|
|
|
| Application of compressed sensing-based seismic data regularization technology in the Tarim block |
ZHENG Duo-Ming1( ), WANG De-Ying2,3, WU Yu-Bing1, KOU Long-Jiang2( ), WANG De-Ying2,3, WU Yu-Bing1, KOU Long-Jiang2( ), CHEN Yang-Yang1, JIN Bao-Zhong2 ), CHEN Yang-Yang1, JIN Bao-Zhong2 |
1. Tarim Oilfield Company, PetroChina,Korla 841000,China
2. Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration & Development-Northwest(NWGI),PetroChina,Lanzhou 730020,China
3. School of Geosciences,China University of Petroleum(East China),Qingdao 257061,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Tarim Basin,one of China's most significant oil exploration areas,exhibits thick sedimentary rock layers and frequent tectonic movements.These characteristics have led to the formation of abundant source,reservoir,and cap rocks,creating favorable conditions for the generation and storage of resources like petroleum.However,the high topographic relief in the area poses significant challenges to observation system arrangement and acquisition engineering design.Moreover,undulating surfaces and complex subsurface structures affect the propagation of seismic waves,impairing the quality of seismic exploration data and complicating data preprocessing,imaging,and reservoir prediction.Given the data loss of the Tarim block caused by suboptimal data collection,this study conducted high-precision reconstruction of seismic data using the compressed sensing technique,aiming to provide seismic records with high integrity,reliability,and precision for the preprocessing/superimposition phase.Compressed sensing,a novel sampling technique,plays a significant role in data reconstruction.The key to this technique is the adequate sparse representation of seismic data.However,conventional transform methods like Fourier transform and discrete cosine transform(DCT) are merely applicable to simple global structures.Considering the high complexity of the Tarim block data,this study employed the Shearlet transform as the sparse basis function for data reconstruction through compressed sensing.The technology of this study was finally applied to process the actual data of the Tarim Basin,demonstrating high accuracy and applicability for the area.
|
|
Received: 29 December 2023
Published: 26 February 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
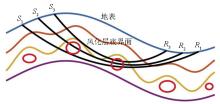
|
Impact of complex near-surface velocities on imaging
blue line—surface;orange,yellow,purple line—structural layers;red line—small-scale structures such as beads and cavities;black line—schematic of seismic wave propagation paths
|

| 稀疏变换方法 | 特点 | | 傅里叶变换(Fourier) | 计算速度快,识别信号的全局特征,
不能识别局部特征 | | 离散余弦变换(DCT) | 能量集中于低频,不能识别局部特征 | 短时傅里叶变换
(short-time Fourier) | 可识别局部特征,但窗口形态固定 | | 曲波变换(Curvelet) | 多尺度性,多方向性,各向异性,
有效表征曲线特征,无自适应性 | | 剪切波变换(Shearlet) | 多尺度性,多方向性,各向异性,
有效表征曲线特征,局部特征
刻画能力强,无自适应性 |
|
Characteristics of five sparse representation methods
|
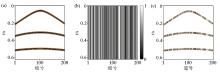
|
Random undersampling of synthetic seismic data
a—synthetic seismic data;b—0% random undersampling matrix;c—0% missing data
|
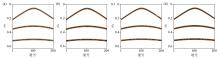
|
Reconstruction results of four single transformations
a—reconstruction result based on Fourier transform;b—reconstruction result based on DCT transform;c—reconstruction result based on Curvelet transform;d—reconstruction result based on Shearlet transform
|
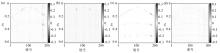
|
Reconstruction error of four single transformations
a—reconstruction error based on Fourier transform;b—reconstruction error based on DCT transform;c—reconstruction error based on Curvelet transform;d—reconstruction error based on Shearlet transform
|
|
