|
|
|
| Seismic imaging of high-steep structural zone in Biyang Depression |
DUAN Ying1( ), ZHANG Gao-Cheng2, TAN Ya-Li1 ), ZHANG Gao-Cheng2, TAN Ya-Li1 |
1. Geophysical Exploration Center,China Earthquake Administration,GEC,Zhengzhou 450002,China
2. Exploration & Development Research Institute of Henan Oilfield Company,SINOPEC,Zhengzhou 450018,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Seismic imaging of the high-steep structural zone in southern Biyang Depression is difficult.In order to improve imaging accuracy,in this paper,the authors studied and applied tomographic static correction technology of undulating surface in the piedmont zone,employed prestack multi-domain noise suppression technology based on low-frequency fault surface waves protection,velocity modeling technology of high-steep structure in the piedmont zone and reverse-time migration technology of undulating surface,and thus improved the seismic imaging accuracy of complex structures in the high-steep structure zone in this area.As a result,large boundary fault zone characterization is more accurate,and the stratigraphic contact relation and structure imaging are clear.
|
|
Received: 18 December 2019
Published: 20 August 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
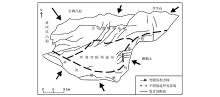
|
Biyang depression structure diagram
|
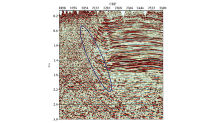
|
Typical seismic profile of the work area
|
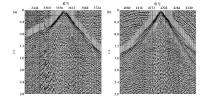
|
Different shots in the southern mountainous area(a) and the northern flat area(b)
|
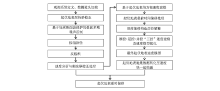
|
Processing flow chart
|
|
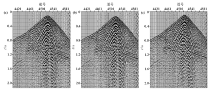
Comparison of effects of original shot (a), model static correction (b) and tomographic static correction (c)
|
|
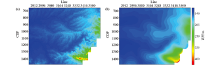
Comparison of surface elevation plan (a) and smooth undulations (b)
|
|
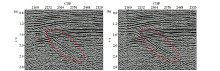
Comparison of conventional process denoising (a) and low-frequency protection denoising (b) sections
|
|
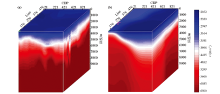
Comparison of initial velocity model(a) and final velocity model(b) in depth domain
|
|
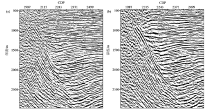
Comparison of kirchhoff prestack depth migration(a) and inverse time migration(b) sections
|
|
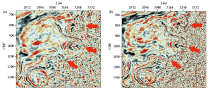
Comparison of the slice processed in the past(a) and the slice processed in this time(b) with t=1800 ms
|
| [1] |
曾庆才, 王德发, 吴官生, 等. 陡坡带构造下伏地层地震成像精度影响分析[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2006(4):61-64.
|
| [1] |
Zeng Q C, Wang D F, Wu G S, et al. The influence from underlying layers of steep slope zone on the precision of seismic imaging[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2006(4):61-64.
|
| [2] |
张永华, 杨道庆, 罗家群, 等. 泌阳凹陷陡坡带高精度三维地震攻关研究与效果[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2009,44(s1):110-114.
|
| [2] |
Zhang Y H, Yang D Q, Luo J Q, et al. High precision 3D seismic research and results on steep slope in Biyang Depression[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2009,44(s1):110-114.
|
| [3] |
李锋, 顾汉明. 泌阳凹陷南部陡坡带地震资料的炮域波动方程叠前深度偏移[J]. 地质科技情报, 2007(3):104-108.
|
| [3] |
Li F, Gu H M. Wave-equation PreSDM in shot domain of seismic data from steep slope zone in Southern Biyang depression[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2007(3):104-108.
|
| [4] |
姚振方, 刘振东, 商建立, 等. 叠前深度偏移技术在泌阳凹陷南部陡坡带的应用[J]. 河南石油, 2006,20(4):18-20,24
|
| [4] |
Yao Z F, Liu Z D, Shang J L, et al. The application of PSDM for steep slope zone in southern Biyang Depression[J]. Henan Petroleum, 2006,20(4):18-20,24.
|
| [5] |
曾庆才, 曾同生, 欧阳永林, 等. 盐下高陡构造成像技术——以塔里木盆地库车坳陷克深地区为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017,44(6):871-879.
|
| [5] |
Zeng Q C, Zeng T S, Ouyang Y L, et al. Subsalt high steep structure imaging technique:A case study of Keshen area in Kuqa depression,Tarim Basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017,44(6):871-879.
|
| [6] |
谢万学, 李德珍, 金德刚, 等. 起伏地表叠前成像技术在川东高陡构造工区中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018,33(5):2020-2026.
|
| [6] |
Xie W X, Li D Z, Jin D G, et al. Application of pre-stack seismic imaging from rugged topography in complex structure survey of eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018,33(5):2020-2026.
|
| [7] |
刘定进, 蒋波, 李博, 等. 起伏地表逆时偏移在复杂山前带地震成像中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2016,51(2):315-324,207.
|
| [7] |
Liu D J, Jiang B, Li B, et al. Rugged-topography reverse time migration application on complex piedmont zone[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2016,51(2):315-324,207.
|
| [8] |
卜旭强 泌阳凹陷南部陡坡带砂砾岩体预测技术与方法[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2018,32(6):52-55,118-119.
