|
|
|
| Application of the seismic meme inversion method in predicting superimposed thin sandstones: A case study of the Gaotaizi oil layer in the Qian'an oilfield,southern Songliao Basin |
YANG Guang1( ), WANG Li-Xian1, HU Jia1, LIU Zhi-Jun1, ZHANG Hong-Jie1, WANG Yun-He1, SUN Long1, ZHANG Xu-Sheng2, CHEN Yan-Hu2( ), WANG Li-Xian1, HU Jia1, LIU Zhi-Jun1, ZHANG Hong-Jie1, WANG Yun-He1, SUN Long1, ZHANG Xu-Sheng2, CHEN Yan-Hu2( ) ) |
1. Research Institute of Geophysical Exploration, Jilin Oilfield Company,PetroChina, Songyuan 138000, China
2. Beijing Zhongheng Lihua Petroleum Technology Research Institute, Beijing 100101, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract To address the challenges in predicting superimposed thin sandstones in lacustrine basins,this study proposed a technical workflow for their prediction using the seismic meme inversion(SMI) method.First,an initial inversion model was constructed using log curves from sample wells selected based on seismic waveform similarity.Second,the initial inversion model was iteratively optimized in a Bayesian framework to yield high-resolution SMI results.Third,the SMI results were integrated with low-frequency inversion results to yield high vertical resolution while effectively characterizing the lateral superimposed patterns and boundaries of sand bodies.Case studies demonstrate that the SMI method achieved a prediction accuracy of 2 m to 3 m for superimposed thin sandstones.The coincidence rates for calibration and validation wells reached 91.5 % and 85.2 %,respectively,confirming the effectiveness of the SMI method and the high precision of the inversion results.Overall,this study provides an effective technical approach to predicting superimposed thin sandstones in lacustrine basins.
|
|
Received: 24 February 2025
Published: 07 August 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
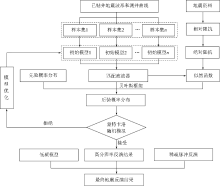
|
FIg.1 Flowchart of SMI inversion technology
|
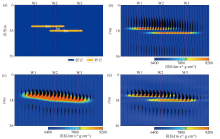
|
Comparison of superimposed thin sandstone geological model, forward-modeled seismic traces and inversion results from different methods
a—stacked thin sand bodies geological model;b—impedance model overlaid with seismic waveform;c—sparse spike inversion results overlaid with seismic waveform;d—waveform-indicated inversion results overlaid with seismic waveform
|
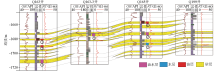
|
Correlation profile of sandstone in tied wells Q163—Q163-3—Q165—Q199
|
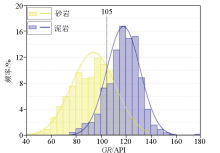
|
Histogram of lithofacies identification
|
|
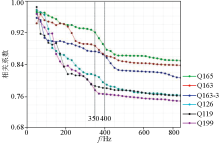
Line chart for maximum cutoff frequency analysis
|
|
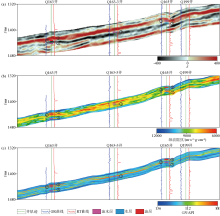
Seismic and inversion profiles across wells Q163—Q163-3—Q165—Q199
a—seismic section;b—sparse spike inversion P-impedance section;c—waveform-indicated inversion GR property section
|
|
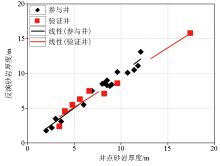
Crossplot of predicted sandstone thickness from inversion vs. sandstone thickness from well-log
|

| 井类型 | 井名 | 井点砂岩
厚度/m | 预测砂岩
厚度/m | 绝对误差
/m | 相对误差
