|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics and salinization mechanisms of shallow surface substrate in the Taonan area, western Songnen Plain |
Siqinbilige ( ), KONG Fan-Peng( ), KONG Fan-Peng( ), LIU Hong-Bo, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Ye, DONG Kai ), LIU Hong-Bo, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Ye, DONG Kai |
| Mudanjiang Natural Resources Comprehensive Survey Center, China Geological Survey, Changchun 130102, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study investigated the shallow surface substrate in the Taonan area, western Songnen Plain. Accordingly, it revealed the elemental differentiation between surface (0~20 cm) and deeper (150~200 cm) soils in the shallow surface substrate layer, as well as the genetic mechanisms of salinization in this layer. The results show that compared to deeper soils, surface soils in the Taonan area are strongly enriched in organic carbon (Corg) and N and slightly enriched in Br, P, S, Se, and total carbon (TC). In contrast, no significant differences are identified in heavy metals, rare earth elements (REEs), and other trace elements. These findings suggest the primary causes of the enrichment of various element indicators in surface soils include agricultural activities, biogeochemical cycles, and water-salt migration. The factor analysis indicates that for surface soils, factor F1 is dominated by the heavy metal-REE combination (variance contribution rate: 26.66%), with its spatial distribution associated with fluvial deposition and agricultural activities. Furthermore, factor F2 for these soils is the salt-related element combination (including CaO and MgO; variance contribution rate: 11.24%), indicating the risk of salinization in low-lying zones. In contrast, for deeper soils, factor F1 is the combination of elements such as Al2O3, B, La, and Sc (variance contribution rate: 27.34%), reflecting the compositional characteristics of bedrocks or soil parent materials. Factor F2 for these soils is the combination of elements related to geological settings and salinity (variance contribution rate: 13.09%), indicating geological settings and salinization. The weathering and leaching coefficient, represented by the Ba value, shows significant spatial differentiation. Compared to deeper soils, surface soils manifest a larger range of high Ba values, primarily distributed in the zone south of Jubao Township and west of Datong Township, as well as the southern part of Erlong Township. This distribution, coinciding with the high-value zones of salt-related factor F2, is principally affected by topography and deep parent material types. In the low-lying plain area and the front of alluvial fans, the low-lying terrains, poor drainage, and intense evaporation lead to salt accumulation, causing a high risk of salinization. In the hilly area, the high values of factor F2 are associated with the bedrock lithology, with salts originating from weathered bedrocks. The results of this study will provide a geochemical basis for land resource optimization and ecological restoration in the Taonan area.
|
|
Received: 02 March 2025
Published: 30 December 2025
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
KONG Fan-Peng
E-mail: 422865187@qq.com;315706831@qq.com
|
|
|
|
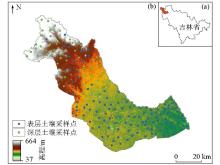
|
Schematic diagram of the geographical location and sampling point distribution in the study area
|
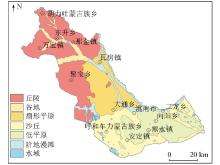
|
Schematic diagram of the geographical location and sampling point distribution in the study area
|

元素含量比值(表层
土壤/深层土壤) | 特征 | 元素 | | ≤0.5 | 明显贫化 | | | 0.5~0.9 | 弱贫化 | | | 0.9~1.1 | 无变化 | Ag、Al2O3、Ba、Be、Ce、Cu、Ga、
Ge、K2O、La、Li、MgO、Mn、Nb、
Ni、Pb、Rb、Sb、Sc、SiO2、Sr、Th、
Tl、U、V、Y、Zn | | 1.1~1.5 | 弱富集 | As、Au、B、Bi、Cd、Co、Cr、F、I、
Mo、Na2O、Sn、TFe2O3、Ti、
W、Zr | | 1.5~2.0 | 中富集 | CaO、Hg、P | | ≥2.0 | 强富集 | Br、Cl、Corg、N、S、Se、TC |
|
Element content ratio characteristics between surface and deep soils
|

