|
|
|
| Migration and enrichment patterns of vanadium in the soil and plant system of farmland |
ZHAO Yu-Yan( ), JIANG Tao, YANG Bing-Han, ZHANG Ze-Yu, LI Zheng-He, LI Bing, TANG Xiao-Dan( ), JIANG Tao, YANG Bing-Han, ZHANG Ze-Yu, LI Zheng-He, LI Bing, TANG Xiao-Dan( ) ) |
| College of Geoexploration Science and Technology, Jilin University, Changchun 130026, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Vanadium (V) is an essential trace element required by organisms for maintaining their normal life activities. It is also a harmful element listed as a priority environmental pollutant by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). The study of the migration and enrichment patterns of V in the soil and plant system is of great practical significance for further understanding the ecological geochemical behavior of V and ensuring the safety of agricultural products and human health. This study systematically sampled the soil and plants in some ordinary farmland in Linyi City, Shandong Province and analyzed and tested the contents of V and its associated elements in the soil and plant samples. Moreover, this study conducted the source analysis and pollution assessment of V and investigated the migration and transformation patterns of V in the soil-plant system using statistical methods such as descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, and cluster analysis, as well as the single factor pollution index method, the potential ecological risk index method, and the biological enrichment coefficient method. The results are as follows: V is relatively concentrated in the study area, and its content increases with an increase in the Fe and Ti contents and decreases with an increase in the SiO2, Na2O, Sr, and CaO contents; The V in the study area mainly originates from the weathering of parent rocks, and the parts with a high V content is related to magnetite; As shown by the results of the single factor index method and the potential ecological risk index method, V is relatively clean in the soils of the study area, but attention should be paid to the pollution of the associated Cd; V is enriched primarily in the roots of plants, and plants' absorption capacity of V is generally negatively correlated with the contents of Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni, Co, Cd, and especially Cr in soils and is positively correlated with the As content in soils. This study enriches the ecological geochemical theory of V and provides a scientific basis for regional agricultural production, environmental quality assessment, and ecological pollution control.
|
|
Received: 21 April 2022
Published: 05 July 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|

| ICP-MS | XRF | | 分析参数 | 设定值 | 分析参数 | 设定值 | | 功率/W | 1150 | 初始化元素 | Ag | | 采样锥孔径/mm | 1.2 | 初始化通道 | 2210 | | 截取锥孔径/mm | 1.0 | 管流/μA | 250 | | 冷却气流量/(L·min-1) | 18 | 管压/kV | 40 | | 辅助器流量/(L·min-1) | 1.2 | 计数率 | 1 | | 雾化器流量/(L·min-1) | 0.86 | 真空时间/s | 25 | | 扫描次数 | 20 | 测量时间/s | 100 | | 测量时间/s | 60 | 测量次数 | 3 |
|
Instrument operating parameters
|
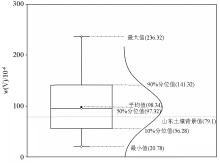
|
Box diagram of V content in topsoil
|

| 作物种类 | 最小值/
10-6 | 最大值/
10-6 | 均值/
10-6 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | | 樱桃 | 35.66 | 136.86 | 77.49 | 24.67 | 0.32 | | 西瓜 | 46.63 | 184.28 | 108.87 | 33.79 | 0.31 | | 花生 | 31.88 | 113.87 | 76.51 | 57.97 | 0.76 | | 板栗 | 35.13 | 74.75 | 55.83 | 28.01 | 0.50 | | 地瓜 | 33.90 | 148.10 | 74.82 | 80.75 | 1.08 | | 核桃 | 37.39 | 122.33 | 71.51 | 60.06 | 0.84 | | 玉米 | 52.04 | 121.71 | 83.00 | 49.26 | 0.59 |
|
Characteristic values of V content in crop root soil
|

