|
|
|
| Prediction of oil column heights in fault-controlled tabular reservoirs through time-frequency analysis based on improved generalized S-transform |
YUAN Xiao-Man1( ), LI Xiang-Wen2,3( ), LI Xiang-Wen2,3( ), ZHANG Jie1, DAN Guang-Jian2, LU Zhong-Yuan1, HAN Chong-Yang2, ZHANG Lei2, XU Jian-Yang2 ), ZHANG Jie1, DAN Guang-Jian2, LU Zhong-Yuan1, HAN Chong-Yang2, ZHANG Lei2, XU Jian-Yang2 |
1. China National Petroleum Corporation,PetroChina Tarim Oilfield Company,Korla 841001,China
2. BGP Inc.,China National Petroleum Corporation,Korla 841000,China
3. Optical Science and Technology(Chengdu) Ltd.,China National Petroleum Corporation,Chengdu 611730,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The fault-controlled carbonate area in the northern depression of the Tarim Basin possesses abundant oil and gas resources.Identifying the oil-water contact (OWC) of fault-controlled tabular reservoirs is critical for their effective exploitation.However,OWC identification through drilling is costly and challenging.In contrast,it is efficient to identify the OWC using geophysical methods.This study proposed a time-frequency analysis method based on generalized S-transform.As revealed by the joint analysis of extensive time-frequency analysis results of through-well seismic channels and production performance analysis data,the depth/time-varying main frequency of seismic data is positively correlated with the oil layer thickness.Hence,this study proposed to identify the OWC using the abnormal inflection point of the energy envelope of seismic channel time-frequency gather.Experimental results demonstrate that oil layer thickness results obtained are uncertain,generally reliable,and reliable in the case of oil column height (OCH)<120 m,120 m≤OCH≤250 m,and OCH≥250 m,respectively.The method proposed in this study was applied to a fault fracture zone of an area of the Fuman oilfield,obtaining the main predicted oil layer thicknesses between 200 m and 520 m,aligning with the actual exploitation results.Therefore,the method of this study can be employed to guide exploitation.
|
|
Received: 11 August 2023
Published: 27 June 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
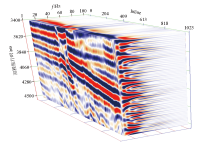
|
3D data volume stereogram of time-frequency analysis
|
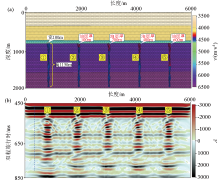
|
Geological model of fractured reservoir with different oil layer thicknesses(a) and forward modeling results profile(b)
|
fig.2b;b~f—the positions of fracture zones ① to ⑤ in fig.2 are shown respectively
">
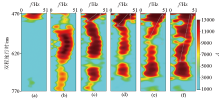
|
Comparison of time-frequency gathers for forward seismic data of different geological bodies
a—blue dashed line position in fig.2b;b~f—the positions of fracture zones ① to ⑤ in fig.2 are shown respectively
|

| 序号 | 模型油层
厚度/m | 频谱衰减
高度/ms | 预测油层
厚度/m | 误差/% | | 1 | 0 | 6 | 18 | — | | 2 | 100 | 28 | 84 | 16 | | 3 | 200 | 60 | 180 | 10 | | 4 | 400 | 130 | 390 | 2.5 | | 5 | 600 | 195 | 585 | 2.5 |
|
Comparison statistics of model oil layer thickness predicted by time-frequency analysis
|
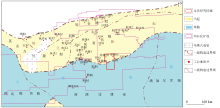
|
Structural distribution of the study area
|

| 储集体结构 | 地震反射特征 | 测井特征 | 实钻特征 | | 电阻率/(Ω·m) | 密度/(g·cm-3) | 声波时差/(m·μs-1) | 钻井情况 | 钻时/(min·m-1) | | 裂缝—基岩段 | 连续状 | 2 000以上 | 2.7~2.8 | 50 | 见气测 | 25~40 | | 裂缝—孔洞段 | 弱连续杂乱 | 500~2 000 | 2.5~2.6 | 40~50 | 漏失无放空 | 13~25 | | 断层角砾段 | 串珠 | 40~2 000 | 2.5~2.6 | 35~45 | 漏失量较大或钻遇放空 | 5~12 |
|
Identification of drilling,logging and logging characteristics of different transverse structures in strike-slip fault fractured zone
|
|
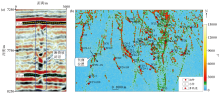
Seismic profile characteristics of vertical fault fractured-zone(a) and amplitude attribute map of Ordovician in the study area(b)
|
|
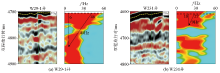
Comparison of cross well seismic profiles and time-frequency profiles
|
|
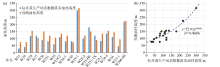
Comparison between the drilling oil column height in the study area(a) and the predicted oil layer thickness using this method(b)
|
|
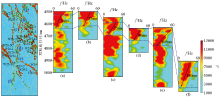
Comparison chart of oil layer thickness prediction for a fractured zone in the study area
|
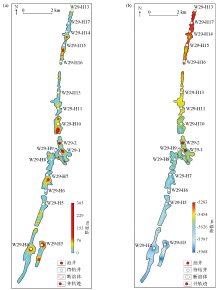
|
Plan view of predicted oil layer thickness in a fractured zone(a) and the OWC(b)
|
| [1] |
张明, 李相文, 金梦, 等. 超深断控缝洞型储层迭代反演方法——以富满油田为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(1):22-30.
