|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics of selenium, fluorine, iodine in surface soil of the agricultural land in Ruoqiang County, Xinjiang |
MA Chang-Lian1,2,3( ), ZHOU Jin-Long1,2,3( ), ZHOU Jin-Long1,2,3( ), ZENG Yan-Yan1,2,3, REN Gui-Bing1,2,3, WANG Song-Tao4 ), ZENG Yan-Yan1,2,3, REN Gui-Bing1,2,3, WANG Song-Tao4 |
1. College of Water Conservancy and Civil Engineering,Xinjiang Agricultural University,Urumqi 830052,China
2. Xinjiang Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering Research Center, Urumqi 830052, China
3. Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Engineering Security and Water Disasters Prevention,Urumqi 830052,China
4. No.2 Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology Party of Xinjiang Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources Exploration and Development, Changji 831100, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study investigated the surface soil of the agricultural land in Ruoqiang County, Xinjiang. Based on 142 surface soil samples collected in 2016, this study analyzed the selenium (Se), fluorine (F), iodine (I), Al2O3, and SiO2 contents and the physicochemical proxies such as soil organic carbon (OrgC), total nitrogen (N), and pH of the surface oil in the study area. Then, this study explored the contents and distribution of biological elements Se, F, and I in the study area, as well as their influencing factors. The results are as follows. The soil in the study area is alkaline to strongly alkaline, with average Se, F, and I contents of 0.23×10-6, 645×10-6, and 1.06×10-6, respectively. The average contents of Se and I are lower than their national soil background values, while the average content of F is much higher than its national soil background value. The Se, F, and I contents are positively correlated with each other and all of them are significantly positively correlated with total N. The Se content is negatively correlated with the SiO2 content, while the I content is positively correlated with the Al2O3 content. The contents, distribution, and geochemical characteristics of Se, F, and I are controlled by parent materials and soil types. Among different parent materials, the Se, F, and I contents are higher in the soil of diluvium areas but are the lowest in the soil of alluvium-diluvium areas. Among different types of soil, the contents of the three elements are high in the irrigation-silted soil, while the Se content is the highest and the F and I contents are the lowest in the forest-shrub-grassland soil.
|
|
Received: 14 October 2021
Published: 03 January 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
ZHOU Jin-Long
E-mail: 2506786060@qq.com;zjzhoujl@163.com
|
|
|
|
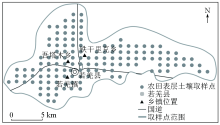
|
The location of the study area and sampling sites distribution
|

| 分析指标 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 单位 | 重复样合格率 | | Se | 非色散原子荧光光谱法(AFS) | 0.01 | 10-6 | >98% | | F | 离子选择电极法(IS) | 36.0 | 10-6 | >98% | | I | 阳离子树脂交换—电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法 | 0.09 | 10-6 | >98% | | OrgC | 重铬酸钾容量法 | 0.063 | 10-2 | >98% | | N | 凯氏氮分析法 | 19.58 | 10-6 | >98% | | SiO2 | X波长色散X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | 0.055 | 10-2 | >98% | | Al2O3 | X波长色散X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | 0.049 | 10-2 | >98% | | pH | 电位法 | 0.03 | | >98% |
|
Analytical methods and detection limits of geochemical indicators of soils
|

