|
|
|
| Exploring the occurrence characteristics of geothermal resources in the Nangong geothermal field based on the magnetotelluric method |
LU Xing-Chen1,2( ), XING Qian1( ), XING Qian1( ), XU Yong2, LYU Guo-Sen3, CHEN Xiang-Zhong4, WANG Rui-Xing4, HUANG Shen-Shuo4 ), XU Yong2, LYU Guo-Sen3, CHEN Xiang-Zhong4, WANG Rui-Xing4, HUANG Shen-Shuo4 |
1. Sinopec Star Petroleum Co.,Ltd.,Beijing 100083,China
2. Sinopec Green Energy Geothermal Development Co.,Ltd.,Xiong'an 071800,China
3. School of Environmental Studies,China University of Geosciences(Wuhan),Wuhan 430074,China
4. Beijing Judeng Geological Exploration Technology Co.,Ltd.,Beijing 102299,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract To clarify the occurrence characteristics of geothermal resources in the Nangong geothermal field,this study revealed the subsurface strata and structures in the geothermal field using the magnetotelluric(MT) method in combination with drilling and geologic data.Furthermore,this study systematically analyzed the distributions of shallow and deep geothermal resources and elucidated the heat source mechanisms.Finally,this study constructed the geological model of the Nangong geothermal field.The results show that within a depth of 4000 m,the strata in the Nangong geothermal field comprise the Quaternary,Neogene,Paleogene,Permian,Carboniferous,Ordovician,and Cambrian strata from top to bottom.On the east side of the urban area of Nangong City, there are two concealed NE-trending normal faults(i.e.,F1 and F2),exhibiting a NW dip direction and steep dip angles.The fault-affected zone displays well-developed tectonic fractures and high water abundance.The Nangong geothermal field presents a dual geothermal reservoir system,comprising shallow porous sandstone reservoirs in the Neogene Minghuazhen(lower portion) and Guantao formations,and deep fissured-karstic bedrock reservoirs in the Paleozoic Cambrian-Ordovician strata.These reservoirs host significant geothermal resources in the Nangong area.The Nangong geothermal field belongs to a heat conduction-type geothermal system within a sedimentary basin.Specifically,the heat of shallow geothermal reservoirs(temperatures:30 ℃ to 63 ℃) is sourced from the vertical conduction of regionally high terrestrial heat flow,whereas the heat of deep geothermal reservoirs(temperatures:60 ℃ to 78 ℃) originates primarily from hydrothermal convection ascending through tectonic fractures along F1 and F2,and heat transfer from surrounding rocks.The geological model for geothermal reservoirs constructed in this study demonstrates that the deep fissured-karstic bedrock reservoirs in the Nangong geothermal field are characterized by high connectivity,deep circulation,considerable thickness,extensive karst fissure development,and high permeability.Therefore,deep geothermal reservoirs in the karst fissure zone along F2 are recommended for prioritized exploitation.
