|
|
|
| REE geochemical anomalies in soils of the Ximeng-Lancang area in southwestern Yunnan and their discovery and their implications for ore prospecting |
XIE Kui-Rui1,2( ), SONG Xu-Feng1,2, ZHOU Kun1,3, ZHOU Yu-Guo2,4( ), SONG Xu-Feng1,2, ZHOU Kun1,3, ZHOU Yu-Guo2,4( ), SHE Zhong-Ming5, TANG Jian1,2 ), SHE Zhong-Ming5, TANG Jian1,2 |
1. Yunnan Institute of Geological Survey, Kunming 650214, China
2. Key Laboratory of Sanjiang Metallogeny and Resources Exploration and Utilization,Ministry of Natural Resources, Kunming 650061, China
3. Yunnan Nuclear Industry Geological Survey Institute, Kunming 650106, China
4. School of Earth Science, Yunnan University, Kunming 650091, China
5. Yunnan Geological Exploration Fund Management Center, Kunming 650224, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Ximeng-Lancang area in southwestern Yunnan resides in the southern section of the Nujiang-Lancangjiang-Jinshajiang orogenic belt in Southwest China. The 1∶50,000 geochemical soil survey revealed 24 rare-earth-element (REE) geochemical anomalies, which are primarily distributed in the Carboniferous Pingzhang Formation mafic volcanic rocks and the Carboniferous-Permian Yutangzhai Formation sedimentary carbonate rocks within and near the Changning-Menglian deep fault zone. Furthermore, the AP00 REE geochemical anomalies ranking high in the evaluation were analyzed in detail through a 1∶10,000 geochemical soil survey, a 1∶10,000 special geological survey, and light-duty prospecting engineering in mountainous areas. A new type of REE ores in weathering crusts has been first discovered in sedimentary carbonate strata, with preliminarily estimated REE resources reaching a medium scale, suggesting a prospecting breakthrough. This finding shows a new prospecting approach, which can be referenced for similar research. As revealed by a comprehensive analysis of the regional geological and geochemical settings and the data of AP00 REE anomalies, the AP00 REE ores in weathering crusts have undergone a gradual enrichment and mineralization process involving four different geological processes, suggesting polygenetic compound REE ores. Considering the low leaching efficiency of AP00 REE ores and significant structural (magmatic) superimposed mineralization of the heavy REE yttrium, it is inferred that yttrium-dominated primary REE ores might exist in the deep part, implying high potential for heavy-REE ores.
|
|
Received: 14 January 2022
Published: 27 June 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
6])
">
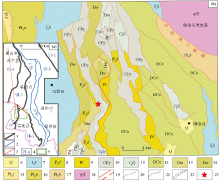
|
Geological map of Ximeng-Lancang area (simplified revision according to reference[6])
|

| 地层单元 | 参数 | Y | La | Ce | Eu | Tb | Yb | REE | | N-Q | 平均值 | 35.2 | 49.5 | 97.1 | 1.65 | 1.27 | 3.91 | 193 | | 富集系数 | 1.17 | 1.09 | 1.03 | 1.19 | 1.09 | 1.18 | 1.07 | | J | 平均值 | 21.5 | 37.0 | 76.0 | 1.09 | 0.84 | 2.47 | 141 | | 富集系数 | 0.71 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.75 | 0.78 | | P | 平均值 | 45.8 | 46.8 | 99.3 | 1.71 | 1.37 | 4.61 | 207 | | 富集系数 | 1.52 | 1.03 | 1.06 | 1.23 | 1.17 | 1.39 | 1.15 | | CPy | 平均值 | 169 | 101 | 137 | 3.53 | 3.45 | 9.10 | 442 | | 富集系数 | 5.62 | 2.22 | 1.46 | 2.54 | 2.94 | 2.75 | 2.45 | | | 平均值 | 63.1 | 75.3 | 145 | 3.37 | 2.34 | 5.18 | 305 | | 富集系数 | 2.09 | 1.66 | 1.54 | 2.43 | 2.00 | 1.56 | 1.70 | | DC | 平均值 | 18.2 | 32.9 | 74.1 | 0.88 | 0.71 | 2.16 | 131 | | 富集系数 | 0.60 | 0.72 | 0.79 | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.65 | 0.73 | | D | 平均值 | 41.3 | 53.3 | 102 | 1.76 | 1.45 | 4.70 | 207 | | 富集系数 | 1.37 | 1.17 | 1.08 | 1.26 | 