|
|
|
| Major controlling factors of low-resistance shale gas reservoirs |
CUI Rui-Kang1( ), SUN Jian-Meng1, LIU Xing-Jun2, WEN Xiao-Feng2 ), SUN Jian-Meng1, LIU Xing-Jun2, WEN Xiao-Feng2 |
1. China University of Petroleum (East China),Qingdao 266580,China
2. Changqing Branch,China National Logging Corporation,Xi'an 710065,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Longmaxi Formation is one of the major exploration horizons of shale in China at present. The gas-bearing sediments in the Lower Paleozoic Longmaxi Formation in the Yangtze area, South Sichuan are characterized by low resistivity. Therefore, it is difficult to distinguish the gas-bearing sediments from aquifers only using logging response. Given this, this study investigated the genetic mechanisms of low-resistivity gas-bearing sediments in the study area in depth using existing data of conventional logging, core drilling, and production-related dynamic conditions, as well as a large number of core analyses and experiments, including casting thin sections, QEMSCAN, and X whole-rock diffraction. According to the study results, three major controlling factors in the low-resistivity gas-bearing sediments of the Lower Paleozoic Longmaxi Formation in the Yangtze region, South Sichuan include the additional conductivity of clay minerals, the complete graphitization of over-mature organic matter, and the distribution pattern of organic matter laminae. The practical application results indicate that the low-resistivity gas-bearing sediments in the study area were formed due to the organic matter laminae developing and the partial graphitization of organic matter. That is, the low resistivity of the shale gas reservoirs tends to be caused by the mutual superimposition and effects of multiple factors. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the geological, logging, and core data according to various zones and horizons and employ the correlation between upper and lower horizons and between adjacent wells to determine the major controlling factors of the low resistivity of the shale gas reservoirs.
|
|
Received: 12 March 2021
Published: 25 February 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|
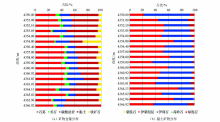
|
Mineral content distribution and clay mineral distribution map of the study area
|
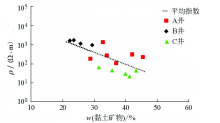
|
Clay minerals and resistivity diagram
|

|
Mineral quantitative analysis diagram
|
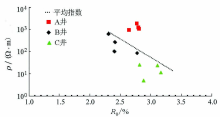
|
Statistical relationship between resistivity and RO
|
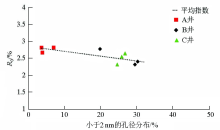
|
Statistical relationship between RO and aperture distribution
|
|
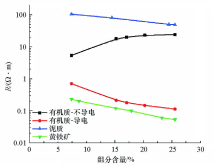
Influence of various rock components on resistivity
|
|
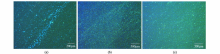
Distribution characteristics of organic lamination under fluorescence microscope
a—a gray-black siliceous mudstone of the Longmaxi Formation with a sampling depth of 3 084.09 m, a resistivity of 0.1 Ω·m, a high content of bright clay minerals (zeolite), bedding joints, and obvious organic lamination; b—black shale of Longmaxi Formation with a sampling depth of 3 931.72 m and a measured resistivity of 10 Ω·m. Due to the disordered distribution of organic matter and clay minerals, the lamina is discontinuous; c—black shale of Longmaxi Formation with sampling depth of 4 039.3 m, measured resistivity of 15.42 Ω·m, low organic matter content and scattered laminae
|
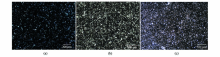
|
Characteristics of organic lamination under polarizing microscope