| 指标 | 背景值[17] | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 中位数 | 标准偏差 | 变异系数/% | 富集系数q/% | 富集比例/% | | OrgC | 1.45 | 10.69 | 0.10 | 0.48 | 0.38 | 0.88 | 183.3 | 33.1 | 0.7 | | N | 442 | 1306 | 81 | 451 | 432 | 235.10 | 52.1 | 101.9 | 48.6 | | pH | 6.7 | 9.15 | 7.55 | 8.37 | 8.54 | 0.35 | 4.2 | 124.9 | 100.0 | | Se | 0.29 | 0.91 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 52.2 | 79.3 | 23.9 | | F | 478 | 952 | 386 | 645 | 630 | 122.9 | 19.1 | 134.9 | 100.0 | | I | 3.76 | 1.90 | 0.44 | 1.06 | 1.10 | 0.33 | 31.1 | 28.2 | 0 | | SiO2 | 66.0 | 68.75 | 31.78 | 54.36 | 62.89 | 6.65 | 12.2 | 82.4 | 5.6 | | Al2O3 | 12.5 | 52.96 | 5.09 | 10.11 | 10.06 | 3.73 | 36.9 | 80.9 | 0.7 |
|
Descriptive statistics of physicochemical parameters of surface soils(n=142)
|

| 元素 | 特征值 | 土壤类型 | 灌淤土
(n=126) | 棕漠土
(n=5) | 林灌草地土
(n=5) | 其他土
(n=6) | | Se | 极大值/10-6 | 0.56 | 0.19 | 0.91 | 0.20 | | 极小值/10-6 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.08 | | 平均值/10-6 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.36 | 0.14 | | 标准差/10-6 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.04 | | 变异系数/% | 47.8 | 20.0 | 86.1 | 28.6 | | F | 极大值/10-6 | 952 | 750 | 607 | 770 | | 极小值/10-6 | 386 | 520 | 490 | 551 | | 平均值/10-6 | 649 | 596 | 555 | 672 | | 标准差/10-6 | 126.29 | 80.01 | 46.19 | 74.96 | | 变异系数/% | 19.5 | 13.4 | 8.3 | 11.2 | | I | 极大值/10-6 | 1.90 | 1.60 | 0.94 | 1.90 | | 极小值/10-6 | 0.44 | 0.80 | 0.62 | 0.52 | | 平均值/10-6 | 1.07 | 1.05 | 0.72 | 1.02 | | 标准差/10-6 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.46 | | 变异系数/% | 29.9 | 26.7 | 15.3 | 45.1 |
|
Content characteristics of Se, F and I in different soil types
|

| 元素 | 特征值 | 成土母质 | 冲积物
(n=24) | 冲积洪积物
(n=22) | 风积物
(n=90) | 洪积物
(n=6) | | Se | 极大值/10-6 | 0.26 | 0.40 | 0.56 | 0.91 | | 极小值/10-6 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.11 | | 平均值/10-6 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.36 | | 标准差/10-6 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.27 | | 变异系数/% | 33.3 | 47.4 | 44.0 | 75.0 | | F | 极大值/10-6 | 878 | 841 | 952 | 896 | | 极小值/10-6 | 464 | 397 | 386 | 551 | | 平均值/10-6 | 635 | 628 | 648 | 705 | | 标准差/10-6 | 160.39 | 163.56 | 128.41 | 266.43 | | 变异系数/% | 25.3 | 26.0 | 19.8 | 37.8 | | I | 极大值/10-6 | 1.90 | 1.80 | 1.70 | 1.90 | | 极小值/10-6 | 0.56 | 0.44 | 0.51 | 0.72 | | 平均值/10-6 | 1.08 | 0.99 | 1.06 | 1.19 | | 标准差/10-6 | 0.01 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.37 | | 变异系数/% | 0.9 | 36.4 | 29.2 | 31.1 |
|
Content characteristics of Se, F and I in soils derived from different parent materials
|

| 成土母质 | 样品数 | 元素 | F | I | OrgC | N | SiO2 | Al2O3 | pH | | 冲积物 | 24 | | 0.528** | 0.656** | 0.693** | 0.729** | -0.884** | 0.540** | -0.025 | | 冲积洪积物 | 22 | | 0.371 | 0.597** | 0.735** | 0.677** | -0.477** | 0.021 | -0.050 | | 风积物 | 90 | Se | 0.269* | 0.214* | 0.080 | 0.316** | -00528** | -0.029 | 0.080 | | 洪积物 | 6 | | -0.238 | -0.227 | 0.231 | 0.197 | -0.983** | -0.850* | 0.195 | | 汇总 | 142 | | 0.256** | 0.238** | 0.118 | 0.373** | -0.595** | -0.035 | 0.033 | | 冲积物 | 24 | | | 0.320 | 0.332 | 0.398 | -0.494 | -0.008 | 0.242 | | 冲积洪积物 | 22 | | | 0.310 | 0.187 | 0.280 | -0.030 | 0.174 | 0.461* | | 风积物 | 90 | F | | 0.410** | 0.137 | 0.243* | 0.085 | 0.179 | -0.306* | | 洪积物 | 6 | | | 0.968** | -0.610 | 0.771 | 0.136 | 0.546 | -0.880* | | 汇总 | 142 | | | 0.409** | 0.130 | 0.283** | -0.015 | 0.159 | -0.092 | | 冲积物 | 24 | | | | 0.666** | 0.690** | -0.695** | -0.649** | 0.155 | | 冲积洪积物 | 22 | | | | 0.681** | 0.701** | -0.127 | 0.338 | 0.441 | | 风积物 | 90 | I | | | 0.197 | 0.406** | -0.072 | 0.234* | -0.052 | | 洪积物 | 6 | | | | -0.464 | 0.708 | 0.108 | 0.461 | -0.811 | | 汇总 | 142 | | | | 0.200* | 0.512** | -0.147 | 0.211** | 0.062 |
