|
|
|
| Investigation and suitability study of pre-selected sites for geological disposal of high level radioactive waste |
LUO Hui1,2( ), CHENG Wei-Ming1,2( ), CHENG Wei-Ming1,2( ), ZHOU Zhi-Chao1,2, LIU Jian1,2, LI Ya-Wei1,2, TIAN Xiao1,2, YUN Long1,2 ), ZHOU Zhi-Chao1,2, LIU Jian1,2, LI Ya-Wei1,2, TIAN Xiao1,2, YUN Long1,2 |
1. Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology,Beijing 100029, China
2. CAEA Innovation Center for Geological Disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste, Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, Beijing 100029, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Based on the requirement of safe disposal of high-level radioactive waste, this study aims at the pre-selection area of the preferred pre-selection area of China's high-level radioactive waste disposal bank (Beishan pre-selection area). The data and materials of geology, hydrogeology, future natural change, geochemistry, construction and engineering, environmental protection and social economy were obtained by using the methods of geology, geophysics, hydrogeology and geochemistry. The constructability of preselected rock mass is demonstrated from the perspectives of engineering construction and engineering safety. The acceptability of the preselected rock mass in transport condition, land use, social economy and humanity was confirmed. On this basis, a relatively perfect site investigation and suitability comprehensive analysis method for the disposal warehouse is established, and a candidate site for the granite disposal warehouse is selected from the computational sub-section through the comprehensive analysis of site suitability and the comprehensive comparison of site identification and safety in the lot. The research results will directly serve the site screening and site characteristics evaluation of China's high-level radioactive waste geological disposal repository, and have important practical significance to ensure the safe management of nuclear waste and the sustainable development of nuclear energy in China.
|
|
Received: 20 August 2023
Published: 23 January 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
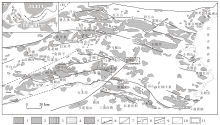
14])
1—Mesozoic granite; 2—late Paleozoic granite; 3—early Paleozoic granite; 4—Precambrian granite; 5—craton; 6—high pressure metamorphic zone; 7—suture tape; 8—ophiolite belt (① Hongshishan ophiolite belt; ② Shibanjing-Xiaohuangshan ophiolite belt; ③ Hongliuhe-Niuquanzi-Xichangjing ophiolite belt; ④ Huitongshan-Zhangfangshan ophiolite belt); 9—fault or inferred fault; 10—Quaternary and outcrop boundary; 11—location of the research area
">
|
Regional tectonics (a) and intrusive rock distribution (b) in Beishan area (modified according to reference [14])
