|
|
|
| Application of multi-component carbon isotope logging in natural gas exploration: A case study of the BD21 area, Qiongdongnan Basin |
HU Yi-Tao1( ), ZHANG Huan-Xu2, NI Peng-Bo3, HAO Wei3, QU Yu-Yang2, XIAO Han-Li2 ), ZHANG Huan-Xu2, NI Peng-Bo3, HAO Wei3, QU Yu-Yang2, XIAO Han-Li2 |
1. Zhanjiang Branch, China France Bohai Geoservices Co., Ltd., Zhanjiang 524057, China
2. Suzhou Grand Energy Technology Co. Ltd., Suzhou 215129, China
3. China France Bohai Geoservices Co., Ltd., Tianjin 300450, China |
|
|
|
|
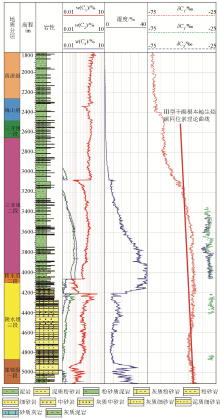
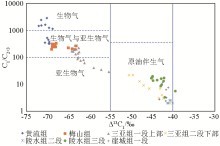
Abstract This study aims to ascertain the accumulation characteristics of natural gas in the deep-water oil and gas fields in the Qiongdongnan Basin. To this end, it performed continuous multi-component carbon isotope measurements for natural gas wells in the basin. Based on the comparative analysis of a continuous carbon isotope profile from a key well in the basin and the carbon isotope values from key intervals in surrounding wells, this study delved into the genetic types and sources of natural gas in the key well. The results show that dry gas occurs above the first member of the Sanya Formation, dominated by biogenic and secondary biogenic gases. In contrast, wet thermogenic gas exists below the second member of the formation, primarily including associated gas. Besides, natural gas in the BD21-1 block originates from two sources: Eocene high-maturity oil-formed gas and low-maturity gas with a special genesis from the Yacheng Formation. Overall, multi-component carbon isotope logging is effective in investigating the genetic types, sources, and maturity of natural gas.
|
|
Received: 01 April 2022
Published: 16 April 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|

深度/
m | 碳同位素/‰ | 深度/
m | 碳同位素/‰ | | δ13C1 | δ13C2 | δ13C3 | δ13C1 | δ13C2 | δ13C3 | | 1519 | -51.49 | -32.27 | -31.85 | 3839 | -50.56 | -31.50 | -31.45 | | 1820 | -51.28 | -31.93 | -31.59 | 3954 | -51.73 | -32.36 | -32.55 | | 2015 | -51.47 | -32.23 | -32.08 | 3993 | -50.85 | -31.68 | -31.67 | | 2320 | -51.60 | -31.96 | -32.66 | 4002 | -50.99 | -31.49 | -31.59 | | 2706 | -51.51 | -32.30 | -32.28 | 4096 | -50.65 | -31.77 | -31.40 | | 3023 | -51.92 | -31.81 | -32.52 | 4154 | -51.40 | -32.47 | -31.90 | | 3197 | -51.01 | -31.70 | -32.47 | 4320 | -51.29 | -32.17 | -31.36 | | 3312.37 | -51.60 | -32.52 | -32.26 | 4675 | -50.76 | -31.92 | -31.65 | | 3538 | -51.83 | -32.40 | -32.47 | 4821 | -50.89 | -32.10 | -32.01 | | 3538 | -51.58 | -32.58 | -32.18 | 4955 | -51.20 | -31.80 | -32.11 | | 3546 | -50.99 | -31.94 | -31.87 | 5115 | -50.75 | -32.15 | -31.60 | | 3546 | -50.70 | -31.53 | -31.53 | 三开
校验 | -51.20 | -32.20 | -32.43 | | 3550 | -50.41 | -31.62 | -31.41 | 四开
校验 | -50.99 | -31.80 | -31.90 | | 3638 | -50.91 | -31.78 | -31.60 | 标准差 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.40 |
|
Verification report of carbon isotope measurement
|
|
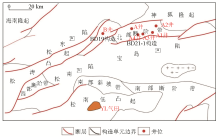
Well location in Qiandongnan Basin
|
|
Multicomponent carbon isotope profiles
|

| 层位 | 碳同位素/‰ | | δ13C1 | δ13C2 | δ13C3 | | 黄流组 | | | | | 梅山组 | | | | | 三亚组一段 | | | | | 三亚组二段 | | | | | 陵水组二段 | | | | | 陵水组三段 | | | | | 崖城组 | | | |
|
Multicomponent carbon isotope characteristics of natural gas
|
|
Natural gas origin identification of well A
|
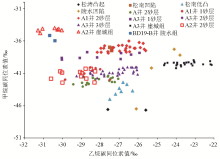
7], [8], [13], [21]. Other data are derived from isotopic logging and are all carbon isotope data of mud gas while drilling. Same as in Fig.5)
">
|