| 元素 | V | Cu | Pb | Zn | Ni | Co | Cd | Cr | As | | V | 1 | 0.318** | 0.081 | 0.199** | 0.697** | 0.891** | -0.055 | 0.926** | 0.351** | | Cu | | 1 | 0.351** | 0.858** | 0.675** | 0.434** | -0.06 | 0.266** | 0.06 | | Pb | | | 1 | 0.507** | 0.041 | 0.08 | -0.021 | 0.101 | 0.462** | | Zn | | | | 1 | 0.333** | 0.285** | -0.154* | 0.219** | 0.129 | | Ni | | | | | 1 | 0.816** | 0.051 | 0.634** | 0.178** | | Co | | | | | | 1 | -0.014 | 0.930** | 0.352** | | Cd | | | | | | | 1 | -0.068 | 0.160* | | Cr | | | | | | | | 1 | 0.393** | | As | | | | | | | | | 1 |
|
Correlation analysis of V and heavy metal contents in soil
|
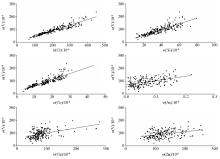
|
Correlation of V and heavy metal contents in soil
|

| 元素 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe | K | MgO | Na2O | SiO2 | Sr | | 相关系数 | 0.279 | -0.176** | 0.637** | 0.275 | 0.125 | -0.464** | -0.143* | -0.367** | | 元素 | Ti | B | F | | | | | | | 相关系数 | 0.653** | 0.187 | 0.347 | | | | | |
|
Correlation analysis of V and rock-making elements
|
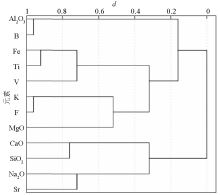
|
Cluster analysis pedigree diagram of V and rock-making elements
|
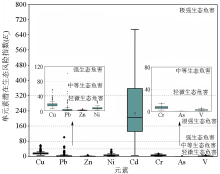
|
Ecological risk index of heavy metal elements in soil
|

| 作物 | 西瓜 | 花生 | 玉米 | 地瓜 | | 富集系数 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.07 | | 作物 | 樱桃 | 板栗 | 核桃 | | | 富集系数 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.17 | |
|
Enrichment coefficients of V in crops
|

| 作物种类 | 器官 | 最小值/
10-6 | 最大值/
10-6 | 中位数/
10-6 | 均值/
10-6 | | 西瓜 | 根 | 5.68 | 89.44 | 25.54 | 36.44 | | 茎 | 3.63 | 74.53 | 13.83 | 21.92 | | 叶 | 4.87 | 72.32 | 27.39 | 28.84 | | 皮 | 0.06 | 4.86 | 0.86 | 1.03 | | 籽 | 0.10 | 1.50 | 0.83 | 0.84 | | 果实 | 0.03 | 2.52 | 0.40 | 0.64 | | 花生 | 根 | 24.74 | 92.68 | 58.31 | 55.88 | | 茎 | 3.20 | 43.80 | 11.43 | 14.89 | | 叶 | 13.60 | 38.75 | 18.09 | 20.56 | | 果实 | 9.75 | 16.71 | 10.13 | 12.31 | | 玉米 | 根 | 12.12 | 25.264 | 22.46 | 20.31 | | 茎 | 1194 | 20.74 | 18.71 | 18.31 | | 叶 | 4.73 | 15.51 | 9.51 | 9.47 | | 果实 | 7.06 | 20.98 | 9.29 | 11.40 | | 地瓜 | 茎 | 2.64 | 22.26 | 8.24 | 10.54 | | 叶 | 0.30 | 10.73 | 4.19 | 4.54 | | 果实 | 2.48 | 8.88 | 3.74 | 4.44 | | 樱桃 | 叶 | 1.06 | 5.86 | 3.00 | 3.11 | | 果实 | 0.13 | 1.37 | 0.51 | 0.57 | | 板栗 | 叶 | 4.30 | 16.62 | 9.67 | 8.54 | | 果实 | 2.32 | 16.33 | 3.41 | 5.55 | | 核桃 | 叶 | 3.07 | 17.93 | 9.29 | 10.25 | | 果实 | 7.47 | 17.50 | 9.31 | 10.64 |
|
Characteristic values of V content in different organs of crops
|

