|
|
|
| Grain-scale experimental study of samples using the large-scale micro-channel system survey technique for the cold, semi-arid grassland landscape: A case study of the rare Li-Be ores in the Qiemoge Mountain |
BAO Shan-Dong( ), XIE Xiang-Lei, WANG Ya-Dong, XU Yun-Fu, ZHANG Xin-Yuan, ZENG Biao ), XIE Xiang-Lei, WANG Ya-Dong, XU Yun-Fu, ZHANG Xin-Yuan, ZENG Biao |
| Key Laboratory of the Northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, Qinghai Geological Survey Institute, Xining 810012, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Qiemoge Mountain area in Tianjun County, Qinghai Province has a cold, semi-arid grassland landscape. A pegmatite belt with a width of 300~500 m and an intermittent extended length of 7 km has developed on the surface of this area. The rare Li-Be ores have been discovered during the current exploration in this area. To provide a reliable geochemical basis for the prospecting of rare metals and rare earth elements (REE) in areas with similar landscapes, this study conducted the grain-scale experiment and validity investigation in this study area using the large-scale micro-channel system geochemical survey technique. Based on the 1∶25,000 geochemical survey, grain sizes of -4~+ 20 meshes, -4~+ 40 meshes, -10~+ 40 meshes, and -10~+ 60 meshes were adopted in sampling for the experimental study in the zones bearing pegmatite veins. The contents of Cu, W, Sn, Be, Li, Nb, Rb, Zr, La, and Y were analyzed. The results show that relevant elements exhibited significant enrichment and dispersion characteristics and the geochemical distribution of these elements agreed well with the geological and mineral characteristics when grain sizes of -4~+ 40 meshes and -10~+ 40 meshes were adopted for the sampling of Be, Li, Nb, Rb, and Zr, grain sizes of -10~+ 40 meshes were adopted for the sampling of rare earth elements such as La and Y, and grain sizes of -10~+ 60 meshes were adopted for the sampling of nonferrous metal elements such as Cu, W, and Sn. The results of this study prove that the large-scale micro-channel system survey technique can obtain significant results in the geochemical prospecting of rare metals and REEs in areas with similar landscapes.
|
|
Received: 26 December 2021
Published: 05 July 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
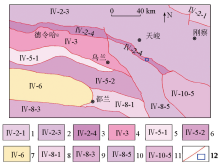
|
Geotectonic location map of study area
1—central Qilian magmatic arc; 2—south Qilian magmatic arc; 3—Zongwulongshan-Xiahe terrestrial rift; 4—Quanji plot; 5—Tanjianshan magmatic arc; 6—ophiolite melange belt in northern Chaidamu basin; 7—Chaidamu basin; 8—the northern slope of Qimantage-Xiariha magmatic arc; 9—northern Kunlun magmatic arc; 10—continental margin arc of the Elashan; 11—Zeku foreland basin; 12—boundary faults and study area