|
Pearson correlation coefficients of physicochemical parameters in surface soils in the study area
|

| 指标 | 主成分1 | 主成分2 | 主成分3 | 主成分4 | | Se | 0.027 | 0.245 | 0.836 | -0.031 | | F | 0.059 | 0.794 | -0.003 | -0.285 | | I | 0.172 | 0.804 | 0.110 | 0.147 | | OrgC | 0.984 | 0.066 | 0.112 | -0.024 | | N | -0.085 | 0.650 | 0.384 | 0.348 | | SiO2 | 0.019 | 0.006 | -0.916 | -0.027 | | Al2O3 | 0.981 | 0.101 | -0.118 | -0.063 | | pH | -0.056 | 0.016 | -0.015 | 0.938 | | 特征值 | 1.975 | 1.775 | 1.724 | 1.111 | | 方差贡献率/% | 24.690 | 22.184 | 21.550 | 13.887 | | 累积方差贡献率/% | 24.690 | 46.874 | 68.424 | 82.311 |
|
Pearson principal component analysis of element contents of surface soils in the study area
|

| 元素 | 分级 | 缺乏 | 边缘 | 适量 | 高 | 过剩 | | Se | 含量范围/10-6 | ≤0.125 | 0.125~0.175 | 0.175~0.4 | 0.4~3.0 | ≥3.0 | | 样品数 | 29 | 22 | 80 | 11 | 0 | | 比例/% | 20.4 | 15.5 | 56.3 | 7.8 | 0.0 | | F | 含量范围/10-6 | ≤400 | <400~500 | >500~550 | >550~700 | ≥700 | | 样品数 | 2 | 17 | 14 | 58 | 51 | | 比例/% | 1.4 | 12.0 | 9.9 | 40.8 | 35.9 | | I | 含量范围/10-6 | ≤1 | <1~1.50 | >1.50~5 | >5~100 | ≥100 | | 样品数 | 70 | 65 | 11 | 0 | 0 | | 比例/% | 49.3 | 43.0 | 7.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
|
Classification criteria and statistics of Se,F and I contents of surface soils
|
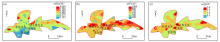
|
Grade zoning map of selenium, fluorine and iodine content in topsoil of the study area
|
| [1] |
高冉, 潘继花, 李伟, 等. 日照市茶园土壤硒含量及影响因素研究[J]. 山东农业科学, 2021, 53(1):82-86.
|
| [1] |
Gao R, Pan J H, Li W, et al. Study on soil selenium content and its influencing factors in typical tea garden of Rizhao City[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 53(1):82-86.
|
| [2] |
潘自平, 刘新红, 孟伟, 等. 贵阳中心区土壤氟的地球化学特征及其环境质量评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2018, 31(1): 87-94.
|
| [2] |
Pan Z P, Liu X H, Meng W, et al. Geochemical characteristics of fluorine in soils and its environmental quality in central district of guiyang[J]. Researchof Environmental Sciences, 2018, 31(1): 87-94.
|
| [3] |
王卫星, 曹淑萍, 李攻科, 等. 津北水土环境氟地球化学特征及其环境质量评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(1):207-214.
|
| [3] |
Wang W X, Cao S P, Li G K, et al. Geochemical characteristics and environmental quality assessment of luorine in soil and water in northern Tianjin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(1): 207-214.
|
| [4] |
周骏. 浙江省土壤中硒、碘的环境与生物地球化学特征研究[D] 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016.
|
| [4] |
Zhou J. Environmental and biogeochemical characteristics of selenium and iodine of soil in Zhejiang Province[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2016.
|
| [5] |
宋泽峰, 蔡奎, 冯星, 等. 冀中南平原土壤碘地球化学特征研究[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(6): 2144-2151.
|
| [5] |
Song Z F, Cai K, Feng X, et al. Iodine geochemistry studies of soil in central south Hebei plain[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(6): 2144-2151.
|
| [6] |
罗璐. 典型流域土壤水系沉积物碘的空间分布特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.
|
| [6] |
Luo L. Study on the spatial distribution of iodine in terrestrial soil and sediment in the typical valley[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2019.
|
| [7] |
唐将, 李勇, 邓富银, 等. 三峡库区土壤中硒、碘、氟分布特征与规律研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2005(4): 491-495.
|
| [7] |
Tang J, Li Y, Deng F Y, et al. The distribution characteristics of Se, I, F in soils in the district of three gorges reservoir[J]. Resource and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2005(4):491-495.
