|
|
|
| Contamination characteristics and risk assessment of soil heavy metals in a typical industrial town in Shandong Province, China |
ZENG Jiao1,2( ), KONG Ling-Hao1,2( ), KONG Ling-Hao1,2( ), LIU Shu-Liang1,2, CHU Hong-Xian1,2, ZHAO Zheng-Peng1,2, YANG Kai-Li1,2, GUO Xu-Jun1,2, CHEN Liang1,2 ), LIU Shu-Liang1,2, CHU Hong-Xian1,2, ZHAO Zheng-Peng1,2, YANG Kai-Li1,2, GUO Xu-Jun1,2, CHEN Liang1,2 |
1. Yantai Center of Coastal Zone Geological Survey, China Geological Survey, Yantai 264000, China
2. Ministry of Natural Resources Observation and Research Station of Land-Sea Interaction Field in the Yellow River Estuary, Yantai 264000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract To investigate the contamination, source, and ecological risk of soil heavy metals in a typical industrial town in Shandong Province, China, this study collected 499 topsoil samples from the study area from August to October 2022. The contents and spatial distributions of heavy metals like Hg, Cd, As, Pb, Cu, Cr, Zn, and Ni in the samples were analyzed using classical statistics and spatial interpolation methods. The source apportionment of heavy metals in the study area was explored through the principal component analysis (PCA). The contamination levels of heavy metals in the study area were assessed using the contamination index method. The results indicate that the average contents of Hg, Cd, As, and Pb in soils all exceeded their background values in Yantai City, and high-value zones were observed for all eight elements, indicating various degrees of enrichment. The analysis of coefficients of variation reveals that except for Ni, other heavy metals were significantly influenced by human activities. The PCA suggests that Cd, Pb, Cu, Zn, and Cr originated primarily from industrial and traffic sources. As and Hg were predominantly derived from industrial, agricultural, and domestic sources, while Ni was primarily from natural soil parent materials. The analyses based on the single-factor contamination index, geoaccumulation index, and Nemerow contamination index show that apart from Hg and Cd, other soil heavy metals in the study area exhibited no or slight contamination overall, demonstrating that the study area was principally contaminated by Hg and Cd. The potential ecological risk assessment suggests that the overall heavy metal contamination posed a minor risk level. A few sites with relatively severe contamination were primarily located around the industrial area. The waste gas, wastewater, and industrial residue generated by industrial activities constituted the dominant factor influencing the enrichment of heavy metals in surrounding soils. Overall, soil heavy metal contamination in the study area was at a moderate to low level, with some metals, particularly Hg and Cd, severely exceeding standard levels, warranting attention. It is recommended to strengthen the monitoring of heavy metals in soils around the industrial area, and adopt scientific and reasonable measures to ensure sustainable soil utilization.
