|
|
|
| 1:50 000 electro-geochemical survey in the Luokedun lead-zinc polymetallic deposit, Inner Mongolia |
Shuai LI1,2,3, Bin-Bin SUN2,3( ), Mei-Lan WEN1( ), Mei-Lan WEN1( ), Chao WU2,3, Ling HE2,3, Dao-Ming ZENG2,3, Xiao-Meng CHENG2,3, Yin-Wei WEN4 ), Chao WU2,3, Ling HE2,3, Dao-Ming ZENG2,3, Xiao-Meng CHENG2,3, Yin-Wei WEN4 |
1. Earth Sciences College, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin 541004, China
2. Key Laboratory of Geochemical Exploration ,Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,Langfang 065000, China
3. UNESCO International Center on Global-Scale Geochemistry, Langfang 065000, China
4. Inner Mongolia Xingye Mining Co., Ltd., Chifeng 024000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract With the electro-geochemical survey technology becoming more and more "portable", it is possible to conduct electro-geochemical survey of small or medium scales. In this paper, an effect comparison test of electro-geochemicalsurvey and soil survey at the scale of 1:50,000 was carried out within 40 km2 of the hydrothermal type lead-zinc polymetallic ore district in the aeolian sand shallow covered area of Luokedun, Inner Mongolia. The results are as follows: ①Electro-geochemical survey can delineate comprehensive anomalies of Pb-Zn-Ag-As-Bi-Cd, which have the same composition as the known orebodies. The locations of the anomalies are consistent with the known orebodies/ore spots in spatial distribution. ② Compared with the soil survey results, the results of anomaly range, contrast and continuity from the electro-geochemical survey are more superior in that soil soil survey can only find anomalies of spotted distribution in the outcropping area of the hill residual soil. ③The electro-geochemical survey also finds comprehensive anomalies of multiple elements in the aeolian sand shallow covered area in the northwest of the survey area. Based on these anomalies, the 1:10,000 induced-current middle-gradient survey and drilling verification test was carried out. A 6-meter-thick Ag-Cu rich orebody was discovered at the depth of about 540 meter, which seems to have been a breakthrough in ore prospecting. The above test results show that the electro-geochemical survey at the scale of 1:50,000 can effectively delineate the prospecting targets in the shallow covered area of aeolian sand. The electro-geochemical survey can be popularized and applied in future work.
|
|
Received: 09 October 2019
Published: 24 June 2020
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Bin-Bin SUN,Mei-Lan WEN
E-mail: sunbinbin@igge.cn;meilanwen112@126.com
|
|
|
|
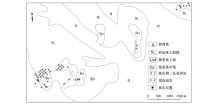
|
Generalized geologic map of the lead-zinc polymetallic ore in Loukedun exploration area,Dong Ujimqin Banner, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
|

| 地电化学泡塑样品元素含量测定方法 | 土壤样品元素含量测定方法 | 等离子体质谱法
(ICP-MS) | 等离子体光谱法
(ICP-OES) | 氢化物-原子
荧光光谱法
(HG-AFS) | 无火焰原子
吸收光谱法
(AAN) | 等离子体质
谱法
(ICP-MS) | 压片法X-
射线荧光光谱
(XRF) | 氢化物-原子
荧光光谱法
(HG-AFS) | Au、Ag、Bi、Cd、Co、
Cu、La、Mo、Ni、Pb、
Sb、Ti、U、Zn | Al、Cr、Fe、K | As、Se | Au | Ag、Bi、Cd、Co、
Cu、La、Mo、Pb、
Sb、U、Zn | Al2O3、Cr、Fe2O3、
K2O、Ni、Ti | As、Se |
|
Determination methods for samples of electro-geochemistry and soil survey
|

