|
|
|
| Prediction and comparison of organic carbon content in topsoils based on geostatistics and machine learning models: A case study of Baoqing County |
LIU Hong-Bo1,2( ), SHI Jia-Hui3, WANG Si-Yin3, PEI Jiu-Bo3( ), SHI Jia-Hui3, WANG Si-Yin3, PEI Jiu-Bo3( ) ) |
1. Mudanjiang Natural Resources Comprehensive Survey Center, China Geological Survey, Mudanjiang 157000, China
2. Hulunbuir Black Soil Critical Zone Scientific Observation and Research Station, Hulunbuir 021599, China
3. College of Land and Environment, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang 110866, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study aims to accurately predict the organic carbon content in black soils at the county level, thereby supporting county-level agricultural production and carbon peak and neutrality goals. This study examined 427 soil samples obtained from a surface substrate survey of the black soil area in Baoqing County. Employing deterministic interpolation (inverse distance weighting, IDW), geostatistics (ordinary Kriging method, OK), and machine learning (random forest, RF), this study constructed assessment models to predict the organic carbon content in topsoils in Baoqing County and to compare their prediction accuracy and performance. The results show that the IDW, OK, and RF models yielded average organic carbon contents of 27.21×10-3, 26.33×10-3, and 32.05×10-3, respectively. The RF model outperformed the other two models in terms of root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and the coefficient of determination (R2). Specifically, the RF model achieved R2 values of 0.73 and 0.53 on training and validation sets, respectively, suggesting significantly higher accuracy. This superior performance demonstrates that the RF model can more fully explore potential patterns in data through the nonlinear interaction of environmental variables. Overall, the RF model, incorporating multiple environmental variables, proved to be the optimal approach for predicting the organic carbon content in topsoils in Baoqing County, demonstrating high prediction accuracy. This study provides valuable theoretical and methodological insights for assessing the spatial variations in soil organic matter relevant to county-level agricultural production and regional differences in carbon peak and neutrality goals within black soil areas.
|
|
Received: 12 December 2024
Published: 23 October 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
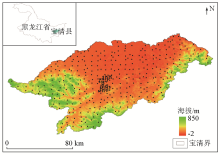
|
Topography of the study area and location of sampling sites
|
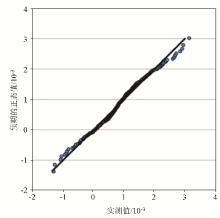
|
Data normal distribution plot
|

| 参数 | 线性模型 | 球状模型 | 指数模型 | 高斯模型 | | R2 | 0.839 | 0.289 | 0.928 | 0.292 | | RSS | 8.645×10-3 | 0.0382 | 4.243×10-3 | 0.0381 | | 块金系数/% | 64.0 | 0.7 | 49.9 | 13.6 |
|
Parameters of the semi-variance function model
|
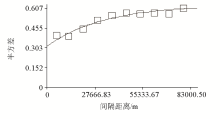
|
Soil organic carbon content semi-variance function
|
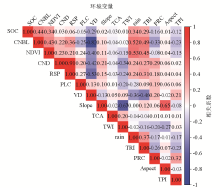
|
Heat map of correlations across environmental variables
|
|
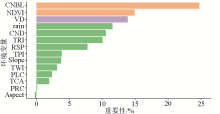
Importance analysis of characteristics of environmental variables
|
|
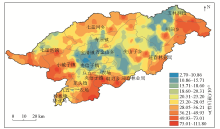
Prediction of spatial distribution of soil organic carbon in Baoqing County using inverse distance weighting
|
|
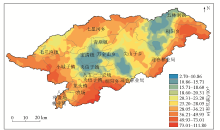
Prediction of spatial distribution of soil organic carbon in Baoqing County using ordinary kriging
|
|
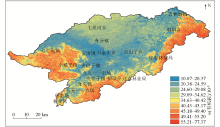
Prediction of spatial distribution of soil organic carbon in Baoqing County using random forest
|

| 预测方法 | 最大值/
10-3 | 最小值/
10-3 | 均值/
10-3 | 标准差/
10-3 | 方差 | 变异系
数/% | | 反距离权重法 | 111.79 | 4.70 | 27.21 | 16.22 | 269.58 | 59.61 | | 普通克里金法 | 98.45 | 4.62 | 26.33 | 15.56 | 242.19 | 59.10 | | 随机森林模型 | 77.03 | 10.08 | 32.05 | 13.05 | 122.20 | 40.72 |
|
Statistical analysis of the results of spatial prediction of organic carbon content
|

| 预测方法 | 训练集 | 验证集 | | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | | 反距离权重法 | 0.32 | 2.45 | 1.43 | 0.42 | 1.73 | 1.49 | | 普通克里金法 | 0.39 | 2.25 | 1.43 | 0.43 | 2.20 | 1.48 | | 随机森林模型 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 1.57 | 1.15 |
|
Results of organic carbon interpolation accuracy analysis
|
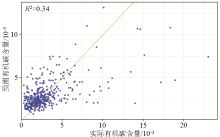
|
Inverse distance weighting method prediction versus actual values
|
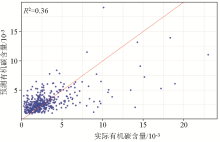
|
Ordinary kriging prediction versus actual values
|
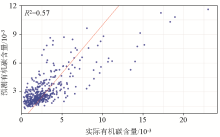
|
Random forest prediction versus actual values
|
| [1] |
唐宽燕. 内蒙古草原土壤有机碳空间变化及其驱动因子研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2023.