a—a gray-black siliceous mudstone of the Longmaxi Formation with a sampling depth of 3 084.09 m and a measured resistivity of 0.1 Ω·m. Multiple laminas stack each other to form an organic-rich layer with no obvious interface; b—black shale of Longmaxi Formation with a sampling depth of 3 931.72 m and a measured resistivity of 10 Ω·m. Some laminar organic matter is distributed in blocks, and multiple laminates stack each other to form organic matter bearing layers with no obvious interface; c—black shale of Longmaxi Formation with a sampling depth of 4 039.3 m and a measured resistivity of 15.42 Ω·m. The organic-rich laminae and organic-containing laminae stack each other to form graded layers
|

| 矿物名称 | 含量/% | 矿物名称 | 含量/% | | 石英 | 48.72 | 蒙脱石 | 0.43 | | 伊利石 | 13.80 | 金红石 | 0.37 | | 钠长石 | 8.56 | 磷灰石 | 0.29 | | 方解石 | 8.41 | 石膏/硬石膏 | 0.10 | | 钾长石 | 3.68 | 中长石 | 0.02 | | 黄铁矿 | 3.62 | 锆石 | 0.01 | | 白云石 | 3.48 | 高岭石 | 0.01 | | 绿泥石 | 3.19 | 闪锌矿 | 0.01 | | 黑云母 | 2.66 | 角闪石 | 0.01 | | 白云母 | 1.98 | 海绿石 | 0.01 | | 奥长石 | 0.63 | 钠云母 | 0.01 |
|
Mineral composition of shale thin sections
|
|
QEMSCAN Shale Sections
|
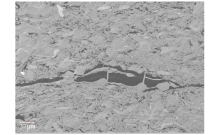
|
Clay laminae filled with organic matter
|
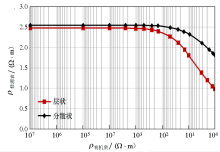
|
Relation between the resistivity of source rocks rich in organic matter and the resistivity of organic matter
|
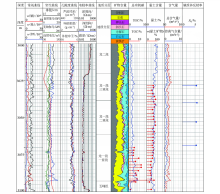
|
Logging interpretation results of Well A
|

| 矿物类型 | 体积分数/% | 平均值/% | | 硅质矿物 | 16.9~62.2 | 34.83 | | 黏土矿物 | 12.7~69.5 | 33.75 | | 碳酸盐矿物 | 0~70.4 | 27.15 |
|
Core mineral analysis
|
| [1] |
于庆洲. 低阻油层的主要成因机理研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2005.
|
| [1] |
Yu Q Z. Mechanism study on the main causes of forming low resistivity pay [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2005.
|
| [2] |
孙建孟. 基于新“七性”关系的煤层气、页岩气测井评价[J]. 测井技术, 2013,37(5):457-465.
|
| [2] |
Sun J M. Coalbed methane and shale gas evaluation based on new seven related[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2013,37(5):457-465.
|
| [3] |
张晋言, 孙建孟. 利用测井资料评价泥页岩油气“五性”指标[J]. 测井技术, 2012,36(2):146-153.
|
| [3] |
Zhang J Y, Sun J M. Log evaluation on shale hydrocarbon reservoir[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2012,36(2):146-153.
|
| [4] |
张作清, 郑炀, 孙建孟. 页岩气评价“六性关系”研究[J]. 油气井测试, 2013,22(1):65-70.
|
| [4] |
Zhang Z Q, Zheng Y, Sun J M. “Six parameter relationship” study of shale gas reservoir[J]. Well Testing, 2013,22(1):65-70.
|
| [5] |
孙建孟, 陈钢花, 杨玉征, 等. 低阻油气层评价方法[J]. 石油学报, 1998(3):83-88.
|
| [5] |
Sun J M, Chen G H, Yang Y Z, et al. Low contrast resistivity reservoir evaluation method[J]. Acta Petrolei Sincia, 1998(3):83-88.
|
| [6] |
孙建孟, 熊铸, 罗红, 等. 扬子地区下古生界页岩气储层低阻成因分析及测井评价[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2018,42(5):47-56.
|
| [6] |
Sun J M, Xiong Z, Luo H, et al. Mechanism analysis and logging evaluation of low resistivity in lower Paleozoic shale gas reservoirs of Yangtze region[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum:Edition of Natural Science, 2018,42(5):47-56.
|
| [7] |
谢小国, 罗兵, 尹亮先, 等. 低阻页岩气储层影响因素分析[J]. 四川地质学报, 2017,37(3):433-437.
|
| [7] |
Xie X G, Luo B, Yin L X, et al. Influence Factors of Low Resistivity Shale Gas Reservoir[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2017,37(3):433-437.
|
| [8] |
杨小兵, 杨争发, 谢冰, 等. 页岩气储层测井解释评价技术[J]. 天然气工业, 2012,32(9):33-36,128-129.
|
| [8] |
Yang X B, Yang Z F, Xie B, et al. Logging interpretation and evaluation technology of shale gas reservoir [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2012,32(9):33-36,128-129.
|
| [9] |
徐锦绣, 吕洪志, 刘欢, 等. 渤海LD油田低阻油层成因机理与评价方法[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018,30(3):47-55.
