|
|
|
| Factors influencing the application of ESPAC-based microtremor survey in shallow surface environments |
YANG Lang-Yong-Hang( ), LI Hong-Xing( ), LI Hong-Xing( ) ) |
| School of Geophysics and Measurement Technology,East China University of Technology,Nanchang 330013,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The extended spatial autocorrelation (ESPAC)-based microtremor exploration(natural-source surface wave exploration) technology has been extensively used in shallow formation exploration owing to its simplicity,efficiency,and accuracy.However,the imaging effect of dispersion energy extracted based on the ESPAC method is unsatisfactory in practical applications.In particular,different observation array arrangements influence the extraction of dispersion curves from collected data.By investigating the imaging principle of the ESPAC method,this study conducted the simulation experiment of natural-source microtremor recording through ambient noise simulation.It compared the differences in dispersion energy under various dominant frequency distributions of wavelets.Moreover,it quantitatively analyzed the influence of different station arrangements and acquisition durations on the imaging quality of dispersion energy.The comparative study reveals the imaging patterns of the ESPAC method in shallow surface exploration.The ESPAC method can maximize the imaging quality of dispersion energy in the fundamental mode while considering both efficiency and exploration costs.The results of this study were applied to engineering application cases to further verify the simulation results.
|
|
Received: 11 December 2023
Published: 21 October 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
Natural source surface wave exploration principle diagram
|
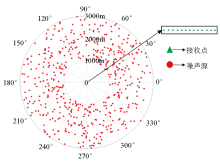
|
Noise source distribution
|

| 层状模型 | P波速度/
(m·s-1) | S波速度/
(m·s-1) | 密度/
(kg·m-3) | 厚度/m | | 第一层 | 800 | 200 | 2000 | 20 | | 第二层 | 1200 | 400 | 2000 | ∞ |
|
Model parameter
|
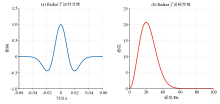
|
Rake wavelet with dominant frequency of 20 Hz
|
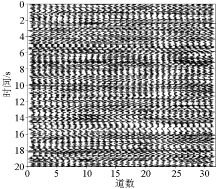
|
Analog acquisition records(31 stations,spacing of 2 m)
|
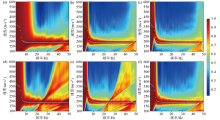
|
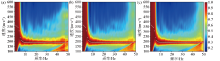
Comparison of dispersion diagrams of different station layouts
a—number of stations 11,spacing of 2 meters;b—number of stations 21,spacing of 2 meters;c—number of stations 31,spacing of 2 meters;d—number of stations 11,spacing of 4 meters;e—number of stations 16, spacing of 4 meters;f—number of stations 16, spacing of 2 meters;the white scatter represents the theoretical dispersion curve
|
|
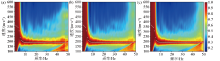
Comparison of dispersion diagrams with different acquisition durations
a—5 minutes collection time;b—10 minutes collection time;c—20 minutes collection time;number of stations 21,spacing of 2 meters;the white scatter represents the theoretical dispersion curve
|
|
Comparison of dispersion diagrams under different wavelet dominant frequencies
a—dominant frequency 1~10 Hz;b—dominant frequency 1~15 Hz;c—dominant frequency 1~20 Hz;number of stations 21,spacing of 2 meters;the white scatter represents the theoretical dispersion curve
|

| 岩性名称 | 视S波速度vs/(m·s-1) | | 换填石料(黄沙、垫层)、混凝土 | 100~400 | | 基岩 | 450~800 |
|
Physical parameters of different lithology
|
|
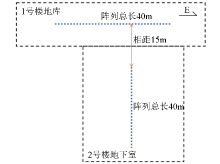
Schematic of survey line arrangement
|