|
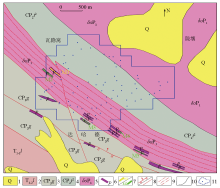
|
Geological map of Qiemogeshan area
1—Quaternary strata; 2—early-middle Triassic Longwuhe formation; 3—Carboniferous-middle Permian Guokeshan formation; 4—Carboniferous-middle Permian Tuergendaban formation; 5—early Permian quartz diorite; 6—granite pegmatite veins; 7—lithium/beryllium orebody; 8—reverse faults and faults of unknown nature; 9—ductile shear zones; 10—geological boundary; 11—sampling point and range
|
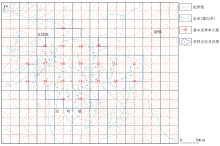
|
Distribution map of sampling points in study area
|

| 样品粒级 | 参数 | Be | Cu | La | Li | Nb | Rb | Sn | W | Y | Zr | | -4~+20目 | 最小值/10-6 | 1.25 | 11.40 | 19.20 | 11.00 | 6.50 | 43.70 | 1.36 | 0.32 | 12.30 | 89.30 | | 最大值/10-6 | 50.70 | 165.00 | 46.30 | 161.00 | 20.10 | 295.00 | 10.29 | 9.27 | 40.00 | 239.00 | | 平均值/10-6 | 2.59 | 22.54 | 34.23 | 49.66 | 11.84 | 100.99 | 2.51 | 1.13 | 20.92 | 139.58 | | 中位数/10-6 | 2.38 | 22.00 | 34.00 | 36.20 | 10.85 | 101.00 | 2.38 | 0.91 | 20.95 | 131.00 | | 标准离差/10-6 | 0.67 | 6.66 | 5.52 | 37.89 | 3.41 | 31.46 | 0.58 | 0.66 | 4.56 | 30.47 | | 浓集系数 | 1.33 | 1.11 | 1.06 | 1.63 | 1.03 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.68 | 1.04 | 0.85 | | 变异系数CV1 | 1.565 | 0.723 | 0.161 | 0.763 | 0.288 | 0.414 | 0.523 | 0.969 | 0.247 | 0.229 | | 变异系数CV0 | 0.26 | 0.295 | 0.161 | 0.763 | 0.288 | 0.312 | 0.233 | 0.592 | 0.218 | 0.218 | | -4~+40目 | 最小值/10-6 | 1.45 | 10.60 | 22.10 | 8.40 | 6.50 | 40.70 | 1.44 | 0.33 | 13.70 | 89.10 | | 最大值/10-6 | 55.80 | 78.60 | 55.40 | 198.00 | 18.80 | 343.00 | 10.47 | 182.00 | 35.80 | 223.00 | | 平均值/10-6 | 2.69 | 23.76 | 32.45 | 45.47 | 12.13 | 106.30 | 2.61 | 1.12 | 20.65 | 143.75 | | 中位数/10-6 | 2.48 | 24.20 | 31.70 | 39.20 | 11.45 | 113.00 | 2.45 | 0.95 | 20.20 | 136.00 | | 标准离差/10-6 | 0.86 | 7.44 | 6.18 | 28.05 | 3.60 | 32.52 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 4.59 | 33.59 | | 浓集系数 | 1.38 | 1.17 | 1.00 | 1.49 | 1.05 | 1.06 | 1.02 | 0.67 | 1.03 | 0.87 | | 变异系数CV1 | 1.653 | 0.416 | 0.233 | 0.763 | 0.297 | 0.409 | 0.513 | 2.037 | 0.234 | 0.234 | | 变异系数CV0 | 0.322 | 0.313 | 0.191 | 0.617 | 0.297 | 0.306 | 0.261 | 0.619 | 0.223 | 0.234 | | -10~+40目 | 最小值/10-6 | 1.51 | 11.90 | 23.20 | 15.90 | 6.80 | 47.70 | 1.39 | 0.33 | 12.20 | 79.50 | | 最大值/10-6 | 58.00 | 73.30 | 88.00 | 168.00 | 20.00 | 243.00 | 12.48 | 11.40 | 50.60 | 237.00 | | 平均值/10-6 | 2.60 | 22.42 | 34.85 | 39.04 | 12.39 | 104.63 | 2.49 | 1.50 | 23.18 | 141.90 | | 中位数/10-6 | 2.55 | 21.85 | 34.90 | 36.30 | 11.80 | 106.00 | 2.48 | 1.51 | 22.25 | 136.00 | | 标准离差/10-6 | 0.49 | 5.19 | 5.60 | 14.80 | 3.41 | 28.10 | 0.44 | 0.76 | 5.76 | 34.03 | | 浓集系数 | 1.33 | 1.11 | 1.08 | 1.28 | 