| 变异系数范围 | 地电化学测量元素 | 土壤测量元素 | | Cv<0.5 | Mo、Sb、U | Ag、Al2O3、Co、Cr、Cu、Fe2O3、K2O、La、Ni、Pb 、Ti、U、Zn | | 0.5≤Cv<1 | Ag、As、Au、Bi、Cd、Co、Cr、Fe、K、La、Ni、Pb、Se、Ti、Zn、 | Au、Cd、Mo、Sb、Se | | Cv≥1 | Al、Cu | As、Bi |
|
Statistical table for Cv of element content of electro-geochemistry and soil survey(n=542)
|

| 参数 | 高程/m | pH | 电导率/(μs·cm-1) | 电流/mA | | 最大值 | 1 003 | 9.54 | 692 | 84.2 | | 最小值 | 874 | 5.63 | 13.2 | 1.00 | | 平均值 | 916 | 7.18 | 94.0 | 15.0 | | 标准差 | 24.7 | 0.60 | 67.7 | 8.80 | | 变异系数 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.72 | 0.58 |
|
Statistical table for terrain and electron parameters of soil in the test area(n=542)
|
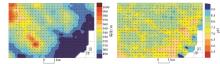
|
Contour of elevation and pH in the test area
|
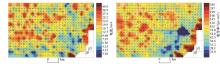
|
Contour of current and conductivity in the test area
|

| 元素 | Ag | Al | As | Au | Bi | Cd | Co | Cr | Cu | Fe | K | La | Mo | Ni | Pb | Sb | Se | Ti | U | Zn | | X+1.5S | 65.1 | 5.96 | 1.13 | 4.07 | 0.14 | 42.8 | 3.74 | 12.1 | 8.65 | 6.39 | 1.41 | 7.09 | 0.43 | 7.34 | 5.48 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 187 | 33.8 | 28.5 | | X+2S | 74.7 | 7.10 | 1.29 | 4.50 | 0.16 | 48.7 | 4.25 | 13.6 | 9.78 | 7.58 | 1.67 | 8.37 | 0.47 | 8.63 | 6.24 | 0.38 | 0.05 | 221 | 38.8 | 32.3 | | X+4S | 113 | 11.7 | 1.96 | 6.22 | 0.24 | 72.5 | 6.30 | 19.6 | 14.3 | 12.3 | 2.68 | 13.5 | 0.62 | 13.8 | 9.30 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 354 | 58.9 | 47.7 | | X+8S | 190 | 20.8 | 3.28 | 9.65 | 0.40 | 120 | 10.4 | 31.7 | 23.3 | 21.8 | 4.69 | 23.8 | 0.92 | 24.2 | 15.4 | 0.69 | 0.11 | 622 | 99.1 | 78.3 |
|
Anomaly threshold classification of contents for elements of electro-geochemistry survey in the test area
|

| 元素 | Ag | Al2O3 | As | Au | Bi | Cd | Co | Cr | Cu | Fe2O3 | K2O | La | Mo | Ni | Pb | Sb | Se | Ti | U | Zn | | X+1.5S | 90.1 | 11.9 | 10.1 | 1.26 | 0.29 | 101 | 9.47 | 46.1 | 16.3 | 3.35 | 3.00 | 28.6 | 0.61 | 21.0 | 20.6 | 0.75 | 0.19 | 1.56 | 1.55 | 49.0 | | X+2S | 96.8 | 12.6 | 11.1 | 1.44 | 0.32 | 111 | 10.6 | 51.0 | 18.0 | 3.69 | 3.07 | 31.2 | 0.66 | 23.5 | 21.7 | 0.82 | 0.21 | 1.68 | 1.67 | 53.9 | | X+4S | 124 | 15.4 | 15.0 | 2.14 | 0.44 | 147 | 15.0 | 70.6 | 24.9 | 5.09 | 3.34 | 41.6 | 0.88 | 33.8 | 25.8 | 1.09 | 0.30 | 2.15 | 2.14 | 73.6 | | X+8S | 177 | 21.1 | 22.7 | 3.54 | 0.67 | 221 | 23.7 | 110 | 38.7 | 7.87 | 3.90 | 62.5 | 1.30 | 54.2 | 34.0 | 1.63 | 0.48 | 3.11 | 3.07 | 113 |
|
Anomaly threshold classification of contents for elements of soil survey in the test area
|
|
Geochemical distribution of cumulative frequency of soil elements in the test area
|
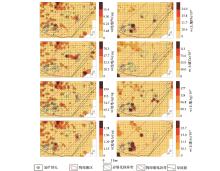
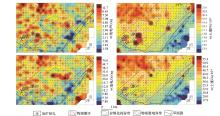
|
Geochemical anomaly distribution of Pb、Zn、Ag、As of electro-geochemistry and soil survey
|
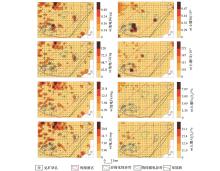
|
Geochemical anomaly distribution of Bi、Cd、Fe、Al of electro-geochemistry and soil survey
|
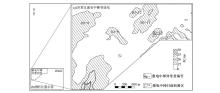
|
Induced electric medium ladder scanning surface in the test area
|
| [1] |
孙彬彬, 刘占元, 周国华. 地电化学方法技术研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 物探与化探, 2015,39(1):16-21.

