|
|
|
| Application of the opposing coils transient electromagnetic method in a shallow groundwater-rich area: A case study of Xiacun Town, Xinyu City |
ZHU Xiao-Wei1( ), DING Chen2( ), DING Chen2( ), XUE Kai-Xi3, CHEN Jun3, HAN Kai-Min4, LUO Qiang1, YI Guang-Sheng3 ), XUE Kai-Xi3, CHEN Jun3, HAN Kai-Min4, LUO Qiang1, YI Guang-Sheng3 |
1. Jiangxi Building Materials Product Quality Supervision and Inspection Station Co. Ltd., Nanchang 330001, China
2. College of Civil and Transportation Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
3. School of Civil & Architecture Engineering, East China University of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China
4. School of Architectural Engineering, Guangzhou City Construction College, Guangzhou 510925, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Unfavorable geobodies such as Karsts, weak soil, and water-rich areas are extensively distributed in China. Under heavy rainfall, they are prone to geologic hazards like collapse. A severe geological collapse occurred in Xiacun Town, Yushui District, Xinyu City, near the Shanghai-Kunming high-speed railway. The space around the collapsed foundation pit was limited, with many interference sources like underground pipelines. With early signals subjected to the mutual inductance effects of receiver and transmitter coils, the conventional transient electromagnetic method exhibited low detection accuracy and anti-interference ability, encountering significant shallow blind zones. To locate unfavorable geobodies in the study area and provide suggestions for the prevention and control of geologic hazards, this study innovatively applied the opposing-coils transient electromagnetic method (OCTEM), supplemented by borehole-based verification. The results show that: (1) The OCTEM exhibited high accuracy, as demonstrated by the high consistency between the geophysical exploration results and the drilling results of the study area; (2) The low-resistivity zone spread across the study area, and the low-resistivity anomalies revealed by geophysical exploration were caused by groundwater according to borehole-based verification; (3) The strata from top to bottom were composed of soft plastic silty clay, hard plastic silty clay, soft plastic silty clay, and moderately weathered limestones; (4) The subsurface micro-confined water in the collapse area surged upward, gradually eroding the soft plastic silty clay layer around the area. The static water level in the collapsed foundation pit manifested an elevation of 55.60 m, located approximately 1.4 m below the surface; (5) A groundwater channel existed under the collapse area, with soil caves formed in the limestone layer under the prolonged erosion effect of water flow; (6) Long-term groundwater extraction may expand the underground seepage zone; (7) The administrative department in charge must promptly contain groundwater in the collapse area to prevent it from further eroding the surrounding unconsolidated soil layer.
|
|
Received: 27 December 2023
Published: 21 October 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
The ground collapse scene
|
|
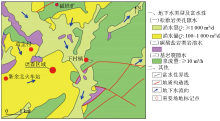
Hydrogeological diagram of Xiachun Town and nearby area
|
|
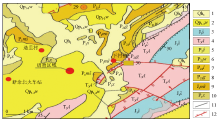
Schematic diagram of engineering geology of Xiacun Town and nearby area