1—Mesozoic granite; 2—late Paleozoic granite; 3—early Paleozoic granite; 4—Precambrian granite; 5—craton; 6—high pressure metamorphic zone; 7—suture tape; 8—ophiolite belt (① Hongshishan ophiolite belt; ② Shibanjing-Xiaohuangshan ophiolite belt; ③ Hongliuhe-Niuquanzi-Xichangjing ophiolite belt; ④ Huitongshan-Zhangfangshan ophiolite belt); 9—fault or inferred fault; 10—Quaternary and outcrop boundary; 11—location of the research area
|
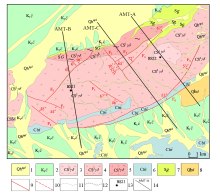
|
Geological schematic map of granite mass in Suanjingzi section
1—Holocene alluvial deposits; 2—lower Cretaceous Chijinbao formation; 3—Sandaomingshui east fine-grained granodiorite unit; 4—Sandaomingshui granodiorite unit; 5—Sandaomingshui north gneissic granodiorite unit; 6—lower Carboniferous Baishan formation; 7—middle Silurian Gongpoquan group; 8—Qingbaikou system Yuanzaoshan group Dahuoluoshan formation; 9—measured fault; 10—inferred fault; 11—integrate geological boundaries; 12—angle unconformity geological boundary; 13—boreholes and their numbering;14—geophysical survey line
|
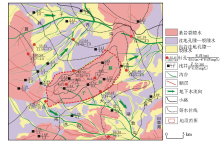
|
Contour map of groundwater level of granite mass in Suanjingzi section
|

|
Distribution characteristics of main interstitial materials of granite mass in Suanjingzi section
|
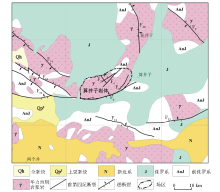
|
Seismic structure map of the Suanjingzi nearby area
|
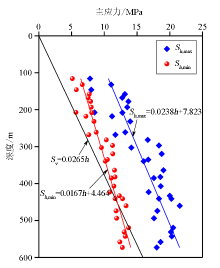
|
The variation pattern of in-situ stress of granite mass in Suanjingzi section with depth
|

| 属性 | 影响因素 | 指标 | 算井子地段 | | | 安全性 | 地质 | | | 岩体出露的面积 | 176 km2 | | 地球物理探测的岩体深度 | 2000 m | | 钻孔验证的最深岩体深度(钻孔数量) | 600 m(2口) | | 岩体内出露最大的岩块面积 | 50 km2 | | 地球物理探测的岩体深部完整性 | 好 | | 钻孔验证的岩体深部完整性 | 好(2口深度大于500 m的钻孔) | | 岩体内出露的岩性种类 | 1种(花岗闪长岩) | | 水文地质 | | | 岩体内地下水位埋深 | 8.20~61.24 m | | 岩体与最近排泄区的距离(名称,方位) | 180 km(额济纳旗盆地,西) | | 岩体内地下水水力梯度 | 10‰ | | 岩体内完整岩石渗透率 | 1×10-11~1×10-10 m/s | | 岩体内裂隙带渗透率 | 1×10-8~1×10-6 m/s | | 地球化学 | | | 岩体内地下水pH值 | 7.0~8.0 | | 岩体内地下水Eh值 | -232~60 mV | | 岩体内地下水温度 | 9~19 ℃ | | 岩体内地下水TDS | 0.7~12.0 g/L | | 岩体内地下水类型 | Cl·SO4-Na和SO4·Cl-Na型 | | 岩体内岩石类型 | 花岗闪长岩 | | 岩体内裂隙充填物类型 | 方解石、黏土矿物、褐铁矿、绿帘石、石英等 | | 未来自然变化 | | | 岩体与最近活动断裂的距离(断裂名称) | 155 km(三危山断裂) | | 岩体所在地震构造区中最大弥散地震震级(地震构造区名称) | 5.5级(北山地震构造区) | | 人类活动 | | | 岩体与最近地表水体的距离(名称) | 140 km(疏勒河) | | 岩体内矿(点)数量(矿种) | 0个 | | 岩体外围5km内矿(点)数量 | 0个 | | 可建造性 | 工程和建造 | 岩体地表地质灾害 | 无 | | | 可接受性 | 废物运输 | | | 岩体与最近铁路的距离(名称) | 75 km(京新铁路) | | 岩体与最近公路的距离(名称) | 45 km(京新高速) | | 岩体与大厂距离 | 145 km | | 岩体与大厂、铁路和公路之间沿途人口 | 极其稀少 | | 岩体与大厂、铁路和公路之间沿途地势 | 平坦 | | 环境保护 | | | 岩体与最近地表水体的距离(名称) | 120 km(干海子) | | 岩体对国家级保护区的影响 | 无 | | 土地利用 | | | 岩体土地类型 | 低产草地 | | 岩体土地用途 | 放牧 | | 岩体土地利用价值 | 极小 | | 岩体土地所在辖区 | 内蒙古额济纳旗 | | 社会经济和人文条件 | | | 岩体内常住人口数量 | 2人 | | 岩体与最近城市的距离 | 145 km(玉门) |
|
Comprehensive analysis of the suitability in the Suanjingzi area
|
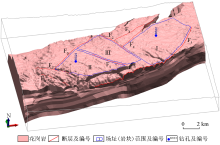
|
Three dimensional spatial distribution of granite mass in Suanjingzi section
|