|
| [1] |
Sun B B, Liu Z Y, Zhou G H. Research status and development trends for geoelectrochemical methods[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015,39(1):16-21.

|
| [2] |
罗先熔. 再论地球电化学测量法寻找隐伏矿床[J]. 桂林冶金地质学院学报, 1994,14(3):295-302.
|
| [2] |
Luo X R. Secondary discussion on prospecting buried ore by geoelectrochemical methdd[J]. Journal of Guilin College of Geology, 1994,14(3):295-302.
|
| [3] |
谢学锦, 王学求. 深穿透地球化学新进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2003,10(1):225-238.
|
| [3] |
Xie X J, Wang X Q. Recent developments on deep-penetrating geochemistry[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003,10(1):225-238.
|
| [4] |
罗先熔. 勘查地球化学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2007.
|
| [4] |
Luo X R. Exploration geochemistry [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007.
|
| [5] |
康明, 罗先熔. 金属矿床地电化学勘查方法研究现状及前景展望[J]. 地质论评, 2005,51(4):452-457.

|
| [5] |
Kang M, Luo X R. The Present and future of electrogeochemical method for metallic ore deposit prospecting[J]. Geological Review, 2005,51(4):452-457.

|
| [6] |
任天祥, 伍宗华, 汪明启. 近十年化探新方法新技术研究进展[J]. 物探与化探, 1997,22(6):411-417.
|
| [6] |
Ren T X, Wu Z H, Wang M Q. New advances in the research on new methods and new techniques for geochemical exploration in the past ten years[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1997,22(6):411-417.
|
| [7] |
刘攀峰, 罗先熔, 文美兰, 等. 近三十年来我国地电化学技术研究回顾与展望[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2018,38(1):47-55.
|
| [7] |
Liu P F, Luo X R, Wen M L, et al. Retrospect and prospect for geo-electrochemical technology research in the past three decades of China[J]. Joumal of Guilin University of Technology, 2018,38(1):47-55.
|
| [8] |
丁汝福. 国内外寻找隐伏矿化探新方法研究进展[J]. 地质与勘探, 1999,35(2):32-36.
|
| [8] |
Ding R F. Advance on new geochemical exploring technologys for prospecting buried deposit[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1999,35(2):32-36.
|
| [9] |
王学求. 寻找和识别隐伏大型特大型矿床的勘查地球化学理论方法与应用[J]. 物探与化探, 1998, 22(2):81-89+108.
|
| [9] |
Wang X Q. Geochemical methods and application for giant ore deposits in concealed terrains[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1998,22(2):81-89,108.

|
| [10] |
蒋永建, 魏俊浩, 周京仁, 等. 勘查地球化学新方法在矿产勘查中的应用及其地质效果[J]. 物探与化探, 2010,34(2):134-138.