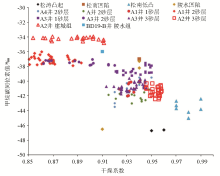
δ13c1-drying values of multi-well reservoir in fault in BD21(The carbon isotope and component data of Songtao bulge,Songnan Sag, Songnan low bulge and Lingshui sag were obtained from natural gas production, and the data were cited from references [7], [8], [13], [21]. Other data are derived from isotopic logging and are all carbon isotope data of mud gas while drilling. Same as in Fig.5)
|
|
δ13C1~δ13C2values of multi-well reservoir in BD21
|
| [1] |
Cesar J, Mayer B, Deblonde C, et al. Alternative indicators to assess the distribution characteristics of methane,ethane,and propane derived from petroleum in the Montney Formation,Western Canada[J]. Fuel, 2021, 294(15):1-14.
|
| [2] |
Ellis L, Berkman T, Uchytil S, et al. Integration of mud gas isotope logging (MGIL) with field appraisal at Horn Mountain Field,deepwater Gulf of Mexicl[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2007, 58(3):443-463.

|
| [3] |
慈兴华, 张焕旭, 牛强, 等. 碳同位素现场检测技术分析致密油气充注特征——以渤海湾盆地民丰洼陷北斜坡为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(11):10-17.
|
| [3] |
Ci X H, Zhang H X, Niu Q, et al. Analysis of tight oil and gas charging characteristics by the carbon isotope filed detection technology:A case study of the northern slope of the Minfeng sub-sag in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(11):10-17.
|
| [4] |
谢玉洪. 中国海洋石油总公司油气勘探新进展及展望[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2018, 23(1):26-35.
|
| [4] |
Xie Y H. New progress and prospect of oil and gas exploration of China National Offshore Oil Corporation[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2018, 23(1):26-35.
|
| [5] |
王振峰, 孙志鹏, 朱继田, 等. 南海西部深水区天然气地质与大气田重大发现[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(10):11-20.
|
| [5] |
Wang Z F, Sun Z P, Zhu J T, et al. Natural gas geological characteristics and great discovery of large gas fields in deep water area of the western South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(10):11-20.
|
| [6] |
施和生, 杨计海, 张迎朝, 等. 琼东南盆地地质认识创新与深水领域天然气勘探重大突破[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(6):691-698.
|
| [6] |
Shi H S, Yang J H, Zhang Y Z, et al. Geological understanding innovation and major breakthrough to natural gas exploration in deep water in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(6):691-698.
|
| [7] |
郭书生, 廖高龙, 梁豪. 琼东南盆地BD21井深水区天然气勘探重大突破及意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(5):49-59.
|
| [7] |
Guo S S, Liao G L, Liang H, et al. Major breakthrough and significance of deep-water gas exploration in Well BD21 in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(5):49-59.
|
| [8] |
梁刚, 甘军, 游君君, 等. 琼东南盆地低熟煤型气地球化学特征及勘探前景[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(7):895-903.
|
| [8] |
Liang G, Gan J, You J J, et al. Geochemical characteristics and exploration prospect of low mature coal-derived gas in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Natrual Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(7):895-903.
|
| [9] |
石晓, 刘汉彬, 张佳, 等. 激光光谱技术在稳定同位素组成分析中的应用现状[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2016, 33(4):237-243.
|
| [9] |
Shi X, Liu H B, Zhang J, et al. Laser spectrometry for stable isotope analysisand its application status[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2016, 33(4):237-243.
|
| [10] |
牛强, 瞿煜扬, 慈兴华, 等. 碳同位素录井技术发展现状及展望[J]. 录井工程, 2019, 30(3):8-15,184.
|
| [10] |
NIu Q, Qu Y Y, Ci X H, et al. Development status and prospect of carbon isotope logging technology[J]. Mud Logging Engineering, 2019, 30(3):8-15,184.