|
|
Received: 30 December 2024
Published: 22 July 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
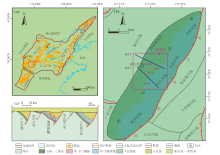
Bohai Bay Basin(a),Nangong Sag and its surrounding structures (b) and the A-A' section (c)
|
|
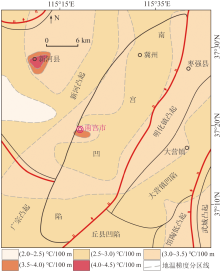
Zoning map of geothermal gradient in Nangong geothermal field and its surrounding areas
|
|
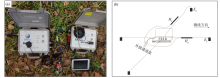
Aether instrument system(a) and instrument layout diagram(b)
|

| 地层 | 岩性 | 电阻率范围 | | 第四系、新近系 | 粉砂、黏土质粉砂、棕色粉砂质黏土 | <15 Ω·m | | 古近系 | 砂砾岩、粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、砂岩、
泥岩 | <10 Ω·m | | 石炭系、二叠系 | 砂岩、泥岩,夹煤层及薄层灰岩 | 15~25 Ω·m | | 寒武系、奥陶系 | 白云质灰岩、灰岩、白云岩等 | >25 Ω·m |
|
Statistics of formation electrical parameters in the study area
|
|
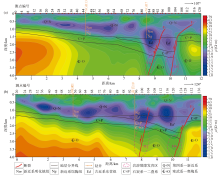
MT1 line (a) and MT2 line (b) resistivity contour section and inferred result diagram
|

| 地层时代 | 底板埋深/m | 厚度/m | 岩性特征 | | Q | 400~600 | 400~600 | 粉砂质黏土,粉细砂、中细砂夹 | | Nm | 950~1200 | 450~650 | 黏土岩、砂质黏土岩与浅棕色粉砂岩、含砾砂岩互层 | | Ng | 1300~1600 | 350~550 | 砂质泥岩、粉砂岩、泥岩、含砾粉砂岩 | | Ed | 1600~1800 | 0~2000 | 碎屑沉积泥岩、砂质泥岩、砂岩 | | C+P | 1600~2300 | 250~350 | 砂岩、泥岩,夹煤层及薄层灰岩 | | €+O | >4000 | >2000 | 岩性以厚层微晶灰岩、云斑灰岩、含燧石条带灰岩为主,夹白云质灰岩、细晶白云岩、泥质白云岩 |
|
Statistical table of stratigraphic information in Nangong area
|
|
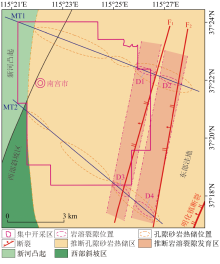
Inferred geothermal reservoir area of Nangong geothermal field
|
|
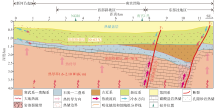
Geological model of geothermal reservoir in Nangong geothermal field
|
| [1] |
Capaccioni B, Vaselli O, Tassi F, et al. Hydrogeochemistry of the thermal waters from the sciacca geothermal field(Sicily,southern Italy)[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2011, 396(3-4):292-301.
|
| [2] |
王贵玲, 张薇, 梁继运, 等. 中国地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(4):449-459.
|
| [2] |
Wang G L, Zhang W, Liang J Y, et al. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(4):449-459.
|
| [3] |
Lyu G S, Zhang X, Wei D H, et al. Water-rock interactions,genesis mechanism,and mineral scaling of geothermal waters in northwestern Sichuan,SW China[J]. Water, 2023, 15(21):3730.
|
| [4] |
韩术合, 裴秋明, 许健, 等. 综合物探方法在内蒙古敖汉旗林家地地热资源勘查中的应用试验[J]. 物探与化探, 2024, 48(4):962-970.
|
| [4] |
Han S H, Pei Q M, Xu J, et al. Application of comprehensive geophysical prospecting in the exploration of geothermal resources in the Linjiadi area,Aohan Banner,Inner Mongolia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4):962-970.
|
| [5] |
雷清, 叶高峰, 吴晓飞, 等. 大地电磁测深法在冀中坳陷深部碳酸盐岩热储调查评价中的应用[J]. 地质论评, 2024, 70(2):795-806.
|
| [5] |
Lei Q, Ye G F, Wu X F, et al. Application of the magnetotelluric sounding method in the investigation and evaluation of deep carbonate rock heat storage in the Jizhong Depression[J]. Geological Review, 2024, 70(2):795-806.
|
| [6] |
吕国森, 章旭, 张云辉, 等. 川西鲜水河、安宁河和龙门山断裂带地热水的水文地球化学特征及成因模式的讨论[J]. 中国地质, 2024, 51(1):341-359.
|
| [6] |
Lyu G S, Zhang X, Zhang Y H, et al. Discussion on hydrogeochemical characteristics and genetic model of geothermal waters in Xianshuihe,Anninghe and Longmenshan fault zones in western Sichuan,China[J]. Geology in China, 2024, 51(1):341-359.
