|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics and influential factors of soil selenium in typical agricultural area, Chongqing |
YU Fei1( ), ZHANG Feng-Lei1, ZHANG Yong-Wen1,2, WANG Rui1,3, WANG Jia-Bin1 ), ZHANG Feng-Lei1, ZHANG Yong-Wen1,2, WANG Rui1,3, WANG Jia-Bin1 |
1. Southeast Sichuan Geological Group,Chongqing Bureau of Geology and Minerals Exploration,Chongqing Key Laboratory of land quality geological survey,Chongqing 400038,China
2. College of Earth Sciences,Chengdu University of Technology,Chengdu 610059,China
3. School of Earth Sciences,China University of Geosciences,Beijing 100083,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Nanchuan District is a typical agricultural area in Chongqing. The authors investigated the geochemical characteristics and influential factors of soil Se from Nanchuan District of Chongqing City to provide some scientific bases for the survey of environment background and regional production as well as human health. More than 8 496 soil samples from the topsoil layers(0~20 cm)all over the Nanchuan District were collected and analyzed for content and distribution of soil Se and their relationships with parent material, soil properties (pH and Corg), altitude and human factors. The research results show that the content of total selenium ranges from 0.056×10-6 to 10.80×10-6 with a mean value of 0.46×10-6, which indicates that the most of the soils are in the category of Se-sufficiency to Se-abundance, with 42.31% being Se-enrichment. The spatial characteristics of soil Se content in Nanchuan District show "high in the south and low in the north", and the soil Se enrichment areas are mainly distributed in Shuijiang Town, Nanping Town, Nanchuan urban area and Jinfo Mountain. Among the types of soils existing in the Nanchuan District, Se content is the highest in industrial and mining land soil and the lowest in farmland. The spatial characteristics of soil Se content and strata show a similar variation pattern. The soil Se enrichment is mainly distributed in Permian, Triassic (Feixianguan Formation and Jialingjiang Formation), Silurian, Ordovician and Cambrian strata, which indicates that the soil Se content is mainly controlled by parent materials in Nanchuan District. In addition, Se content in soil is significantly positively correlated with soil organic matter and altitudes, but significantly negatively correlated with soil pH.
|
|
Received: 08 October 2019
Published: 28 August 2020
|
|
|
|
|
|
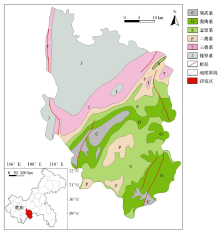
|
Geographical location and geological map of the study area
|

| 地区 | 含量范围/10-6 | 平均值/10-6 | 参考文献 | | 重庆市南川区 | 0.056~10.80 | 0.46 | 本文 | | 三峡库区(重庆段) | 0.006~5.79 | 0.16 | [1] | | 重庆市江津区 | 0.049~3.11 | 0.32 | [8] | | 陕西紫阳 | 0.0015~36.68 | 0.94 | [13] | | 湖北省恩施市 | 2.70~87.3 | 9.36 | [11] | | 江西省丰城市 | 0.40~0.99 | 0.54 | [15] | | 贵州 | 0.06~1.33 | 0.37 | [16] | | 广东 | 0.03~1.42 | 0.28 | [17] | | 香港 | 0.07~2.26 | 0.76 | [18] | | 黑龙江省 | 0.008~0.660 | 0.15 | [2] | | 东北平原 | 0.01~5.3 | 0.18 | [9] | | 北京平原 | 0.04~5.26 | 0.2 | [19] | | 河北平原 | 0.05~0.34 | 0.19 | [20] | | 中国 | 0.05~0.99 | 0.29 | [21] | | 世界 | 0.03~2.00 | 0.4 | [5] |
|
Se contents in surface soils in the study area and other region of China
|

| 含量分级 | 硒含量阈值/10-6 | 硒效应 | 比例/% | | 缺乏 | ≤0.125 | 缺Se | 1.71 | | 边缘 | 0.125~0.175 | 潜在缺Se | 0.96 | | 中等 | 0.175~0.40 | 足Se | 54.83 | | 高 | 0.40~3.0 | 富Se | 42.31 | | 过剩 | ≥3.0 | Se中毒 | 0.19 |
|
Classification of soil Se content in the study area
|
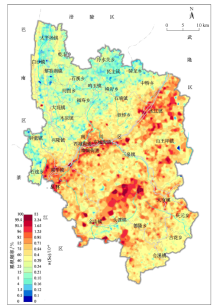
|
Content distribution map of soil in the study area
|