| 地貌类型 | 贫化(<0.9) | 无变化(0.9~1.1) | 弱富集(1.1~1.5) | 中富集(1.5~2.0) | 强富集(>2.0) | | 丘陵区 | | Ag、Al2O3、Ba、Be、Ce、Cu、Ga、Ge、K2O、Li、
Mn、Na2O、Pb、pH、Rb、Sc、SiO2、Sn、Tl、W、Zn | Au、Bi、Co、Cr、La、MgO、
Mo、Nb | As、CaO、Cd、Hg、
I、Zr | B、Br、Cl、Corg、
N、P、S、Se、TC | | 扇形平原区 | | Al2O3、As、B、Ba、Be、Ce、Co、Cu、Ga、Ge、I、
K2O、La、Li、Mn、Mo、Na2O、Nb、Ni、Pb、pH、
Rb、Sb、Sc、SiO2、Sn、Sr、Th、Tl、V、Y、Zn | Ag、Cd、Cr、F、MgO、TFe2O3、
Ti、Zr | Au、Bi、Br、CaO、
Hg、P | Cl、Corg、N、S、
Se、TC | | 阶地漫滩区 | | Al2O3、Ba、Be、Ce、Ga、Ge、K2O、La、Li、Pb、
pH、Rb、Sc、SiO2、Sr、Th、Tl、U、W、Zn | Ag、As、Au、B、Cd、Cl、Co、Cr、
F、I、MgO、Mn、Mo、Nb、Ni、
Sb、Sn、TFe2O3、Ti、V、Y、Zr | Bi、Br、CaO、Cu、
P、S | Corg、Hg、N、Se、
TC | | 低平原区 | | Al2O3、Ba、Be、Ce、Ga、Ge、I、K2O、La、Li、
Na2O、Pb、pH、Rb、Sc、SiO2、Sr、Th、Ti、Tl、U、
Y、Zn | Sb、Sn、TFe2O3、V、W、Zr | Hg、P、S | Br、Cl、Corg、N、
Se、TC | | 沙丘区 | | Ag、Al2O3、Au、B、Ba、Be、Bi、Ce、Cr、Cu、F、
Ga、Ge、I、K2O、La、Mn、Nb、Ni、Pb、pH、Rb、
Sb、Sc、SiO2、TFe2O3、Th、Ti、Tl、U、Y、Zn、Zr | Cd、Hg、Mo、Na2O、Sn | Br、Cl、P、TC、W | CaO、Corg、N、
S、Se |
|
Element content ratio characteristics between surface and deep soils in different geomorphic type areas
|

| 方法 | 检测结果 | | KMO度量值 | 0.845 | Bartlett的球形
度检验 | 近似卡方 | 11807.559 | | df | 1378 | | Sig. | 0 |
|
KMO and Bartlett's test for surface soil data
|

| 方法 | 检测结果 | | KMO度量值 | 0.799 | Bartlett的球形
度检验 | 近似卡方 | 8465.708 | | df | 1431 | | Sig. | 0 |
|
KMO and Bartlett's test for deep soil data
|
|
Scree plot of factor analysis
|

| 因子 | 表层土壤因子组合 | 深层土壤因子组合 | | F1 | Ba-Be-Ce-Co-Cu-Cd-Ga-Ge-
Mn-La-Li-Nb-Ni-Pb-Rb-Sc-
Th-U-Tl-V-Y | Al2O3-B-Be-Cd-Ce-Co-Cu-
Ga-Ge-La-Li-Mn-Mo-Ni-Pb-
Sb-Sc-TFe2O3-Th-V-Y | | F2 | CaO-MgO-Sr-K2O-SiO2 | Au-CaO-K2O-MgO-Rb-Sb-
SiO2-Sr-TC-Tl | | F3 | Au-Corg-Hg-N-Se-TC | Ba-P-Ti-Zr | | F4 | Cr-P-Ti-pH-Zr | Corg-N-S | | F5 | Al2O3-TFe2O3 | Na2O-Nb | | F6 | Ag-As-B | F-I-pH | | F7 | Mo-S-Y | Se-U |
|
Characteristics of factor element combinations in surface and deep soils of the study area
|
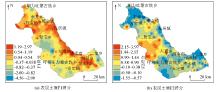
|
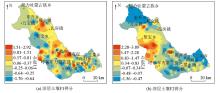
Score of F1 and F2 factors in surface soil
|
|
Score of F1 and F2 factors in deep soil
|