1 —clay layer containing sand gravel layer (slope deposit, residual deposit); 2—loam, sand gravel (alluvial); 3—Shuibei Formation: quartzite, sandy shale; 4—Anyuan Group: fine sand, siltstone; 5—limestone, dolomite; 6—Wangpanli member: sandstone, mudstone; 7—Laoshan member: sandstone, mudstone; 8—Guanshan member: arkose quartzite, siltstone; 9—Mingshan Formation: siliceous rock, shale; 10—Xiaojiangbian Formation: nodular limestone, dolomite; 11—geological boundary; 12—tectonic line
|
16]
">
|
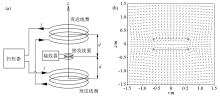
OCTEM device schematic(a) and primary field magnetic field lines synthesized by OCTEM two-coil source (b)[16]
|

|
The field work of opposing coils transient electromagnetic method
|
|
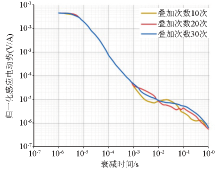
Secondary field attenuation voltage curves corresponding to different stacking ties
|
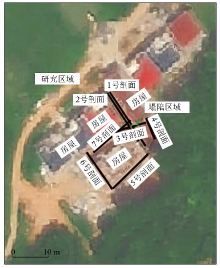
|
Layout of OCTEM measuring points on the project site
|
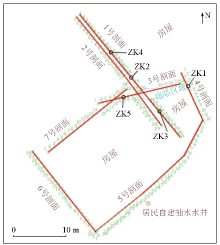
|
OCTEM measuring points and drilling position layout
|
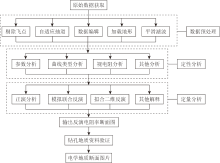
|
Data processing flow chart of OCTEM
|
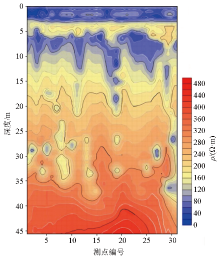
|
Profile of inversion of survey line No.1
|
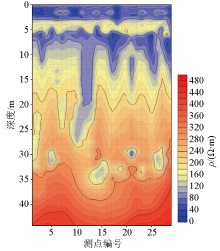
|
Profile of inversion of survey line No. 2
|
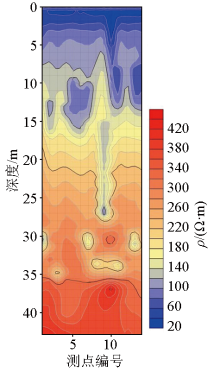
|
Profile of inversion of survey line No. 3
|

|
Profile of inversion of survey line No. 4
|
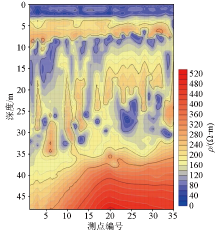
|
Profile of inversion of survey line No. 5
|
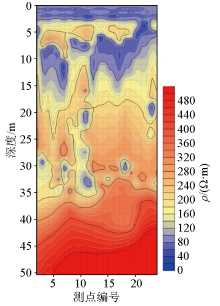
|
Profile of inversion of survey line No. 6
|
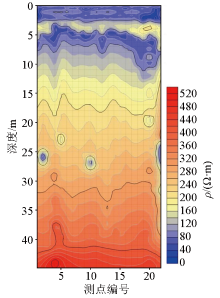
|
Profile of inversion of survey line No. 7
|
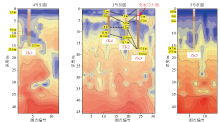
|
Results of geophysical exploration section and borehole column chart
|
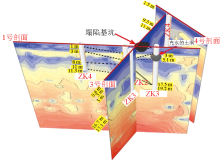
|
Geophysical inversion map and 3D comparison of borehole
|

| 钻孔编号 | 孔深/m | 孔口高程/m | 地层埋深/m | 岩性 | 地下水位
稳定深度/m | | ZK1 | 15.6 | 57.38 | 0~1.5 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,软弱可塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,零星可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状 | 1.78 | | 1.5~9.5 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,硬可塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,零星可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有砂岩细砂砾 | | 9.5~11.0 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,软弱可塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,零星可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有砂岩、石英岩等细砂砾 | | 11.0~15.3 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,软塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有砂岩、石英岩、花岗岩等中粗砂 | | 15.3~15.6 | 中风化石灰岩:青灰色,隐晶质结构,薄中厚层状构造,矿物成分以碳酸钙为主,节理裂隙较发育,钙质充填,局部有溶蚀现象,岩心多呈现短柱状,局部呈现块状,少量长柱状,锤击声脆 | | ZK2 | 13.7 | 56.95 | 0~3.0 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,软弱可塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,零星可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状 | 1.35 | | 3.0~5.9 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,硬可塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,零星可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有砂岩细砂砾 | | 5.9~8.2 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,软弱可塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有砂岩、石英岩等细砂砾 | | 8.2~12.8 