|
|
|
| Discussion on the delimitation, exploitation, and utilization of arid saline lacustrine sedimentary type selenium-rich land: A case study of the Hongshuiquan area, Qinghai Province |
MA Qiang( ), MIAO Guo-Wen( ), MIAO Guo-Wen( ), ZHU Ming-Xia, WANG Shuai, HE Lian-Zhen, MA Nan ), ZHU Ming-Xia, WANG Shuai, HE Lian-Zhen, MA Nan |
| The Fifth Geological Exploration Institute of Qinghai Province, Engineering Technology Research Center for Selenium-Rich Resource Utilization of Qinghai Province, Xining 810099, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Based on the summary of the genetic types and elemental characteristics of national selenium (Se)-rich land, this study explored the arid saline lacustrine sedimentary type Se-rich land. According to the requirements for the delimitation and identification of natural Se-rich land, this study assessed and delimited the Se content, environmental quality, and fertility of soils in Hongshuiquan Township, Ping'an District, Haidong City, Qinghai Province. The results indicate that the soils in the Hongshuiquan area are alkaline, exhibiting a high background level of available Se. Specifically, the content of soil Se ranged from 0.037 mg/kg to 6.544 mg/kg, with an average of 0.352 mg/kg. The contents of Cd, Hg, Pb, and Cr in the soils did not exceed their contamination risk screening values for agricultural land. Additionally, soil As shows potential risk in local plots. In terms of fertility status, the soils exhibit abundant available phosphorus and potassium, and moderate nitrogen and organic matter. Based on the above results and the designated values for Se-rich land in the alkaline soil area, while excluding soil contamination risk zones and considering the continuity, scale, and development and utilization of plots, this study delimited 43 591 mu (1 mu=0.066 7 hectares) of natural green Se-rich land in the Hongshuiquan area, including 13 513 mu for direct agricultural use, and 30 078 mu for potentially utilizable forest land and grassland. Considering local conditions, this study suggests the development of the integrated agriculture and animal husbandry industry in the Hongshuiquan area, centering on the delimited zones and extending to the peripheries with moderate Se content. Planting grain crops and green forage grass in the delimited zones, surrounded by free-range grazing, forming an industrial layout of land with high Se content for grain crops and land with moderate Se content for grazing. Overall, this study holds critical reference significance for further exploring Se-rich land resources in Qinghai Province, scientifically planning the selenium industry, highlighting location advantages, and efficiently transforming resource value.
|
|
Received: 31 July 2024
Published: 07 August 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
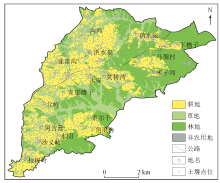
|
Land use types and soil point locations in the study area
|
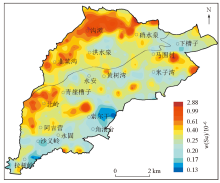
|
Geochemical distribution of soil Se in the study area
|

| 分类 | 分项 | w(Se)/10-6 | | 成土母质 | 风成黄土 | 0.25 | | 西宁群泥岩风化物 | 0.36 | | 民和组砂泥岩风化物 | 0.29 | 土地利用
类型 | 耕地 | 0.38 | | 草地 | 0.35 | | 林地 | 0.34 | | 土壤类型 | 淡栗钙土+红黄土 | 0.24 | | 黄土性暗栗钙土+耕种暗栗钙土 | 0.31 | | 耕种栗钙土 | 0.34 |
|
Comparative statistics of soil Se mean values in different sub-units of the study area
|

| 指标 | 等级 | 标准值域 | 样品数 | 占比/% | | 有机质 | Ⅰ | >15 | 182 | 61 | | Ⅱ | 10~15 | 95 | 32 | | Ⅲ | <10 | 22 | 7 | | 全氮 | Ⅰ | >1.0 | 188 | 63 | | Ⅱ | 0.8~1.0 | 66 | 22 | | Ⅲ | <0.8 | 45 | 15 | | 有效磷 | Ⅰ | >10 | 247 | 82 | | Ⅱ | 5~10 | 47 | 16 | | Ⅲ | <5 | 5 | 2 | | 速效钾 | Ⅰ | >120 | 239 | 80 | | Ⅱ | 80~120 | 54 | 18 | | Ⅲ | <80 | 6 | 2 |
|
Evaluation results of land fertility in the study area(n=299)
|
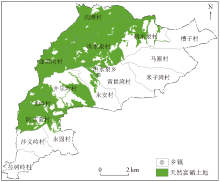
|
Delimited range of natural selenium-rich land in the study area
|
| [1] |
齐玉薇, 史长义. 硒的生态环境与人体健康[J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 2005, 22(2):63-66.
