|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics and ecological health-related ranges of Copper in soil in Huaying Mountain-Xicao in Linshui County, Sichuan Province |
ZHAO Xiao-Yuan1( ), YANG Zhong-Fang1( ), YANG Zhong-Fang1( ), CHENG Hui-Yi1, MA Xu-Dong1, WANG Jue1, LI Zhi-Kun1, WANG Chen1, LI Ming-Hui2, LEI Feng-Hua2 ), CHENG Hui-Yi1, MA Xu-Dong1, WANG Jue1, LI Zhi-Kun1, WANG Chen1, LI Ming-Hui2, LEI Feng-Hua2 |
1. School of Earth Sciences and Resources,China University of Geosciences,Beijing 100083,China
2. Chengdu Center,China Geological Survey,Chengdu 610081,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Copper (Cu) is an essential trace element for the human body. However, there is no recommended value for Cu content in crops in China, and there is no standardon Cu content in soil for developing Cu-rich land resources. This paper takes the Huaying Mountain-Xicao cultivated land areas in Linshui County, Sichuan Province as the study area. Based on the survey results of the Cu contents in surface soil, crops, and root soil obtained from the 1∶50 000 land quality geochemical survey, this study investigated the contents and distribution of Cu in soil and crops and analyzed the influencing factors of the biological enrichment coefficient (BAF) of Cu in corn seeds. Moreover, it established a BAF prediction model of Cu in corn seeds and proposed the optimal ranges of Cu contents for developing Cu-rich corn and land resources. The study results are as follows. The Cu content in the surface soil of the study area ranges from 3.33×10-6 to 173×10-6, with an average and a median of 26.85×10-6 and 25.60×10-6, respectively. The soil with high Cu content is mainly distributed in the areas in Huaying Mountain in Linshui County where basalts, carbonate rocks, and carbonaceous shales are soil-forming rocks. In contrast, the soil with low Cu content is distributed in areas in Xicao where Jurassic sandshaleserves as soil-forming rocks. The Cu content in corn seeds in the study area ranges from 0.80×10-6 to 2.71×10-6, with an average and a median of 1.76×10-6 and 1.82×10-6 respectively. To ensure the safety of human beings in terms of Cu intake, the optimal Cu contents in corn seeds and soil in the study area should be 0.756×10-6~10.080×10-6 and 12.67×10-6~169.00×10-6, respectively.
|
|
Received: 27 May 2021
Published: 25 February 2022
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
YANG Zhong-Fang
E-mail: zhaoxiaoyuan@cugb.edu.cn;zfyang01@126.com
|
|
|
|
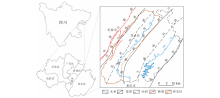
|
Location of the study area
|
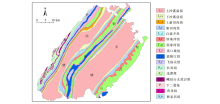
|
Geological map of Linshui County
|
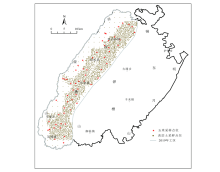
|
Sample distribution map of the study area
|

| 样品类型 | 元素 | 处理方法 | 分析方法 | 项目要求检出限/10-6 | 检出限/10-6 | | 表层土 | Cu | HNO3-HF-HClO4溶样 | ICP-MS | 1 | 1 | | 农作物 | Cu | 微波消解法 | ICP-MS | 1 | 0.005 | | 根系土 | Al2O3 | 粉末压片法 | XRF | 0.05* | 0.05* | | SiO2 | 粉末压片法 | XRF | 0.1* | 0.05* | | TFe2O3 | 粉末压片法 | XRF | 0.05* | 0.05* | | Corg | 重铬酸钾氧化 | VOL | 0.1* | 0.05* | | Cu | HCl - HNO3-HF-HClO4溶样 | ICP-AES | 1 | 0.8 |
|
Analysis methods and detect limits for samples
|

| 含量范围 | 准确度(ΔlgC) | 精密度(RSD)/% | | 检出限3倍以内 | ≤±0.10 | ≤17 | | 检出限3倍以上 | ≤±0.05 | ≤10 | | 1%~5% | ≤±0.04 | ≤8 | | >5% | ≤±0.02 | ≤3 |
|
Requirements for accuracy and precision of soil sample analysis methods
|