| 对比因素 | 对比指标 | 算井子Ⅰ号场址 | 算井子Ⅱ号场址 | | 地质 | 场址地表面积 | 45 km2 | 25 km2 | | 场址地表可扩展面积 | 23 km2 | 23 km2 | | 场址内地球物理探测的岩体深度 | 2000 m | 2000 m | | 场址内经钻孔验证的最深岩体深度(钻孔编号) | 600 m(BS22) | 600 m(BS23) | | 场址内已知断层数量(不包括边界断层) | 0条 | 0条 | | 场址内经钻孔验证的岩体深部完整性(孔深大于500m的钻孔数量) | 好(1口) | 好(1口) | | 场址内岩性种类 | 1种 | 1种 | | 水文地质 | 岩体地下水位埋深 | 61.24 m | 8.20 m | | 场址离最近排泄区的距离(排泄区名称) | >180 km(额济纳旗盆地) | >180 km(额济纳旗盆地) | | 场址所在岩体的地下水水力梯度 | 10‰ | 10‰ | | 场址所在岩体内完整岩石渗透率 | 1×10-11~1×10-10 m/s | 1×10-11~1×10-10 m/s | | 场址所在岩体内节理带渗透率 | 1×10-8~1×10-6 m/s | 1×10-8~1×10-6 m/s | | 地球化学 | 场址内地下水pH值 | 7.0~8.0 | 7.0~8.0 | | 场址内地下水Eh值 | -232~60 mV | -232~60 mV | | 场址内地下水温度 | 9~19 ℃ | 9~19 ℃ | | 场址内地下水TDS | 0.7~12.0 g/L | 0.7~12.0 g/L | | 场址内地下水类型 | Cl·SO4-Na和SO4·Cl-Na型 | Cl·SO4-Na和SO4·Cl-Na型 | | 场址内岩石类型 | 花岗闪长岩 | 花岗闪长岩 | | 场址内裂隙充填物类型 | 方解石、黏土矿物、褐铁矿、
绿帘石、石英等 | 方解石、黏土矿物、褐铁矿、
绿帘石、石英等 | 未来
自然变化 | 场址与最近活动断裂的距离(断裂名称) | 155 km(三危山断裂) | 155 km(三危山断裂) | | 场址所在地震构造区中最大弥散地震震级(地震构造区名称) | 5.5级(北山地震构造区) | 5.5级(北山地震构造区) | | 人类活动 | 场址与最近地表水体的距离(水体名称) | 120 km(干海子) | 120 km(干海子) | | 场址与最近矿(点)的距离(名称) | 20 km(小红山铁矿) | 28 km(小红山铁矿) |
|
Comprehensive comparison of site safety in the Suanjingzi area
|
| [1] |
Savage D. The scientific and regulatory basis for the geological disposal of radioactive waste[M]. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons,1995.
|
| [2] |
潘自强, 钱七虎. 高放废物地质处置战略研究[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2009.
|
| [2] |
Pan Z Q, Qian Q H. Strategic research for deep geological disposal of high level radioactive waste[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2009.
|
| [3] |
王驹. 我国高放废物深地质处置战略规划探讨[J]. 铀矿地质, 2004, 20(4):196-203.
|
| [3] |
Wang J. Srategic program for deep geological disposal of high level radioactive waste in China[J]. Uranium Geology, 2004, 20(4):196-203.
|
| [4] |
Wang J, Chen L, Su R, et al. The Beishan underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China: Planning, site selection, site characterization and in situ tests[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 10(3): 411-435.

|
| [5] |
王驹, 苏锐, 陈亮, 等. 中国高放废物地质处置地下实验室场址筛选[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2022, 39 (1):1-13.
|
| [5] |
Wang J, Su R, Chen L, et al. Site selection of underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2022, 39 (1):1-13.
|
| [6] |
陈伟明, 王驹. 高放废物地质处置场址安全要求[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2006, 23(2):100-106.
|
| [6] |
Chen W M, Wang J. Site safety requirements for high level waste disposal[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2006, 23(2):100-106.
|
| [7] |
陈亮, 王驹, 杨峰, 等. 高放废物地质处置地下实验室开挖及精细探测关键技术[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2023, 40(1):1-16.
|
| [7] |
Chen L, Wang J, Yang F, et al. Excavation and fine detection technology of the underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2022, 40 (1) :1-16.
|
| [8] |
蒋实, 罗辉, 陈伟明, 等. 高放废物地质处置算井子地段地质条件适宜性研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5):1208-1216.