|
| [1] |
Qi Y W, Shi C Y. Se ecological environment and human body health[J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 2005, 22(2):63-66.
|
| [2] |
李家熙, 张光弟, 葛晓立, 等. 人体硒缺乏与过剩的地球化学环境特征及其预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000.
|
| [2] |
Li J X, Zhang G D, Ge X L, et al. Prediction and geochemical environmental character of human selenium imbalances[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2000.
|
| [3] |
尹红星, 张殊佳, 郑学仿, 等. 硒的抗肿瘤作用研究综述[J]. 大连大学学报, 2008, 29(6):18-25.
|
| [3] |
Yin H X, Zhang S J, Zheng X F, et al. Review in the antitumor research of selenium[J]. Journal of Dalian University, 2008, 29(6):18-25.
|
| [4] |
付巧玲, 邱顺才. 论土壤硒驱动机制——以河南省崤山地区为例[J]. 地质与勘探, 2023, 59(3):580-590.
|
| [4] |
Fu Q L, Qiu S C. On the driving mechanism of soil Se:Taking the Xiaoshan area of Henan Province as an example[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2023, 59(3):580-590.
|
| [5] |
余涛, 杨忠芳, 王锐, 等. 恩施典型富硒区土壤硒与其他元素组合特征及来源分析[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6):1119-1125.
|
| [5] |
Yu T, Yang Z F, Wang R, et al. Characteristics and sources of soil selenium and other elements in typical high selenium soil area of Enshi[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6):1119-1125.
|
| [6] |
冯彩霞. 扬子地块周边  、P硅岩建造中硒的富集机理对比研究——以渔塘坝、紫阳富硒区为例[D]. 贵阳: 中国科学院研究生院(地球化学研究所), 2004. 、P硅岩建造中硒的富集机理对比研究——以渔塘坝、紫阳富硒区为例[D]. 贵阳: 中国科学院研究生院(地球化学研究所), 2004.
|
| [6] |
Feng C X. The enriching-mechanism of selenium of Cambrian and Permian silicalite formation in the peripheral margins of Yangtze block[D]. Guiyang: Institute of Geochemistry,Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2004.
|
| [7] |
任海利, 高军波, 龙杰, 等. 贵州开阳地区富硒地层及风化土壤地球化学特征[J]. 地球与环境, 2012, 40(2):161-170.
|
| [7] |
Ren H L, Gao J B, Long J, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium-rich strata and weathered soil from Kaiyang County,Guizhou Province[J]. Earth and Environment, 2012, 40(2):161-170.
|
| [8] |
陈继平, 任蕊, 王晖, 等. 关中塿土地区土壤pH变化对硒形态及有效性的影响[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(1):254-260.
|
| [8] |
Chen J P, Ren R, Wang H, et al. Effect of Lou soil pH change on selenium forms and availability[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(1):254-260.
|
| [9] |
王惠艳, 曾道明, 郭志娟, 等. 天然富硒土地划定的富硒阈值[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(1):333-342.
|
| [9] |
Wang H Y, Zeng D M, Guo Z J, et al. Selenium threshold for the delimitation of natural selenium-enriched land[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(1):333-342.
|
| [10] |
周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3):319-336.
|
| [10] |
Zhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3):319-336.
|
| [11] |
刘道荣, 焦森. 天然富硒土壤成因分类研究及开发适宜性评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5):1157-1163.
|
| [11] |
Liu D R, Jiao S. Assessment of genetic classification and development suitability of natural selenium-rich soil[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5):1157-1163.
|
| [12] |
王凌霄, 余涛, 李凤嫣, 等. 土壤中硒的生物有效性表征方法及影响因素研究进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2023, 42(2):239-253.