|
|
Received: 21 June 2024
Published: 07 August 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Study area and distribution of sampling sites
|

| 指标 | 方法来源 | 测定仪器 | | As | 《岩石矿物分析》氢化物发生—原子荧光光谱法测定砷、锑、铋(DZG20.01—2011) | 原子荧光光度计(AFS-8330) | Cu、Ni、
Zn | 《岩石矿物分析》电感耦合等离子体发射法测定27种主、次、痕量元素(DZG20.01—2011) | 等离子光谱仪(iCAP 6300) | Cr、Cd、
Pb | 《岩石矿物分析》电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定30种痕量元素(DZG20.01—2011) | 等离子体质谱(iCAP Q) | | Hg | 《岩石矿物分析》冷蒸汽—原子荧光光谱法测定汞(DZG20.01—2011) | 原子荧光仪(XGY1011A) |
|
Methods and instruments for determination of heavy metals in soil
|

| 元素 | Hg | Cd | As | Pb | Ni | Cu | Cr | Zn | | 毒性响应系数(${T}_{r}^{i}$) | 40 | 30 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 1 |
|
Toxic response coefficient of heavy metal elements
|

| 单因子指数法 | 内梅罗指数法 | 地累积指数法 | 潜在生态风险指数法 | | Pi | 污染程度 | PN | 污染程度 | Igeo | 污染程度 | ${E}_{r}^{i}$ | RI | 风险等级 | | Pi≤1 | 无污染 | PN≤0.7 | 清洁 | Igeo≤0 | 无 | ${E}_{r}^{i}$<40 | RI<150 | 轻微危害 | | 1<Pi≤2 | 轻微污染 | 0.7<PN≤1 | 警戒 | 0<Igeo≤1 | 无—中度 | 40≤${E}_{r}^{i}$<80 | 150≤RI<300 | 中等危害 | | 2<Pi≤3 | 轻度污染 | 1<PN≤2 | 轻度污染 | 1<Igeo≤2 | 中度 | 80≤${E}_{r}^{i}$<160 | 300≤RI<600 | 强危害 | | 3<Pi≤5 | 中度污染 | 2<PN≤3 | 中度污染 | 2<Igeo≤3 | 中—强度 | 160≤${E}_{r}^{i}$<320 | 600≤RI<1200 | 很强危害 | | Pi>5 | 重度污染 | PN>3 | 重度污染 | 3<Igeo≤4 | 强度 | ${E}_{r}^{i}$≥320 | RI≥1200 | 极强危害 | | | | | 4<Igeo≤5 | 强度—极强 | | | | | | | | Igeo>5 | 极强 | | | |
|
Standard for evaluation of heavy metals in soil
|

| 重金属 | 均值/10-6 | 标准差 | 偏度 | 峰度 | 变异系数/% | 范围/10-6 | 背景值[38]/10-6 | 背景值变异系数/% | | Hg | 0.051 | 30.9 | 2.8 | 13 | 60.3 | 0.005~0.258 | 34 | 47.0 | | Cu | 22.19 | 29.6 | 13.1 | 200.2 | 133.5 | 2.66~529.00 | 26 | 52.0 | | Ni | 20.44 | 10.9 | 11.3 | 171.7 | 33.3 | 4.90~203.00 | 24.6 | 39.0 | | Zn | 54.6 | 50.5 | 18.2 | 371.7 | 92.5 | 13.3~1100.0 | 60.4 | 30.0 | | As | 7.52 | 2.9 | 3.8 | 39.2 | 39.0 | 1.4~41.50 | 6.4 | 34.0 | | Cr | 50.32 | 24.1 | 13.2 | 212.2 | 47.9 | 17.7~472.00 | 57 | 38.0 | | Cd | 0.160 | 0.4 | 16.9 | 323.5 | 218.1 | 0.029~7.200 | 0.12 | 35.0 | | Pb | 30.070 | 18.8 | 12 | 181.6 | 62.5 | 12.857~347.100 | 27.2 | 23.0 |
|
Statistical characteristics of heavy metal contents in soils
|
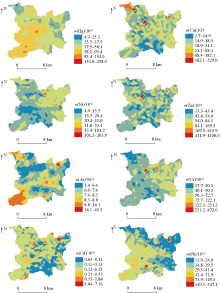
|
The spatial distribution of heavy metal elements in soils in the study area
|

| 元素 | Hg | Cu | Ni | Zn | As | Cr | Cd | Pb | | Hg | 1 | | | | | | | | | Cu | 0.067 | 1 | | | | | | | | Ni | -0.012 | 0.152** | 1 | | | | | | | Zn | 0.102* | 0.844** | 0.176** | 1 | | | | | | As | 0.312** | 0.309** | 0.053 | 0.137** | 1 | | | | | Cr | -0.004 | 0.661** | 0.361** | 0.848** | -0.030 | 1 | | | | Cd | 0.308** | 0.513** | 0.058 | 0.505** | 0.490** | 0.284** | 1 | | | Pb | 0.377** | 0.399** | 0.023 | 0.430** | 0.421** | 0.215** | 0.793** | 1 |
|
Pearson correlation analysis of soil heavy metals
|

| 元素 | 主成分 | | 1 | 2 | 3 | | Hg | 0.323 | 0.564 | 0.243 | | Cu | 0.841 | -0.27 | -0.18 | | Ni | 0.247 | -0.373 | 0.872 | | Zn | 0.865 | -0.39 | -0.188 | | As | 0.468 | 0.567 | 0.215 | | Cr | 0.7 | -0.616 | 0.012 | | Cd | 0.797 | 0.384 | -0.062 | | Pb | 0.727 | 0.459 | -0.055 | | 特征值 | 3.494 | 1.74 | 1.04 | | 贡献率/% | 43.130 | 21.479 | 12.838 | | 累积贡献率/% | 43.13 | 64.609 | 77.447 |