| 样品数 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 中位值 | 平均值 | 全国值[21] | 四川值[22] | | 3306 | 173 | 3.33 | 25.6 | 26.85 | 22.6 | 29.7 |
|
Cu content of topsoil sampling in the study area10-6
|
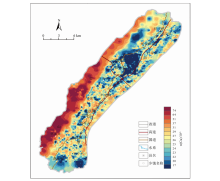
|
Geochemical map of Cu content of topsoil in the study area
|

| 指标 | 砂页岩n=3039 | | 石灰岩n=200 | | 炭质页岩n=43 | | 玄武岩n=24 | | 中位值 | 平均值 | 中位值 | 平均值 | 中位值 | 平均值 | 中位值 | 平均值 | | w(Cu)/10-6 | 25.3 | 24.53 | | 38.95 | 47.49 | | 63.7 | 68.03 | | 79.3 | 74.44 | | pH | 5.25 | | | 6.64 | | | 5.17 | | | 5.73 | |
|
Content of Cu and pH of different parent material
|

| 用地类型 | pH≤5.5 | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 6.5<pH≤7.5 | pH>7.5 | | 果园 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 200 | | 其他 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 100 |
|
Risk screening values of Cu pollution in soil10-6
|
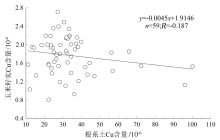
|
Scatter plot of Cu content in corn seeds and soil
|

| 土壤理化性质 | Corg | SiO2/Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | | 生物富集系数(BAF) | -0.472** | 0.437* | -0.801** |
|
Correlation analysis of BAF with soil elements
|
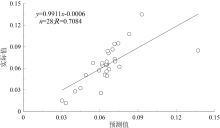
|
Scatter plot of BAF predicted value and measured value
|

| 食品种类 | 城市 | 农村 | 合计 | | 粮谷薯类 | 246.67 | 259.72 | 254.5 | | 蔬菜类 | 295.96 | 245.53 | 265.67 | | 水果类 | 28.09 | 8.94 | 16.58 | | 畜禽肉类 | 139.84 | 134.08 | 136.38 | | 鱼虾水产类 | 9.68 | 5.74 | 7.31 | | 蛋类 | 26.95 | 10.52 | 17.08 | | 奶及其制品类 | 59.64 | 9.97 | 29.80 | | 大豆及其制品类 | 14.64 | 5.40 | 9.08 | | 食用油 | 43.65 | 51.59 | 48.42 | | 食盐 | 8.17 | 7.56 | 7.80 |
|
The average intake of all kinds of food in Sichuan Province g/d
|
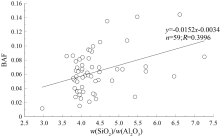
|
Scatter plot of BAF and SiO2/Al2O3content
|
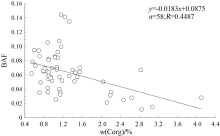
|
Scatter plot of BAF and Corg content
|
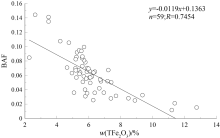
|
Scatter plot of BAF and TFe2O3 content
|
| [1] |
Bonnie R S, Marc S, Daniel K, et al. Copper and human health: Biochemistry, genetics, and strategies for modeling dose-response relationships[J]. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part B, 2007,10(3):157-222.

|
| [2] |
McBride M B. Trace metals and sulfur in soils and forage of a chronic wasting disease locus[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2007,4(2):134-139.

