|
|
|
| Lithology identification based on Bayesian probability using adaptive kernel density |
Ze-Yuan CAI1,2,3( ), Bao-Liang LU1,2,3( ), Bao-Liang LU1,2,3( ), Sheng-Qing XIONG4, Wan-Yin WANG1,2,3 ), Sheng-Qing XIONG4, Wan-Yin WANG1,2,3 |
1. Insititute of Gravity and Magnetic Technology,Chang’an University,Xi’an 710054,China
2. College of Geology Engineering and Geomatics,Chang’an University,Xi’an 710054,China
3. Key Laboratory of Western China’s Mineral Resources and Geological Engineering,Ministry of Education,Chang’an University,Xi’an 710054,China
4. China Aero Geophysivey and Remote Sensing Center for Natural and Resources,Beijing 100083,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Accurately characterizing rock types and their structural relationships can provide important information for researches on energy and mineral exploration, deep structure and tectonic, and so on. At present, geophysical data can be used to identify lithology through the differences between the corresponding physical property parameters of different rocks (such as density, susceptibility, resistivity, speed,etc.). However, different rock physical properties often coincide at a certain degree, on the other hand the result of lithological identification is not accurate enough when a single physical property is used. Therefore, it is of great significance to use multi-source data for lithological identification. Bayesian method belongs to the statistical classification methods, which relies on probability for classification, and the calculation of probability density depends on the correlation between sample attributes. On such a basis, the authors introduce the Bayesian probability model based on adaptive kernel density estimation to lithology identification. This method has good adaptability for many different types of physical property parameters and such the predicted lithology classification results with probability parameters, fuzzy intervals, and a variety of lithology classification results. This method has a strong scalability that can process both parametric and non-parametric information at the same time to maximally the known geological information and physical parameters. Synthetic models prove that this method has the ability to provide more stable and accurate results of lithology recognition compared with the methods of traditional Gaussian algorithm and fixed bandwidth kernel density estimation.
|
|
Received: 17 February 2020
Published: 28 August 2020
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Bao-Liang LU
E-mail: 847330992@qq.com;lulb@chd.edu.cn
|
|
|
|
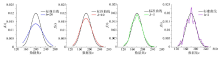
|
Probability density function curve under different bandwidth
|

| 岩石名称 | 密度/(kg·m-3) | 磁化率/(10-5SI) | 电阻率/(Ω·m) | | 板 岩 | 2630~2850 | 0~160 | 3~8 | | 片麻岩 | 2570~2830 | 180~280 | 40~60 | | 花岗岩 | 2580~2640 | 0~160 | 10~30 |
|
Statistical table of model parameters
|
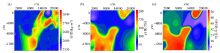
|
Physical properties of the model
a— density of the model;b—magnetic susceptibility of the model;c—resistivity of the model
|
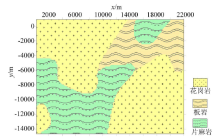
|
rock distribution of the model
|
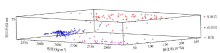
|
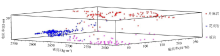
Interaction diagram of physical parameters of 250 training samples
|
|
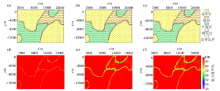
Classification results of 250 training samples
Figures a~f respectively represent the Bayesian classification results, corresponding probability distribution map of the traditional Gaussian classification, fixed bandwidth kernel density estimation, adaptive bandwidth kernel density estimation for 250 training sample points
|
|
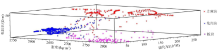
Interaction diagram of physical parameters of 435 training samples
|
|
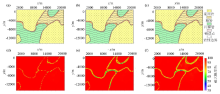
Classification results of 435 training samples
Figures a~f respectively represent the Bayesian classification results, corresponding probability distribution map of the traditional Gaussian classification, fixed bandwidth kernel density estimation, adaptive bandwidth kernel density estimation for 435 training sample points
|
|
Interaction diagram of physical parameters of 869 training samples
|
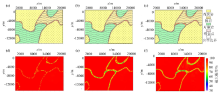
|
Classification results of 435 training samples
Figures a~frespectively represent the Bayesian classification results, corresponding probability distribution map of the traditional Gaussian classification, fixed bandwidth kernel density estimation, adaptive bandwidth kernel density estimation for 869 training sample points
|