|
| [1] |
Tang K Y. Study on the spatial variation of soil organic carbon and its driving factors in the Inner Mongolian steppes[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2023.
|
| [2] |
向婷. 黄土丘陵区小流域土壤有机碳空间分布特征及驱动因素分析[D]. 延安: 延安大学, 2024.
|
| [2] |
Xiang T. Spatial distribution characteristics and driving factors of soil organic carbon in small watershed in Loess Hilly Region[D]. Yan’an: Yan’an University, 2024.
|
| [3] |
侯红星, 葛良胜, 孙肖, 等. 地表基质在中国黑土地资源调查评价中的应用探讨——基于黑龙江宝清地区地表基质调查[J]. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(9):2264-2276.
|
| [3] |
Hou H X, Ge L S, Sun X, et al. A study on the application of ground substrate in the survey and evaluation of China’s black soil resources:Based on ground substrate survey in Baoqing,Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2022, 37(9):2264-2276.
|
| [4] |
梅帅, 童童, 应纯洋, 等. 基于机器学习的数字土壤制图研究进展[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2024, 41(4):744-756.
|
| [4] |
Mei S, Tong T, Ying C Y, et al. Advances in digital soil mapping based on machine learning[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2024, 41(4):744-756.
|
| [5] |
韩杏杏, 陈杰, 王海洋, 等. 基于随机森林模型的耕地表层土壤有机质含量空间预测——以河南省辉县市为例[J]. 土壤, 2019, 51(1):152-159.
|
| [5] |
Han X X, Chen J, Wang H Y, et al. Spatial prediction of SOM content in topsoil based on random forest algorithm:A case study of Huixian City,Henan Province[J]. Soils, 2019, 51(1):152-159.
|
| [6] |
乔婷, 姚彩燕, 于东升, 等. 水田土壤有机碳时空演变下的最优插值方法[J]. 福建农林大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 49(5):683-694.
|
| [6] |
Qiao T, Yao C Y, Yu D S, et al. Optimal interpolation method for spatial-temporal evolution of soil organic carbon in paddy fields[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University:Natural Science Edition, 2020, 49(5):683-694.
|
| [7] |
陈琳, 任春颖, 王宗明, 等. 基于克里金插值的耕地表层土壤有机质空间预测[J]. 干旱区研究, 2017, 34(4):798-805.
|
| [7] |
Chen L, Ren C Y, Wang Z M, et al. Prediction of spatial distribution of topsoil organic matter content in cultivated land using Kriging methods[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2017, 34(4):798-805.
|
| [8] |
杨其坡, 武伟, 刘洪斌. 基于地形因子和随机森林的丘陵区农田土壤有效铁空间分布预测[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(3):422-431.
|
| [8] |
Yang Q P, Wu W, Liu H B. Prediction of spatial distribution of soil available iron in a typical hilly farmland using terrain attributes and random forest model[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(3):422-431.
|
| [9] |
王雨雪, 杨柯, 高秉博, 等. 基于两点机器学习方法的土壤有机质空间分布预测[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(12):65-73.
|
| [9] |
Wang Y X, Yang K, Gao B B, et al. Prediction of the spatial distribution of soil organic matter based on two-point machine learning method[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(12):65-73.
|
| [10] |
沈琛琛, 肖文发, 朱建华, 等. 基于机器学习算法的华中天然林土壤有机碳特征与关键影响因子[J]. 林业科学, 2024, 60(3):65-77.
|
| [10] |
Shen C C, Xiao W F, Zhu J H, et al. Characterization of soil organic carbon and key influencing factors of natural forests in Central China based on machine learning algorithms[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2024, 60(3):65-77.