|
| [3] |
郭小燕, 杨玉霞. 环境地球化学与人体健康的关系[J]. 环境与发展, 2012,24(2):210-213.
|
| [3] |
Guo X Y, Yang Y X. Environmental geochemistry in relation to human health[J]. Environment and Development, 2012,24(2):210-213.
|
| [4] |
马国瑞, 石伟勇. 农作物营养失调症原色图谱[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2002:76-77.
|
| [4] |
Ma G R, Shi W Y. Primary color map of crop malnutrition disease[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2002: 76-77.
|
| [5] |
Brian J A. Heavy metals in soils:Trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability[M]. Third Edition. Berlin: Springer Netherlands, 2013:100-103.
|
| [6] |
Mclaren R G, Crawford D V. Studies on soil copper I. The fractionation of copper in soils[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2006,24(2):172-181.
|
| [7] |
孔维屏, 武玫玲. 土壤铁锰氧化物对铜离子富集作用的初步研究[J]. 土壤, 1992,24(1):41-42.
|
| [7] |
Kong W P, Wu M L. Preliminary study on the enrichment of copper ions by iron and manganese oxides in soil[J]. Soils, 1992,24(1):41-42.
|
| [8] |
刘斌, 黄玉溢, 陈桂芬. 广西耕地土壤铜的含量及其影响因素[J]. 南方农业学报, 2006,37(6):91-93.
|
| [8] |
Liu B, Huang Y Y, Chen G F. Study on Cu content in cultivated soils and its influence factors in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2006,37(6):91-93.
|
| [9] |
Sauvé S, McBride M B, Norvell W A, et al. Copper solubility and speciation of in situ contaminated soils:Effects of copper level, pH and organic matter[J]. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 1997,100(1-2):133-149.
|
| [10] |
Degryse F, Smolders E, Parker D R. Partitioning of metals (Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) in soils:Concepts, methodologies, prediction and applications-a review[J]. Cheminform, 2010,41(4):590-612.
|
| [11] |
Du L G, Vanthuyne D R J, Vandecasteele B, et al. Influence of hydrological regime on pore water metal concentrations in a contaminated sediment-derived soil[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007,147(3):615-625.

|
| [12] |
Weber F A, Voegelin A, Kretzschmar R. Multi-metal contaminant dynamics in temporarily flooded soil under sulfate limitation[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009,73(19):5513-5527.

|
| [13] |
Kelderman P, Osman A A. Effect of redox potential on heavy metal binding forms in polluted canal sediments in Delft (The Netherlands)[J]. Water Research, 2007,41(18):4251-4261.
|
| [14] |
蒋廷惠, 胡蔼堂, 秦怀英. 土壤中锌, 铜, 铁, 锰的形态与有效性的关系[J]. 土壤通报, 1989,5(12):228-231.
|
| [14] |
Jiang T H, Hu A T, Qin H Y. Relationship between the forms and availability of Zn, Cu, Fe and Mn in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 1989,5(12):228-231.
|
| [15] |
孔维屏. 土壤中铜的形态及转化的研究概况[J]. 土壤学进展, 1986(6):15-22.
|
| [15] |
Kong W P. Study on the form and transformation of Cu in soil[J]. Progress in Soil Science, 1986(6):15-22.
|
| [16] |
隆茜, 张经. 陆架区沉积物中重金属研究的基本方法及其应用[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2002(3):25-35.
|
| [16] |
Long Q, Zhang J. The method of heavy metals study in shelf sediments and it's application[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2002(3):25-35.
|
| [17] |
郭晓方, 卫泽斌, 丘锦荣, 等. 玉米对重金属累积与转运的品种间差异[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2010,26(4):367-371.
|
| [17] |
Guo X F, Wei Z B, Qiu J R, et al. Differences between corn cultivars in accumulation and translocation of heavy metals[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2010,26(4):367-371.
|
| [18] |
常玉虎, 赵元艺, 曹冲, 等. 德兴铜矿区主要流域内环境介质中重金属含量特征与健康风险评价[J]. 地质学报, 2015,89(5):889-908.
|
| [18] |
Chang Y H, Zhao Y Y, Cao C, et al. Characteristics of heavy metals content and assessment of health risk in different environment media in the Dexing copper mining area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015,89(5):889-908.
|
| [19] |
Hou S N, Zheng N, Tang L, et al. Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk assessment of human exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb pollution in urban street dust across China between 2009 and 2018[J]. Environment International, 2019,128:430-437.