| 富集系数 | 富集程度 | 元素 | | <0.8 | 贫化 | Ag、Cl、F、I、Sr、Zn | | 0.8~1.2 | 无变化 | Al2O3、As、Au、B、Ba、Be、Bi、CaO、Cd、Ce、
Co、Cr、Cu、Ga、Ge、Hg、K2O、La、Li、MgO、
Mn、Mo、Na2O、Nb、Ni、Pb、Rb、Sb、Sc、SiO2、
Sn、TFe2O3、Th、Ti、Tl、U、V、W、Y、Zr | | 1.2~2.0 | 弱富集 | Br、P、S、Se、TC | | 2.0~3.0 | 中富集 | Corg、N | | >3.0 | 强富集 | |
|
Characteristic of element enrichment coefficient
|

| 类型 | 地貌类型 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 中位数 | 标准离差 | 变异系数 | | 表层土壤 | 低平原 | 0.591 | 2.121 | 1.005 | 0.985 | 0.362 | 0.36 | | 阶地漫滩 | 0.456 | 1.757 | 0.890 | 0.762 | 0.401 | 0.45 | | 丘陵 | 0.467 | 2.171 | 1.095 | 0.938 | 0.441 | 0.40 | | 沙丘 | 0.037 | 1.171 | 0.785 | 0.729 | 0.212 | 0.27 | | 扇形平原 | 0.467 | 1.952 | 1.024 | 1.044 | 0.434 | 0.42 | | 全区 | 0.037 | 2.171 | 0.965 | 0.896 | 0.362 | 0.375 | | 深层土壤 | 低平原 | 0.178 | 1.617 | 0.946 | 0.877 | 0.285 | 0.30 | | 阶地漫滩 | 0.765 | 2.309 | 1.123 | 0.841 | 0.580 | 0.52 | | 丘陵 | 0.466 | 2.766 | 1.159 | 0.817 | 0.645 | 0.56 | | 沙丘 | 0.630 | 2.090 | 0.919 | 0.810 | 0.290 | 0.32 | | 扇形平原 | 0.546 | 3.710 | 1.227 | 0.788 | 0.972 | 0.79 | | 全区 | 0.178 | 3.710 | 0.994 | 0.810 | 0.484 | 2.05 |
|
Characteristics of weathering and leaching coefficient parameters for different landforms in surface and deep soils
|
|
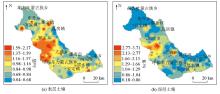
Contour of weathering and leaching coefficients for surface and deep soils
|
|
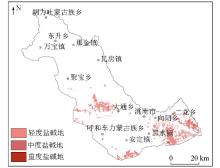
Distribution map of different salinity and alkalinity degrees in the study area
|
| [1] |
自然资源部. 关于印发《自然资源调查监测体系构建总体方案》的通知[EB/OL].(2020-01-17)[2020-02-07]. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202001/t20200117_2498071.html.
|
| [1] |
Official website of the Ministry of Natural Resources. Notice of the Ministry of Natural Resources on Issuing the Overall Plan for the Construction of the Natural Resources Survey and Monitoring System[EB/OL].(2020-01-17)[2020-02-07]. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202001/t20200117_2498071.html.
|
| [2] |
自然资源部办公厅. 关于印发《地表基质分类方案(试行)》的通知[EB/OL].(2020-12-22)[2024-11-10]. https://m.mnr.gov.cn/gk/tzgg/202012/t20201222_2596025.html.

|
| [2] |
Notice of the General Office of the Ministry of Natural Resources on Issuing the Classification Scheme of Surface Substrates (Trial)[EB/OL].(2020-12-22)[2024-11-10]. https://m.mnr.gov.cn/gk/tzgg/202012/t20201222_2596025.html.