|
| [8] |
Jiang S, Luo H, Chen W M, et al. Suitability of geological conditions in Suanjingzi area for the disposal of high-level radioactive wastes[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5) : 1208-1216.
|
| [9] |
王驹, 苏锐, 陈亮, 等. 论我国高放废物地质处置地下实验室发展战略[J]. 中国核电, 2018, 11(1): 109-115.
|
| [9] |
Wang J, Su R, Chen L, et al. The development strategy of the underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high level radioactive waste in China[J]. China Nuclear Power, 2018, 11(1):109-115.
|
| [10] |
云龙, 张进, 王驹, 等. 甘肃北山南部活动断裂的发现及其区域构造意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 2021, 27(2):195-207.
|
| [10] |
Yun L, Zhang J, Wang J, et al. Discovery of active faults in the southern Beishan area,NW China: Implications for regional tectonics[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2021, 27(2):195-207.
|
| [11] |
赵星光, 王驹, 马利科, 等. 高放废物地质处置库北山预选区新场岩体地应力场分布规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(S2): 3750-3759.
|
| [11] |
Zhao X G, Wang J, Ma L K, et al. Distribution characteristics of geostress field in Xinchang rock block of candidate Beishan area for high level radioactive waste repository in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(S2): 3750-3759.
|
| [12] |
赵宏刚, 梁积伟, 王驹, 等. 甘肃北山算井子埃达克质花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(2):329-352.
|
| [12] |
Zhao H G, Liang J W, Wang J, et al. Geochronology and geochemical characteristics of the Suanjingzi adakitic granites in the Beishan Mountains, Gansu Province,China, and their tectonic significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(2):329-352.

|
| [13] |
国家核安全局. HAD 401/06—2013 核安全导则高水平放射性废物地质处置设施选址[S]. 北京: 国家核安全局, 2013.
|
| [13] |
National Nuclear Safety Administration. HAD 401/06—2013 Nuclear safety guidelines for site selection of high-level radioactive waste geological disposal facilities[S]//. Beijing: National Nuclear Safety Administration,2013.
|
| [14] |
苗来成, 朱明帅, 张福勤. 北山地区中生代岩浆活动与成矿构造背景分析[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(4): 1190-1204.
|
| [14] |
Miao L C, Zhu M S, Zhang F Q. Tectonic setting of Mesozoic magmatism and associated metallogenesis in Beishan area[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(4): 1190-1204.
|
| [15] |
甘肃省地质调查院. 区域地质调查报告(1∶25万马鬃山幅)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2001.
|
| [15] |
Gansu Provincial Geological Survey Institute. Regional geological survey report (1∶250,000 Mazoushan width)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2001.
|
| [16] |
中华人民共和国环境保护行业标准. HJ/T 5.2—1993 核设施环境保护管理导则放射性固体废物浅地层处置环境影响报告书的格式与内容[S]. 北京: 国家环境保护局, 1993.
|
| [16] |
Environmental Protection Industry Standards of the People's Republic of China. HJ/T 5.2—1993 Environmental protection regulation guidelines for nuclear facilities-Standard format and content of environmental impact reports for shallow ground disposal of solid radioactive waste[S]. Beijing: State Environmental Protection Administration, 1993.
|
| [17] |
中华人民共和国国家标准. GB/T 15950—1995 低、中水平放射性废物近地表处置场环境辐射监测的一般要求[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社,1995.
|
| [17] |
National Standards of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 15950—1995 General requirements for environmental radiation monitoring around near surface disposal sites of low-intermediate level radioactive solid waste[S]. Beijing: Standard Press of China, 1995.
|
| [1] |
LUO Hui, JIANG Shi, ZHAO Hong-Gang, LI Ya-Wei, TIAN Xiao. Application of 3D geological modeling in screening of sites preselected for geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes: A case study of Tianhu preselected site, Xinjiang[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(6): 1488-1496. |
| [2] |
JIANG Shi, LUO Hui, CHEN Wei-Ming, LI Ya-Wei, JIN Yuan-Xin. Suitability of geological conditions in Suanjingzi area for the disposal of high-level radioactive wastes[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1208-1216. |
|
|
|
|

