|
|
|
| Neural network seismic prediction of sand and mudstone lithology of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Sag |
ZHANG Peng-Fei( ), ZHANG Shi-Hui( ), ZHANG Shi-Hui( ) ) |
| Institute of Geophysics and Geomatics,China University of Geosciences(Wuhan),Wuhan 430074,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The traditional seismic P-wave impedance inversion method has the problems of low lithologic resolution and multi-solution,and it is hence difficult for the inversion results to meet the requirements of finely characterizing the lithologic distribution.In this paper,by constructing a normalized pseudo-gamma curve containing lithology and P-wave impedance information as a lithology index indicator curve,the neural network method is used to convert seismic data into a gamma data volume which is more closely related to lithology.Through the neural network seismic inversion,the sand and mudstone lithologic inversion data volume is obtained.This method was used to invert the sand and mudstone lithology of the Pinghu Formation in the Xihu Sag.Compared with traditional methods,the prediction accuracy of the mudstone thickness is up to 93%,which more accurately characterizes the distribution of underground sand and mudstone,and provides a basis for later oil and gas exploration.
|
|
Received: 18 June 2020
Published: 20 August 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
ZHANG Shi-Hui
E-mail: symdwjz@foxmail.com;zsh2008@cug.edu.cn
|
|
|
|
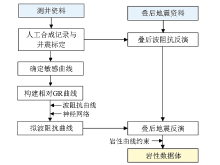
|
Sketch of poststack seismic neural network inversion constrained by well logs
|
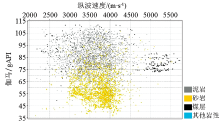
|
The cross plot of all kinds lithology of Gamma ray and P-velocity
|
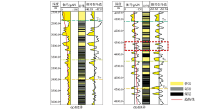
|
Comparison result of gamma and relative gamma for two wells
|
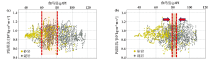
|
Comparation of gamma(a),relative gamma(b) and P-impedance cross plot
|
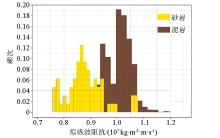
|
Pseudo-wave impedance curve and lithology probability intersection diagram
|
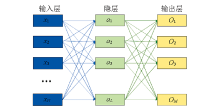
|
Schematic diagram of neural network algorithm
|
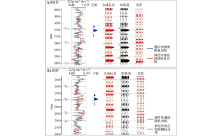
|
Comparison of neural network seismic inversion results and actual P-wave impedance curve
|
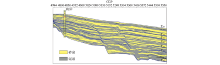
|
Comparison of lithology and inversion results of well B2
|
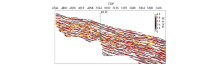
|
Section of source rocks of well B1 in the Pinghu Formation(yellow part is high-quality source rock (TOC abundance>1) section)
|
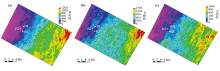
|
Thickness slice of mudstone in Pinghu Formation in Xihu Sag
a—thickness slice of mudstone in upper Pinghu Formation;b—thickness slice of mudstone in middle Pinghu Formation;c—thickness slice of mudstone in lower Pinghu Formation
|

| 井名 | 实测/m | 泥岩厚度反演/m | 相对误差 | | B1 | 508.4 | 542.5 | +6.71% | | B2 | 417.0 | 442.6 | +6.01% | | B3 | 463.1 | 493.2 | +6.45% |
|
Comparison between inverted mudstone thickness and measured mudstone thickness
|
| [1] |
Hampson D P, Todorov T, Russell B. Use of multi-attribute transforms to predict log properties from seismic data[J]. Geophysics, 2001,66(1):220-236.
|
| [2] |
张绍红, 林昌荣. 砂泥岩地层概率神经网络岩性反演技术应用研究[J]. 西安石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2008,23(4):1-4.
|
| [2] |
Zhang S H, Lin C R. Application of probabilistic neural network in the lithology inversion of sandstone-mudstone strata[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University:Natural Science Edition, 2008,23(4):1-4.
|
| [3] |
Tahmasebi P, Hezarkhani A. A hybrid neural networks-fuzzy logic-genetic algorithm for grade estimation[J]. Computers and Geosciences, 2012,42:18-27.
|
| [4] |
余为维, 冯磊, 杜艳艳, 等. 测井约束与神经网络联合反演储层预测技术[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2016,31(5):2232-2238.
|
| [4] |
Yu W W, Feng L, Du Y Y, et al. Reservoir prediction technology based on joint inversion of logging-constrained and neural network[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2016,31(5):2232-2238.
|
| [5] |
赵鹏飞, 刘财, 冯晅, 等. 基于神经网络的随机地震反演方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019,62(3):1172-1180.
|
| [5] |
Zhao P F, Liu C, Feng X, et al. Stochastic seismic inversion based on neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019,62(3):1172-1180.