|
| [7] |
王贵玲. 开发地热新能源,构建清洁低碳、安全高效的能源体系[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7):1921-1922.
|
| [7] |
Wang G L. Develop new geothermal energy and build a clean,low-carbon,safe and efficient energy system[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7):1921-1922.
|
| [8] |
章旭, 张文, 吕国森, 等. 川西阿坝州壤古温泉成因机制研究:来自水文地球化学和地球物理勘探的证据[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2023, 43(2):388-403.
|
| [8] |
Zhang X, Zhang W, Lyu G S, et al. Geochemical,geophysical genesis of the ranggu geothermal spring in Aba prefecture,western Sichuan:Evidence from hydrogeochemical and geophysical exploration[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2023, 43(2):388-403.
|
| [9] |
王社教, 李峰, 闫家泓, 等. 油田地热资源评价方法及应用[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(5):553-564.
|
| [9] |
Wang S J, Li F, Yan J H, et al. Evaluation methods and application of geothermal resources in oilfields[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(5):553-564.
|
| [10] |
饶松, 肖红平, 王朱亭, 等. 渤海湾盆地馆陶组热储特征与地热资源评价[J]. 天然气工业, 2023, 43(5):141-152.
|
| [10] |
Rao S, Xiao H P, Wang Z T, et al. Geothermal reservoir characteristics and geothermal resource evaluation of Guantao Formation in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2023, 43(5):141-152.
|
| [11] |
卢荣茂. 河北省南宫市地热资源浅析[J]. 河北煤炭, 2004(6):31-32.
|
| [11] |
Lu R M. Analysis of the geothermal resources in NanGong,Hebei Province[J]. Hebei Coal, 2004(6):31-32.
|
| [12] |
Wang Z T, Jiang G Z, Zhang C, et al. Estimating geothermal resources in Bohai Bay Basin,Eastern China,using Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2019, 78(12):355.
|
| [13] |
王颖, 陈学蓉. 大地电磁法在南宫地热勘查中的应用[J]. 中文科技期刊数据库(全文版)自然科学, 2022(6):279-282.
|
| [13] |
Wang Y, Chen X R. Application of magnetotelluric method in geothermal exploration in Nangong[J]. Chinese Science and Technology Journal Database(Full-textEdition) Natural Science, 2022(6):279-282.
|
| [14] |
Liu T S, Ding W L, Zhang R F, et al. Cenozoic tectonostratigraphy and structural styles in the Nangong Sag,Bohai Bay Basin,Eastern China:Implications for the generation of oil-gas traps[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2023,149:106081.
|
| [15] |
Spichak V, Manzella A. Electromagnetic sounding of geothermal zones[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2009, 68(4):459-478.
|
| [16] |
Spichak V, Zakharova O, Rybin A, et al. Estimation of the sub-surface temperature by means of magnetotelluric sounding[C]// Stanford:Stanford Geothermal Program,32nd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering 2007,2007.
|
| [17] |
张炯, 黄少鹏, 傅饶, 等. 大地电磁测深在火山区地热研究中的应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(1):279-290.
|
| [17] |
Zhang J, Huang S P, Fu R, et al. Application of magnetotellurics in geothermal exploration and research in volcano areas[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(1):279-290.
|
| [18] |
Simpson F, Bahr K. Practical magnetotellurics[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005.
|
| [19] |
Zhang L L, Hao T Y, Xiao Q B, et al. Magnetotelluric investigation of the geothermal anomaly in Hailin,Mudanjiang,northeastern China[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2015,118:47-65.
|
| [20] |
Arafa-Hamed T, Abdel Zaher M, El-Qady G, et al. Deep heat source detection using the magnetotelluric method and geothermal assessment of the Farafra Oasis,Western Desert,Egypt[J]. Geothermics, 2023,109:102648.
|
| [21] |
于晓卫. 南宫凹陷中、新生界油气地质条件研究[D]. 青岛: 山东科技大学, 2010.