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,软塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,可见较多铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有砂岩、石英岩、浅色变质岩等中粗砂 | | 12.8~13.7 | 中风化石灰岩:青灰色,隐晶质结构,薄中厚层状构造,矿物成分以碳酸钙为主,节理裂隙较发育,钙质充填,局部有溶蚀现象,岩心多呈现短柱状,局部呈现块状,少量长柱状,锤击声脆 | | ZK3 | 19.2 | 57.36 | 0~3.0 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,软弱可塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,零星可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状 | 1.76 | | 3.0~5.1 | 土洞:地下水填充 | | 5.1~17.5 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,软塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,可见较多铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有花岗岩、浅色变质岩等中粗砂 | | 17.5~19.2 | 中风化石灰岩:青灰色,隐晶质结构,薄中厚层状构造,矿物成分以碳酸钙为主,节理裂隙较发育,钙质充填,局部有溶蚀现象,岩心多呈现短柱状,局部呈现块状,少量长柱状,锤击声脆 | | ZK4 | 11.3 | 56.77 | 0~1.0 | 素填土:浅灰色或浅红色,结构松散,均匀性较差,主要成分为粘性土,局部含有砾石和碎石,还有少量砼块,砂砾为近期平整场地所至,砼块为民房旧居拆除遗留 | 1.37 | | 1.0~3.0 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,软弱可塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,零星可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有砂岩细砂砾 | | ZK4 | 11.3 | 56.77 | 3.0~8.0 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,硬可塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,零星可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有砂岩、石英岩等细砂砾 | 1.37 | | 8.0~11.0 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,软塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有石英岩、花岗岩等中粗砂 | | 11.0~11.3 | 中风化石灰岩:青灰色,隐晶质结构,薄中厚层状构造,矿物成分以碳酸钙为主,节理裂隙较发育,钙质充填,局部有溶蚀现象,岩心多呈现短柱状,局部呈现块状,少量长柱状,锤击声脆 | | ZK5 | 17.3 | 56.88 | 0~0.8 | 素填土:浅灰色或浅红色,结构松散,均匀性较差,主要成分为粘性土,局部含有砾石和碎石,还有少量砼块,砂砾为近期平整场地所至,砼块为民房旧居拆除遗留 | 1.28 | | 0.8~3.0 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,软弱可塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,零星可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有砂岩细砂砾 | | 3.0~5.0 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,硬可塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,零星可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有砂岩、石英岩等细砂砾 | | 5.0~16.7 | 粉质黏土:浅灰色,褐黄色,软塑,切面光滑,稍有光泽,韧性中等,干强度中等,可见铁锰质结合及高岭土团块,形态主要呈现为黏、粉粒状,局部含有石英岩、花岗岩等中粗砂 | | 16.7-17.3 | 中风化石灰岩:青灰色,隐晶质结构,薄中厚层状构造,矿物成分以碳酸钙为主,节理裂隙较发育,钙质充填,局部有溶蚀现象,岩心多呈现短柱状,局部呈现块状,少量长柱状,锤击声脆 |
|
Geological drilling data statistics in the study area
|
| [1] |
Gaur V P, Kar S K, Srivastava M. Development of ground fissures: A case study from southern parts of Uttar Pradesh,India[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 2015, 86(6):671-678.

|
| [2] |
吴超凡, 邱占林, 杨为民, 等. 汶川地震诱发的地面塌陷成因[J]. 山地学报, 2012, 30(1):70-77.
|
| [2] |
Wu C F, Qiu Z L, Yang W M, et al. Cause of ground collapse triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Mountain Research, 2012, 30(1):70-77.
|
| [3] |
彭青阳. 综合物探方法在地面塌陷勘察中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2017, 14(1):31-36.
|
| [3] |
Peng Q Y. The application of integrated geophysical method toground collapse exploration[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2017, 14(1):31-36.
|
| [4] |
胡让全, 黄健民. 综合物探方法在广州市金沙洲岩溶地面塌陷、地面沉降地质灾害调查中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(3):610-615.
|
| [4] |
Hu R Q, Huang J M. The application of integrated geophysical techniquestothe investigation of Karst graound collapse and ground subsidence in Jingshazhou area,Guangzhou City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(3):610-615.