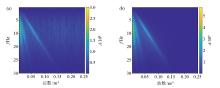
Spectrum before and after Shearlet reconstruction
a—spectrum of seismic records with 50% random missing data;b—spectrum of Shearlet reconstructed data
|

|
Random undersampling of 3D synthetic seismic data
a—3D synthetic seismic data;b—50% random sampling matrix;c—50% missing data
|
|
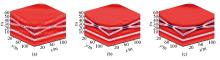
Reconstruction results of three single transformations
a—reconstruction result based on Fourier transform;b—reconstruction result based on DCT transform;c—reconstruction result based on Shearlet transform
|

|
Reconstruction error of three single transformations
a—reconstruction error based on Fourier transform;b—reconstruction error based on DCT transform;c—reconstruction error based on Shearlet transform
|
|
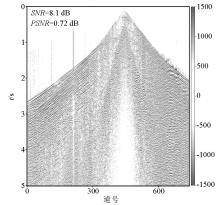
Real single shot
|
|
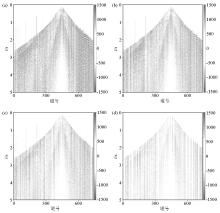
Missing single shot
a—seismic records with 20% random missing data;b—seismic records with 40% random missing sata;c—seismic records with 60% random missing data;d—seismic records with 80% random missing data
|
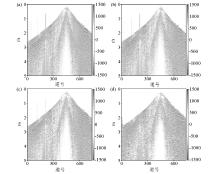
|
Reconstructed single shot
a—reconstructed seismic records with 20% random missing data(SNR=11.5 dB;PSNR=2.7 dB);b—reconstructed seismic records with 40% random missing sata(SNR=10.43 dB;PSNR=1.2 dB);c—reconstructed seismic records with 60% random missing data(SNR=8.93 dB;PSNR=0.89 dB);d—reconstructed seismic records with 80% random missing data(SNR=8.36 dB;PSNR=0.78 dB)
|
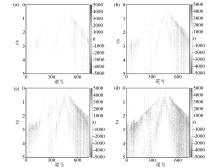
|
Error of reconstruction
a—reconstruction error with 20% random missing data;b—reconstruction error with 40% random missing data;c—reconstruction error with 60% random missing data;d—reconstruction error with 80% random missing data
|
|
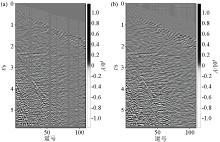
Comparison of original shot records before and after reconstruction
a—original single shot(SNR=5.39 dB;PSNR=0.2 dB);b—reconstructed single shot(SNR=7.53 dB;PSNR=1.6 dB)
|
|
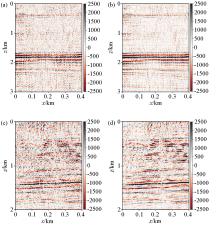
Stacking comparison before and after reconstruction
a—original data stack with local magnification 1;b—reconstructed data stack with local magnification 1;c—original data stack with local magnification 2;d—reconstructed data stack with local magnification 2
|
| [1] |
Tseng P. Applications of a splitting algorithm to decomposition in convex programming and variational inequalities[J]. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 1991, 29(1):119-138.
|
| [2] |
Wang D Y, Zhang K, Li Z C, et al. Seismic data reconstruction using Shearlet and DCT dictionary combination[C]// SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts,2021:2615-2619.
|
| [3] |
Lions P L, Mercier B. Splitting algorithms for the sum of two nonlinear operators[J]. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 1979, 16(6):964-979.
|
| [4] |
Bauschke H H, Burachik R S, Combettes P L, et al. Fixed-point algorithms for inverse problems in science and engineering[M]. New York: NY Springer New York, 2011.
|
| [5] |
Passty G B. Ergodic convergence to a zero of the sum of monotone operators in Hilbert space[J]. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 1979, 72(2):383-390.
|
| [6] |
包乾宗, 陈文超, 高静怀. 基于第二代Curvelet变换的地震资料随机噪声衰减[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2010, 38(1):66-70.
|
| [6] |
Bao Q Z, Chen W C, Gao J H. Seismic data random noise attenuation based on the second generation Curvelet transform[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2010, 38(1):66-70.
|
| [7] |
Wang D Y, Zhang K, Li Z C, et al. Complex structure reconstruction using segmented random sampling and combined dictionary[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 2023, 54(2):155-173.
