|
|
|
| Modelling and analysis study of electromagnetic field distribution around submarine cable |
Tuan-Jie GAN1, Jian-Ping CHEN1( ), Xi YANG1, Qing-Dong ZHOU1, Liang ZENG2 ), Xi YANG1, Qing-Dong ZHOU1, Liang ZENG2 |
1. Jiangmen Power Supply Bureau, Guangdong Electrifc Network Liability Co., Ltd., Jiangmen 510630, China
2. Guangdong Electric Power Design Institute Liability Co., Ltd., China Energy Resource Construction Group, Guangzhou 510663, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The detection and identification technology in the maintenance and construction of submarine cables has become a very important research content. In this paper, a 2.5-dimensional high-precision finite element numerical simulation algorithm of the frequency domain CSEM method was used to simulate and analyze the submarine cable model. Based on the horizontal terrain and undulating terrain submarine cable models, this study focused on the simulation and analysis of the characteristics of the electromagnetic field distribution with the changing of seawater layer thickness and the submarine interface. Numerical examples show that the magnetic field component Hy is very sensitive to the thickness of the seawater layer. When the thickness is changed by 0.2m, the Hy error anomaly amplitude can reach 5%, thus demonstrating that the CSEM theory is feasible for detection and identification of submarine cables.
|
|
Received: 26 August 2019
Published: 24 June 2020
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Jian-Ping CHEN
E-mail: jmchenjianping@126.com
|
|
|
|
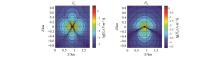
|
Numerical solution of Ex and Hy for y=0 m section
|
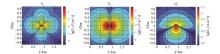
|
Numerical solution of Ex、Ey and Hy for y=100 m section
|
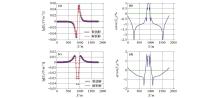
|
Comparison between numerical solution and analytical solution of y=100 m profile
|
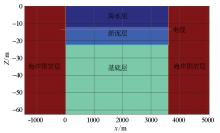
|
Schematic diagram of submarine cable model in horizontal terrain
|
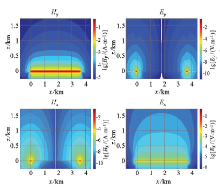
|
Section of electromagnetic field component
|
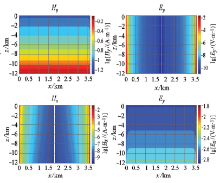
|
Section of electromagnetic field components in seawater layer
|
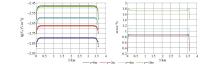
|
Comparison of different depths of Ex component
|
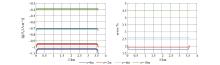
|
Comparison of different depths of Hy component
|
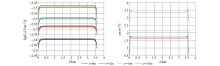
|
Comparison of different depths of Ex component
|
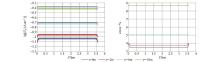
|
Comparison of different depths of Hy component
|
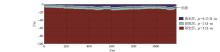
|
Submarine cable model in undulating terrain
|
|
Component diagram of electromagnetic field in x and y directions of submarine cable model (calculation area)
|
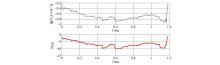
|
Hy distribution of magnetic field component of z=0 m line
|
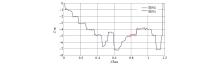
|
Mud layer top interface
|
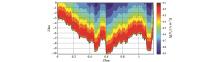
|
Hy section of magnetic field component
|
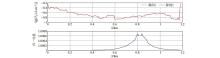
|
Hy normalization results
|
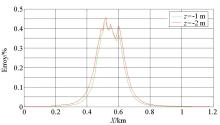
|
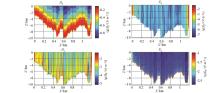
Distribution of Hy normalized error deviation of magnetic field components in different horizons
|
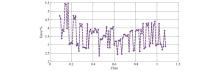
|
Distribution of Hy normalized error deviation of plane magnetic field component z=-1 m
|
| [1] |
罗深荣. 侧扫声纳和多波束测深系统在海洋调查中的综合应用[J]. 海洋测绘, 2003,23(1):22-24.
|
| [1] |
Luo S R. Comprehensive utilization of side scan sonar and multi-beam sounding system in oceanographic research[J]. Ocean Mapping, 2003,23(1):22-24.
|
| [2] |
李家彪. 多波束勘测原理技术与方法[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1999.
|
| [2] |
Li J B. Multi-beam survey principle technology and method[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1999.
|
| [3] |
钟献盛, 裴彦良. 应用磁力仪探测海底电缆方法的探讨[J]. 海洋科学, 2001,25(9):10-11.

|
| [3] |
Zhong X S, PEI Y L. Discussion of the survey method of the sea bed cables using Magnetometer[J]. Marine Sciences, 2001,25(9):10-11.