| 部位 | Cu | Pb | Zn | Ni | Co | Cd | Cr | As | | 根 | -0.239 | -0.247 | -0.122 | -0.191 | -0.071 | -0.398* | -0.075 | -0.184 | | 茎 | -0.024 | 0.077 | -0.133 | -0.204 | -0.262 | -0.359 | -0.365* | 0.353 | | 叶 | -0.214 | -0.132 | -0.355 | -0.038 | -0.234 | -0.115 | -0.417* | 0.14 | | 皮 | -0.08 | -0.021 | -0.151 | -0.182 | -0.208 | -0.173 | -0.257 | 0.013 | | 籽 | -0.244 | -0.145 | -0.308 | -0.512** | -0.590** | -0.188 | -0.606** | 0.132 | | 果实 | -0.279 | -0.224 | -0.319 | -0.347 | -0.399* | -0.119 | -0.409* | 0.174 |
|
Correlation statistics between V uptake capacity in watermelon organs and heavy metal contents in soil
|
| [1] |
曾英, 倪师军, 张成江. 钒的生物效应及其环境地球化学行为[J]. 地球科学进展, 2004, 19(S1):472-476.
|
| [1] |
Zeng Y, Ni S J, Zhang C J. Biological effect and environment geochemical behavior of vanadium[J]. Advance in Earth Science, 2004, 19(S1):472-476.
|
| [2] |
杨金燕, 唐亚, 李廷强, 等. 我国钒资源现状及土壤中钒的生物效应[J]. 土壤通报, 2010, 41(6):1511-1517.
|
| [2] |
Yang J Y, Tang Y, Li T Q, et al. Soil biogeochemistry and resources situation of vanadium in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2010, 41(6):1511-1517.
|
| [3] |
Larsson M A, Baken S, Gustafsson J P, et al. Vanadium bioavailability and toxicity to soil microorganisms and plants[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2013, 32(10):2266-2273.
|
| [4] |
袁莉, 杨鹰, 高铭宇, 等. 微量元素钒的生物学效应[J]. 中国兽医科技, 1999, 29(1):21-23.
|
| [4] |
Yuan L, Yang Y, Gao M Y, et al. Biological effects of trace element vanadium[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science and Technology, 1999, 29(1):21-23.
|
| [5] |
吴涛, 兰昌云. 环境中的钒及其对人体健康的影响[J]. 广东微量元素科学, 2004, 11(1):11-15.
|
| [5] |
Wu T, Lan C Y. Vanadium in environment and its harm to human health[J]. Trace Elements Science, 2004, 11(1):11-15.
|
| [6] |
王平利, 张成江. 土壤中钒的环境地球化学研究现状[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2004, 26(3):247-251.
|
| [6] |
Wang P L, Zhang C J. Environment geochemistry research progress of vanadium in soil[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2004, 26(3):247-251.
|
| [7] |
张庆强. 土壤中钒的潜在生态风险研究[D]. 北京: 北京师范大学, 2009.
|
| [7] |
Zhang Q Q. Potential ecological risk of vanadium in the soil[D]. Beijing: Beijing Normal University, 2009.
|
| [8] |
滕彦国, 张庆强, 肖杰, 等. 攀枝花公园土壤中钒的地球化学形态及潜在生态风险[J]. 矿物岩石, 2008, 28(2):102-106.
|
| [8] |
Teng Y G, Zhang Q Q, Xiao J, et al. Geochemical speciation and potential ecological risk of vanadium in the soil in the panzhihua park[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2008, 28(2):102-106.
|
| [9] |
矫旭东, 滕彦国. 土壤中钒污染的修复与治理技术研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2008, 39(2):448-452.
|
| [9] |
Jiao X D, Teng Y G. Techniques on soil remediation and disposal of vanadium pollution[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2008, 39(2):448-452.
|
| [10] |
龙治杰. 攀枝花地区土壤重金属分布特征及钒元素来源解析[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2018.
|
| [10] |
Long Z J. A study on the spatial distribution of heavy metal elements and source apportionment of vanadium in Panzhihua area soil[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018.
|
| [11] |
Aihemaiti A, Gao Y, Meng Y, et al. Review of plant-vanadium physiological interactions,bioaccumulation,and bioremediation of vanadium-contaminated sites[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 712:135637.