| 地层 | 最小值/10-6 | 平均值/10-6 | 最大值/10-6 | 标准差/10-6 | 变异系数/% | 样本数 | | J3p | 0.064 | 0.243 | 0.593 | 0.06 | 24.62 | 653 | | J3sn | 0.075 | 0.251 | 0.783 | 0.07 | 27.41 | 602 | | J2s | 0.071 | 0.235 | 4.154 | 0.13 | 53.6 | 1609 | | J1z-J2x | 0.056 | 0.326 | 2.708 | 0.19 | 57.97 | 547 | | T3xj | 0.062 | 0.391 | 1.773 | 0.22 | 55.83 | 400 | | T2l | 0.124 | 0.411 | 2.565 | 0.23 | 55.12 | 301 | | T1j | 0.108 | 0.734 | 10.802 | 0.66 | 89.29 | 562 | | T1f | 0.098 | 0.902 | 3.439 | 0.48 | 53.03 | 211 | | P | 0.123 | 1.026 | 5.15 | 0.594 | 57.903 | 498 | | O | 0.084 | 0.479 | 3.227 | 0.27 | 55.53 | 1604 | | S | 0.056 | 0.573 | 5.166 | 0.37 | 64.27 | 1509 | | ∈ | 0.066 | 0.475 | 3.388 | 0.26 | 54.52 | 450 |
|
Se contents in different strata of soil in the study area
|

| 指标 | N | P | S | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | | Se | 0.577** | 0.402** | 0.662** | -0.267** | -0.027 | 0.344** | 0.057** | 0.126** | -0.276 | -0.152 |
|
The correlation coefficients between Se and major elements in soils in study area
|

| 元素 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Zn | Pb | | Se | 0.301** | 0.501** | 0.463** | 0.382** | 0.065** | 0.313** | 0.194** | 0.190** |
|
The correlation coefficients between Se and heavy metal contents in soils in study area
|
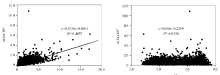
|
Correlation coefficients between Se and organic matter or pH of soil in the study area
|

| 海拔/m | 最小值/10-6 | 平均值/10-6 | 最大值/10-6 | 标准差/10-6 | 变异系数/% | 样品数 | | 0~500 | 0.09 | 0.31 | 1.76 | 0.27 | 0.87 | 625 | | 500~1000 | 0.06 | 0.43 | 10.8 | 0.38 | 0.9 | 6825 | | 1000~1500 | 0.06 | 0.54 | 3.4 | 0.32 | 0.59 | 1343 | | 1500~2000 | 0.2 | 0.99 | 4.44 | 0.6 | 0.61 | 129 | | ≥2000 | 0.64 | 1.38 | 2.89 | 0.53 | 0.38 | 23 |
|
Se contents in different altitude of soil in the study area
|

| 土地利用类型 | 农田 | 旱地 | 林地 | 园地 | 草地 | 村庄 | 城镇 | 工矿区 | 其他用地 | | 样品数 | 2831 | 2193 | 2849 | 250 | 192 | 456 | 56 | 9 | 110 | | 平均含量/10-6 | 0.4 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.51 | 0.9 | 0.69 | 0.5 |
|
Se concentrations in different land use types of soil in the study area
|
| [1] |
罗友进, 韩国辉, 孙协平, 等. 三峡库区(重庆段)土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤, 2018,50(1):131-138.
|
| [1] |
Luo Y J, Han G H, Sun X P, et al. Distribution of soil selenium in three gorges reservoir region (Chongqing section) and its influential factors[J]. Soil, 2018,50(1):131-138.
|
| [2] |
迟凤琴, 徐强, 匡恩俊, 等. 黑龙江省土壤硒分布及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2016,53(5):1262-1274.
|
| [2] |
Chi F Q, Xu Q, Kuang E J, et al. Distribution of Selenium and Its Influencing Factors in Soils of Heilongjiang Province,China[J]. Acta Pedolgica Sinica, 2016,53(5):1262-1274.
|
| [3] |
Wang J, Li H R, Li Y H, et al. Speciation, distribution, and bioavailability of soil selenium in the Tibetan Plateau Kashin-Beck Disease area—A case study in Songpan County, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 2013,156(1/3):367-375.
|
| [4] |
Rayman M P. Selenium and hum an health[J]. Lancet, 2012,379(9822):1256-1268.