|
| [3] |
郝爱兵, 殷志强, 李洪宇, 等. 地表基质的科学内涵与理论框架[J]. 地质学报, 2024, 98(11):3225-3237.
|
| [3] |
Hao A B, Yin Z Q, Li H Y, et al. The scientific connotation and theoretical framework of ground substrate[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2024, 98(11):3225-3237.
|
| [4] |
孔繁鹏, 赵建, 刘玖芬, 等. 关于构建东北黑土地地表基质监测网的思考[J]. 自然资源情报, 2024(11):18-24.
|
| [4] |
Kong F P, Zhao J, Liu J F, et al. Reflections on the construction of ground substrate monitoring network of black soil in northeast China[J]. Natural Resources Information, 2024(11):18-24.
|
| [5] |
葛良胜, 杨贵才. 自然资源调查监测工作新领域:地表基质调查[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 2020, 33(9):4-11,67.
|
| [5] |
Ge L S, Yang G C. New field of natural resources survey and monitoring:Ground substrate survey[J]. Natural Resource Economics of China, 2020, 33(9):4-11,67.
|
| [6] |
刘洪博, 孔繁鹏, 赵建, 等. 地表基质调查技术方法探索与实验——以黑龙江省宝清县黑土地调查为例[J]. 地理信息世界, 2022, 29(6):1-5.
|
| [6] |
Liu H B, Kong F P, Zhao J, et al. Exploration and experiment of surface substrate investigation technique:A case study of black soil investigation in Baoqing County,Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geomatics World, 2022, 29(6):1-5.
|
| [7] |
张思源, 袁帅, 邢怡, 等. 西北干旱农牧交错带地表基质调查成果经验[J]. 地质论评, 2024, 70(3):331-332.
|
| [7] |
Zhang S Y, Yuan S, Xing Y, et al. Experience and achievements of ground substrate survey in northwest arid agricultural-pastoral ecotones[J]. Geological Review, 2024, 70(3):331-332.
|
| [8] |
周雪妮, 曹亚廷, 计扬. 岷江上游干旱河谷区汶川段风化壳剖面元素地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2024, 48(3):597-608.
|
| [8] |
Zhou X N, Cao Y T, Ji Y. Element geochemical characteristics of weathering crust profiles of the Wenchuan section in the upper arid valley of the Minjiang River[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3):597-608.
|
| [9] |
刘腾, 蒋炜. 广东惠州金山新城规划区土壤地球化学背景值及分区研究[J]. 矿产勘查, 2024, 15(12):2318-2328.
|
| [9] |
Liu T, Jiang W. Study on soil geochemical background value and zoning of Jinshan new town planning area in Huizhou,Guangdong Province[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2024, 15(12):2318-2328.
|
| [10] |
鲍丽然, 龚媛媛, 严明书, 等. 渝西经济区土壤地球化学基准值与背景值及元素分布特征[J]. 地球与环境, 2015, 43(1):31-40.
|
| [10] |
Bao L R, Gong Y Y, Yan M S, et al. Element geochemical baseline and distributions in soil in Chongqing west economic zone,China[J]. Earth and Environment, 2015, 43(1):31-40.
|
| [11] |
曾琴琴, 王永华, 刘才泽, 等. 四川省南部县土壤地球化学元素分布特征研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2021, 41(4):656-662.
|
| [11] |
Zeng Q Q, Wang Y H, Liu C Z, et al. A study on distribution of elements of soil in Nanbu County,Sichuan Province[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2021, 41(4):656-662.
|
| [12] |
周道玮, 胡娟, 李强, 等. 松嫩平原盐碱地研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2025, 44(5):1671-1677.
|
| [12] |
Zhou D W, Hu J, Li Q, et al. Research progress of salt-affected land in Songnen Plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2025, 44(5):1671-1677.
|
| [13] |
林年丰, 汤洁. 松嫩平原环境演变与土地盐碱化、荒漠化的成因分析[J]. 第四纪研究, 2005, 25(4):474-483.
|
| [13] |
Lin N F, Tang J. Study on the environment evolution and the analysis of causes to land salinization and desertification in Songnen plain[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2005, 25(4):474-483.
|
| [14] |
刘俊贺, 迟云平, 谢远云, 等. 松嫩沙地地球化学特征及其对风尘物质贡献的指示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3):252-263.
|
| [14] |
Liu J H, Chi Y P, Xie Y Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Songnen sandy land and its indication of contribution to aeolian dust[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3):252-263.
|
| [15] |
蓝天. 吉林省西部土壤盐渍化地球化学评价与成因分析[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023.
|
| [15] |
Lan T. Geochemical evaluation and cause analysis of soil salinization in the west of Jilin Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023.