|
| [8] |
Herrmann F J, Wang D L, Verschuur D J E. Adaptive curvelet-domain primary-multiple separation[J]. Geophysics, 2008, 73(3):A17-A21.
|
| [9] |
Gan S W, Wang S D, Chen Y K, et al. Compressive sensing for seismic data reconstruction via fast projection onto convex sets based on seislet transform[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2016,130:194-208.
|
| [10] |
郭念民, 李海山, 冯雪梅, 等. 非抽样离散小波变换叠前地震数据重建方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2014, 49(3):508-516,416-417.
|
| [10] |
Guo N M, Li H S, Feng X M, et al. Pre-stack seismic data reconstruction based on the undecimated wavelet transform[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2014, 49(3):508-516,416-417.
|
| [11] |
Yang J L, Ni Y D, Zou X F, et al. A new random sampling method based on compressed sensing[C]// Copenhagen:Proceedings 80th EAGE Conference and Exhibition 2018,EAGE Publications BV,2018.
|
| [12] |
冯飞, 王征, 刘成明, 等. 基于Shearlet变换稀疏约束地震数据重建[J]. 石油物探, 2016, 55(5):682-691.
|
| [12] |
Feng F, Wang Z, Liu C M, et al. Seismic data reconstruction based on sparse constraint in the Shearlet domain[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2016, 55(5):682-691.
|
| [13] |
李海山, 吴国忱, 印兴耀. 形态分量分析在地震数据重建中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2012, 47(2):236-243,181-182.
|
| [13] |
Li H S, Wu G C, Yin X Y. Morphological component analysis in seismic data reconstruction[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2012, 47(2):236-243,181-182.
|
| [14] |
周亚同, 刘志峰, 张志伟. 形态分量分析框架下基于DCT与曲波字典组合的地震信号重建[J]. 石油物探, 2015, 54(5):560-568,581.
|
| [14] |
Zhou Y T, Liu Z F, Zhang Z W. Seismic signal reconstruction under the morphological component analysis framework combined with discrete cosine transform(DCT)and curvelet dictionary[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2015, 54(5):560-568,581.
|
| [15] |
张凯, 张医奎, 李振春, 等. MCA框架下Shearlet和DCT字典组合地震数据重建[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2019, 54(5):1005-1013,1056,940-941.
|
| [15] |
Zhang K, Zhang Y K, Li Z C, et al. Seismic data reconstruction with the discrete cosine transform and Shearlet dictionaries under the morphological component analysis framework[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2019, 54(5):1005-1013,1056,940-941.
|
| [16] |
周亚同, 王丽莉, 蒲青山. 压缩感知框架下基于K-奇异值分解字典学习的地震数据重建[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2014, 49(4):652-660,2.
|
| [16] |
Zhou Y T, Wang L L, Pu Q S. Seismic data reconstruction based on K-SVD dictionary learning under compressive sensing framework[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2014, 49(4):652-660,2.
|
| [17] |
秦宁, 梁鸿贤, 王常波, 等. 压缩感知地震数据重建中不同采样方式的影响[C]// SPG/SEG南京2020年国际地球物理会议论文集,2020:290-293.
|
| [17] |
Qin N, Liang H X, Wang C B, et al. Impact of different sampling methods in compressed sensing seismic data reconstruction[C]// Proceedings of the SPG/SEG Nanjing 2020 International Geophysical Conference,2020:290-293.
|
| [18] |
江萍, 张凯, 张医奎, 等. 基于形态分量分析的含噪地震数据重建方法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(2):573-580.
|
| [18] |
Jiang P, Zhang K, Zhang Y K, et al. Noisy seismic data reconstruction method based on morphological component analysis framework[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(2):573-580.
|
| [1] |
LIAO Zhen, MA Ji-Tao, CHEN Xiao-Hong, LI Wen-Jin. A Marchenko theory-based method for internal multiple suppression[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(1): 52-62. |
| [2] |
WANG Xing-Yu, LIU Yan-Li, WANG Tong, RONG Li-Xin. Advances and performance of seismic exploration experiments in the western Yin'e Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(6): 1599-1608. |
|
|
|
|