|
| [11] |
宋祥, 魏兵. Isologger气体同位素录井仪[J]. 录井工程, 2017, 28(2):95-98,137.
|
| [11] |
Song X, Wei B. Isologger gas isotope logger[J]. Mud Logging Engineering, 28(2):95-98,137.
|
| [12] |
耿恒, 陈沛, 陈鸣. 实时甲烷碳同位素录井在南海西部YC1-1-1井的应用[J]. 录井工程, 2016, 27(4):45-48,93-94.
|
| [12] |
Geng H, Chen P, Chen M. Application of rea-time methane carbon isotope logging in YC1-1-1 well in the west of the South China Sea[J]. Mud Logging Engineering, 2016, 27(4):45-48,93-94.
|
| [13] |
张迎朝, 甘军, 徐新德, 等. 琼东南盆地深水东区Y8-1含气构造天然气来源及侧向运聚模式[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(8):2609-2618.
|
| [13] |
Zhang Y Z, Gan J, Xu X D, et al. The source and natural gas lateral migration accumulation model of Y8-1 gas bearing structure,east deep water in the Qiongdongnan basin[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(8):2609-2618.
|
| [14] |
张迎朝, 徐新德, 甘军, 等. 琼东南盆地深水大气田地质特征、成藏模式及勘探方向研究[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(7):1620-1633.
|
| [14] |
Zhang Y Z, Xu X D, Gan J, et al. Study on the geological characteristics,accumulation model and exploration direction of the giant deepwater gas field in the Qiongdongnan basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(7):1620-1633.
|
| [15] |
陈建平, 王绪龙, 倪云燕, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘天然气成因类型与气源[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(3):461-473.
|
| [15] |
Chen J P, Wang X L, Ni Y Y, et al. Genetic type and source of natural gas in the southern margin of Junggar Basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum and Development, 2019, 46(3):461-473.
|
| [16] |
戴金星. 各类天然气的成因鉴别[J]. 中国海上油气, 1992, 6(1):11-19.
|
| [16] |
Dai J X. Identification of various genetic natural gases[J]. China Offshore Oil & Gas, 1992, 6(1):11-19.
|
| [17] |
戴金星. 各类烷烃气的鉴别[J]. 中国科学:B辑, 1992, 2:185-193.
|
| [17] |
Dai J X. Identification of various alkane gas[J]. Scientia Sinica:B, 1992, 2:185-193.
|
| [18] |
戴金星. 煤成气及鉴别理论研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(14):1291-1305.
|
| [18] |
Dai J X. Coal-derived gas theory and its discrimination[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(14):1291-1305.
|
| [19] |
梁刚, 甘军, 徐新德, 等. 实时碳同位素录井技术在琼东南盆地松涛凸起天然气成因及成藏分析中的应用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(3):56-61.
|
| [19] |
Liang G, Gan J, Xu X D, et al. Application of real-time carbon isotope logging technology in genesis and reservoir formation of natural gas in Songtao uplift,Qiongdongnan basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(3):56-61.
|
| [20] |
刘妍鷨, 陈红汉, 苏奥, 等. 从含油气检测来洞悉琼东南盆地东部发育始新统烃源岩的可能性[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(9):1539-1547.
|
| [20] |
Liu Y H, Chen H H, Su A, et al. Eocene source rock determination in Qiongdongnan Basin,the south Chian Sea:A hydrocarbon detection perspective[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(9):1539-1547.
|
| [21] |
梁刚, 甘军, 游君君, 等. 琼东南盆地低熟煤型气地球化学特征及勘探前景[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(7):895-903.
|
| [21] |
Liang G, Gan J, You J J, et al. Geochemical characteristics and exploration prospect of low mature coal-derived gas in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(7):895-903.
|
| [1] |
HE Li-Juan, WANG Zhen-Feng, DENG Yong, ZHANG Yi, ZHONG Ze-Hong, ZHANG Zhi-Rang, WANG Li-Jie. The application of virtual-well technique to reservoir prediction in deep-water area of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(2): 390-397. |
| [2] |
LIU Ai-qun, CHEN Dian-yuan, LI Qiang, ZHANG Li-li. PROGRESS OF RESEARCH ON QIONGDONGNAN BASIN SLOPE FAULT ZONE VELOCITY[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(6): 922-927. |
|
|
|
|