|
Principal component analysis of soil heavy metals
|
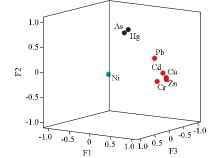
|
Components graph of heavy metal elements in rotated space
|

| 元素 | 污染指数范围 | 污染指数均值 | 不同污染级别样点占比/% | | 无污染 | 轻微污染 | 轻度污染 | 中度污染 | 重度污染 | | Hg | 0.14~7.59 | 1.51 | 26.1 | 55.5 | 13.0 | 3.6 | 1.8 | | Cu | 0.10~20.35 | 0.85 | 87.4 | 10.2 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 | | Ni | 0.20~8.46 | 0.85 | 83.4 | 15.8 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.4 | | Zn | 0.22~18.21 | 0.90 | 81.6 | 17.6 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.4 | | As | 0.22~6.48 | 1.18 | 30.1 | 67.5 | 2.0 | 0 | 0.4 | | Cr | 0.31~8.23 | 0.88 | 86.8 | 12.6 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.4 | | Cd | 0.24~59.57 | 1.34 | 46.5 | 47.5 | 3.6 | 0.8 | 1.6 | | Pb | 0.47~12.76 | 1.11 | 42.5 | 55.5 | 1.4 | 0 | 0.6 |
|
Single factor pollution assessment of heavy metal elements in soils
|

内梅罗指
数范围 | 内梅罗指
数均值 | 不同污染指数分级样点占比/% | | 清洁 | 警戒 | 轻度污染 | 中度污染 | 重度污染 | | 0.71~43.14 | 1.64 | 0 | 13.6 | 72.7 | 9.8 | 3.8 |
|
Evaluation of Nemerow comprehensive pollution Index
|

| 元素 | 地累积指数
范围 | 地累积指数
均值 | 不同污染指数分级样点占比/% | | 无污染 | 无—中度污染 | 中度污染 | 中度—强污染 | 强度污染 | 强—极强污染 | 极强污染 | | Hg | -2.79~2.92 | 0.38 | 26.1 | 55.5 | 16.6 | 1.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cu | -3.87~3.76 | -1.02 | 95.6 | 3.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | | Ni | -2.88~2.50 | -0.90 | 98.4 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Zn | -2.77~3.60 | -0.83 | 98.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | | As | -2.78~2.11 | -0.45 | 86.6 | 13.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cr | -2.27~2.46 | -0.82 | 99.0 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cd | -2.63~5.31 | -0.49 | 88.0 | 9.6 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.2 | | Pb | -1.67~3.09 | -0.53 | 94.4 | 5.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 |
|
Pollution assessment by cumulative index method
|

| 元素 | ${E}_{r}^{i}$指数范围 | 均
值 | 不同污染指数分级样点占比/% | 轻微
危害 | 中等
危害 | 强危害 | 很强
危害 | 极强
危害 | | Hg | 5.8~303.5 | 60.2 | 26.1 | 55.5 | 16.6 | 1.8 | 0 | | Cu | 0.5~101.7 | 4.3 | 99.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | | Ni | 1.0~42.3 | 4.3 | 99.8 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Zn | 0.2~18.2 | 0.9 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | As | 2.2~64.8 | 11.8 | 99.6 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cr | 0.6~16.6 | 1.8 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cd | 7.3~1790.1 | 40.2 | 81.6 | 14.8 | 2.4 | 0.6 | 0.6 | | Pb | 2.4~63.8 | 5.5 | 99.8 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
|
Assessment of potential ecological risk of single heavy metal element
|

综合潜在生态
风险指数范围 | 均值 | 不同污染指数分级样点占比/% | 轻微
危害 | 中等
危害 | 强危害 | 很强
危害 | 极强
危害 | | 37.8~864.7 | 121.4 | 0 | 0.14 | 0.73 | 0.10 | 0.04 |
|
Assessment of potential ecological risk of heavy metal elements
|
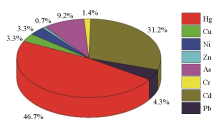
|
The contribution of heavy metal RI
|
| [1] |
李晓曼, 李青青, 杨洁, 等. 上海市典型工业用地土壤和地下水重金属复合污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(12):5687-5697.