|
| [8] |
Bu X Q. The prediction techniques and methods for gravel rock mass of the Steep Slope Zone in Southern Biyang Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2018,32(6):52-55,118-119.
|
| [9] |
付兆辉, 秦伟军. 断陷盆地陡坡带高精度地震勘探技术应用[J]. 西北地震学报, 2012,34(2):114-120.
|
| [9] |
Fu Z H, Qin W J. High precision seismic exploration techniques and application on the abrupt slope belt of faulted basin[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 2012,34(2):114-120.
|
| [10] |
蒲春志, 张高成, 杨兴圣, 等. 泌阳凹陷陡坡带高精度融合处理成像关键技术[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2014,28(4):55-57.
|
| [10] |
Pu C Z, Zhang G C, Yang X S, et al. The key techniques of high precision fusion imaging for steep slope of Biyang depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2014,28(4):55-57.
|
| [11] |
张林, 杨勤勇, 张兵, 等. 复杂近地表初至波层析反演静校正技术研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017,32(2):816-821.
|
| [11] |
Zhang L, Yang Q Y, Zhang B, et al. Tomography inversion by first breaks in areas with complex near surface[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017,32(2):816-821.
|
| [12] |
杨智超, 侯泽富, 王佚, 等. 四川盆地复杂地表高精度建模技术及其应用[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2019,42(4):75-83.
|
| [12] |
Yang Z C, Hou Z F, Wang Y, et al. High-precision modeling for complex surface conditions and its application to Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2019,42(4):75-83.
|
| [13] |
巫芙蓉, 郭海洋, 刁永波, 等. 塔里木盆地秋里塔格构造带双复杂构造地震处理技术[J]. 天然气工业, 2019,39(4):28-36.
|
| [13] |
Wu F R, Guo H Y, Diao Y B, et al. Seismic processing technologies for double complex structures in the Qiulitage structural belt,Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019,39(4):28-36.
|
| [14] |
王川, 李振春, 李文燕, 等. 复杂近地表三维初至波走时层析方法研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018,33(5):1967-1973.
|
| [14] |
Wang C, Li Z C, Li W Y, et al. 3D first-arrival travel-time tomography based on complex near-surface model[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018,33(5):1967-1973.
|
| [15] |
董兵波. 面向陡坡带砂砾岩体的叠前宽频保幅处理技术研究[J]. 当代化工研究, 2019,(7):75-76.
|
| [15] |
Dong B B. Research on pre-stack broadband amplitude-preserving processing technology for Glutenite in Steep Slope Zone[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2019,(7):75-76.
|
| [16] |
苏勤, 贺振华, 田彦灿, 等. 山前带复杂构造成像中叠前深度偏移方法研究及应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009,20(4):571-575.
|
| [16] |
Su Q, He Z H, Tian Y C, et al. Research and application of pre-stack depth migration method in piedmont complex structure imaging[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009,20(4):571-575.
|
| [17] |
王丽, 王芳琳, 赵传雪, 等. 叠前逆时深度偏移技术在江苏高陡构造地区的应用[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2015,37(5):634-638.
|
| [17] |
Wang L, Wang F L, Zhao C X, et al. The application of prestack depth reverse-time migration in steep dip structures area of the Jiangsu oilfield[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015,37(5):634-638.
|
| [18] |
张海洋, 汤国松, 郭廷超, 等. 逆时偏移技术在ZL地区复杂断裂带的应用[J]. 复杂油气藏, 2016,9(4):26-29.
|
| [18] |
Zhang H Y, Tang G S, Guo T C, et al. Application of reverse-time migration technology in complex fault zone in ZL area[J]. Complex Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 2016,9(4):26-29.
|
| [19] |
王吉梅. 建南及周缘高陡构造的解释[J]. 江汉石油职工大学学报, 2017,30(6):14-16.
|
| [19] |
Wang J M. Interpretation of high and steep structures in Jiannan and its Periphery area[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum University of Staff and Workers, 2017,30(6):14-16.
|
| [20] |
刘红伟, 刘洪, 李博, 等. 起伏地表叠前逆时偏移理论及GPU加速技术[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011,54(7):1883-1892.
|
| [20] |
Liu H W, Liu H, Li B, et al. Pre-stack reverse time migration for rugged topography and GPU acceleration technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011,54(7):1883-1892.
|
| [21] |
曲英铭. 起伏地表直接成像技术研究进展[J]. 石油物探, 2019,58(5):625-644.
|
| [21] |
Qu Y M. Research progress of topographic imaging methods[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019,58(5):625-644.
|
| [22] |
杜喜善, 王博雅, 魏涛, 等. 逆时偏移技术在饶阳凹陷变质岩成像研究中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2016,13(6):717-724.
|
| [22] |
Du X S, Wang B Y, Wei T, et al. The application of reverse time migration technology to metamorphic rock imaging research in Raoyang[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2016,13(6):717-724.
|
| [1] |
WANG Tong, Liu Jian-Xun, WANG Xing-Yu, LI Guang-Cai, TIAN Mi. Suppression of random noise in deep seismic reflection data using adaptive threshold-based Shearlet transform[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3): 704-713. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Si-Wei, WU Rong-Xin, HAN Zi-Ao, WU Hai-Bo. The application of bilateral filtering to denoise processing of ground penetrating radar data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2): 496-501. |
|
|
|
|