|
| [20] |
杨刚, 沈飞, 钟贵江, 等. 西南山地铅锌矿区耕地土壤和谷类产品重金属含量及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2011,31(9):2014-2021.
|
| [20] |
Yang G, Shen F, Zhong G J, et al. Concentration and health risk of heavy metals in crops and soils in a zinc-lead mining area in southwest mountainous regions[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011,31(9):2014-2021.
|
| [21] |
中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990: 86-87.
|
| [21] |
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Background values of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990:86-87.
|
| [22] |
曾昭华. 四川省土壤元素含量和生态农业地质研究[J]. 四川地质学报, 2005,25(1):44-50.
|
| [22] |
Zeng Z H. A study of elemental contents in soil and ecologic and agricultural geology in Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2005,25(1):44-50.
|
| [23] |
生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB 15618—2018 土地环境质量农用地污染风险管控标准[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018:1-4.
|
| [23] |
Ministry of ecological environment, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 15618—2018 Soil environmental quality-risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land [S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2018:1-4.
|
| [24] |
中华人民共和国农业部. NY 861—2004 粮食(含谷物、豆类、薯类)及制品中铅、铬、镉、汞、硒、砷、铜、锌等八种元素限量[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005:1-4.
|
| [24] |
Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China. NY 861—2004 Limits of eight elements in cereals, legume, tubes and it products[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2005:1-4.
|
| [25] |
Chopra A K, Pathak C. Accumulation of heavy metals in the vegetables grown in waste water irrigated areas of Dehradun, India with reference to human health risk[J]. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 2015,187(7):1-8.
|
| [26] |
刘敏, 颜玲, 刘蒙蒙, 等. 四川省居民膳食营养状况分析[J]. 预防医学情报杂志, 2018,34(3):357-361.
|
| [26] |
Liu M, Yan L, Liu M M, et al. The dietary status of residents in Sichuan province[J]. Journal of Preventive Medicine Information, 2018,34(3):357-361.
|
| [27] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. WS/T578.3—2017 中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量第3部分: 微量元素[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017: 1-4.
|
| [27] |
National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. WS/T 578.3—2017 Chinese dietary reference intake-Part 3: Trace element[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2017:1-4.
|
| [28] |
南京大学. 土壤学基础与土壤地理学[M]. 北京: 人民教育出版社, 1980: 28-30.
|
| [28] |
Nanjing University. Fundamentals of soil science and soil geography[M]. Beijing: People's Education Press, 1980:28-30.
|
| [29] |
尚爱安, 刘玉荣, 梁重山. 土壤中重金属的生物有效性研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2000,32(6):294-300.
|
| [29] |
Shang A A, Liu Y R, Liang Z S. Research progress on bioavailability of heavy metals in soil[J]. Soils, 2000,32(6):294-300.
|
| [30] |
冯志刚, 王世杰, 孙承兴. 引起红土表层硅铝比值增大原因的可能性探讨[J]. 地球与环境, 2002,30(4):7-14.
|
| [30] |
Feng Z G, Wang S J, Sun C X. Discussion on possible causes of increases in Si/Al ratioin surface layers of some lateritic profiles[J]. Geology Geochemistry, 2002,30(4):7-14.
|
| [31] |
Geering H R, Hodgson J F. Micronutrient cation complexes in soil solution: III. characterization of soil solution ligands and their complexes with Zn2+ and Cu2+[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1969,33(1):54-59.

|
| [32] |
Nielsen N E. The effect of plants on the copper concentration in the soil solution[J]. Plant & Soil, 1976,45(3):679-687.
|
| [33] |
袁可能. 土壤化学[M]. 北京: 农业出版社, 1990: 117-119.
|
| [33] |
Yuan K N. Soil chemistry[M]. Beijing: Agriculture Press, 1990:117-119.
|
| [34] |
崔妍, 丁永生, 公维民, 等. 土壤中重金属化学形态与植物吸收的关系[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 2005,31(2):59-63.
|
| [34] |
Cui Y, Ding Y S, Gong W M, et al. Study on the correlation between the chemical forms ofthe heavy metals in soil and the metal uptake by plant[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2005,31(2):59-63.
|
| [35] |
Apul D, Gardner K, Eighmy T T, et al. Simultaneous application of dissolution/precipitation and surface complexation/surface precipitation modeling to contaminantleaching[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005,39(15):5736-5741.