|
| [12] |
Wang L X, Yu T, Li F Y, et al. A summary of research progress on bioavailability assessment method of selenium in soil and its influencing factors[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2023, 42(2):239-253.
|
| [13] |
李永华, 王五一. 硒的土壤环境化学研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 2002, 33(3):230-233.
|
| [13] |
Li Y H, Wang W Y. Process on the study soil environmental chemistry of selenium[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2002, 33(3):230-233.
|
| [14] |
Adeleke R, Nwangburuka C, Oboirien B. Origins,roles and fate of organic acids in soils:A review[J]. South African Journal of Botany, 2017,108:393-406.
|
| [15] |
程楠. 新疆焉耆盆地土壤硒来源、生物有效性及其主控因子研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2023.
|
| [15] |
Cheng N. Source,bioavailability and controlling factors of soil selenium in Yanqi basin,Xinjiang[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2023.
|
| [16] |
王志强, 杨建锋, 石天池. 宁夏石嘴山地区富硒土壤及其利用前景[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(1):228-237.
|
| [16] |
Wang Z Q, Yang J F, Shi T C. A preliminary study of Se-rich soil in the Shizuishan area,Ningxia and its potential for application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1):228-237.
|
| [17] |
张亚峰, 姬丙艳, 沈骁, 等. 西宁盆地咸水湖相沉积型富硒土壤的形成机理及意义[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(2):470-476.
|
| [17] |
Zhang Y F, Ji B Y, Shen X, et al. Formation mechanism and significance of saltwater lacustrine sedimentary selenium-rich soil in Xining Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2):470-476.
|
| [18] |
中华人民共和国国土资源部.土地质量地球化学评价规范:DZ/T 0295—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
|
| [18] |
Ministry of Land and Resources.Determination of land quality geochemical evaluation:DZ/T 0295—2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [19] |
中华人民共和国农业农村部.绿色食品产地环境质量:NY/T 391—2021[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2021.
|
| [19] |
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs.Environmental quality of green food production areas:NY/T 391—2021[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2021.
|
| [20] |
奚小环, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 等. 基于大数据的中国土壤背景值与基准值及其变化特征研究——写在《中国土壤地球化学参数》出版之际[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5):1095-1108.
|
| [20] |
Xi X H, Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, et al. Big data based studies of the variation features of Chinese soil's background value versus reference value:A paper written on the occasion of Soil Geochemical Parameters of China's publication[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5):1095-1108.
|
| [21] |
张亚峰, 苗国文, 马强, 等. 青海省海东市平安区土壤Se的地球化学特征[J]. 地球与环境, 2019, 47(1):74-80.
|
| [21] |
Zhang Y F, Miao G W, Ma Q, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Se in soil of the Pingan district,Haidong City,Qinghai Province[J]. Earth and Environment, 2019, 47(1):74-80.
|
| [22] |
黄淇, 成杭新, 陈出新, 等. 北京市房山区富硒土壤调查与评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(5):889-894.
|
| [22] |
Huang Q, Cheng H X, Chen C X, et al. The investigation and evaluation of selenium-rich soil in Fangshan district of Beijing city[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(5):889-894.
|
| [23] |
生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局.土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准:GB 15618—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.
|
| [23] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment, State Administration for Market Regulation.Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land:GB 15618—2018[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018.
|
| [24] |
马强, 张亚峰, 黄强, 等. 青海省富硒土壤标准探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(3):772-780.
|
| [24] |
Ma Q, Zhang Y F, Huang Q, et al. Discussion on the standard of selenium-rich soil in Qinghai province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3):772-780.
|
| [1] |
ZHANG Ya-Feng, Yao Zhen, ZHU Ming-Xia, MA Qiang, SHEN Xiao, WANG Shuai, HE Lian-Zhen, DAI Lu. Delimitation of natural Se-rich land in Sanhe Town, Haidong City, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1620-1626. |
| [2] |
MA Qiang, ZHANG Ya-Feng, HUANG Qiang, JI Bing-Yan, Miao Guo-Wen, MA Feng-Juan, MA Ying. Exploring the standards of Se-rich soil in Qinghai Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3): 772-780. |
|
|
|
|