|
| [10] |
Jiang Y J, Wei J H, Zhou J R, et al. The Application of new geochemical exploration methods to mineral exploration and its geological effect[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2010,34(2):134-138.

|
| [11] |
邱炜, 潘彤, 李永虎. 地电化学测量法寻找隐伏金矿的机理及其应用效果[J]. 物探与化探, 2011,35(2):203-205.

|
| [11] |
Qiu W, Pan T, Li Y H. The Mechanism and application effect of the geo-electrochem ical method in search for concealed gold deposits[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2011,35(2):203-205.

|
| [12] |
智超, 向武, 曾键年, 等. 地电提取法在深部找矿中的试验——以安徽胡村铜钼矿为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2015,39(1):149-155.

|
| [12] |
Zhi C, Xiang W, Zeng J N, et al. The tentative application of the geoelectro-chemical extraction method to the deep prospecting:A case study of the Hucun copper-molybdenum deposit in Anhui Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015,39(1):149-155.

|
| [13] |
孙彬彬. 地电化学异常形成机理及找矿技术规范化研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2017.
|
| [13] |
Sun B B. Study on formation mechanism of geoelectric chemistry amomaly and standardization of this ore propecting technology [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017.
|
| [14] |
陈亚东. 内蒙古东乌旗洛恪顿铅锌多金属矿区地电化学方法技术研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
|
| [14] |
Chen Y D. The research of methods and techniques of Geoelectrochemistry of Luokedun plumbum-zinc multi-metal deposit in Inner Mongolia[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2015.
|
| [15] |
孙彬彬, 刘占元, 周国华. 固体载体型元素提取器研制[J]. 物探与化探, 2011,35(3):375-378.

|
| [15] |
Sun B B, Liu Z Y, Zhou G H. The development of the solid carrier elements extractor[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2011,35(3):375-378.

|
| [16] |
蓝天, 罗先熔, 陈晓青. 湖南国庆矿区地电化学方法寻找隐伏铜矿预测研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2018,54(3):563-573.
|
| [16] |
Lan T, Luo X R, Chen X Q. Prediction of concealed copper deposits by the geoelectric-geochemical method in the Guoqing mine area,Hunan Province[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2018,54(3):563-573.
|
| [17] |
叶信栋, 孙彬彬, 周国华, 等. 河北蔡家营铅锌多金属矿地电化学提取有效性及提取条件试验[J]. 地质与勘探, 2018,54(5):979-987.
|
| [17] |
Ye X D, Sun B B, Zhou G H, et al. Effectiveness and conditions tests of geo-electrochemical electrochemical extraction in the Caijiaying Pb-Zn polvmetallic mining area,Hebei Province[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2018,54(5):979-987.
|
| [18] |
藏金生, 李诗言, 蔡新明. 化探中五个常用参数的应用[J]. 科技视界, 2013(28):8-10,31.
|
| [18] |
Zang J S, Li S Y. The Application of five common parameters to geochemical exploratio[J]. Science & Technology Vision, 2013(28):8-10,31.
|
| [19] |
孙彬彬, 张学君, 刘占元, 等. 地电化学异常形成机理初探[J]. 物探与化探, 2015,39(6):1183-1187.

|
| [19] |
Sun B B, Zhang X J, Liu Z Y, et al. A preliminary study of the formation mechanism of the geoelectric chemistry anomaly[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2015,39(6):1183-1187.
|
| [1] |
LIANG Xin-Qiang, QIAO Zhan-Hua, YAN Qiang, WANG Liang, LI Jian-Feng, LIU Xiao-Hui, WANG Miao. Application of geophysical methods in the exploration of Fuxingtun silver-lead-zinc polymetallic deposit and its metallogenic mechanism[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2): 323-336. |
| [2] |
GONG Sheng-Ping, LU Gui-Fu, XI Ming-Jie, MA Sheng-Ming, SU Wen-Li. The application of integrated geophysical and geochemical methods to the prospecting of copper polymetallic deposits in the arid desert area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 1-10. |
|
|
|
|