|
| [21] |
Yu X W. Study on Mesozoic and Cenozoic petroleum geological conditions in Nangong sag[D]. Qingdao: Shandong University of Science and Technology, 2010.
|
| [22] |
刘琼颖, 何丽娟. 渤海湾盆地新生代以来构造—热演化模拟研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(1):219-235.
|
| [22] |
Liu Q Y, He L J. Tectono-thermal modeling of the Bohai Bay basin since the Cenozoic[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(1):219-235.
|
| [23] |
姜光政, 高堋, 饶松, 等. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第四版)[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(8):2892-2910.
|
| [23] |
Jiang G Z, Gao P, Rao S, et al. Compilation of heat flow data in the continental area of China(4th edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(8):2892-2910.
|
| [24] |
Qiu N S, Chang J, Zhu C Q, et al. Thermal regime of sedimentary basins in the Tarim,Upper Yangtze and North China Cratons,China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2022,224:103884.
|
| [25] |
王凯, 张杰, 白大为, 等. 雄安新区地热地质模型探究:来自地球物理的证据[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(5):1453-1468.
|
| [25] |
Wang K, Zhang J, Bai D W, et al. Geothermal-geological model of Xiongan New Area:Evidence from geophysics[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(5):1453-1468.
|
| [26] |
Cagniard L. Basic theory of the magneto-telluric method of geophysical prospecting[J]. Geophysics, 1953, 18(3):605.
|
| [27] |
Hager W, Zhang H C. A survey of nonlinear conjugate gradient methods[J]. Pacific Journal of Optimization, 2006, 2(1):35-58.
|
| [28] |
张一, 刘鹏磊, 王玉敏, 等. 综合物探技术在济南北部地热勘查中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2024, 48(1):58-66.
|
| [28] |
Zhang Y, Liu P L, Wang Y M, et al. Application of integrated geophysical exploration technology in the geothermal exploration of northern Jinan[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1):58-66.
|
| [29] |
王贵玲, 蔺文静. 我国主要水热型地热系统形成机制与成因模式[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7):1923-1937.
|
| [29] |
Wang G L, Lin W J. Main hydro-geothermal systems and their genetic models in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7):1923-1937.
|
| [30] |
许红, 张海洋, 张德润, 等. 下扬子区海陆盆地构造分割的深大断裂证据与地质构造意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(3):16-23.
|
| [30] |
Xu H, Zhang H Y, Zhang D R, et al. The deep faults separating land and sea basins in Lower Yangtze region and their tectonic significance[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(3):16-23.
|
| [31] |
孙耀庭, 徐守余, 张世奇, 等. 渤海湾盆地临清坳陷西部中生界烃源岩生烃演化[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(10):1910-1916.
|
| [31] |
Sun Y T, Xu S Y, Zhang S Q, et al. Evolution of the Mesozoic source rocks in the west Linqing depression[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(10):1910-1916.
|
| [32] |
Qiu N S, Xu W, Zuo Y H, et al. Meso-Cenozoic thermal regime in the Bohai Bay Basin,eastern North China Craton[J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 57(3):271-289.
|
| [33] |
Yang M B, Liu G P, Liu Z, et al. Geochemical characteristics of geothermal and hot spring gases in Beijing and Zhangjiakou Bohai fault zone[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2022,10:933066.
|
| [1] |
SUN Dong-Hua, CHEN Wei, CHENG Sha-Sha, SHI Lian-Cheng, ZHANG Jun-Wei, QI Ping, YANG Yu-Qin. A 3D geological modeling technology using multivariate geoscience information for exploration of sandstone-type uranium deposits[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(3): 631-641. |
| [2] |
WANG He-Yu, WU Guo-Peng, CHEN Guo-Xiong, CHAI Jian-Zhou, MAO Jie, WANG De-Tao. Microtremor survey-based investigation of deep geothermal- and water-controlling structures in the Salt Lake geothermal field, Yuncheng City, Shanxi Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(1): 32-40. |
|
|
|
|