|
| [16] |
张哲寰, 戴慧敏, 宋运红, 等. 黑龙江省乌裕尔河流域土壤中某些微量元素地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(5):1097-1104.
|
| [16] |
Zhang Z H, Dai H M, Song Y H, et al. Geochemical characteristics of some soil trace elements in the Wuyuer River Basin,Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5):1097-1104.
|
| [17] |
陆继龙, 周永昶, 周云轩. 吉林省黑土某些微量元素环境地球化学特征[J]. 土壤通报, 2002, 33(5):365-368.
|
| [17] |
Lu J L, Zhou Y C, Zhou Y X. Environmental geochemical characteristics of some microelements in the black soil of Jilin Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2002, 33(5):365-368.
|
| [18] |
赵万苍, 刘连文, 陈骏, 等. 中国沙漠元素地球化学区域特征及其对黄土物源的指示意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2019, 49(9):1425-1438.
|
| [18] |
Zhao W C, Liu L W, Chen J, et al. Regional characteristics of element geochemistry in China desert and its indicative significance for loess provenance[J]. Scientia Sinica:Terrae, 2019, 49(9):1425-1438.
|
| [19] |
宋运红, 杨凤超, 刘凯, 等. 三江平原耕地土壤重金属元素分布特征及影响因素的多元统计分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(5):1064-1075.
|
| [19] |
Song Y H, Yang F C, Liu K, et al. A multivariate statistical analysis of the distribution and influencing factors of heavy metal elements in the cultivated land of the Sanjiang Plain[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5):1064-1075.
|
| [20] |
孙璐, 董燕, 凤蔚, 等. 雄安新区土壤地球化学特征及控制因素[J]. 地理研究, 2022, 41(6):1715-1730.
|
| [20] |
Sun L, Dong Y, Feng W, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil elements and its driving mechanisms in the Xiong'an new area,China[J]. Geographical Research, 2022, 41(6):1715-1730.
|
| [21] |
陈华强. 基于SPSS的因子分析在多目标地球化学分区中的应用——以广东省龙门县为例[J]. 中国高新技术企业, 2011(33):71-73.
|
| [21] |
Chen H Q. Application of factor analysis based on SPSS in multi-objective geochemical zoning:A case study of Longmen County,Guangdong Province[J]. China High-Tech Enterprises, 2011(33):71-73.
|
| [22] |
俞伯汀, 管敏琳, 王其春, 等. 耕地土壤地球化学元素富集与风化淋溶特征分析——以杭州市为例[J]. 环境生态学, 2024, 6(9):8-16.
|
| [22] |
Yu B T, Guan M L, WAGN Q C, et al. Analysis of geochemical element enrichment and weathering leaching characteristics in farmland soil:A case study of Hangzhou City[J]. Environmental Ecology, 2024, 6(9):8-16.
|
| [23] |
卢钊, 周萍, 王玉真. 陕西紫阳富硒土元素迁移特征及其质量评估[J]. 中国矿业, 2022, 31(8):69-78.
|
| [23] |
Lu Z, Zhou P, Wang Y Z. Element migration characteristics and quality assessment of selenium-rich soils in Ziyang,Shaanxi[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2022, 31(8):69-78.
|
| [24] |
张倩, 韩贵琳. 九龙江流域土壤稀土元素分布特征及控制因素[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2022, 31(7):1494-1502.
|
| [24] |
Zhang Q, Han G L. Distribution and controlling factors of soil rare earth elements in Jiulongjiang River catchment[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2022, 31(7):1494-1502.
|
| [25] |
中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T0295—2016土地质量地球化学评价规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
|
| [25] |
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China. DZ/T0295—2016Determinationoflandqualitygeochemicalevaluation[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [1] |
CHEN Geng-Hu, LANG Xing-Hai, WANG Zhao-Shuai, DONG Wei-Cai, WANG Deng-Ke, XIANG Zuo-Peng, LI Zhuang, YE Zi-Feng, WU Chang-Yi, WANG Xu-Hui, WU Tian-Wen, LUO Chao. Geochemical characteristics and anomaly assessments of soils in the Songshunangou gold mining area, Qinghai Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(6): 1281-1290. |
| [2] |
GONG Jian-Sheng, LANG Xing-Hai, WANG Zhao-Shuai, DENG Yu-Lin, WU Chang-Yi, HE Qing, LI Zhi-Jun, DING Feng, ZHAN Hong-Yu, LOU Yu-Ming. Geochemical characteristics and anomaly assessments of stream sediments in the Xiongcun ore concentration area and its periphery, Xietongmen County, Tibet[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(6): 1291-1302. |
|
|
|
|

