of Zhangye map-sheet(J-47-Ⅺ) and Shandan map-sheet (J-47-Ⅻ) geochemical map[R]. Lanzhou: The Second Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources Exploration of BGMR of Gansu Province,1990.
|
| [8] |
甘肃地矿局地球化学探矿队. 酒泉幅(J-47-Ⅲ)、祁连山幅(J-47-Ⅸ)地球化学图说明书[R]. 兰州: 甘肃省地矿局第二地质矿产勘查院,1995.
|
| [8] |
The Geochemical Exploration Team of Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Gansu Province. Direction of Jiuquan map-sheet(J-47-Ⅲ) and Qilianshan map-sheet (J-47-Ⅸ) geochemical map[R]. Lanzhou: The Second Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources Exploration of BGMR of Gansu Province,1995.
|
| [9] |
赵良菊, 肖洪浪, 郭天文, 等. 甘肃省河西灌漠土微量元素的空间变异特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 2004, 18(5):27-30,34.
|
| [9] |
Zhao L J, Xiao H L, Guo T W, et al. Spatial variabilitiy of trace elements of irrigated desert soil in Zhangye and Wuwei,Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2004, 18(5):27-30,34.
|
| [10] |
赵翠翠, 南忠仁, 刘晓文, 等. 绿洲农田土壤主要微量元素的影响因素及分布特征研究——以张掖甘州区和临泽县为例[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2010, 24(10):127-132.
|
| [10] |
Zhao C C, Nan Z R, Liu X W, et al. Spatial distribution and affecting factors of main trace elements in oasis cropland—A case of Ganzhou District and Linze of Zhangye[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2010, 24(10):127-132.
|
| [11] |
赵蕊. 河西地区主要绿洲城市农田土壤重金属污染研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2020.
|
| [11] |
Zhao R. Study on heavy metal pollution in farmland soil of main oasis cities in Hexi Region[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2020.
|
| [12] |
刘文辉. 甘肃省张掖—永昌地区土壤有机碳密度算及其空间分布特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(5):883-888.
|
| [12] |
Liu W H. The soil organic carbon density and its distribution charactoristics in Zhangye-Yongchang area,Gansu Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(5):883-888.
|
| [13] |
任晓辉, 高宗军, 安永会, 等. 张掖市甘州区北部土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020, 34(7):163-169.
|
| [13] |
Ren X H, Gao Z J, An Y H, et al. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in northern Ganzhou District,Zhangye City[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2020, 34(7):163-169.
|
| [14] |
王磊, 卓小雄, 吴天生, 等. 基于1:25万和1:5万土地质量地球化学调查评价的土壤元素累积趋势预测——以广西南宁市西乡塘区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(1):1-13.
|
| [14] |
Wang L, Zhuo X X, Wu T S, et al. Prediction of the soil element accumulation trends based on 1:250,000 and 1:50,000 geochemical surveys and assessments of land quality:A case study of Xixiangtang District,Nanning City,Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1):1-13.
|
| [15] |
Fu K D, Gao J P, Fang X M, et al. Relationship model of sediment grain size and Tibetan Plateau uplift in middle-west parts of Qilian Mountain[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2001, 44(1):210-217.
|
| [16] |
郑文俊, 袁道阳, 何文贵. 祁连山东段天桥沟—黄羊川断裂古地震活动习性研究[J]. 地震地质, 2004, 26(4):645-657.
|
| [16] |
Zheng W J, Yuan D Y, He W G. Characteristics of palaeo-earthquake activity along the active Tianqiaogou-Huangyangchuan fault on the eastern section of the Qilianshan Mountains[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2004, 26(4):645-657.
|
| [17] |
Li Y L, Yang J C, Tan L H, et al. Impact of tectonics on alluvial landforms in the Hexi Corridor,Northwest China[J]. Geomorphology, 1999, 28(3/4):299-308.
|
| [18] |
程麟生, 陈玉春, 李素华, 等. 黑河地区行星边界层大气的气候分析[J]. 高原气象, 1990, 9(2):158-168.
|
| [18] |
Cheng L S, Chen Y C, Li S H, et al. Climatic analyses of the planetary boundary layer atmosphere in the Heihe Region[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 1990, 9(2):158-168.
|
| [19] |
Yang D L, Liu W, Wang J P, et al. Wind erosion forces and wind direction distribution for assessing the efficiency of shelterbelts in Northern China[J]. Aeolian Research, 2018,33:44-52.