|
| [4] |
张伟, 孙伯娜, 王朝, 等. 海底管线路由探测方法研究[J]. 港工技术, 2015,52(6):111-113.
|
| [4] |
Zhang W, Sun B N, Wang C, et al. Study on seabed pipeline routing detection[J]. Port Engineering Technology, 2015,52(6):111-113.
|
| [5] |
岑贞锦, 蒋道宇, 张维佳, et al. 海底电缆检测技术方法选择分析[J]. 南方能源建设, 2017,4(3):85-96.
|
| [5] |
Cen Z J, Jiang D Y, Zhang W J, et al. Analysis on selection of submarine cable detection technology[J]. Southern Energy Construction, 2017,4(3):85-96.
|
| [6] |
郝威, 周学军. 采用瞬变电磁法的海底光缆定位[J]. 光纤与电缆及其应用技术, 2005(1):20-22.

|
| [6] |
Hao W, Zhou X J. Submarine optical cable positioning using transient electromagnetic method[J]. Optical Fiber and Cable and their Application Technology, 2005(1):20-22.
|
| [7] |
于波, 刘雁春, 边刚, 等. 海洋工程测量中海底电缆的磁探测法[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2006,31(5):454-457.
|
| [7] |
Yu B, Liu Y C, Bian G, et al. Magnetism detecting method for seabed cable in marine engineering surveying[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan Univers, 2006,31(5):454-457.
|
| [8] |
Dalian R J. Magnetism detecting method for seabed cable in marine engineering surveying[J]. Geomatics & Information Science of Wuhan University, 2006,31(5):454-457.
|
| [9] |
Yu B, Liu Y C, Zhai G J, et al. Magnetic detection method foe seabed cable in marine engineering surveying[J]. Geo-spatial Information Science, 2007,31(3):454-457.
|
| [10] |
高震, 汪洋, 郑新龙, 等. 基于海底电缆故障探测及维护的分析研究[J]. 电源技术应用, 2013(1):63.
|
| [10] |
Gao Z, Wang Y, Zheng X L, et al. Analysis and research on fault detection and maintenance based on submarine cable[J]. Power Technology Application, 2013(1):63.
|
| [11] |
李晶. 海底电缆外部探测方法与应用浅析[J]. 水道港口, 2018,178(3):123-127.
|
| [11] |
Li J. Analysis on method and application of submarine cable detection[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2018,178(03):123-127.
|
| [12] |
Cox C. Electromagnetic induction in the oceans and inferences on the constitution of the earth[J]. Geophys Surv, 1980,4(1-2):137-156.

|
| [13] |
Mitsuhata Y. 2-D electromagnetic modeling by finite-element method with a dipole-dipole source and topography[J]. Geophysics, 2000,65(2):465-475.

|
| [14] |
Li Y G, Dai S K. Finite element modelling of marines controlled-source electromagnetic responses in two-dimensional dipping anisotropic conductivity structures[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2011,185(2):622-636.

|
| [15] |
薛东川, 戴世坤. 频率域2.5维电磁测深有限元模拟中的吸收边界条件[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2008,32(6):57-61.
|
| [15] |
Xue D C, Dai S K. Absorbing boundary condition for simulation 2.5-D electromagnetic sounding in frequency domain by finite element method[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum:Edition of Natural Sciences, 2008,32(6):57-61.
|
| [16] |
Key K, Ovall J. A parallel goal-oriented adaptive finite element method for 2.5-D electromagnetic modelling[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2011,186(1):137-154.

|
| [17] |
戴世坤, 王顺国, 张钱江, 等. 频率域可控源电磁法2.5D正反演[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013(9):2513-2523.
|
| [17] |
Dai S K, Wang S G, Zhang Q J, et al. 2.5D forward and inversion of CSEM in frequency domain[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013(9):2513-2523.
|
| [18] |
Li Y, Key K . 2D marine controlled-source electromagnetic modeling: Part 1—An adaptive finite-element algorithm[J]. Geophysics, 2007,72(2):51-62.
|
| [19] |
汤文武, 柳建新, 叶益信, et al. 基于节点有限元与矢量有限元的可控源电磁三维正演对比[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2018,53(03):192-199.
|
| [19] |
Tang W W, Liu J X, Ye Y X, et al. Comparison of 3D controlled-source electromagnetic forward modeling based on the nodal finite element and the edge-based finite element[J]. OGP, 2018,53(3):617-624.
|
| [20] |
徐世浙. 地球物理中的有限单元法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994.
|
| [20] |
Xu S Z. The finite element method in geophysics[M]. Bejing: Science Press, 1994.
|
| [1] |
ZHANG Jian-Zhi, HU Fu-Hang, LIU Hai-Xiao, XING Guo-Zhang. TEM response characteristics of borehole in goaves of old coal mines[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 191-197. |
| [2] |
XIAO Yan-Shan, ZHOU Zheng-Hua, SU Jie, WEI Xin. Discussion about the theoretical basis of the down-hole method for shear wave velocity test under surface forward and reverse horizontal hammer strikes[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1288-1294. |
|
|
|
|