绝对值/% | | 参与井 | Q118 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 10.0 | | Q118-2 | 6.9 | 7.5 | -0.6 | 8.7 | | Q119 | 6.0 | 5.5 | 0.5 | 8.3 | | Q126 | 9.6 | 10.2 | -0.6 | 6.3 | | Q162 | 11.4 | 10.5 | 0.9 | 7.9 | | Q162-1 | 11.8 | 11.1 | 0.7 | 5.9 | | Q162-2 | 9.0 | 8.4 | 0.6 | 6.7 | | Q162-3 | 8.5 | 8.3 | 0.2 | 2.4 | | Q163 | 8.5 | 9.0 | -0.5 | 5.9 | | Q163-1 | 3.0 | 3.5 | -0.5 | 16.7 | | Q163-2 | 6.9 | 7.5 | -0.6 | 8.7 | | Q163-3 | 8.2 | 8.6 | -0.4 | 4.9 | | Q163-4 | 4.0 | 4.5 | -0.5 | 12.5 | | Q163-5 | 2.6 | 2.2 | 0.4 | 15.4 | | Q164 | 10.7 | 10.1 | 0.6 | 5.6 | | Q164-1 | 8.0 | 8.5 | -0.5 | 6.3 | | Q164-2 | 8.8 | 8.2 | 0.6 | 6.8 | | Q164-3 | 3.6 | 3.1 | 0.5 | 13.9 | | Q164-4 | 12.1 | 13.1 | -1.0 | 8.3 | | 验证井 | Q2-3 | 4.8 | 5.5 | -0.7 | 14.6 | | Q2-5 | 9.6 | 8.6 | 1.0 | 10.4 | | Q2-9 | 17.4 | 15.8 | 1.6 | 9.2 | | Q2-11 | 6.6 | 7.5 | -0.9 | 13.6 | | Q2-13 | 8.2 | 7.1 | 1.1 | 13.4 | | Q3-1 | 4.0 | 4.6 | -0.6 | 15.0 | | Q3-2 | 3.4 | 2.4 | 1.0 | 29.4 | | Q3-3 | 5.6 | 6.3 | -0.7 | 12.5 |
|
Statistics of sandstone thickness coincidence rate of SMI inversion
|
| [1] |
杨华童, 林小兵, 张萱, 等. 塔里木盆地牙哈地区巴什基奇克组水下分流河道迁移叠置演化规律及地质意义[J]. 特种油气藏, 2024, 31(2):93-102.
|
| [1] |
Yang H T, Lin X B, Zhang X, et al. Evolution of migration and superposition of underwater distributary channel of Bashi Kichik Formation in Yaha area of Tarim Basin and its geological significance[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2024, 31(2):93-102.
|
| [2] |
雷涛, 莫松宇, 李晓慧, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地气田二叠系山西组砂体叠置模式及油气开发意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(2):147-159.
|
| [2] |
Lei T, Mo S Y, Li X H, et al. Sand body superposition model of Permian Shanxi formation in Daniudi gas field of Ordos basin and its significance for oil and gas development[J]. China Industrial Economics, 2024, 36(2):147-159.
|
| [3] |
张雨欣, 李长洪, 沈文洁, 等. 长庆油田上古生界河流相砂岩叠置模式研究及其在提高水平井储层钻遇率中的应用[J]. 录井工程, 2023, 34(2):129-138.
|
| [3] |
Zhang Y X, Li C H, Shen W J, et al. Study on superimposed patterns of upper Paleozoic fluvial sand bodies and its application in improving reservoir drilling rate of horizontal wells in Changqing Oilfield[J]. Mud Logging Engineering, 2023, 34(2):129-138.
|
| [4] |
邓守伟, 范晶, 王颖. 松辽盆地南部中浅层石油地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 24(2):33-42.
|
| [4] |
Deng S W, Fan J, Wang Y. The geological conditions,resource potential,and exploration direction of oil of middle-shallow layers in the southern Songliao Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2019, 24(2):33-42.
|
| [5] |
Mallat S, Zhang Z. Adaptive time-frequency transform[C]// IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech,and Signal Processing,1993.
|
| [6] |
Pinnegar C R, Mansinha L. The S-transform with windows of arbitrary and varying shape[J]. Geophysics, 2003, 68(1):381-385.
|
| [7] |
Puryear C I, Castagna J P. Layer-thickness determination and stratigraphic interpretation using spectral inversion:Theory and application[J]. Geophysics, 2008, 73(2):R37-R48.
|
| [8] |
Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4):1289-1306.
|
| [9] |
张珩, 王建立, 李文滨, 等. 基于压缩感知和反演理论的储层预测研究[J]. 石油物探, 2022, 61(6):1028-1034.
|
| [9] |
Zhang H, Wang J L, Li W B, et al. Reservoir prediction based on compressed sensing and inversion theory[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2022, 61(6):1028-1034.
|
| [10] |
袁萌, 蒲勇, 缪志伟, 等. 涪陵地区凉高山组多期叠置河道砂岩叠前高精度识别及预测[C]// 中国石油学会天然气专业委员会,第33届全国天然气学术年会论文集(01地质勘探),2023.
|
| [10] |
Yuan M, Pu Y, Miao Z W, et al. Pre-stack high-precision identification and prediction of multi-period superimposed river sandstone in the Lianggao Mountain group in Fuling region[C]// Proceedings of the 33rd National Natural Gas Academic Annual Conference of China Petroleum Society (01 Geological Exploration),2023.
|
| [11] |
袁川洲, 尹成, 王午琪, 等. 基于改进的积分展开相位谱识别砂岩叠置区[C]// 中国地球物理学会油气地球物理专业委员会,第五届油气地球物理学术年会论文集, 2023.