|
| [1] |
Li X M, Li Q Q, Yang J, et al. Compound pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soil and groundwater of typical industrial lands in Shanghai[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(12):5687-5697.
|
| [2] |
赵琳兴, 雷红平, 王雁鹤, 等. 黄河上游典型工业园区周边土壤重金属污染评价及来源解析[J/OL]. 环境科学,1-24[2024-09-10].DOI:10.13227/j.hjkx.202404210.
|
| [2] |
Zhao L X, Lei H P, Wang Y H, et al. Evaluation and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution around typical Industrial parks in upper reaches of Yellow River[J/OL]. Environmental Science,1-24 [2024-09-10].DOI:10.13227/j.hjkx.202404210.
|
| [3] |
赵庆令, 李清彩, 马龙, 等. 单县表层土壤重金属污染特征、健康风险及溯源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2025, 46(1):442-452.
|
| [3] |
Zhao Q L, Li Q C, Ma L, et al. Characteristics,health risks,and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in surface soil in Shanxian County[J]. Environmental Science, 2025, 46(1):442-452.
|
| [4] |
徐玉玲, 冯巩俐, 蒋晓煜, 等. 兰州市某交通干道土壤重金属分布特征及其对绿化植物的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(4):1341-1348.
|
| [4] |
Xu Y L, Feng G L, Jiang X Y, et al. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in soil and its influence on greening plants in a main road of Lanzhou City,Northwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(4):1341-1348.
|
| [5] |
Hu B F, Jia X L, Hu J, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and health risks in the soil-plant-human system in the Yangtze River Delta,China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14(9):1042.
|
| [6] |
韩冰, 黄勇, 李欢, 等. 北京市房山区土壤重金属元素分布、富集特征及来源解析[J]. 物探与化探, 2024, 48(3):820-833.
|
| [6] |
Han B, Huang Y, Li H, et al. Distributions, enrichment characteristics,and sources of heavy metals in soils in Fangshan District,Beijing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3):820-833.
|
| [7] |
夏敏, 赵炳梓, 张佳宝. 基于GIS的黄淮海平原典型潮土区土壤重金属积累研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2013, 50(4):684-692.
|
| [7] |
Xia M, Zhao B Z, Zhang J B. Gis-based research on soil heavy metal accumulation in a fluvo-aquic soil area typical of the Huang-Huai-Hai plain[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2013, 50(4):684-692.
|
| [8] |
高智群, 张美剑, 赵科理, 等. 土壤—水稻系统重金属空间异质性研究——以浙江省嵊州市为例[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(1):215-224.
|
| [8] |
Gao Z Q, Zhang M J, Zhao K L, et al. Heavy metal contamination in soil-rice system and its spatial variation in Shengzhou City[J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(1):215-224.
|
| [9] |
邱孟龙, 李芳柏, 王琦, 等. 工业发达城市区域耕地土壤重金属时空变异与来源变化[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(2):298-305.