1.08 | 1.04 | 0.97 | 0.9 | 1.15 | 0.86 | | 变异系数CV1 | 1.751 | 0.377 | 0.229 | 0.629 | 0.275 | 0.332 | 0.478 | 0.849 | 0.298 | 0.24 | | 变异系数CV0 | 0.188 | 0.232 | 0.161 | 0.379 | 0.275 | 0.269 | 0.175 | 0.508 | 0.248 | 0.24 | | -10~+60目 | 最小值/10-6 | 1.03 | 6.37 | 14.40 | 11.30 | 6.70 | 43.40 | 1.04 | 0.36 | 9.50 | 53.90 | | 最大值/10-6 | 54.30 | 81.60 | 47.40 | 175.00 | 24.40 | 382.00 | 13.49 | 22.70 | 39.70 | 256.00 | | 平均值/10-6 | 2.30 | 23.57 | 32.60 | 38.11 | 12.30 | 97.60 | 2.45 | 1.20 | 20.63 | 129.29 | | 中位数/10-6 | 2.17 | 23.00 | 31.70 | 32.65 | 11.05 | 95.80 | 2.19 | 0.96 | 19.10 | 120.50 | | 标准离差/10-6 | 0.61 | 7.26 | 6.20 | 23.62 | 4.14 | 30.43 | 0.92 | 0.72 | 5.88 | 31.92 | | 浓集系数 | 1.18 | 1.16 | 1.01 | 1.25 | 1.07 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.72 | 1.02 | 0.79 | | 变异系数CV1 | 1.788 | 0.399 | 0.190 | 0.790 | 0.337 | 0.454 | 0.701 | 1.587 | 0.298 | 0.278 | | 变异系数CV0 | 0.265 | 0.308 | 0.19 | 0.62 | 0.337 | 0.312 | 0.378 | 0.598 | 0.285 | 0.247 | | 青海省丰度[17]/10-6 | 1.95 | 20.24 | 32.41 | 30.45 | 11.52 | 100.53 | 2.56 | 1.67 | 20.13 | 164.54 |
|
Characteristic of grain-size element parameters from different samples in the study area
|
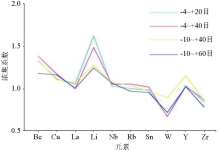
|
Concentration coefficient curves of each particle
|
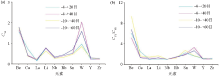
|
The CV1 curve (a) and CV1/CV0 curve (b) of each particle size were studied
|
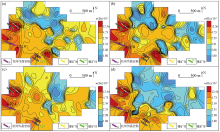
|
Geochemical maps of element Be in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
|
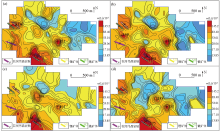
|
Geochemical maps of element Li in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
|
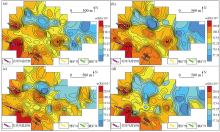
|
Geochemical maps of element Rb in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
|
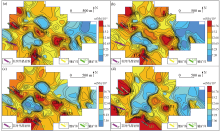
|
Geochemical maps of element Nb in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
|
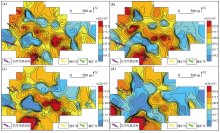
|
Geochemical maps of element Zr in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
|
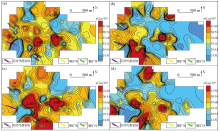
|
Geochemical maps of element La in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
|
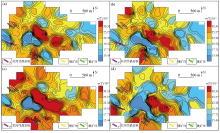
|
Geochemical maps of element Y in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
|
| [1] |
张素荣, 杨帆, 张华, 等. 青藏高原条件下现场分析方法的适应性[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(1):100-105.
|
| [1] |
Zhang S R, Yang F, Zhang H, et al. The suitability of field analytical methods under the special conditions of Tibetan plateau[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(1):100-105.
|
| [2] |
李超, 罗先熔, 邱炜, 等. 青海省都兰县金水口地区水系沉积物地球化学异常特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(5):1397-1410.