|
| [11] |
Yuan C Z, Yin C, Wang W Q, et al. Sandstone superposition identification based on improved integral phase spectrum[C]// Proceedings of the 5th Annual Conference of Petroleum and Gas Geophysics of China Geological Society of Exploration, 2023.
|
| [12] |
赵百强, 尹成, 王午琪, 等. 调谐厚度下薄互层叠置砂岩的响应特征与敏感属性分析[C]// 中国地球物理学会油气地球物理专业委员会,第五届油气地球物理学术年会论文集, 2023.
|
| [12] |
Zhao B Q, Yin C, Wang W Q, et al. Response characteristics and sensitive attribute analysis of thin interbedded sandstone in superposition zone under tuning thickness[C]// Proceedings of the 5th Annual Conference of Petroleum and Gas Geophysics of the Geophysical Society of China, 2023.
|
| [13] |
石岩, 李国良, 李玉英, 等. 层状分频构形反演技术的研究与应用——以苏76区块为例[J]. 录井工程, 2023, 34(2):123-128.
|
| [13] |
Shi Y, Li G L, Li Y Y, et al. Research and application of layered frequency-division configuration inversion technology:A case study of Su 76 block[J]. Mud Logging Engineering, 2023, 34(2):123-128.
|
| [14] |
程雯泽, 尹成, 袁川洲, 等. 典型河流相叠置砂岩构型的地震相位特征分析[J]. 石油物探, 2023, 62(6):1115-1125.
|
| [14] |
Cheng W Z, Yin C, Yuan C Z, et al. Seismic phases of typical superimposed fluvial sandstone architectures[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2023, 62(6):1115-1125.
|
| [15] |
陈彦虎. 地震波形指示反演方法、原理及其应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.
|
| [15] |
Chen Y H. Method, principle and application of seismic waveform indication inversion[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2020.
|
| [16] |
陈彦虎, 陈佳. 波形指示反演在煤层屏蔽薄砂岩分布预测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1254-1261.
|
| [16] |
Chen Y H, Chen J. The application of seismic meme inversion to thin sand distribution prediction under coal shield[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1254-1261.
|
| [17] |
顾雯, 章雄, 徐敏, 等. 强屏蔽下薄储层高精度预测研究——以松辽盆地三肇凹陷为例[J]. 石油物探, 2017, 56(3):439-448.
|
| [17] |
Gu W, Zhang X, Xu M, et al. High precision prediction of thin reservoir under strong shielding effect and its application:A case study from Sanzhao Depression,Songliao Basin[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2017, 56(3):439-448.
|
| [18] |
陈彦虎, 毕建军, 邱小斌, 等. 地震波形指示反演方法及其应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(6):1149-1158.
|
| [18] |
Chen Y H, Bi J J, Qiu X B, et al. A method of seismic meme inversion and its application[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(6):1149-1158.
|
| [19] |
卢宝坤, 史謌. 测井资料与地震属性关系研究综述[J]. 北京大学学报:自然科学版, 2005, 41(1):154-160.
|
| [19] |
Lu B K, Shi G. A review of study on relation between well logging data and seismic attributes[J]. Acta Scicentiarum Naturalum Universitis Pekinesis, 2005, 41(1):154-160.
|
| [20] |
王俊, 鲍志东, 王云龙, 等. 松辽盆地南部乾安地区上白垩统青三段高分辨率层序地层及沉积特征[J]. 古地理学报, 2017, 19(2):327-340.
|
| [20] |
Wang J, Bao Z D, Wang Y L, et al. High-resolution sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary characteristics of the Member 3 of Qingshankou Formation of Upper Cretaceous in Qian'an area,south Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography:Chinese Edition, 2017, 19(2):327-340.
|
| [21] |
王俊, 赵家宏, 腾军, 等. 浅水三角洲前缘砂岩地震沉积学研究——以松南乾安地区上白垩统青三段为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(3):570-583.
|
| [21] |
Wang J, Zhao J H, Teng J, et al. Seismic sedimentology research on shallow water Delta Front Sandbodies:A case study on Member 3 of upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in Qian'an area,south Songliao Basin,NE China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(3):570-583.
|
| [1] |
GAO Jun, XU Rui, HUANG Jia-Chen, YUAN Shu-Jin. Feature identification model and seismic reservoir prediction of channel turbidite bodies: A case study of the MC block,Lower Congo Basin,West Africa[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(4): 919-924. |
| [2] |
WANG Shu, WANG Rui, YANG Jia-Yi, ZHAO Wei-Sheng, LIAO Jian. High-resolution direct inversion of Poisson's impedance and fracture parameters using prestack seismic anisotropy data based on the non-stationary convolution model[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(3): 642-652. |
|
|
|
|