|
| [9] |
Qiu M L, Li F B, Wang Q, et al. Spatio-temporal variation and source changes of heavy metals in cultivated soils in industrial developed urban areas[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(2):298-305.
|
| [10] |
杨勇, 梅杨, 张楚天, 等. 基于时空克里格的土壤重金属时空建模与预测[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(21):249-255.
|
| [10] |
Yang Y, Mei Y, Zhang C T, et al. Spatio-temporal modeling and prediction of soil heavy metal based on spatio-temporal Kriging[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(21):249-255.
|
| [11] |
Jiang Y X, Chao S H, Liu J W, et al. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province,China[J]. Chemosphere, 2017,168:1658-1668.
|
| [12] |
刘坤, 李雨桐, 余海, 等. 重庆某工业园土壤重金属污染特征、风险及源解析[J]. 中国环境监测, 2024, 40(2):74-83.
|
| [12] |
Liu K, Li Y T, Yu H, et al. Pollution characteristics,risk assessment and sources analysis of soil heavy metals in an industrial park of Chongqing[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2024, 40(2):74-83.
|
| [13] |
杨艳, 刘彬, 夏飞强, 等. 皖南典型区耕地土壤重金属富集特征、来源识别及健康风险评估[J]. 物探与化探, 2024, 48(1):255-263.
|
| [13] |
Yang Y, Liu B, Xia F Q, et al. Enrichment characteristics,source identification,and health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in typical cultivated land in the mountainous area of southern Anhui Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1):255-263.
|
| [14] |
丁祥, 袁贝, 杜平, 等. 典型矿冶城市土壤重金属累积驱动因子研究和概率风险评估[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(2):31-41.
|
| [14] |
Ding X, Yuan B, Du P, et al. Heavy metal accumulation in soils of a typical mining community:Driving factors and probabilistic health risk assessment[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(2):31-41.
|
| [15] |
车凯, 陈崇明, 郑庆宇, 等. 燃煤电厂重金属排放与周边土壤中重金属污染特征及健康风险[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(10):4578-4589.
|
| [15] |
Che K, Chen C M, Zheng Q Y, et al. Heavy metal emissions from coal-fired power plants and heavy metal pollution characteristics and health risks in surrounding soils[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(10):4578-4589.
|
| [16] |
Liang J H, Liu Z Y, Tian Y Q, et al. Research on health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil based on multi-factor source apportionment:A case study in Guangdong Province,China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023,858:159991.
|
| [17] |
于元赫, 吕建树, 王亚梦. 黄河下游典型区域土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6):2865-2874.
|
| [17] |
Yu Y H, Lyu J S, Wang Y M. Source identification and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils in typical areas around the lower Yellow River[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6):2865-2874.
|
| [18] |
艾建超, 王宁, 杨净. 基于UNMIX模型的夹皮沟金矿区土壤重金属源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(9):3530-3536.
|
| [18] |
Ai J C, Wang N, Yang J. Source apportionment of soil heavy metals in Jiapigou goldmine based on the UNMIX model[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(9):3530-3536.
|
| [19] |
董騄睿, 胡文友, 黄标, 等. 基于正定矩阵因子分析模型的城郊农田土壤重金属源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(7):2103-2111.
|
| [19] |
Dong L R, Hu W Y, Huang B, et al. Source appointment of heavy metals in suburban farmland soils based on positive matrix factorization[J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(7):2103-2111.
|
| [20] |
郭军康, 赵隽隽, 李怡凡, 等. 矿区土壤重金属污染修复技术研究进展[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2023, 40(2):249-260.
|
| [20] |
Guo J K, Zhao J J, Li Y F, et al. Research progress on remediation technology for heavy metal-contaminated soil in mines[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2023, 40(2):249-260.
|
| [21] |
白贵琪, 傅开彬, 谌书, 等. 建设用地重金属污染修复技术筛选模型构建[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(8):4147-4153.