| 训练样本/个 | 错误率/% | | 传统高斯算法 | 固定带宽核密度估计 | 自适应带宽核密度估计 | | 250 | 4.52 | 4.48 | 4.17 | | 435 | 4.58 | 4.51 | 4.09 | | 870 | 4.46 | 4.37 | 4.20 |
|
Statistical table of model error rate
|
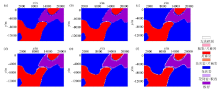
|
Forecast classification results
a~f are the classification results when the probability difference is 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50% and 60% respectively
|
| [1] |
Lortzer G J M, 杨谦, 译. 岩性反演的完整方法第一部分:理论[J]. 国外油气勘探, 1993,5(4):414-428.
|
| [1] |
Lortzer G J M, Yang Q, Trans. Complete lithology inversion method of the first part theory[J]. Foreign Oil and Gas Exploration, 1993,5(4):414-428.
|
| [2] |
田玉昆, 周辉, 袁三一. 基于马尔科夫随机场的岩性识别方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013,56(4):1360-1368.
|
| [2] |
Tian Y K, Zhou H, Yuan S Y. Lithologic discrimination method based on Markov random-field[J]. Chinese J. Geophycs, 2013,56(4):1360-1368.
|
| [3] |
靳军, 刘楼军, 邵雨, 等. 综合地球物理方法识别准噶尔盆地的岩性圈闭[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2002,37(3):287-290,299.
|
| [3] |
Jin J, Liu L J, Shao Y, et al. Discussion on identifying method for identification of lithologic traps in Junggar Basin by comprehensive geophysical method[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2002,37(3):287-290, 299.
|
| [4] |
洪忠, 张猛刚, 苏明军. 应用地震波形分类技术识别岩相的适用性和局限性[J]. 物探与化探, 2013,37(5):904-910.
|
| [4] |
Hong Z, Zhang M G, Su M J. The applicability and limitations of the seismic wave-form classification technology to the identification of lithological facies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013,37(5):904-910.
|
| [5] |
Tjelmeland , Håkon , Luo X, et al. A Bayesian model for lithology/fluid class prediction using a Markov mesh prior fitted from a training image[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2019,67(3):609-623
|
| [6] |
宫清顺, 黄革萍, 孟祥超, 等. 三塘湖盆地火山岩岩性识别方法[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2012,17(3):37-41,6.
|
| [6] |
Gong Q S, Huang G P, Meng X C, et al. Methods for lithology discrimination of volcanics in Santanghu Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2012,17(3):37-41,6.
|
| [7] |
徐德龙, 李涛, 黄宝华, 等. 利用交会图法识别国外M油田岩性与流体类型的研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2012,27(3):1123-1132.

|
| [7] |
Xu D L, Li T, Huang B H, et al. Research on the identification of the lithology and fluid type of foreign Moilfield by using the crossplot method[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2012,27(3):1123-1132 .

|
| [8] |
李伟才, 姚光庆, 黄银涛, 等. 文昌13-1油田低阻油层测井岩性识别方法研究[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2012,34(12):81-85,7.
|
| [8] |
Li W C, Yao G Q, Huang Y T, et al. Study on identification method of logging lithology for low resistivity reservoir in Wenchang 13-1 Oilfield[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2012,34(12):81-85,7.
|
| [9] |
范宜仁, 黄隆基, 代诗华. 交会图技术在火山岩岩性与裂缝识别中的应用[J]. 测井技术, 1999(1):53-56,64.
|
| [9] |
Fan Y R, Huang L J, Dai S H. Application of crossplot technique to the determination of lithology composition and fracture identification of igneous rock[J]. Well Logging Technology, 1999(1):53-56,64.
|
| [10] |
田艳, 孙建孟, 王鑫, 等. 利用逐步法和Fisher判别法识别储层岩性[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2010,33(2):126-129, 134.
|
| [10] |
Tian Y, Sun J M, Wang X, et al. Identifying reservoir lithology by step-by-step method and Fisher discriminant[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2010,33(2):126-129,134.
|
| [11] |
王辉, 黎明碧, 唐勇, 等. 基于小波神经网络的ODP1148A井岩性预测[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2014,29(1):392-399.

|
| [11] |
Wang H, Li M B, Tang Y, et al. Tang YThe lithology prediction of ODP hole 1148A based on the wavelet neural network[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2014,29(1):392-399.