|
| [5] |
龚培俐, 李维. 瞬变电磁法在采空塌陷灾害中的应用——以神东煤矿采空区调查为例[J]. 地质力学学报, 2018, 24(3):416-423.
|
| [5] |
Gong P L, Li W. Application of transient electromagnetic method in collapse hazard of goaf:Take the investigation of the goaf in Shendong coal mine as an example[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2018, 24(3):416-423.
|
| [6] |
Ba X Z, Li L P, Wang J, et al. Near-surface site investigation and imaging of Karst cave using comprehensive geophysical and laser scanning:A case study in Shandong,China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2020, 79(12):298.
|
| [7] |
陈健强, 李雁川, 田浩, 等. 含水采空区全空间瞬变电磁响应分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(2):546-550.
|
| [7] |
Chen J Q, Li Y C, Tian H, et al. Whole-space transient electromagnetic detection of water-bearing goaf[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2):546-550.
|
| [8] |
Liu R, Sun H F, Qin J W, et al. A multi-geophysical approach to assess potential sinkholes in an urban area[J]. Engineering Geology, 2023,318:107100.
|
| [9] |
Wang J, Zhang X P, Du L Z, et al. Comparing methods of 3D acquisition of simulated multi-electrode resistivity data using TOPSIS[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2018,159:631-639.
|
| [10] |
谢嘉, 刘洋, 李兴强, 等. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在岩溶塌陷区探测应用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(3):212-218,226.
|
| [10] |
Xie J, Liu Y, Li X Q, et al. The application of Opposing Coils Transient Electromagnetics in the detection of Karst subsidence area[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(3):212-218,226.
|
| [11] |
Solla M, Pérez-Gracia V, Fontul S. A review of GPR application on transport infrastructures:Troubleshooting and best practices[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(4):672.
|
| [12] |
Börner R U. Numerical modelling in geo-electromagnetics:Advances and challenges[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2010, 31(2):225-245.
|
| [13] |
Kalscheuer T, Juhojuntti N, Vaittinen K. Two-dimensional magnetotelluric modelling of ore deposits:Improvements in model constraints by inclusion of borehole measurements[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2018, 39(3):467-507.
|
| [14] |
张帆, 冯国瑞, 戚庭野, 等. 瞬变电磁法勘探煤矿不同层间距双层积水采空区的可行性研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(5):1215-1225.
|
| [14] |
Zhang F, Feng G R, Qi T Y, et al. Feasibility of the transient electromagnetic method in the exploration of double-layer waterlogged goafs with different layer spacings in coal mines[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5):1215-1225.
|
| [15] |
高远. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在城镇地质灾害调查中的应用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(3):152-156.
|
| [15] |
Gao Y. The application of opposing coils transient electromagnetics method in geological hazard investigation of town[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2018, 46(3):152-156.
|
| [16] |
席振铢, 龙霞, 周胜, 等. 基于等值反磁通原理的浅层瞬变电磁法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(9):3428-3435.
|
| [16] |
Xi Z Z, Long X, Zhou S, et al. Opposing coils transient electromagnetic method forshallowsubsurfacedetection[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(9):3428-3435.
|
| [17] |
赖耀发. 基于等值反磁通的频率域电磁测深研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2022.
|
| [17] |
Lai Y F. Research on frequency domain electromagnetic sounding based on equivalent anti-flux[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2022.
|
| [18] |
姚富宝. 基于OCTEM法的城市道路塌陷地质病害风险评估[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2022.
|
| [18] |
Yao F B. Risk assessment of urban road collapse geological diseases based on OCTEM method[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2022.
|
| [19] |
赵虎, 王玲辉, 程强, 等. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁成像技术及工程应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(5):2244-2250.
|
| [19] |
Zhao H, Wang L H, Cheng Q, et al. Opposing coils transient electromagnetics imaging technology and engineering application[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(5):2244-2250.
|
| [20] |
王亮, 龙霞, 王婷婷, 等. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在城市浅层空洞探测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(5):1289-1295.
|
| [20] |
Wang L, Long X, Wang T T, et al. Application of theopposing-coils transient electromagnetic method in detectionofurbanshallowcavities[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5):1289-1295.