|
| [21] |
Bai G Q, Fu K B, Chen S, et al. Construction of screening model for remediation of heavy metal pollution in construction land[J]. Construction of screening model for remediation of heavy metal pollution in construction land[J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43(8):4147-4153.
|
| [22] |
赵鑫娜, 杨忠芳, 余涛. 矿区土壤重金属污染及修复技术研究进展[J]. 中国地质, 2023, 50(1):84-101.
|
| [22] |
Zhao X N, Yang Z F, Yu T. Review on heavy metal pollution and remediation technology in the soil of mining areas[J]. Geology in China, 2023, 50(1):84-101.
|
| [23] |
李锋, 刘思源, 李艳, 等. 工业发达城市土壤重金属时空变异与源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(2):934-944.
|
| [23] |
Li F, Liu S Y, Li Y, et al. Spatiotemporal variability and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in a industrially developed city[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(2):934-944.
|
| [24] |
陈明, 李名阅, 周锦阳, 等. 西北某重工业区降尘重金属污染特征及源解析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2024, 47(2):155-164.
|
| [24] |
Chen M, Li M Y, Zhou J Y, et al. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in the atmosphere dustfall of a typical heavy industrial city in northwest China[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2024, 47(2):155-164.
|
| [25] |
赵庆令, 李清彩, 安茂国, 等. 基于PMF-PCA/APCS与PERI的菏泽油用牡丹种植区表层土壤重金属潜在来源识别及生态风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(9):5253-5263.
|
| [25] |
Zhao Q L, Li Q C, An M G, et al. Potential source identification and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface soil of Heze oil peony planting area based on PMF-PCA/APCS and PERI[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(9):5253-5263.
|
| [26] |
张文强, 滕跃, 柳浩然, 等. 聊城市典型农业区土壤重金属分布特征、生态风险及来源解析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2024, 38(4):171-180.
|
| [26] |
Zhang W Q, Teng Y, Liu H R, et al. Distribution, ecological risks,and sources of heavy metals in soil of typical agricultural areas in Liaocheng City[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2024, 38(4):171-180.
|
| [27] |
赵玉杰, 师荣光, 白志鹏, 等. 山东淄博玉米产区土壤砷含量空间变异研究[J]. 环境科学, 2006, 27(8):1676-1681.
|
| [27] |
Zhao Y J, Shi R G, Bai Z P, et al. Spatial variability analysis of soil arsenic in Zibo maize producing area,Shandong Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2006, 27(8):1676-1681.
|
| [28] |
王菲, 费敏, 韩冬锐, 等. 山东省典型污灌区土壤—小麦重金属健康风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(6):3609-3618.
|
| [28] |
Wang F, Fei M, Han D R, et al. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil and wheat grain in the typical sewage irrigated area of Shandong Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(6):3609-3618.
|
| [29] |
李梦婷, 沈城, 吴健, 等. 快速城市化区域不同用地类型土壤重金属含量分布特征及生态风险[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(10):4889-4896.
|
| [29] |
Li M T, Shen C, Wu J, et al. Content and ecological risks of heavy metals in soil with different land uses in a rapidly urbanizing area[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(10):4889-4896.
|
| [30] |
孟令华, 杜小亮, 刘乾, 等. 泰安市城区土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2022, 12(5):41-49.
|
| [30] |
Meng L H, Du X L, Liu Q, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of Heavy metals in soil in urban area of Tai'an[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 12(5):41-49.
|
| [31] |
代杰瑞, 庞绪贵, 宋建华, 等. 山东淄博城市和近郊土壤元素地球化学特征及生态风险研究[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(3):617-627.
|
| [31] |
Dai J R, Pang X G, Song J H, et al. A study of geochemical characteristics and ecological risk of elements in soil of urban and suburban areas of Zibo City,Shandong Province[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(3):617-627.
|
| [32] |
王碧莹, 李振函, 李海岗, 等. 黄河口国家公园湿地土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 济南大学学报:自然科学版, 2024, 38(3):267-273.