|
| [12] |
吴施楷, 曹俊兴. 基于连续限制玻尔兹曼机的支持向量机岩性识别方法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2016,31(2):821-828.
|
| [12] |
Wu S K, Cao J X. Lithology identification method based on continuous restricted Boltzmann machine and support vector machine[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2016,31(2):821-828.
|
| [13] |
安鹏, 曹丹平. 基于深度学习的测井岩性识别方法研究与应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018,33(3):1029-1034.
|
| [13] |
An P, Cao D P. Research and application of logging lithology identification based on deep learning[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018,33(3):1029-1034.
|
| [14] |
Corina A N, Hovda S. Automatic lithology prediction from well logging using kernel density estimation[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018,170:664-674.

|
| [15] |
付光明, 严加永, 张昆, 等. 岩性识别技术现状与进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017,32(1):26-40.
|
| [15] |
Fu G M, Yan J Y, Zhang K, et al. Current status and progress of lithology identification technology[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017,32(1):26-40.
|
| [16] |
严加永, 吕庆田, 陈向斌, 等. 基于重磁反演的三维岩性填图试验——以安徽庐枞矿集区为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2014,30(4):1041-1053.

|
| [16] |
Yan J Y, Lyu Q T, Chen X B, et al. 3D lithologic mapping test based on 3D inversion of gravity and magnetic data: A case study in Lu-Zong ore concentration district, Anhui Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014,30(4):1041-1053.

|
| [17] |
刘云祥, 何展翔, 张碧涛, 等. 识别火成岩岩性的综合物探技术[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2006,29(2):115-118,5.
|
| [17] |
Liu Y X, He Z X, Zhang B T, et al. Integrated geophysical techniques for identification of igneous rocks[J]. Progress in Exploration Geophysics, 2006,29(2):115-118,5.
|
| [18] |
Paasche H, Eberle D. Automated compilation of pseudo-lithology maps from geophysical data sets: A comparison of Gustafson-Kessel and fuzzy c-means cluster algorithms[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 2011,42(4):275-285.

|
| [19] |
Deng C, Pan H, Luo M. Joint inversion of geochemical data and geophysical logs for lithology identification in CCSD main hole[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2017,174(12):4407-4420.
|
| [20] |
Konaté A A, Ma H L, Pan H P, et al. Lithology and mineralogy recognition from geochemical logging tool data using multivariate statistical analysis[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2017,128:55-67.

|
| [21] |
Keykhay Hosseinpppr M, Kohsary A-H, Hossein Morshedy A, et al. A machine learning-based approach to exploration targeting of porphyry Cu-Au deposits in the Dehsalm district, Eastern Iran[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020,116(C):223-234.
|
| [22] |
Rosenblatt M. Remarks on some nonparametric estimates of a density function[J]. Ann. Math. Statist., 1956,27(3):832-837.
|
| [23] |
E. Parzen. On estimation of a probability density function and mode[J]. Ann. Math. Statist., 1962,33(3):1065-1076.
|
| [24] |
Kazakos D. Choice of kernel function for density estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1980,2(3):255-258.

|
| [25] |
Bolance C, Guillen M, Nielsen J P. Kernel density estimation ofactuarial loss functions[J]. Mathematics and Economics, 2003,32(1):19-36.
|
| [26] |
Fukunaga K, Hostetler L D. The estimation of the gradient of adensity function with applications in pattern recognition[J]. Trans Information Theory, 1975,21(2):32-40.
|
| [27] |
于传强, 郭晓松, 张安, 等. 基于估计点的滑动窗宽核密度估计算法[J]. 兵工学报, 2009,30(2):231-235.

|
| [27] |
Yu C Q, Guo X S, Zhang A, et al. Slide Bandwidh Kernel Density Estimation Algorithm Based on Estimate Point[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2009,30(2):231-235.
|
| [1] |
LIU Hong-Zhou, WANG Meng-Hua, ZHANG Hao, PENG Ling-Li, LI Wen, ZHANG Jie, ZHAO Zhi-Peng, WU Ze-Jing. Accurate prediction of channel sand based on frequency-divided configuration inversion method:A case study of Zhaohuangzhuang area in Jizhong Sag,Huabei Oilfield[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1311-1319. |
| [2] |
LIU Hui, LI Jing, ZENG Zhao-Fa, WANG Tian-Qi. Stochastic inversion of surface wave dispersion curves based on Bayesian theory[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4): 951-960. |
|
|
|
|