|
| [20] |
陈启新. 地形高差对风速影响的探讨[J]. 山西水利科技, 2002(1):10-12.
|
| [20] |
Chen Q X. Discussing into influence of topographic height difference on wind velocity[J]. Shanxi Hydrotechnics, 2002(1):10-12.
|
| [21] |
张晓雅, 赵锐锋, 张丽华, 等. 不同生态保护地植物特征和土壤性质的对比研究——以黑河中游湿地为例[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(9):3027-3039.
|
| [21] |
Zhang X Y, Zhao R F, Zhang L H, et al. Comparative study of plant characteristics and soil properties in different ecological protected areas:A case study of middle reaches of the Heihe River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(9):3027-3039.
|
| [22] |
秦晓燕. 张掖市城市湿地土壤盐分、pH值和含水量的空间异质性分析[J]. 地下水, 2011, 33(1):8-11.
|
| [22] |
Qin X Y. Zhangye city wetland soil salinity,PH value and the spatial heterogeneity of water content[J]. Ground Water, 2011, 33(1):8-11.
|
| [23] |
张鑫. 安徽铜陵矿区重金属元素释放迁移地球化学特征及其环境效应研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2005.
|
| [23] |
Zhang X. Geochemical characteristics and environmental effects of heavy metal elements release and migration in Tongling mining area,Anhui Province[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2005.
|
| [24] |
黄璜. 绿洲农田土壤中主要微量元素的地球化学特征及环境影响研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2010.
|
| [24] |
Huang H. Study on geochemical characteristics and environmental impact of major trace elements in oasis farmland soil[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2010.
|
| [25] |
黄成敏, 王成善. 风化成土过程中稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 稀土, 2002, 23(5):46-49.
|
| [25] |
Huang C M, Wang C S. Geochemical features of rare earth elements in process of rock weathering and soil formation[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2002, 23(5):46-49.
|
| [26] |
徐俊, 宋佳, 刘英, 等. 不同pH条件下有色冶炼厂周边道路尘及土壤中重金属释放特征[J]. 湖北理工学院学报, 2018, 34(2):19-23.
|
| [26] |
Xu J, Song J, Liu Y, et al. Release characteristics of heavy metal in road dust and soil around non-ferrous smelters under different pH conditions[J]. Journal of Hubei Polytechnic University, 2018, 34(2):19-23.
|
| [27] |
杨春华. 残坡积土壤层中铁锰氧化物的吸附特性及其地球化学找矿意义[J]. 地球科学, 1986, 11(4):423-430.
|
| [27] |
Yang C H. Absorption characteristics of Fe-Mn oxides in residual soils and its significance in geochemical prospecting[J]. Earth Sciences, 1986, 11(4):423-430.
|
| [28] |
梁俊, 赵政阳, 樊明涛. 陕西渭北苹果园土壤中汞、镉污染与分布特征研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2008, 24(3):209-213.
|
| [28] |
Liang J, Zhao Z Y, Fan M T. Spatial distribution and pollution of mercury and cadmium in Weibei apple orchard soils of Shaanxi Province[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2008, 24(3):209-213.
|
| [29] |
杨秀敏, 任广萌, 李立新, 等. 土壤pH值对重金属形态的影响及其相关性研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2017, 26(6):79-83.
|
| [29] |
Yang X M, Ren G M, Li L X, et al. Effect of pH value on heavy metals form of soil and their relationship[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2017, 26(6):79-83.
|
| [30] |
路永正, 阎百兴. 重金属在松花江沉积物中的竞争吸附行为及pH的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 2010, 23(1):20-25.
|
| [30] |
Lu Y Z, Yan B X. Competitive adsorption of heavy metals on Songhua River sediments and effect of pH[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2010, 23(1):20-25.
|
| [31] |
DZ/T 0167—1995区域地球化学勘查规范(1:200 000)[S].中华人民共和国地质矿产部, 1995.
|
| [31] |
DZ/T 0167—1995 Specification for regional geochemical exploration[S].Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources, People's Republic of China, 1995.
|
| [32] |
冯治汉, 徐家乐. 甘肃省景观地球化学特征及区域化探工作方法研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2003, 39(6):2-5.
|
| [32] |
Feng Z H, Xu J L. Landscape geochemistry features and working methods of regional geochemistry in Gansu Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2003, 39(6):2-5.