|
| [12] |
Aikelaimu A, Jiang J G, Li D A, et al. Toxic metal tolerance in native plant species grown in a vanadium mining area[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2017, 24:26839-26850.
|
| [13] |
汪金舫, 刘铮. 土壤中钒的化学结合形态与转化条件的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 1995, 15(1):34-39.
|
| [13] |
Wang J F, Liu Z. Studies on chemical forms of vanadium in soil and their transformation[J]. China Environment Science, 1995, 15(1):34-39.
|
| [14] |
Shaheen S M, Alessi D S, Tack F, et al. Redox chemistry of vanadium in soils and sediments:Interactions with colloidal materials,mobilization,speciation,and relevant environmental implications:A review[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 265:1-13.
|
| [15] |
Larsson M A, Baken S, Gustafsson J P, et al. Vanadium bioavailability and toxicity to soil microorganisms and plants[J]. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry, 2013, 32(10):2266-2273.
|
| [16] |
滕彦国, 徐争启, 王金生. 钒的环境生物地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011.
|
| [16] |
Teng Y G, Xu Z Q, Wang J S. Environmental biogeochemistry of vanadium[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011.
|
| [17] |
孔凡彬, 刘阳. 单因子指数法和内梅罗指数法在土壤环境质量评价中的比较[J]. 甘肃科技, 2014, 30(3):21-22.
|
| [17] |
Kong F B, Liu Y. Comparison of single factor index method and Nemerow index method in soil environmental quality assessment[J]. Gansu Science and Technology, 2014, 30(3):21-22.
|
| [18] |
周亚龙, 郭志娟, 王成文, 等. 云南省镇雄县土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评估[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1358-1366.
|
| [18] |
Zhou Y L, Guo Z J, Wang C W, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of soils in Zhenxiong County,Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1358-1366.
|
| [19] |
徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(2):112-115.
|
| [19] |
Xu Z Q, Ni S J, Tuo X G, et al. Calculation of heavy metals' toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index[J]. Environment Science and Technology, 2008, 31(2):112-115.
|
| [20] |
夏伟, 吴冬妹, 袁知洋. 土壤—农作物系统中重金属元素迁移转化规律研究——以湖北宣恩县为例[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2018, 32(4):563-568.
|
| [20] |
Xia W, Wu D M, Yuan Z Y. Study on the migration and transformation law of heavy metals in soil-crop system[J]. Resources Environment and Engineering, 2018, 32(4):563-568.
|
| [21] |
庞绪贵, 代杰瑞, 陈磊, 等. 山东省17市土壤地球化学背景值[J]. 山东国土资源, 2019, 35(1):46-56.
|
| [21] |
Pang X G, Dai J R, Chen L, et al. Soil geochemical background value of 17 cities in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2019, 35(1):46-56.
|
| [22] |
庞绪贵, 代杰瑞, 喻超, 等. 山东省17市土壤地球化学基准值[J]. 山东国土资源, 2019, 35(1):36-45.
|
| [22] |
Pang X G, Dai J R, Yu C, et al. Soil geochemical reference value of 17 cities in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2019, 35(1):36-45.
|
| [23] |
林师整. 宁芜地区钒的地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 1980, 9(2):122-133.
|
| [23] |
Lin S Z. Geochemical characteristics of vanadium as exemplified from a certain district in China[J]. Geochimica, 1980, 9(2):122-133.
|
| [24] |
汪金舫, 刘铮. 钒在土壤中的含量分布和影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 1994, 31(1):61-67.
|
| [24] |
Wang J F, Liu Z. Vanadium distribution and its affecting factors in soils of China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1994, 31(1):61-67.
|
| [25] |
Chen L, Liu J R, Hu W F, et al. Vanadium in soil-plant system:Source,fate,toxicity,and bioremediation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 405:124200.