|
| [5] |
Fordyce F M. Selenium deficiency and toxicity in the environment[G]// Selinus O. Essentials of medical geology. British Geological Survey, 2013:373-416.
|
| [6] |
Tan J A, Zhu W, Wang W, et al. Selenium in soil and endemic diseases in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2002,284(1-3):227-235.

|
| [7] |
童建川. 重庆紫色土区硒分布特征研究[J]. 西南师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2016,41(3):170-175.
|
| [7] |
Tong J C. On Distribution of selenium in purple soil region of Chongqing[J]. Journal of Southweat China Normal University:Natural Science Edition, 2016,41(3):170-175.
|
| [8] |
赵婉彤, 童建川, 杨剑虹. 重庆市江津区紫色土壤基本性质对土壤硒含量的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2017,45(5):92-95.
|
| [8] |
Zhao W T, Tong J C, Yang J H. Effects of basic properties of purple soil on soil selenium content in Jiangjin district of Chongqing City[J]. Journal of Anhui Agri. Sci., 2017,45(5):92-95.
|
| [9] |
戴慧敏, 宫传东, 董北, 等. 东北平原土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2015,52(6):1356-1364.
|
| [9] |
Dai H M, Gong C D, Dong B, et al. Distribution of soils Selenium in the Northeast China Plain and its influencing factors[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015,52(6):1356-1364.
|
| [10] |
严明书, 龚媛媛, 杨乐超, 等. 重庆土壤硒的地球化学特征及经济意义[J]. 物探与化探, 2014,38(2):325-330.
|
| [10] |
Yan M S, Gong Y Y, Yang L C, et al. Geochemical characteristics and economic significance of the Se-rice soil in China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014,38(2):325-330.
|
| [11] |
余飞, 贾中民, 李武斌, 等. 锗在土壤-水稻系统的迁移累积及其影响因素[J]. 三峡生态环境监测, 2018,3(1):66-74.
|
| [11] |
Yu F, Jia Z M, Li W B, et al. Translocation and accumulation of germanium in paddy soil-rice plant system[J]. Ecology and Environmental Monitoring of Three Gorges, 2018,3(1):66-74.
|
| [12] |
陈荣彬. 层次分析法在重庆市南川区矿山地质环境评价中的应用[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016.
|
| [12] |
Chen R B. Application of AHP in mine geological environment assessment in Nanchuan district in Chongqing City[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016.
|
| [13] |
张建东, 王丽, 王浩东, 等. 紫阳县土壤硒的分布特征研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2017,48(6):1404-1408.
|
| [13] |
Zhang J D, Wang L, Wang H D, et al. Distribution of soil total selenium in Ziyang, Shaanxi[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2017,48(6):1404-1408.
|
| [14] |
Qin H B, Zhu J M, Liang L, et al. The bioavailability of selenium and risk assessment for human selenium poisoning in high-Se areas, China[J]. Environment International, 2013,52:66-74.