|
| [32] |
Wang B Y, Li Z H, Li H G, et al. Evaluation of soil pollution caused by heavy mental in wetland of the Yellow River Estuary National Park[J]. Journal of University of Jinan:Science and Technology, 2024, 38(3):267-273.
|
| [33] |
赵莉源, 孔令号, 赵志刚, 等. 胶东半岛某金矿周边土壤重金属的污染特征、来源分析及风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 2024, 51(5):1485-1500.
|
| [33] |
Zhao L Y, Kong L H, Zhao Z G, et al. Pollution characteristics,source analysis and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around a gold mine in Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Geology in China, 2024, 51(5):1485-1500.
|
| [34] |
朱林宇. 胶东金矿区土壤重金属时空变异及来源解析研究[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2022.
|
| [34] |
Zhu L Y. Spatiotemporal variation and source apportionment of heavy metals in soils of Jiaodong gold mine[D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2022.
|
| [35] |
李波, 胡舒娅, 赵全升. 莱州湾沿岸海水入侵区地下水化学特征[J]. 世界地质, 2020, 39(4):971-977.
|
| [35] |
Li B, Hu S Y, Zhao Q S. Chemical characteristics of groundwater in coastal seawater intrusion area of Laizhou Bay[J]. Global Geology, 2020, 39(4):971-977.
|
| [36] |
冯晨馨, 邱隆伟, 高茂生, 等. 山东半岛北部泥质海岸带地下水水化学演化[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 8(12):16-25.
|
| [36] |
Feng C X, Qiu L W, Gao M S, et al. Hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in muddy coastal zone of the northern Shandong Peninsula[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 8(12):16-25.
|
| [37] |
万梦雪, 焦文涛, 胡文友, 等. 城市工业区土壤重金属累积特征与来源解析——以上海市闵行区典型工业区为例[J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(6):1886-1898.
|
| [37] |
Wan M X, Jiao W T, Hu W Y, et al. Accumulation and source apportionment of heavy metals in urban-industrial soils—A case study in Minhang District of Shanghai[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2023, 42(6):1886-1898.
|
| [38] |
庞绪贵, 代杰瑞, 陈磊, 等. 山东省17市土壤地球化学背景值[J]. 山东国土资源, 2019, 35(1):46-56.
|
| [38] |
Pang X G, Dai J R, Chen L, et al. Soil geochemical background value of 17 cities in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2019, 35(1):46-56.
|
| [39] |
徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(2):112-115.
|
| [39] |
Xu Z Q, Ni S J, Tuo X G, et al. Calculation of heavy metals' toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 31(2):112-115.
|
| [40] |
杨崛园, 熊健, 李伟, 等. 基于PCA-APCS-MLR模型的西藏扎西岗湿地土壤重金属风险评价及来源解析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2024, 43(6):1807-1816.
|
| [40] |
Yang J Y, Xiong J, Li W, et al. Soil heavy metal risk evaluation and source analysis of Zhaxigang wetland in Tibet based on PCA-APCS-MLR Model[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2024, 43 (6):1807-1816.
|
| [41] |
陈小敏, 朱保虎, 杨文, 等. 密云水库上游金矿区土壤重金属空间分布、来源及污染评价[J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(12):2248-2256.
|
| [41] |
Chen X M, Zhu B H, Yang W, et al. Sources,spatial distribution and contamination assessments of heavy metals in gold mine area soils of Miyun Reservoir upstream,Beijing,China[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34 (12):2248-2256.
|
| [42] |
李浪. 山西省典型工业园区土壤重金属空间分布、来源及风险评价[D]. 太原: 太原科技学, 2023.
|
| [42] |
Li L. Spatial distribution,sources and risk assessment of soil heavy metals in typical Industrial park in Shanxi Province[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, 2023.
|
| [43] |
张东明. 工业区周边农田土壤重金属分布特征及风险评价[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2017.
|
| [43] |
Zhang D M. Heavy metal distribution and risk evaluation in farmland soil around an industrial area in northern Xinjiang[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2017.
|
| [44] |
赖涓涓, 杨德钰, 刘亮, 等. 中国西北地区银川市浅表土重金属污染特征及来源解析[J/OL]. 中国环境科学,1-12[2024-09-10].https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20240326.006.

