|
|
|
| Application of the opposing coils transient electromagnetic method in investigation of mined-out areas of a gold deposit |
REN Xi-Rong( ), LI Xin, ZHOU Zhi-Jie ), LI Xin, ZHOU Zhi-Jie |
| No.2 Exploration Institute of Geological and Mineral Resources,Gansu Bureau of Geological and Minerals Exploration,Lanzhou 730020,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Dashui gold deposit in Maqu County,Gansu Province is a typical mine of the western Qinling region.Owing to continuous mining,many mined-out areas have been formed at different depths below high and steep slopes No.5 and 9,causing local surface collapse and major safety hazards.According to the requirements for environmental protection and safety,there is an urgent need to determine the spatial distribution of concealed collapse to effectively prevent geological disasters.Using the opposing coils transient electromagnetic method (OCTEM),this study conducted the fine-scale interpretation of the anomalies on the typical sections of the exploration area.Based on this,as well as the comprehensive analysis of the hydrogeological data and basic geological data of the exploration area,this study determined the transparent and three-dimensional distribution of the concealed collapse of the Dashui gold deposit.The results of this study show that the subsurface investigation of mined-out areas using the OCTEM can effectively reveal the lithologic and electrical characteristics of concealed strata in mined-out areas.Moreover,the significantly different physical properties between mined-out areas and surrounding rocks can be used to effectively identify the locations and basic morphologies of subsurface mined-out areas.The data on the boundary characteristic points of the mined-out areas on geophysical profiles with multiple exploration lines and three-dimensional modeling allow for the three-dimensional visualization of the spatial morphology of the mined-out areas.The application performance of the OCTEM,along with three-dimensional modeling,provides a technical basis for mine restoration and safety evaluation,thus effectively serving the construction of digital mines.
|
|
Received: 19 May 2022
Published: 27 April 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
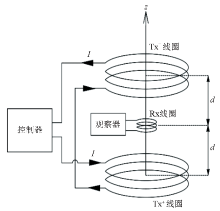
|
Schematic diagram of the OCTEM device
|
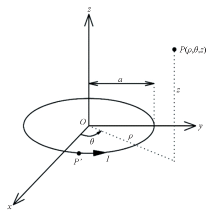
|
Cylindrical coordinates of current loop magnetic field calculation
|
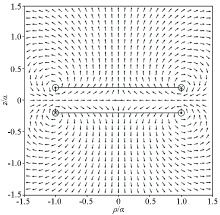
|
Schematic diagram of primary field magnetic field lines synthesized by OCTEM dual-coil source
|

| 岩性 | 样品数 | 电阻率最小~最
大值/(Ω·m) | 电阻率几何平
均值/(Ω·m) | 电性
特征 | | 细沙(充水) | 6 | 1.3~6.6 | 2.1 | 低阻 | | 红黏土 | 11 | 20.8~43.7 | 29 | 低阻 | | 泥岩 | 10 | 43.1~80.3 | 60.7 | 低阻 | | 细沙(含泥) | 8 | 16.8~115.6 | 61.7 | 低阻 | | 砂岩(破碎) | 7 | 55.2~77.4 | 63.6 | 低阻 | | 粉土 | 12 | 90.8~239.7 | 162.3 | 低阻 | | 溶蚀灰岩(含水) | 15 | 103.9~405.5 | 205.9 | 低阻 | | 细沙 | 2 | 270.9~271.2 | 271.1 | 低阻 | | 砂岩(板状) | 5 | 329.4~455.1 | 376.5 | 低阻 | | 含泥砾石 | 13 | 423.0~654.6 | 506.7 | 中等 | | 腐殖土 | 8 | 396.7~865.7 | 560 | 中等 | | 砂岩(块状) | 3 | 772.8~779.3 | 776.1 | 中等 | | 溶蚀灰岩 | 6 | 947.7~1486.5 | 1159.7 | 中等 | | 砾岩 | 18 | 334.4~3860.7 | 1164.2 | 中等 | | 砂砾石 | 9 | 1154.4~1410.9 | 1239.3 | 中等 | | 灰岩 | 14 | 9019.8~17612.3 | 11938.9 | 高阻 | | 结晶灰岩 | 9 | 11358.7~27581.3 | 16680.4 | 高阻 |
|
Statistical of electrical parameters of rock outcrops in the survey area
|
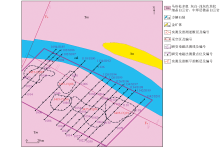
|
Geological map of Dashui gold deposit
|
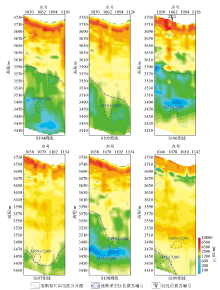
|
Combined inversion resistivity profile of transient electromagnetic profile in goaf 3455-CQ89
|
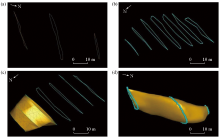
|
Schematic diagram of 3D visualization modeling of goaf
a—boundary coordinate establishment line;b—inter-section interpolation goaf boundary line;c—creation of goaf undulating surfaces;d—3D model of a single goaf
|
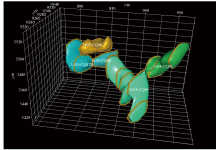
|
3D visualization model of goaf
|
| [1] |
张卫雄, 王有权, 庄飞舟, 等. 甘肃玛曲格萨尔黄金实业股份有限公司大水金矿矿产资源开发与恢复治理方案[R]. 甘肃玛曲格萨尔黄金实业股份有限公司, 2018.