|
| [2] |
Li C, Luo X R, Qiu W, et al. Geochemical anomalies characteristics of stream sediments and ore-search prospect in Jinshuikou area of Dulan County,Qinghai Province[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(5):1397-1410.
|
| [3] |
严明书, 李瑜, 鲍丽然, 等. 1∶5万水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿意义[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(1):10-16.
|
| [3] |
Yan M S, Li Y, Bao L R, et al. Geochemical characteristics of 1∶50,000 stream sediments and in Xainza,Tibet,and their prospecting significance[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(1):10-16.
|
| [4] |
安朝, 杨敏, 陈熙, 等. 东昆仑东段都兰地区地球化学特征及其成矿意义——基于大比例尺微沟系(土壤)测量工作[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020, 56(6):1158-1169.
|
| [4] |
An Z, Yang M, Chen X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and metallogenic significance of the Dulan area in the eastern section of the East Kunlun Mountains derived from large-scale micro channel system (soil) measurement[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 56(6):1158-1169.
|
| [5] |
丁兆举, 常昊, 张年生, 等. 热带雨林景观土壤测量采样深度与样品粒级试验研究——以加纳国雅卡锰金矿为例[J]. 地质与勘探, 2021, 57(3):554-562.
|
| [5] |
Ding Z J, Chang H, Zhang N S, et al. Experimental study on sampling depth and sample granularity of soil survey in tropical rainforest landscape:Taken the Yakau Mn-Au deposit in Ghana as an example[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2021, 57(3):554-562.
|
| [6] |
陈化奇, 李永庆. 岩屑测量方法在干旱荒漠区的找矿效果——以贺兰山北段嘎拉斯台白钨矿的发现为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(1):55-63.
|
| [6] |
Chen H Q, Li Y Q. The prospecting effect of rock debris measurement method in arid desert area:Exemplified by the discovery of the Galasitaischeelite deposit in northern Helan Mountain[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(1):55-63.
|
| [7] |
李冲, 郝志红, 张忠进. 广东北市地区1∶5万水系沉积物测量粒级试验[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(2):303-311.
|
| [7] |
Li C, Hao Z H, Zhang Z J. A study on 1∶50,000 stream sediments survey in Beishiarea,Guangdong Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(2):303-311.
|
| [8] |
赵娟, 马正婷, 柴云, 等. 青海省冷湖行委俄博梁地区稀有稀土元素地球化学特征及找矿潜力分析[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(4):82-87.
|
| [8] |
Zhao J, Ma Z T, Chai Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and prospecting potential of rare rare-earth element in Eboliang area,Lenghu,Qinghai Province[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(4):82-87.
|
| [9] |
车鑫. 青海省天峻县国土空间地理特征研究[D]. 西宁: 青海民族大学, 2020.
|
| [9] |
Che X. Study on the spatial and geographical characteristics of land in Tianjun County of Qinghai Province[D]. Xining: Qinghai Nationalities University, 2020.
|
| [10] |
王秉璋, 韩杰, 谢祥镭, 等. 青藏高原东北缘茶卡北山印支期(含绿柱石)锂辉石伟晶岩脉群的发现及Li-Be成矿意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2020, 44(1):69-79.
|
| [10] |
Wang B Z, Han J, Xie X L, et al. The Discovery of the indosinian(beryl-bearing) spodumene pegmatitic dike swarm in the Chakaibeishan area on the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau:Implications for Li-Be mineralziation[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2020, 44(1):69-79.
|
| [11] |
王登红, 王瑞江, 孙艳, 等. 我国三稀(稀有稀土稀散)矿产资源调查研究成果综述[J]. 地球学报, 2016, 37(5):569-580.
|
| [11] |
Wang D H, Wang R J, Sun Y, et al. A review of achievements in the three-type rare mineral resources(rare resources,rare earth and rarely scattered resources)survey in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2016, 37(5):569-580.
|
| [12] |
李贤芳, 张玉洁, 田世洪. 锂同位素在伟晶岩矿床成因研究中的应用[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(2):419-429.