|
| [11] |
王志远, 汤哲, 周萍, 等. 面向亚热带丘陵区小流域土壤有机碳空间预测的四种模型构建及性能比较[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2023, 44(3):558-566.
|
| [11] |
Wang Z Y, Tang Z, Zhou P, et al. Comparison of four machine learning in predicting soil organic carbon content in a small watershed in the subtropical hilly area[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2023, 44(3):558-566.
|
| [12] |
夏晓莹, 李思瑶, 王杰, 等. 地形因子对天山北坡天山云杉林土壤有机碳的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4):965-973.
|
| [12] |
Xia X Y, Li S Y, Wang J, et al. Effects of topographic factors on soil organic carbon in Picea schrenkiana forest on the northern slope of Tianshan Mountain[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4):965-973.
|
| [13] |
Lal R. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security[J]. Science, 2004, 304(5677):1623-1627.
|
| [14] |
Minasny B, McBratney A B. Digital soil mapping:A brief history and some lessons[J]. Geoderma, 2016,264:301-311.
|
| [15] |
刘洪博, 孔繁鹏, 赵建, 等. 地表基质调查技术方法探索与实验——以黑龙江省宝清县黑土地调查为例[J]. 地理信息世界, 2022, 29(6):1-5.
|
| [15] |
Liu H B, Kong F P, Zhao J, et al. Exploration and experiment of surface substrate investigation technique:A case study of black soil investigation in Baoqing County,Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geomatics World, 2022, 29(6):1-5.
|
| [16] |
Lu J N, Feng S, Wang S K, et al. Patterns and driving mechanism of soil organic carbon,nitrogen,and phosphorus stoichiometry across northern China’s desert-grassland transition zone[J]. Catena, 2023,220:106695.
|
| [17] |
李海涛, 邵泽东. 空间插值分析算法综述[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2019, 28(7):1-8.
|
| [17] |
Li H T, Shao Z D. Review of spatial interpolation analysis algorithm[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2019, 28(7):1-8.
|
| [18] |
杜可, 王乐, 张淑香, 等. 黑土区县域土壤养分空间分布特征及其影响因子[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(6):1465-1474.
|
| [18] |
Du K, Wang L, Zhang S X, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and influence factors of soil nutrients in black soil region counties[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2018, 24(6):1465-1474.
|
| [19] |
凌威, 王新杰, 武文昊. 新疆年均降水量的空间插值方法比较[J]. 辽宁林业科技, 2020(4):5-9,58.
|
| [19] |
Ling W, Wang X J, Wu W H. Comparison on spatial interpolation methods of average annual precipitation in Xinjiang[J]. Liaoning Forestry Science and Technology, 2020(4):5-9,58.
|
| [20] |
Breiman L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1):5-32.
|
| [21] |
李治军, 王华凡, 侯岳, 等. 缺资料地区降雨量空间插值方法比较[J]. 水利科学与寒区工程, 2022, 5(8):68-71.
|
| [21] |
Li Z J, Wang H F, Hou Y, et al. Comparison of spatial interpolation methods for precipitation in regions lacking data[J]. Hydro Science and Cold Zone Engineering, 2022, 5(8):68-71.
|
| [22] |
齐伟恒, 彭琳, 郜鲁涛, 等. 基于ArcGIS地统计分析模块的土壤养分与pH值空间变异分析——以云南省寻甸县为例[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(23):287-291.
|
| [22] |
Qi W H, Peng L, Gao L T, et al. Study on spatial variability of soil nutrients and pH values based on GIS geostatistical analysis module—Taking Xundian Country of Yunnan Province as an example[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(23):287-291.
|
| [23] |
张志坚, 刘苑秋, 吴春生, 等. 基于地统计学和GIS的江西省森林土壤养分空间分布特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2018, 25(1):38-46.
|
| [23] |
Zhang Z J, Liu Y Q, Wu C S, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of forest soil nutrients in Jiangxi Province based on geostatistics and GIS[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 25(1):38-46.
|
| [1] |
XIA Yan, WANG Run-Tao, DU Qian-Qian, WANG Xi-Kuan, Lyu Hong-Jie, HOU Jin-Kai, LI Bing-Hui. Carbon sink in farmland soils in Luoyang City, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(1): 215-228. |
| [2] |
DUAN Xing-Xing, LIU Xiao-Long, HAN Bao-Hua, Adilai·Saitiniyazi , JIN Meng-Ting, LIU Tong. Stocks and content of organic and inorganic carbon in soil of the Loess Plateau region[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(1): 239-247. |
|
|
|
|