|
| [26] |
刘英俊, 曹励明. 元素地球化学导论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社,1987.
|
| [26] |
Liu Y J, Cao L M. Introduction to elemental geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geogical Publishing House,1987.
|
| [27] |
郝立波, 戚长谋. 地球化学原理[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004.
|
| [27] |
Hao L B, Qi C M. Principles of geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geogical Publishing House, 2004.
|
| [28] |
卢良兆, 许文良. 岩石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017.
|
| [28] |
Lu L Z, Xu W L. Petrology[M]. Beijing: Geogical Publishing House, 2017.
|
| [29] |
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. A protocol for the derivation of environmental and human healthsoil quality guidelines[R]. Winnipeg:CCME, 2006.
|
| [30] |
周亚龙, 杨志斌, 王乔林, 等. 雄安新区农田土壤-农作物系统重金属潜在生态风险评估及其源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4):2003-2015.
|
| [30] |
Zhou Y L, Yang Z B, Wang Q L, et al. Potential ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in soil-crop system in Xiong'an New District[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(4):2003-2015.
|
| [31] |
Ekaterina G, Alina B, Natalia R, et al. Monitoring of the migratory ability of heavy metals in the soil-plant system[J]. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry, 2020, 11(3):10351-10357.

|
| [32] |
孙厚云, 卫晓锋, 孙晓明, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿尾矿库复垦土地及周边土壤—玉米重金属迁移富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3):1166-1176.
|
| [32] |
Sun H Y, Wei X F, Sun X M, et al. Bioaccumulation and translocation characteristics of heavy metals in a soil-maize system in reclaimed land and surrounding areas of typical vanadium-titanium magnetite tailings[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3):1166-1176.
|
| [33] |
杨淼. 典型石煤提钒区和蔬菜基地土壤钒污染特征及基准值研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
|
| [33] |
Yang M. Contamination characteristics and permissible value of vanadium in soils from the typical stone coal vanadium extraction plant and vegetable bases[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012.
|
| [34] |
郭昱. 重金属镉、钒在土壤和紫花苜蓿中的积累特征和迁移行为的研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2015.
|
| [34] |
Guo Y. The heavy metal cadmium and vanadium accumulation characteristics and migration behavior research in soil and alfalfa[D]. Urumuchi: Xinjiang University, 2015.
|
| [35] |
刘芷宇. 植物根系吸收土壤中离子的途径[J]. 土壤学报, 1964, 12(2):235-242.
|
| [35] |
Liu Z Y. Pathways through which plant roots absorb ions from soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1964, 12(2):235-242.
|
| [36] |
Zhang L, Fu K, Yang F, et al. Migration and transformation of heavy metals in the soil of the water-level fluctuation zone in the three gorges reservoir under simulated nitrogen deposition[J]. Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 2021(1):1-10.
|
| [37] |
Zhang X, Yang H, Cui Z. Evaluation and analysis of soil migration and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in iron tailings[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 172:475-480.

|
| [38] |
杨洁. 土壤—植物系统中钒的生物有效性研究[D]. 北京: 北京师范大学, 2011.
|
| [38] |
Yang J. The research about vanadium bioavailability in soil-plant system[D]. Beijing: Beijing Normal University, 2011.
|
| [39] |
杨洁, 解琳, 司傲男, 等. 施磷肥土壤中钒的迁移转化规律研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(6):1312-1320.
|
| [39] |
Yang J, Xie L, Si A N, et al. Migration and transformation of vanadium in cultivated soil with phosphate fertilizer[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(6):1312-1320.
|
| [40] |
吴川, 安文慧, 薛生国, 等. 土壤—水稻系统砷的生物地球化学过程研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(7):1429-1439.
|
| [40] |
Wu C, An W H, Xue S G, et al. Arsenic biogeochemical processing in the soil-rice system[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2019, 38(7):1429-1439.
|
| [41] |
Chen L, Liu J R, Hu W F, et al. Vanadium in soil-plant system:Source,fate,toxicity,and bioremediation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 405(34):124200.

|
| [1] |
LIU Qing-Yu, MA Ying, CHENG Li, SHEN Xiao, ZHANG Ya-Feng, MIAO Guo-Wen, HUANG Qiang, HAN Si-Qi. Density and spatial distribution of organic carbon in the topsoil of eastern Qinghai[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 1098-1108. |
| [2] |
LI Sheng-Qing. Speciation and distribution of heavy metals in sediments in Haihe River Basin and their effects on ecological risk assessment[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3): 781-786. |
|
|
|
|