|
| [44] |
Lai J J, Yang D Y, Liu L, et al. Characteristics and source identification of heavy metal pollution in shallow topsoil in Yinchuan City,northwest China[J/OL]. 中国环境科学,1-12[2024-09-10].https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20240326.006.

|
| [45] |
樊新刚, 米文宝, 马振宁, 等. 宁夏石嘴山河滨工业园区表层土壤重金属污染的时空特征[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(5):1887-1894.
|
| [45] |
Fan X G, Mi W B, Ma Z M, et al. Spatial and temporal characteristics of heavy metal concentration of surface soil in Hebin industrial park in Shizuishan northwest China[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34 (5):1887-1894.
|
| [46] |
王中阳. 朝阳地区耕地土壤重金属污染风险评价与来源解析研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2018.
|
| [46] |
Wang Z Y. Research on risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil in Chaoyang Region[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2018.
|
| [47] |
田甜, 杨婷, 邹县梅, 等. 钢铁厂周边土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价——以闽西三明钢铁厂周边农田为例[J]. 农学学报, 2021, 11(6):42-46.
|
| [47] |
Tian T, Yang T, Zou X M, et al. Heavy metals in farmland surrounding the Sanming steel plant in western Fujian:Pollution characteristics and risk assessment[J] Journal of Agriculture, 2021, 11 (6):42-46.
|
| [48] |
谢小进, 康建成, 李卫江, 等. 上海宝山区农用土壤重金属分布与来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 2010, 31(3):768-774.
|
| [48] |
Xie X J, Kang J C, Li W J, et al. Analysis on heavy metal concentrations in agricultural soils of Baoshan,Shanghai[J] Environmental Science, 2010, 31 (3):768-774.
|
| [49] |
王改玲, 李立科, 郝明德, 等. 长期定位施肥对土壤重金属含量的影响及环境评价[J]. 水土保持学报, 2010, 24(3):60-63,70.
|
| [49] |
Wang G L, Li L K, Hao M D, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on heavy-metal contents of soil and environmental quality evaluation[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 24 (3):60-63,70.
|
| [50] |
刘勇, 岳玲玲, 李晋昌. 太原市土壤重金属污染及其潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(6):1285-1293.
|
| [50] |
Liu Y, Yue L L, Li J C. Evaluation of heavy metal contamination and its potential ecological risk to the soil in Taiyuan,China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31 (6):1285-1293.
|
| [51] |
戴前进, 冯新斌, 唐桂萍. 土壤汞的地球化学行为及其污染的防治对策[J]. 地质地球化学, 2002, 30(4):75-79.
|
| [51] |
Dai Q J, Feng X B, Tang G P. The geochemical behavior of mercury in soil and its pollution control[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 2002, 30 (4):75-79.
|
| [52] |
沈城, 刘馥雯, 吴健, 等. 再开发利用工业场地土壤重金属含量分布及生态风险[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(11):5125-5132.
|
| [52] |
Shen C, Liu F W, Wu J, et al. Distribution and ecological risk of heavy metals in the soil of redevelopment industrial sites[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41 (11):5125-5132.
|
| [1] |
WANG Zhi-Qiang, NI Ping, ZHANG Hong-Xu, SHI Tian-Chi, YANG Jian-Feng, ZHANG Hui-Ling. Geochemical characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil-crop systems[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(4): 943-953. |
| [2] |
YU Fei, WANG Rui, ZHOU Jiao, ZHANG Feng-Lei, JIANG Yu-Lian, ZHANG Yun-Yi, ZHU Shi-Lin. Sources of soil heavy metals and health risk assessment of crops in arable land at the periphery of a typical mercury mining area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3): 847-857. |
|
|
|
|