|
| [9] |
Xu J X, Lyu H Z, Liu H, et al. Genesis mechanism and evaluation methods for low-resistivity oil layers in the Bohai LD oilfield[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018,30(3):47-55.
|
| [10] |
赵文龙. 川南地区志留系龙马溪组页岩储层电性研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2015.
|
| [10] |
Zhao W L. Reservoir of electricity of Silurian Longmaxi shale in South Sichuan area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2015.
|
| [11] |
王长江. 延长地区陆相页岩气储层低阻成因机理研究[C]// 西安石油大学、陕西省石油学会.2019油气田勘探与开发国际会议论文集. 2019:642-643.
|
| [11] |
Wang C J. Study on the formation mechanism of low resistivity of continental shale gas reservoir in Yanchang area[C]. Xi’an Shiyou University, Shaanxi Petroleum Society. 2019 International Conference on Oil and Gas Exploration and Development. 2019: 642-643.
|
| [12] |
杨凯. 四川盆地海陆相页岩岩相特征及电学特征差异性研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2018.
|
| [12] |
Yang K. Study on the difference of lithofacies and electrical characteristics of Marine and terrestrial shale in Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018.
|
| [13] |
杨娇, 陆嫣, 刘伟新, 等. 珠江口盆地W油田低阻油层特殊成因机理[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014,26(4):41-45.
|
| [13] |
Yang J, Liu Y, Liu W X, et al. Special origins of low-resistivity oil layers in W oilfield, Pearl River Mouth basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014,26(4):41-45.
|
| [14] |
王维斌, 郭杜凯, 陈旭峰, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地吴起地区延长组长6_1低阻油层成因分析及识别方法[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2017,24(2):38-45,89.
|
| [14] |
Wang W B, Guo D K, Chen X F, et al. Genesis analysis and identification methods of Chang 6_ 1 low resistivity oil pays in Yanchang Formation in Wuqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2017,24(2):38-45,89.
|
| [15] |
王友净, 宋新民, 何鲁平, 等. 高尚堡深层低阻油层的地质成因[J]. 石油学报, 2010,31(3):426-431.
|
| [15] |
Wang Y J, Song X M, He L P, et al. Geologic origin of low-resistivity layers in deep reservoir of Gaoshangpu Oilfield[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010,31(3):426-431.
|
| [16] |
罗水亮, 许辉群, 刘洪, 等. 柴达木盆地台南气田低阻气藏成因机理及测井评价[J]. 天然气工业, 2014,34(7):41-45.
|
| [16] |
Luo S L, Xu H Q, Liu H, et al. Genetic mechanism and logging evaluation of low-resistivity gas reservoirs in the Tainan Gas Field, eastern Qaidam Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014,34(7):41-45.
|
| [17] |
于红岩, 李洪奇, 郭兵, 等. 基于成因机理的低阻油层精细评价方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2012,42(2):335-343.
|
| [17] |
Yu H Y, Li H Q, Guo B, et al. Low-Resistivity oil layers fine evaluation approaches based on mechanism[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2012,42(2):335-343.
|
| [18] |
郑华, 李云鹏, 徐锦绣, 等. 渤海海域低阻油层地质成因机理与识别——以辽东湾旅大A油田为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2018,25(1):22-28.
|
| [18] |
Zheng H, Li Y P, Xu J X, et al. Geological genetic mechanism and identification of low resistivity reservoir in Bohai sea area: a case study of LD—A Oilfield in Liaodong Bay[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2018,25(1):22-28.
|
| [19] |
林国松, 康凯, 郭富欣, 等. 渤海海域蓬莱油田低阻油层成因模式研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019,26(3):68-73.
|
| [19] |
Lin G S, Kang K, Guo F X, et al. Low-resistivity reservoir genesis patterns of Penglai oilfield in Bohai Sea[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019,26(3):68-73.
|
| [20] |
罗兴平, 苏东旭, 王振林, 等. 核磁共振测井在低阻油层评价中的应用——以准噶尔盆地阜东斜坡头屯河组为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2017,38(4):470-476.
|
| [20] |
Luo X P, Su D X, Wang Z L, et al. Application of NMR logging in low-resistivity reservoir evaluation: A case study of Toutunhe Formation on the Eastern Fukang Slope, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2017,38(4):470-476.
|
| [21] |
黄涛. 页岩岩心复电阻率实验室测试与分析[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2016.