1.24 | 1.42 | 1.15 | | Pt3 | 平均值 | 30.5 | 49.5 | 111 | 1.69 | 1.37 | 3.13 | 202 | | 富集系数 | 1.01 | 1.09 | 1.19 | 1.22 | 1.17 | 0.95 | 1.12 | | Pt2 | 平均值 | 23.9 | 42.5 | 90.8 | 1.41 | 1.19 | 2.15 | 163 | | 富集系数 | 0.79 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 1.01 | 1.01 | 0.65 | 0.90 | | ηγT | 平均值 | 34.1 | 50.0 | 122 | 0.95 | 1.49 | 2.67 | 214 | | 富集系数 | 1.13 | 1.10 | 1.29 | 0.69 | 1.27 | 0.81 | 1.19 | | 全区 | 平均值 | 30.1 | 45.4 | 94.0 | 1.39 | 1.17 | 3.13 | 180 | | 中国土壤[20] | 平均值 | 23.0 | 38.0 | 72.0 | 1.20 | 0.80 | 2.60 | 138 |
|
Content characteristics of soil rare earth elements in various geological units and the whole region in Ximeng-Lancang area[19]
|
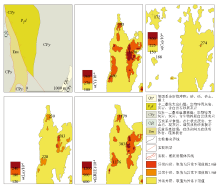
|
Main ore-forming elements and total rare earth elements anomaly analysis in AP00 rare earth anomaly
|

| 地质层位 | ∑REE均值/10-6 | | 矿(化)区风化壳 | 稀土矿化层 | 640 | | 鱼塘寨组碳酸盐岩 | 风化层 | 546 | | 基岩 | 485 | | 大名山组碳酸盐岩 | 风化层 | 259 | | 基岩 | 211 |
|
Content comparison of ∑REE in different geological layers in AP00 anomaly area[6]
|
| [1] |
王学求, 周建, 迟清华, 等. 中国稀土元素地球化学背景与远景区优选[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(6):747-758.
|
| [1] |
Wang X Q, Zhou J, Chi Q H, et al. Geochemical background and distribution of rare earth elements in China:Implications for potential prospects[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2020, 41(6):747-758.
|
| [2] |
刘殿蕊. 云南宣威地区峨眉山玄武岩风化壳中发现铌、稀土矿[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(2):540-541.
|
| [2] |
Liu D R. Nb and REE deposits found in the weathering crusts of Emeishan basalt,Xuanwei area,Yunnan Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(2):540-541.
|
| [3] |
杨瑞东, 王伟, 鲍淼, 等. 贵州赫章二叠系玄武岩顶部稀土矿床地球化学特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(S1):205-208.
|
| [3] |
Yang R D, Wang W, Bao M, et al. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth deposits at the top of Permian basalt in Hezhang,Guizhou[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2006, 25(S1):205-208.
|
| [4] |
曾凯, 李朗田, 祝向平, 等. 滇西勐往—曼卖地区离子吸附型稀土矿成矿规律与找矿潜力[J]. 地质与勘探, 2019, 55(1):19-29.
|
| [4] |
Zeng K, Li L T, Zhu X P, et al. The metallogenic regularity and prospecting potential of rare-earth deposits of ion-adsorbent type in the Mengwang-manmai area,western Yunnan[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2019, 55(1):19-29.
|
| [5] |
罗云平, 龚洪波, 田犁平, 等. 澜沧县富东花岗岩风化壳稀土矿特征[J]. 云南地质, 2016, 35(2):235-238.
|
| [5] |
Luo Y P, Gong H B, Tian L P, et al. The ree deposit feature of fudong granite weathering crust in Lancang[J]. Yunnan Geology, 2016, 35(2):235-238.
|
| [6] |
柏杨, 毕晓路, 钏文韬, 等. 云南省1∶5万澜沧县募乃老厂勐梭矿产地质调查报告[R]. 云南省地质调查院, 2020.
|
| [6] |
Bo Y, Bi X L, Chuan W T, et al. 1∶50,000 Lantcang County Mengsu mineral geological survey report,Yunnan Province[R]. Yunnan Institute of Geological Survey, 2020.
|
| [7] |
周余国, 张帆, 周坤, 等. 滇中富民县宝石洞旅游地质特征与成景机制探讨[J]. 高校地质学报, 2021, 27(4):480-488.
|
| [7] |
Zhou Y G, Zhang F, Zhou K, et al. Discussion on geological characteristics and landscaping mechanism of gemstone cave in Fumin County,central Yunnan[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2021, 27(4):480-488.
|
| [8] |
张克信, 王国灿, 洪汉烈, 等. 青藏高原新生代隆升研究现状[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(1):1-18.
|
| [8] |
Zhang K X, Wang G C, Hong H L, et al. The study of the Cenozoic uplift in the Tibetan Plateau:A review[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(1):1-18.
|
| [9] |
Mantle G W, Collins W J. Quantifying crustal thickness variations in evolving orogens:Correlation between arc basalt composition and Moho depth[J]. Geology, 2008, 36(1):87-90.