|
| [33] |
凌坤跃, 温汉捷, 张正伟, 等. 白云岩风化剖面元素地球化学特征:对黔中九架炉组“三稀金属” 富集机制的启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(11):3385-3397.
|
| [33] |
Ling K Y, Wen H J, Zhang Z W, et al. Geochemical characteristics of dolomite weathering profiles and revelations to enrichment mechanism of trace elements in the Jiujialu Formation,central Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(11):3385-3397.
|
| [34] |
田洋, 赵小明, 王令占, 等. 鄂西南利川三叠纪须家河组地球化学特征及其对风化、物源与构造背景的指示[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(1):261-272.
|
| [34] |
Tian Y, Zhao X M, Wang L Z, et al. Geochemistry of clastic rocks from the Triassic Xujiahe Formation,Lichuan area,southwestern Hubei:Implications for weathering,provenance and tectonic setting[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(1):261-272.
|
| [35] |
Langmuir C H, Vocke R D, Hanson G N, et al. A general mixing equation with applications to Icelandic basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1978, 37(3):380-392.
|
| [36] |
Banerjee R, Iyer S D. Genetic aspects of basalts from the Carlsberg Ridge[J]. Current Science, 2003,85:299-305.
|
| [37] |
何进忠, 姚书振. 新元古代以来甘肃西秦岭造山过程的地球化学证据及其成矿背景[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(3):637-656.
|
| [37] |
He J Z, Yao S Z. Geochemical evidence for the orogenic process of West Qinling in Gansu since Neoproterozoic and its metallogenic background[J]. Geology in China, 2011, 38(3):637-656.
|
| [38] |
徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(2):112-115.
|
| [38] |
Xu Z Q, Ni S J, Tuo X G, et al. Calculation of heavy metals' toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 31(2):112-115.
|
| [39] |
魏复盛, 陈静生, 吴燕玉, 等. 中国土壤环境背景值研究[J]. 环境科学, 1991, 12(4):12-19.
|
| [39] |
Wei F S, Chen J S, Wu Y Y, et al. Study on the background contents on 61 elements of soils in China[J]. Environmental Science, 1991, 12(4):12-19.
|
| [40] |
甘肃省地质局. J-47-Ⅺ(张掖)幅区域地质测量报告[R]. 兰州: 甘肃省地质矿产局, 1973,44-45.
|
| [40] |
Geological Bureau of Gansu Province. J-47-Ⅺ(Zhangye)map-sheet regional geological survey report[R]. Lanzhou: BGMR of Gansu Province, 1973,44-45.
|
| [41] |
麦尔耶姆·亚森, 买买提·沙乌提, 尼格拉·塔什古拉提, 等. 渭干河—库车河绿洲土壤重金属分布特征与生态风险评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(20):226-233.
|
| [41] |
Maieryemu·Yasen, Mamat·Shawuti, Nigela·Tashigulati, et al. Distribution of heavy metal pollution and assessment of its potential ecological risks in Ugan-Kuqa River Delta of Xinjiang[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(20):226-233.
|
| [42] |
韩伟, 王成文, 彭敏, 等. 川南山区土壤与农作物重金属特征及成因[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(5):2480-2489.
|
| [42] |
Han W, Wang C W, Peng M, et al. Characteristics and origins of heavy metals in soil and crops in mountain area of southern Sichuan[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(5):2480-2489.
|
| [43] |
陈红. 植物叶片磁性特征及其对城市颗粒物污染的指示[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2020.
|
| [43] |
Chen H. Magnetic characteristics of plant leaves and its indication to urban particulate pollution[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2020.
|
| [44] |
鲍广强. 基于GIS的黑河流域重金属分布特征及污染风险评估[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2018.
|
| [44] |
Bao G Q. Distribution characteristics and pollution risk assessment of heavy metals in Heihe River Basin based on GIS[D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2018.
|
| [1] |
LIU Kai, DAI Hui-Min, LIU Guo-Dong, LIANG Shuai, WEI Ming-Hui, YANG Ze, SONG Yun-Hong. Organic carbon content-baesd prediction and influencing factors of black soil layer thicknesses[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1368-1376. |
| [2] |
WANG Yong-Feng, WANG Jian, PANG Guo-Tao, ZHU Wei-Ping, WANG Ke-Chao, WANG Xiao-En, WANG Zu-Zhen, LIU Jie. Assessment of primary soil fertility indicators of different forest stand types in the Nanshan forest farm in Jiyuan City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1400-1408. |
|
|
|
|