|
| [12] |
Li X F, Zhang Y J, Tian S H. Application of lithium isotopes in genetic study of pegmatite deposits[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(2):419-429.
|
| [13] |
邱瑜, 卢佳, 田滔, 等. 1∶25,000沟系沉积物地球化学测量方法有效性探讨——以东昆仑巴隆地区为例[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2019, 41(2):250-256.
|
| [13] |
Qiu Y, Lu J, Tian T, et al. A discussion of effectiveness to the 1∶25,000 sulcus sediments geochemical survey:The Balong area of east Kunlun as an example[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 41(2):250-256.
|
| [14] |
冷福荣, 李志强. 1∶20万区域化探方法核心技术“取样粒级”的讨论[J]. 物探与化探, 2009, 33(6):678-685.
|
| [14] |
Leng F R, Li Z Q. A Discussion on the "Samplinggrade",a key technology in 1∶200,000 regional geochemical exploratioa[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(6):678-685.
|
| [15] |
陶春军, 贾十军, 陈富荣, 等. 安徽北淮阳典型矿区水系沉积物采样方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(5):853-860.
|
| [15] |
Tao C J, Jia S J, Chen F R, et al. Research on sampling methods for stream sediments survey in the typical ore district of northern Huaiyang area in Anhui Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(5):853-860.
|
| [16] |
夏锦霞, 李方林, 杨东, 等. 用地球化学异常图和方差分析比较两种采样粒级的化探效果[J]. 物探与化探, 2009, 33(5):524-528.
|
| [16] |
Xia J X, Li F L, Yang D, et al. The application of geochemical anomaly map and varaiance analysis to comparing gochemical exploration effects of two sizes of fractions[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(5):524-528.
|
| [17] |
吴正寿, 赵呈祥, 易平乾, 等. 青海省矿产资源调查评价成果报告[R]. 青海省地质调查院, 2013.
|
| [17] |
Wu Z S, Zhao C X, Yi P Q, et al. Investigation and evaluation of mineral resources in Qinghai Province[R]. Qinghai Geological Survey Institute, 2013.
|
| [18] |
张晶, 杨帆, 刘明义, 等. 稀土配分模式在确定西天山风积物干扰粒级中的应用研究[J]. 西北地质, 2014, 47(2):126-131.
|
| [18] |
Zhang J, Yang F, Liu M Y, et al. Application of REE assemblage in determining the interference granularity of aeolian sediments in West Tianshan[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2014, 47(2):126-131.
|
| [19] |
王乔林. 土壤地球化学测量在甘肃北山白头山铷矿找矿中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2021, 57(1):110-121.
|
| [19] |
Wang Q L. Application of soil geochemical survey in the Baitoushan rubidium deposit,Beishan area,Gansu Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2021, 57(1):110-121.
|
| [20] |
王平, 谈艳, 黄银宝, 等. 沟系岩屑测量在青海省都兰县苏更地区钼矿找矿中的应用[J]. 黄金, 2017, 38(8):16-20.
|
| [20] |
Wang P, Tan Y, Huang Y B, et al. Application of ravine debris survey in the prospectingof molybdenum deposits in Sugeng Region,Dulan County,Qinghai Province[J]. Gold, 2017, 38(8):16-20.
|
| [1] |
LU Jun, WANG Jian-min, WANG Hong-bo, YU Rong-wen, ZHANG Da-peng. THE APPLICATION OF SOIL SURVEY TO THE SANDAOWANZI GOLD DEPOSIT[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2005, 29(6): 515-518. |
| [2] |
MA Xiao-yang, CUI Yu-jun, LI Xiang-you . TECHNIQUES OF1:50000 STREAM SEDIMENT SURVEY IN FOREST-SWAMP AREA OF NORTHERN DA HINGGAN MOUNTAINS[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2002, 26(6): 433-435,449. |
|
|
|
|