|
| [8] |
曾妍妍, 范薇, 陈云飞, 等. 新疆若羌县绿洲带土壤地球化学背景值及质量评价[C]// 2016中国环境科学学会学术年会论文集(第三卷), 2016:1103-1109.
|
| [8] |
Zeng Y Y, Fan W, Chen Y F, et al. Soil geochemical background value and quality evaluation in oasis zone of Ruoqiang County, Xinjiang[C]// Proceedings of the Annual Conference of Chinese Society for EnvironmentalSciences (Vol.3), 2016:1103-1109.
|
| [9] |
曾妍妍, 周金龙, 王松涛, 等. 新疆若羌县农田土壤重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(9):87-91.
|
| [9] |
Zeng Y Y, Zhou J L, Wang S T, et al. Distribution characteristics and assessment for farmland soil heavy metals pollution in Ruoqiang County of Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31(9):87-91.
|
| [10] |
曾妍妍, 周金龙, 郑勇, 等. 新疆若羌县绿洲区富锗土壤地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 土壤通报, 2017, 48(5):1082-1086.
|
| [10] |
Zeng Y Y, Zhou J L, Zhen Y, et al. Geochemical features of germanium-rich soils and its causes in oasis region of Ruoqiang County, Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2017, 48(5):1082-1086.
|
| [11] |
曾妍妍, 周金龙, 陈云飞, 等. 新疆若羌县土壤微量营养元素的空间分布特征及影响因素[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2018, 36(4): 22-28.
|
| [11] |
Zeng Y Y, Zhou J L, Chen Y F, et al. Spatial distribution and its influencing factors of micronutrients in soils of Ruoqiang County, Xinjiang[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2018, 36(4):22-28.
|
| [12] |
范薇, 曾妍妍, 周金龙, 等. 新疆若羌县土壤质量地球化学评价[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(5): 1190-1196.
|
| [12] |
Fan W, Zeng Y Y, Zhou J L, et al. Geochemical evaluation of soil quality in Ruoqiang County,Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(5):1190-1196.
|
| [13] |
陈云飞, 周金龙, 曾妍妍, 等. 塔里木盆地东南缘绿洲带土壤砷含量空间分布特征及污染评价[C]// 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会第17届学术年会论文摘要集, 2019: 945-946.
|
| [13] |
Chen Y F, Zhou J L, Zeng Y Y, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of soil arsenic content in oasis zone of southeast Margin of Tarim Basin[C]// Abstracts of the 17th Annual Conference of Chinese Society of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2019:945-946.
|
| [14] |
国家统计局农村社会经济调查司. 中国县域统计年鉴(乡镇卷)[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020: 672-677.
|
| [14] |
Rural Social and Economic Survey Division, National Bureau of Statistics. China county statistical yearbook (Township)[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2020: 672-677.
|
| [15] |
中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T 0295—2016土地质量地球化学评价规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
|
| [15] |
Ministry of Land and Resources, PRC. DZ/T 0295—2016 Code for geochemical evaluation of land quality[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
|
| [16] |
朱红霞, 陈效民, 杜臻杰. 基于地统计学的土壤氮素与pH的空间变异性研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2010, 41(5):1086-1090.
|
| [16] |
Zhu H X, Chen X M, Du Z J. Spatial variability of soil nitrogen and pH assessed by the method of geostatistics[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2010, 41(5):1086-1090.
|
| [17] |
成杭新, 李括, 李敏, 等. 中国城市土壤化学元素的背景值与基准值[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(3): 265-306.
|
| [17] |
Cheng H X, Li K, Li M, et al. Geochemical background and baseline value of chemical elements in urban soil in China[J]. Earth Science Frontier, 2014, 21(3): 265-306.
|
| [18] |
龚子同, 黄标. 土壤中硒、氟、碘元素的空间分异与人类健康[J]. 土壤学进展, 1994, 22(5):1-12.
|
| [18] |
Gong Z T, Huang B. Spatial differentiation of selenium, fluorine and iodine in soil and human health[J]. Progress in Soil Science, 1994, 22(5): 1-12.
|
| [19] |
鄢明才, 顾铁新, 迟清华, 等. 中国土壤化学元素丰度与表生地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 1997, 21(3):161-167.
|
| [19] |
Yan M C, Gu T X, Chi Q H, et al. Abundance of chemical elements of soils in China and supergenesis geochemistry characteristics[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1997, 21(3): 161-167.
|
| [20] |
黄成敏, 龚子同. 海南岛北部玄武岩上土壤发生研究Ⅲ元素地球化学特征[J]. 土壤学报, 2002, 39(5):643-652.
|
| [20] |
Huang C M, Gong Z T. Studies on soil occurrence over basalt in northern Hainan IslandⅢ Geochemical characteristics of elements[J]. Journal of Soil, 2002, 39(5):643-652.