|
| [36] |
McBride M B, 葛旦之. 土壤固相和液相中铜的形态和分布[J]. 土壤学进展, 1987(1):50-55.
|
| [36] |
McBride M B, Ge D Z. Morphology and distribution of Cu in solid and liquid phases of soil[J]. Progress in Soil Science, 1987(1):50-55.
|
| [37] |
王懿铮, 杨忠芳, 刘旭, 等. 广西贵港市覃塘区土壤Cu地球化学特征与生态健康研究[J/OL]. 中国地质:1-18[2021-04-22]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20200529.1230.002.html
|
| [37] |
Wang Y Z, Yang Z F, Liu X, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Copper in soil and ecological health research in Qintang district of Guigang City in Guangxi[J]. Geology in China:1-18[2021-04-22]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20200529.1230.002.html
|
| [38] |
汪雅谷, 张四荣. 无污染蔬菜生产的理论与实践[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2001: 290-291.
|
| [38] |
Wang Y G, Zhang S R. Theory and practice of pollution-free vegetable production[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2001:290-291.
|
| [39] |
祖艳群, 李元, 陈海燕, 等. 蔬菜中铅镉铜锌含量的影响因素研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2003,22(3):289-292.
|
| [39] |
Zu Y Q, Li Y, Chen H Y, et al. Research on factors influencing concentrations of Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn in vegetables[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2003,22(3):289-292.
|
| [40] |
王新, 吴燕玉. 不同作物对重金属复合污染物吸收特性的研究[J]. 农业环境保护, 1998,17(5):193-195.
|
| [40] |
Wang X, Wu Y Y. Study on the absorption characteristics of heavy metal compound pollutants by different crop[J]. Agro-Environmental Protection, 1998,17(5):193-195.
|
| [41] |
康均行, 吴先萍. 四川省居民营养与健康现状报告——2002年四川省居民营养与健康状况调查[M]. 成都: 四川大学出版社, 2006: 1-2.
|
| [41] |
Kang J X, Wu X P. Report on nutrition and health status of residents in Sichuan province-survey on nutrition and health status of residents in Sichuan province in 2002[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan University Press, 2006:1-2.
|
| [42] |
刘建国. 水稻品种对土壤重金属镉铅吸收分配的差异及其机理[D]. 扬州:扬州大学, 2004: 1-12.
|
| [42] |
Liu J G. Variations among rice cultivars in the uptake and translocation of cadmium and lead from soil,and the mechanisms[D]. Yangzhou:Yangzhou University, 2004:1-12.
|
| [43] |
邵云, 姜丽娜, 李向力, 等. 五种重金属在小麦植株不同器官中的分布特征[J]. 生态环境, 2005,14(2):204-207.
|
| [43] |
Shao Y, Jiang L N, Li X L, et al. Distribution of five heavy metals in different organs of wheat[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2005,14(2):204-207.
|
| [44] |
吴传星. 不同玉米品种对重金属吸收累积特性研究[D]. 成都:四川农业大学, 2010: 50-51.
|
| [44] |
Wu C X. Study on characteristics of heavy metal absorption and accumulation in the different maize varieties[D]. Chengdu:Sichuan Agricultural University, 2010:50-51.
|
| [1] |
GUO Jian-Hong, ZHANG Zhan-Song, ZHANG Chao-Mo, CHEN Zhi-Ruo, ZHANG Peng-Hao, TANG Xiao, QIN Rui-bao, YU Jie. Prediction and application of coalbed methane content based on gray system and logging method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(5): 1190-1200. |
| [2] |
Wang HE, Xian-Rong LUO, Fei OUYANG, Pan-Feng LIU, Yi-Huai SU, Wen-Bin HUANG, Dong WANG, Jun YOU, Xiao-Ming ZHANG. A study of geoelectrochemistry in search for concealed copper-nickel deposits in Hejiaya area, Lueyang County, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(3): 523-532. |
|
|
|
|