|
| [1] |
Zhang W X, Wang Y Q, Zhuang F Z, et al. Mineral resources development and restoration treatment scheme of Dashui Gold Mine of Gansu Maqu Gesar Gold Industry Co.Ltd.[R]. Gansu Maqu Gesar Gold Industry Co. Ltd., 2018.
|
| [2] |
辛静. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在浅部采空区探测中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2019, 16(5):718-722.
|
| [2] |
Xin J. The application of opposing coils transient electromagnetic method to detect shallow goaf[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2019, 16(5):718-722.
|
| [3] |
李貅. 瞬变电磁测深的理论与应用[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 2002.
|
| [3] |
Li X. Theory and application of transient electromagnetic sounding[M]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Science and Technology Press, 2002.
|
| [4] |
薛国强, 李貅, 底青云. 瞬变电磁法理论与应用研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(4):195-200.
|
| [4] |
Xue G Q, Li X, Di Q Y. The progess of TEM in theory and application[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007, 22(4):195-200.
|
| [5] |
孔详儒. 电磁感应研究的进展与展望[J]. 地球物理学进展, 1992, 7(2):11-14.
|
| [5] |
Kong X R. The advance and prospect of the earth's electromagnetic induction study[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 1992, 7(2):11-14.
|
| [6] |
嵇艳鞠, 林君, 于生宝, 等. ATTEM系统中电流关断期间瞬变电磁场响应求解的研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2006, 49(6):1884-1890.
|
| [6] |
Ji Y J, Lin J, Yu S B, et al. A study on solution of transient electromagnetic response during transmitting current turn-off in the ATTEM system[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 2006, 49(6):1884-1890.
|
| [7] |
席振铢, 龙霞, 周胜, 等. 基于等值反磁通原理的浅层瞬变电磁法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(9):3428-3435.
|
| [7] |
Xi Z Z, Long X, Zhou S, et al. Opposing coils transient electromagnetic method for shallow subsurface detection[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 2016, 59(9):3428-3435.
|
| [8] |
席振铢, 宋刚, 周胜, 等. 一种瞬变电磁测量装置及方法[P]. 中国专利,201410092714X,2014-03-14.
|
| [8] |
Xi Z Z, Song G, Zhou S, et al. A transient electromagnetic measuring device and method[P] .China Patent, 201410092714X,2014-03-14.
|
| [9] |
Jackson J D. Chassical electrodynamics[M]. New York: Wiley, 1962.
|
| [10] |
周超, 赵思为. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在煤窑采空区中的应用[C]// 北京: 2018国际地球物理会议暨展览, 2018:1406-1409.
|
| [10] |
Zhou C, Zhao S W. Application of opposing coils transient electromagnetic method in coal mine goaf[C]// Beijing:2018 International Geophysical Conference and Exhibition, 2018:1406-1409.
|
| [11] |
杨建明, 王洪昌, 沙椿. 基于等值反磁通瞬变电磁法的岩溶探测分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(4):846-850.
|
| [11] |
Yang J M, Wang H C, Sha C. An analysis of karst exploration based on opposing coils transient electromagnetic method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(4):846-850.
|
| [12] |
彭星亮, 席振铢, 王鹤, 等. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在地质灾害探测中的应用对比[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2018, 30(8):147-150,153.
|
| [12] |
Peng X L, Xi Z Z, Wang H, et al. Comparison of application of opposing coils transient electromagnetic method in geological disaster detection[J]. Western Exploration Project, 2018, 30(8):147-150,153.
|
| [13] |
高远. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法对石膏矿采空区的探测分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1404-1408.
|
| [13] |
Gao Y. The application effect on detecting goaf of gypsum mine by opposing coils transient electromagnetics method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1404-1408.
|
| [14] |
雷宛, 肖宏跃, 邓一谦. 工程与环境物探教程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006.
|
| [14] |
Lei W, Xiao H Y, Deng Y Q. Engineering and environmental geophysical exploration Tutorial[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006.
|
| [15] |
赖耀发, 席振铢, 张峰, 等. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁电阻率谱系法探测铝土矿[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 52(9):3264-3272.
|
| [15] |
Lai Y F, Xi Z Z, Zhang F, et al. Application of opposing coils transient electromagnetic resistivity spectrum method to detect bauxite deposits[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2021, 52(9):3264-3272.
|
| [16] |
孙怀凤, 吴启龙, 陈儒军, 等. 浅层岩溶瞬变电磁响应规律试验研究[J]. 岩土力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(3):652-661.
|
| [16] |
Sun H F, Wu Q L, Chen R J, et al. Experimental study on transient electromagnetic responses to shallow karst[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(3):652-661.
|
| [17] |
赵东东, 陈基炜, 宗全兵, 等. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在地铁盾构孤石探测中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2021, 18(4):495-502.
|
| [17] |
Zhao D D, Chen J W, Zong Q B, et al. Application of opposing coils transient electromagnetic method in metro shielding boulder detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2021, 18(4):495-502.
|
| [1] |
CHEN Da-Lei, CHEN Wei-Ying, GUO Peng, WANG Run-Sheng, WANG Hong-Jun, ZHANG Chao, MA Qi-He, HE Chun-Yan. The application of SOTEM method to populated areas: A case study of Fangzi coal mine goaf[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(5): 1226-1232. |
| [2] |
LU Yun-Fei, XUE Guo-Qiang, QIU Wei-Zhong, ZHOU Nan-Nan, HOU Dong-Yang. The research on SOTEM and its application in mined-out area of coal mine[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(2): 354-359. |
|
|
|
|