|
| [15] |
吴文良, 张征, 卢勇, 等. 江西省丰城市“中国生态硒谷”创意产业的发展战略[J]. 农产品加工:创新版, 2010(3):72-75.
|
| [15] |
Wu W L, Zhang Z, Lu Y, et al. Expand srategy on creative industry for Chinese ecological Se-tech at Jiangxi Fengcheng[J]. Agricultural Products Processing:Innovational Edition, 2010(3):72-75.
|
| [16] |
何亚琳. 贵州省土壤含硒量及其分布[J]. 土壤学报, 1996,33(4):391-397.
|
| [16] |
He Y L. Contents and distribution in soils of Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1996,33(4):391-397.
|
| [17] |
陈俊坚, 张会化, 余炜敏, 等. 广东省土壤硒空间分布及潜在环境风险分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2012,12(6):1115-1120.
|
| [17] |
Chen J J, Zhang H H, Yu W M, et al. Spatial variation and environmental indications of soil selenium in Guangdong province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2012,12(6):1115-1120.
|
| [18] |
章海波, 骆永明, 吴龙华, 等. 香港土壤研究Ⅱ. 土壤硒的含量、分布及其影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2005,42(3):404-410.
|
| [18] |
Zhang H B, Luo Y M, Wu L H, et al. The Research of soil in Hong Kong II: The content,distribution and influencing factors of selenium[J]. Acta Pedolgica Sinica, 2005,42(3):404-410.
|
| [19] |
郭莉, 杨忠芳, 阮起和, 等. 北京市平原区土壤中硒的含量和分布[J]. 现代地质, 2012,26(5):859-864.
|
| [19] |
Guo L, Yang Z F, Yuan Q H, et al. Content and distribution of selenium in soil of Beijing plain[J]. Geoscience, 2012,26(5):859-864.
|
| [20] |
李振宁. 河北省平原区土壤中硒异常源追踪及生态效应评价[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄经济学院, 2010.
|
| [20] |
Li Z L. The study on source tracking of Se anomaly and ecological appraisal in plain terrain of Hebei[D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang University of Economics, 2010.
|
| [21] |
刘铮. 中国土壤微量元素[M]. 南京: 江苏科学技术出版社, 1996.
|
| [21] |
Liu Z. Chinese soil trace elements[M]. Nanjing: Jiangsu Science and Technology Press, 1996.
|
| [22] |
谭见安. 环境生命元素与克山病[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 1996.
|
| [22] |
Tan J A. Environmental life element sand Keshan disease[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 1996.
|
| [23] |
余涛, 杨忠芳, 王锐, 等. 恩施典型富硒区土壤硒与其他元素组合特征及来源分析[J]. 土壤, 2018,50(6):1119-1125.
|
| [23] |
Yu T, Yang Z F, Wang R, et al. Characteristics and sources of soil selenium and other elements in typical high selenium soil area of Enshi[J]. Soils, 2018,50(6):1119-1125.
|
| [24] |
杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶, 等. 海南岛农田土壤Se的地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012,26(5):837-849.
|
| [24] |
Yang Z F, Yu T, Hou Y Q, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in farmland of Hainan Island[J]. Geoscience, 2012,26(5):837-849.
|
| [25] |
田欢. 典型富硒区岩石—土壤—植物中硒的赋存状态及环境行为研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.
|
| [25] |
Tian H. The occurrence state and speciation of selenium and its environmental behaviors in rock-soil-plant from typical high-Se areas[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017.
|
| [26] |
徐强, 迟凤琴, 匡恩俊, 等. 方正县土壤硒的分布特征及其与土壤性质的关系[J]. 土壤通报, 2015,46(3):597-602.
|
| [26] |
Xu Q, Chi F Q, Kuang E J, et al. Distribution characteristics of selenium in Fangzheng County and its relationship with soil properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2015,46(3):597-602.
|
| [27] |
Gabos M B, Alleoni L R F, Abreu C A. Background levels of selenium in some selected Brazilian tropical soils[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014,145:35-39.

|
| [28] |
Yu T, Yang Z F, Lu Y Y, et al. The origin and geochemical cycle of soil selenium in a Se-rich area of China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014,139:97-108.

|
| [29] |
商靖敏, 罗维, 吴光红, 等. 洋河流域不同土地利用类型土壤硒(Se)分布及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2015,36(1):301-308.
|
| [29] |
Shang J M, Luo W, Wu G H, et al. Spatial distribution of Se in soils from different land use types and its influencing factors within the Yanghe Watershed, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2015,36(1):301-308.
|
| [30] |
王祖伟, 徐利淼, 张文具. 土壤微量元素与人类活动强度的对应关系[J]. 土壤通报, 2002,33(4):303-305.
|
| [30] |
Wang Z W, Xu L M, Zhang W J. Corresponding relationship between trace elements in soil and human activity intensity[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2002,33(4):303-305.
|
| [31] |
Huang S S, Hua M, Feng J S, et al. Assessment of selenium pollution in agricultural soils in the Xuzhou District, Northwest Jiangsu, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009,21(4):481-487.
|
| [32] |
Wu G H, Shang J M, Pan L, et al. Heavy metals in surface sediments from nine estuaries along the coast of Bohai Bay, Northern China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014,82(1-2):194-200.

|
| [33] |
Perkins W T. Extreme selenium and tellurium contamination in soils-An eighty year-old industrial legacy surrounding a Ni refinery in the Swansea Valley [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2011,(412-413):162-169.
|
| [1] |
WANG Zhi-Qiang, YANG Jian-Feng, WEI Li-Xin, SHI Tian-Chi, CAO Yuan-Yuan. Geochemical characteristics and bioavailability of selenium in alkaline soil in Shizuishan area, Ningxia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 229-237. |
| [2] |
XU Yun-Feng, HAO Xue-Feng, QIN Yu-Long, WANG Xian-Feng, XIONG Chang-Li, LI Ming-Ze, WU Weng-Hui, ZHAN Han-Yu. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting direction in Chahe area of Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3): 624-638. |
|
|
|
|