|
| [6] |
黄福强, 李斌, 张异彪, 等. 西湖凹陷斜缆采集关键参数优选研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2020,44(4):770-777.
|
| [6] |
Huang F Q, Li B, Zhang Y B, et al. Optimizing the key acquisition parameters of variable-depth streamer in Xihu sag[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020,44(4):770-777.
|
| [7] |
杨彩虹, 高兆红, 蒋一鸣, 等. 西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带始新统平湖组碎屑沉积体系再认识[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2013,35(9):11-14.
|
| [7] |
Yang C H, Gao Z H, Jiang Y M, et al. Reunderstanding of clastic rock sedimentary facies of Eocene Pinghu formation in Pinghu Slope of Xihu Sag[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2013,35(9):11-14.
|
| [8] |
田杨, 叶加仁, 雷闯, 等. 断陷盆地海陆过渡相烃源岩发育模式:以西湖凹陷平湖组为例[J]. 地球科学, 2019,44(3):898-908.
|
| [8] |
Tian Y, Ye J R, Lei C, et al. Development model for source rock of marine-continental transitional face in faulted Basins:A case study of Pinghu formation in Xihu Sag[J]. Earth Science, 2019,44(3):898-908.
|
| [9] |
苏奥, 陈红汉, 胡飞, 等. 西湖凹陷中央构造带中南部油气成藏条件、特征及富集规律[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015,34(2):123-129.
|
| [9] |
Su A, Chen H H, Hu F, et al. Conditions,characteristics and enrichment regulation of oil and gas accumulation of the South central of central anticlinal zone in the Xihu Sag,East China Sea Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015,34(2):123-129.
|
| [10] |
付志方. 地震储层预测技术及应用研究——以西湖凹陷孔雀亭地区为例[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2007.
|
| [10] |
Fu Z F. Techniques and applied studying of reservoir rrediction based on seismic:take Kongqueting area of Xihu depression as an example[D].Beijing:China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2007.
|
| [11] |
秦兰芝, 徐志星, 刁慧, 等. 西湖凹陷烃源岩地震反演评价与预测[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2017,37(16):66-67, 69.
|
| [11] |
Qin L Z, Xu Z X, Diao H, et al. Seismic inversion evaluation and prediction of hydrocarbon source rocks in Xihu Sag[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2017,37(16):66-67,69.
|
| [12] |
王亚, 易远元, 王成泉, 等. 叠后反演技术在杨税务潜山裂缝孔隙型储层预测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2020,44(5):1208-1214.
|
| [12] |
Wang Y, Yi Y Y, Wang C Q, et al. The application of post-stack inversion technology to the prediction of fracture and pore reservoir in Yangshuiwu buried hill[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020,44(5):1208-1214.
|
| [13] |
侯伯刚, 刘文岭, 罗娜. 地震反演中测井数据的预处理[J]. 物探与化探, 2009,33(3):331-336.
|
| [13] |
Hou B G, Liu W L, Luo N. The preprocessing of well log data for seismic inversion[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2009,33(3):331-336.
|
| [14] |
付康伟, 张学强, 彭炎. BP神经网络算法在陆域天然气水合物成藏预测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2019,43(3):486-493.
|
| [14] |
Fu K W, Zhang X Q, Peng Y. The application of BP neural network algorithm to the prediction of terrestrial gas hydrate accumulation[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019,43(3):486-493.
|
| [15] |
Van der Baan, Christian Jutten M. Neural networks in geophysical applications[J]. Geophysics, 2000,65(4):1032-1047.
|
| [16] |
Manoj C, Nagarajan N. The application of artificial neural networks to magnetotelluric time-series analysis[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2003,153(2):409-423.
|
| [17] |
蔡华, 张建培. 东海西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带断层特征及其封闭性[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2013,29(4):20-26.
|
| [17] |
Cai H, Zhang J C. Characteristics of faults on the Pinghu Slope of Xihu Sag,the east China Sea Shelf basin and their sealing capacity[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2013,29(4):20-26.
|
| [18] |
庞崇友, 张亚东, 章辉若, 等. 地质统计反演在苏里格气田致密薄砂体预测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2017,41(1):16-21.
|
| [18] |
Pang C Y, Zhang Y D, Zhang H R, et al. The application of geostatistics inversion to prediction of compact and thin sand body in Sulige gas field[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017,41(1):16-21.
|
| [1] |
ZHAO Bao-Feng, WANG Qi-Nian, GUO Xin, GUAN Da-Wei, CHEN Tong-Gang, FANG Wen. Gravity survey and audio magnetotellurics-based insights into the deep structures and geothermal resource potential of the Rucheng Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1147-1156. |
| [2] |
HE Sheng, WANG Wan-Ping, DONG Gao-Feng, NAN Xiu-Jia, WEI Feng-Feng, BAI Yong-Yong. Application of the opposing-coils transient electromagnetic method in urban geological surveys[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1379-1386. |
|
|
|
|