|
| [21] |
Xi Z Z, Long X, Huang L, et al. Opposing-coils transient electromagnetic method focused near-surface resolution[J]. Geophysics, 2016, 81(5):E279-E285.
|
| [22] |
何胜, 王万平, 董高峰, 等. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在城市地质调查中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(5):1379-1386.
|
| [22] |
He S, Wang W P, Dong G F, et al. Application of theopposing-coils transient electromagnetic method in urban geological surveys[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5):1379-1386.
|
| [23] |
肖皇屿. 基于BIM+GIS的地质灾害监测预警平台的研究与实现[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2021.
|
| [23] |
Xiao HY. Research and implementation of geological disaster monitoring and early warning platform based on BIM+GIS[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021.
|
| [24] |
Zhang J L, Xiang X B, Li W J. Advances in marine intelligent electromagnetic detection system,technology,and applications:A review[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(5):4312-4326.
|
| [25] |
Sun X M, Wang Y F, Yang X, et al. Three-dimensional transient electromagnetic inversion with optimal transport[J]. Journal of Inverse and Ill-Posed Problems, 2021, 30(4):549-565.
|
| [26] |
任喜荣, 李欣, 周志杰. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在金矿采空区探测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(2):540-546.
|
| [26] |
Ren X R, Li X, Zhou Z J. Application of the opposing coils transient electromagnetic method in investigation of mined-out areas of a gold deposit[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2):540-546.
|
| [27] |
Wang Y, Xi Z Z, Jiang H, et al. The application research on the detection of karst disease of airport runway based on OCTEM[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(2):360-363.
|
| [28] |
杨建明, 王洪昌, 沙椿. 基于等值反磁通瞬变电磁法的岩溶探测分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(4):846-850.
|
| [28] |
Yang J M, Wang H C, Sha C. An analysis of Karst exploration based on opposing coils transient electromagnetic method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(4):846-850.
|
| [29] |
Yang Y, Song X F, Zheng F D, et al. Simulation of fully coupled finite element analysis of nonlinear hydraulic properties in land subsidence due to groundwater pumping[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73(8):4191-4199.
|
| [30] |
Jia L, Meng Y, Li L J, et al. A multidisciplinary approach in cover-collapse sinkhole analyses in the mantle Karst from Guangzhou City (SE China)[J]. Natural Hazards, 2021, 108(1):1389-1410.
|
| [31] |
廖德武, 冉根领, 杜艳松, 等. 瞬变电磁法在岩溶地下水运移通道勘探中的应用研究[J]. 地下水, 2023, 45(6):136-139.
|
| [31] |
Liao D W, Ran G L, Du Y S, et al. Application of transient electromagnetic method in exploration of Karst groundwater migration channels[J]. Ground Water, 2023, 45(6):136-139.
|
| [32] |
吴群英, 胡雄武, 王宏科. 陕北矿区地下水资源地面瞬变电磁法探查实践[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2022, 50(5):208-215.
|
| [32] |
Wu Q Y, Hu X W, Wang H K. Exploration practice of ground transient electromagnetic method for groundwater resources in Northern Shaanxi coal mining area[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(5):208-215.
|
| [33] |
代昱昊, 王华, 彭桂彬. 基于TEM的玉磨铁路隧道渗漏水状态预测方法研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 40(7):88-92,144.
|
| [33] |
Dai Y H, Wang H, Peng GB. Prediction method of leakage state in the Yuxi-Mohan railway tunnel based on TEM[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University:Natural Science, 2021, 40(7):88-92,144.
|
| [34] |
Li R H, Hu X Y, Xu D, et al. Characterizing the 3D hydrogeological structure of a debris landslide using the transient electromagnetic method[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2020,175:103991.
|
| [1] |
LI Hai, ZHAO Pan, LI Ke-Ying, LIU Zheng. Deriving analytical solution of the pseudo wavefield from transient electromagnetic data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1193-1198. |
| [2] |
LI He, LI Xiu, QI Zhi-Peng, CAO Hua-Ke. Seismic prediction of unfavorable geobodies in tunnels using the borehole-roadway transient electromagnetic method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1215-1222. |
|
|
|
|