|
| [10] |
Chapman J B, Ducea M N, DeCelles P G, et al. Tracking changes in crustal thickness during orogenic evolution with Sr/Y:An example from the North American Cordillera[J]. Geology, 2015, 43(10):919-922.
|
| [11] |
Profeta L, Ducea M N, Chapman J B, et al. Quantifying crustal thickness over time in magmatic arcs[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015,5:17786.
|
| [12] |
胡懿灵, 刘治博, 王根厚, 等. 藏北双湖地区早白垩世晚期赞宗错安山岩:青藏高原早期隆升的时间约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(7):2173-2188.
|
| [12] |
Hu Y L, Liu Z B, Wang G H, et al. Late Early Cretaceous andesites at Zanzong Co area in Shuanghu County,northern Tibet:Chronological constraints for early uplift of Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(7):2173-2188.
|
| [13] |
Murphy M A, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. Did the Indo-Asian collision alone create the Tibetan Plateau?[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(8):719.
|
| [14] |
Yin A, Harrison T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000,28:211-280.
|
| [15] |
Kapp P, Yin A, Manning C E, et al. Tectonic evolution of the early Mesozoic blueschist-bearing Qiangtang metamorphic belt,central Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(4):1043.
|
| [16] |
Kapp P, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. Cretaceous-Tertiary shortening,basin development,and volcanism in central Tibet[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2005, 117(7):865.
|
| [17] |
王成善, 朱利东, 刘志飞. 青藏高原北部盆地构造沉积演化与高原向北生长过程[J]. 地球科学进展, 2004, 19(3):373-381.
|
| [17] |
Wang C S, Zhu L D, Liu Z F. Tectonic and sedimentary evolution of basins in the north of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and northward growing process of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2004, 19(3):373-381.
|
| [18] |
Volkmer J E, Kapp P, Guynn J H, et al. Cretaceous-Tertiary structural evolution of the north central Lhasa terrane,Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 2007, 26(6):TC6007.
|
| [19] |
谢岿锐, 付彦平. 云南省1∶5万澜沧县募乃老厂勐梭矿产地质调查土壤地球化学测量报告[R]. 云南省地质调查院, 2020.
|
| [19] |
Xie K R, Fu Y P. Soil geochemical survey report of 1∶ 50,000 Mengsu mineral geological survey,Mengnai Laochang,Lancang County,Yunnan Province[R]. Yunnan Institute of Geological Survey, 2020.
|
| [20] |
迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007.
|
| [20] |
Chi Q H, Yan M C. Handbook of elemental abundance for applied geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007.
|
| [21] |
《矿产资源工业要求手册》编委会. 矿产资源工业要求手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012.
|
| [21] |
Editorial Board of the Mineral Resources Industry Requirements Manual. Mineral resources industry requirements manual[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2012.
|
| [22] |
曹德斌. 滇西昌宁—孟连带古特提斯盆地的地层层序及盆地演化[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2005.
|
| [22] |
Cao D B. Stratigraphic sequence and basin evolution of Changning-Menglian Paleotethys Basin in western Yunnan[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2005.
|
| [23] |
晏中海, 邓祖林, 林洋. 云南双江701地区铀矿化特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代矿业, 2016, 32(12):108-109,112.
|
| [23] |
Yan Z H, Deng Z L, Lin Y. Uranium mineralization characteristics and prospecting prospect in Shuangjiang 701 area,Yunnan Province[J]. Modern Mining, 2016, 32(12):108-109,112.
|
| [24] |
李峰, 陈珲, 鲁文举, 等. 云南澜沧老厂花岗斑岩形成年龄及地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2010, 34(1):84-91.
|
| [24] |
Li F, Chen H, Lu W J, et al. Rock-forming ages of the Laochang granite-porphyry,Lancang,Yunnan and their geological significance[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2010, 34(1):84-91.
|
| [25] |
崔康成. 大麻哈鱼类保护区生境要素与功能区划[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2019.
|
| [25] |
Cui K C. Habitat elements of class salmon and functional division of protected areas[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2019.
|
| [1] |
GAO Peng-Li, REN Da-Lu, LI Chao-Hui, FENG Zhi-Qiang, MIAO Hong-Yun, QIAO Lin, WANG Jian-Wu, YANG Yong-Liang, ZHANG Li-Ming, LI Guang-Hui. Predicting the spatial distribution of soil organic matter using the model consisting of the Boruta algorithm and the optimized GA combined with the geostatistical method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3): 747-758. |
| [2] |
HAN Bing, HUANG Yong, LI Huan, AN Yong-Long. Distributions, enrichment characteristics, and sources of heavy metals in soils in Fangshan District, Beijing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3): 820-833. |
|
|
|
|