|
| [21] |
Huang T. Complex resistivity of shale core laboratory testing and analysis[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016.
|
| [22] |
王香增. 陆相页岩气[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2014.
|
| [22] |
Wang X Z. Continental shale gas [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2014.
|
| [23] |
刘天琳, 姜振学, 张昆, 等. 识别海相页岩石墨化程度的方法和装置[P]. CN107064230A, 2017-08-18.
|
| [23] |
Liu T L, Jiang Z X, Zhang K, et al. Method and apparatus for identifying graphitization degree of Marine shale [P]. CN107064230A, 2017-08-18.
|
| [24] |
Kethireddy N, Heidari Z, Chen H. Quantifying the Effect of Kerogen on Electrical Resistivity Measurements in Organic-Rich Source Rocks[C]//SPWLA 54th Annual Logging Symposium. Society of Petrophysicists and Well-Log Analysts, 2013.
|
| [25] |
张建坤, 何生, 颜新林, 等. 页岩纳米级孔隙结构特征及热成熟演化[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2017,41(1):11-24.
|
| [25] |
Zhang J K, He S, Yan X L, et al. Structural characteristics and thermal evolution of nanoporosity in shales[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum:Edition of Natural Science, 2017,41(1):11-24.
|
| [26] |
李楚雄, 肖七林, 陈奇, 等. 页岩纳米级孔隙在有机质熟化过程中的演化特征及影响因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019,41(6):901-909.
|
| [26] |
Li C X, Xiao Q L, Chen Q, et al. Evolution characteristics and controls of shale nanopores during thermal maturation of organic matter[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019,41(6):901-909.
|
| [27] |
邵龙义, 刘磊, 文怀军, 等. 柴北缘盆地YQ-1井中侏罗统石门沟组泥页岩纳米孔隙特征及影响因素[J]. 地学前缘, 2016,23(1):164-173.
|
| [27] |
Shao L Y, Liu L, Wen H J, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of nanopores in the Middle Jurassic Shimengou Shale in Well YQ-1 of the Northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016,23(1):164-173.
|
| [28] |
霍培丽, 张登峰, 王倩倩, 等. 页岩吸附性能及作用规律[J]. 化工进展, 2016,35(1):74-82.
|
| [28] |
Huo P L, Zhang D F, Wang Q Q, et al. Perspective of adsorption performance of shale[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2016,35(1):74-82.
|
| [29] |
Yang A, Firdaus G, Heidari Z. Electrical resistivity and chemical properties of kerogen isolated from organic-rich mudrocks[J]. Geophysics, 2016,81(6):D643-D655.

|
| [30] |
李凯, 游海涛, 刘兴起. 中国湖泊沉积物纹层年代学研究进展[J]. 湖泊科学, 2017,29(2):266-275.
|
| [30] |
Li K, You H T, Liu X Q. Review on lake sediment varve chronology in China[J]. Lake Science, 2017,29(2):266-275.
|
| [31] |
李婷婷, 朱如凯, 白斌, 等. 酒泉盆地青西凹陷下沟组湖相细粒沉积岩纹层特征及研究意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2015,20(1):38-47.
|
| [31] |
Li T T, Zhu R K, Bai B, et al. Characteristics and Research Significance of Fine Lacustrine Sedimentary Rock Laminations of Xiagou Formation in Qingxi Depression of Jiuquan Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2015,20(1):38-47.
|
| [32] |
施振生, 邱振, 董大忠, 等. 四川盆地巫溪2井龙马溪组含气页岩细粒沉积纹层特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018,45(2):339-348.
|
| [32] |
Shi Z S, Qiu Z, Dong D Z, et al. Laminae characteristics of gas-bearing shale fine-grained sediment of the Silurian Longmaxi Formation of Well Wuxi 2 in Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018,45(2):339-348.
|
| [1] |
YU Chang-Heng, ZHENG Jian, ZHANG Xu-Lin, ZHOU Hao, WANG An-Ping, LIU Lei, LI Yi. Application of the integrated engineering geophysical exploration technology in the predrilling stage of shale gas well platforms in southern Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1): 99-109. |
| [2] |
ZHAO Jun, MENG Xin-Jia, LI Bing, LIU Zhi-Min. Current field distribution characteristics and detection influencing factors of the focusing DC IP method for tunnels[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1): 120-128. |
|
|
|
|