|
| [21] |
杨文娜, 任嘉欣, 李忠意, 等. 主成分分析法和模糊综合评价法判断喀斯特土壤的肥力水平[J]. 西南农业学报, 2019, 32(6):1307-1313.
|
| [21] |
Yang W N, Ren J X, Li Z Y, et al. Soil fertility in karst regionswith analysis of principal component and fuzzy synthetic evaluation[J]. South West China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 32(6):1307-1313.
|
| [22] |
张子龙, 王文全, 缪作清, 等. 主成分分析在三七连作土壤质量综合评价中的应用[J]. 生态学杂志, 2013, 32(6):1636-1644.
|
| [22] |
Zhang Z L, Wang W Q, Miu Z Q, et al. Application of principal component analysis in comprehensive assessment of soil quality under panax notoginseng continuous planting[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2013, 32(6):1636-1644.
|
| [23] |
周越, 吴文良, 孟凡乔, 等. 土壤中硒含量、形态及有效性分析[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2014, 31(6): 527-532.
|
| [23] |
Zhou Y, Wu W L, Meng F Q, et al. Review on the content,specification of selenium and its availability in soils[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2014, 31(6): 527-532.
|
| [24] |
周墨, 陈国光, 张明, 等. 赣南地区土壤硒元素地球化学特征及其影响因素研究:以青塘—梅窖地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(6):1292-1301.
|
| [24] |
Zhou M, Chen G G, Zhang M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of seleniumin soils of south Jiangxi province:A typical area of Qingtang-Meijiao[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(6): 1292-1301.
|
| [25] |
王锐, 余涛, 曾庆良, 等. 我国主要农耕区土壤硒含量分布特征、来源及影响因素[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5):359-366.
|
| [25] |
Wang R, Yu T, Zeng Q L, et al. Distribution characteristics,origin and influencing factors of soil selenium concentration of main farming areas in China[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2017, 7(5): 359-366.
|
| [26] |
解维域, 丁辰, 宋烨, 等. GB/T 5835—2009干制红枣[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009:1-16.
|
| [26] |
Xie W Y, Ding C, Song Y, et al. GB/T 5835—2009 Dired Chinese jujubes[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2009:1-16.
|
| [27] |
薛粟尹, 李萍, 王胜利, 等. 干旱区绿洲土壤氟污染生态风险评估研究[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(3): 1075-1080.
|
| [27] |
Xue L Y, Li P, Wang S L, et al. Study on ecological risk assessment technology of fluoride pollution from arid oasis soil[J]. Environment Science, 2014, 35(3):1075-1080.
|
| [28] |
潘自平, 刘新红, 孟伟, 等. 贵阳中心区土壤氟的地球化学特征及其环境质量评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2018, 31(1):87-94.
|
| [28] |
Pan Z P, Liu X H, Meng W, et al. Geochemical characteristics of fluorine in soils and its environmental quality in central district of guiyang[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 31(1):87-94.
|
| [29] |
成晓梦. 云南不同成土母质土壤剖面中重金属元素地球化学行为与风险分析[D] 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.
|
| [29] |
Chen X M. Geochemical behavior and risk analysis for heavy elements in soil profiles with different parent material, Yunnan Province, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2016.
|
| [30] |
张一鹤, 杨泽, 戴慧敏, 等. 穆棱河—兴凯湖平原土地质量地球化学评价[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(1):62-70.
|
| [30] |
Zhang Y H, Yang Z, Dai H M, et al. Geochemical evaluation of land quality in Muling river-Xingkai lake plain[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(1):62-70.
|
| [31] |
严爱兰. 土壤碘的环境地球化学迁移研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2014, 42(16):5056-5057.
|
| [31] |
Yan A L. Environmental and geochemical migration of iodine in soil[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(16):5056-5057.
|
| [32] |
Whitehead D C. The volatilization from soils and mixtures of soil components of iodine added as potassium iodide[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 1981, 32(1): 97-102.
|
| [1] |
JIANG Bing, LIU Yang, WU Zhen, ZHANG De-Ming, SUN Zeng-Bing, MA Jian. Geochemical characteristics of fluorine in irrigation water and soils in the Gaomi area, Shandong Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1348-1353. |
| [2] |
REN Rui, ZHANG Zhi-Min, WANG Hui, CHEN Ji-Ping, QIAO Xin-Xing, LIANG Dong-Li. Exploring selenium enrichment criteria for soils in the Guanzhong area, Shaanxi Province: A case study of wheat[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1354-1360. |
|
|
|
|