|
| [1] |
Zhang M, Li X W, Jin M, et al. Iterative inversion method for ultradeep fault-controlled fracture-vug reservoirs:A case study of the Fuman oilfield,Tarim Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1):22-30.
|
| [2] |
田军, 杨海军, 朱永峰, 等. 塔里木盆地富满油田成藏地质条件及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(8):971-985.
|
| [2] |
Tian J, Yang H J, Zhu Y F, et al. Geological conditions for hydrocarbon accumulation and key technologies for exploration and development in Fuman oilfield,Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(8):971-985.
|
| [3] |
李相文, 李景叶, 刘永雷, 等. 塔里木盆地超深层走滑断裂带的地震识别方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2022, 57(6):1418-1426.
|
| [3] |
Li X W, Li J Y, Liu Y L, et al. Seismic identification method of ultra-deep strikeslip fault zones in Tarim Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2022, 57(6):1418-1426.
|
| [4] |
李青, 李小波, 谭涛, 等. 断溶体油藏注采井网构建方法[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(2):213-217.
|
| [4] |
Li Q, Li X B, Tan T, et al. Constructing optimum injection-production well pattern for fault-karst reservoirs[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(2):213-217.
|
| [5] |
唐馨, 冯家元, 胡学平. 双相介质油气检测技术在塔河油田白垩系舒善河组的应用[J]. 石油物探, 2022, 61(5):907-917.
|
| [5] |
Tang X, Feng J Y, Hu X P. Application of dual-phase medium oil and gas detection technology in Cretaceous Shushanhe formation of Tahe Oilfield[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2022, 61(5):907-917.
|
| [6] |
马良涛, 范廷恩, 许学良, 等. 油气检测多技术联合在B油田的应用研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(4):961-969.
|
| [6] |
Ma L T, Fan T E, Xu X L, et al. The application of multi-seismic hydrocarbon detection technology to gas identification in B oilfield[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4):961-969.
|
| [7] |
胡瑞卿, 何俊杰, 李华飞, 等. 时频域变分模态分解地震资料去噪方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2021, 56(2):257-264,210.
|
| [7] |
Hu R Q, He J J, Li H F, et al. Seismic data de-noising method based on VMD in time-frequency domain[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2021, 56(2):257-264,210.
|
| [8] |
马艺璇, 李慧莉, 刘坤岩, 等. 基于分频相干体的蚂蚁追踪技术在塔河油田断裂刻画中的应用[J]. 石油物探, 2020, 59(2):258-266.
|
| [8] |
Ma Y X, Li H L, Liu K Y, et al. Application of an ant-tracking technique based on spectral decomposition to fault characterization[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2020, 59(2):258-266.
|
| [9] |
Gabor D. Theory of communication[J]. Journal of the Institute of Electrical Engineers, 1946,93:429-457.
|
| [10] |
Potter R K. Visible speech[M]. New York: Van Nostrand,1947.
|
| [11] |
张固澜. 基于反Q滤波和IGST技术的地震高分辨处理研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016.
|
| [11] |
Zhang G L. High-resolution seismic data processing methods based on inverse Q-filter and IGST[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016.
|
| [12] |
Stockwell R G, Mansinha L, Lowe R P. Localization of the complex spectrum:The S-transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1996,44:998-1001.
|
| [13] |
陶春峰, 詹仕凡, 李磊, 等. 多频解释软件的数据存储与显示[C]// 2018年中国地球科学联合学术年会, 2018.
|
| [13] |
Tao C F, Zhan S F, Li L, et al. Data storage and display of multifrequency interpretation software[C]// 2018 China Earth Science Joint Academic Annual Conference,2018.
|
| [14] |
汪如军, 王轩, 邓兴梁, 等. 走滑断裂对碳酸盐岩储层和油气藏的控制作用——以塔里木盆地北部坳陷为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(3):10-20.
|
| [14] |
Wang R J, Wang X, Deng X L, et al. Control effect of strike-slip faults on carbonate reservoirs and hydrocarbon accumulation:A case study of the northern depression in the Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(3):10-20.
|
| [15] |
张亮亮, 刘永雷, 王建忠, 等. 哈拉哈塘地区缝洞集合体地震特征研究[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2015, 29(1):59-62.
|
| [15] |
Zhang L L, Liu Y L, Wang J Z, et al. Study on seismic characteristics of fracture cave assembly in Halahatang area[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2015, 29(1):59-62.
|
| [16] |
Li X W, Li J Y, Li L, et al. Ultradeep fractured-vuggy reservoir characteristic identification based on well data constrained seismic linear discriminant analysis[J]. Geophysics, 2023, 88(3):M119-M130.
|
|
|
|