| 楼号 | 测线位置 | 测线总长/m | 测线方向 | | 1号 | 地库(中间) | 40 | 西—东 | | 2号 | 地下室(中间) | 40 | 南—北 |
|
Layout of survey lines in Yinshanguanhu area
|
|
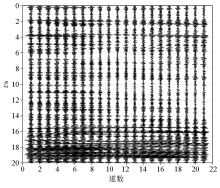
Noise recording segments
|
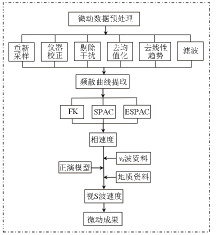
|
Flow chart of natural source surface wave data processing
|
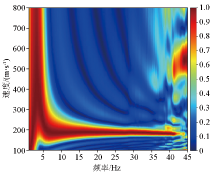
|
Measured dispersion
|
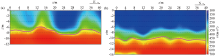
|
Inversion velocity structure
a—basement of building 1;b—basement of building 2
|
| [1] |
赵东. 被动源面波勘探方法与应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2010, 34(6):759-764.
|
| [1] |
Zhao D. Passive surface waves:Methods and applications[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 34(6):759-764.
|
| [2] |
王洪. 物探新技术——微动探测技术介绍[J]. 贵州地质, 2013, 30(1):75-77,60.
|
| [2] |
Wang H. A new geophysical technology:Microtremor survey technology[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2013, 30(1):75-77,60.
|
| [3] |
孙勇军, 徐佩芬, 凌甦群, 等. 微动勘查方法及其研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2009, 24(1):326-334.
|
| [3] |
Sun Y J, Xu P F, Ling S Q, et al. Microtremor survey method and its progress[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2009, 24(1):326-334.
|
| [4] |
王辉, 汶小岗, 李亮, 等. 微动探测方法研究及应用[J]. 陕西煤炭, 2022, 41(2):106-110,156.
|
| [4] |
Wang H, Wen X G, Li L, et al. Research and application of micro-motion detection method[J]. Shaanxi Coal, 2022, 41(2):106-110,156.
|
| [5] |
陈实, 金荣杰, 李延清, 等. 天然源面波勘探采集参数对比试验及工程应用[J]. 新疆地质, 2017, 35(4):483-488.
|
| [5] |
Chen S, Jin R J, Li Y Q, et al. Test and engineering application of acquisition parameters in natural source surface wave exploration[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2017, 35(4):483-488.
|
| [6] |
刘宏岳, 贺华. 复杂场地条件下的地球物理探测方法选择与工程实例[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2014, 11(2):155-159.
|
| [6] |
Liu H Y, He H. The geophysical methods choice under the complicated site condition and case study[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2014, 11(2):155-159.
|
| [7] |
赵雪然. 城市地下空间勘探中的微动技术研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020.
|
| [7] |
Zhao X R. Research on microseismic technology in urban underground space exploration[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020.
|
| [8] |
魏运浩, 李井冈, 姚运生. 微动台阵法探测地下结构的实验研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2015, 35(1):167-171.
|
| [8] |
Wei Y H, Li J G, Yao Y S. Experimental study on detecting the subsurface structure using microtremor array survey method[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2015, 35(1):167-171.
|
| [9] |
Capon J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1969, 57(8):1408-1418.
|
| [10] |
简文彬, 李哲生, 黄真萍, 等. 地基土层构造与地微动频率效应[M]. 南京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2002.
|
| [10] |
Jian W B, Li Z S, Huang Z P, et al. Soil structure and microtremor frequency effect[M]. Nanjing: China Construction Industry Press, 2002.
|
| [11] |
刘永勤, 廖远国, 李学专, 等. 微动探测技术在轨道交通工程勘察中的应用研究[J]. 工程勘察, 2010, 38(S1):1-11.
|
| [11] |
Liu Y Q, Liao Y G, Li X Z, et al. Research on the application of micro-motion detection technology in rail transit engineering investigation[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2010, 38(S1):1-11.
|
| [12] |
Aki K. Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves,with special reference to microtremors[J]. Bulletin of the Earthquake Research Institute, 1957,35:415-456.
|
| [13] |
Okada H. The microtremor survey method[C]// Tulsa: Society Exploration Geophysicists,2003:135.
|
| [14] |
Ling S, Okada H. An extended use of the spatial autocorrelation method for the estimation of geological structure using microtremors[C]// Proceedings of the 89th SEGJ Conference,1993:44-48.
|
| [15] |
Ohori M. A comparison of ESAC and FK methods of estimating phase velocity using arbitrarily shaped microtremor arrays[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2002, 92(6):2323-2332.
|
| [16] |
王继鑫. 基于微动勘探方法的浅层波速结构反演研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地壳应力研究所, 2020.
|
| [16] |
Wang J X. Inversion of shallow wave velocity structure based on microtremor exploration method[D]. Beijing: Institute of Crustal Stress,China Earthquake Administration, 2020.
|
| [17] |
甘棣元. 城市浅地表微动探测信号影响因素的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019.
|
| [17] |
Gan D Y. Study on the influencing factors of urban shallow surface micro-motion detection signal[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019.
|
| [18] |
贾辉, 陈义军, 王铁领, 等. 浅部地层微动勘探关键影响因素探讨[J]. 工程勘察, 2018, 46(9):68-73.
|
| [18] |
Jia H, Chen Y J, Wang T L, et al. Key factors of shallow stratum micro-tremor exploration[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2018, 46(9):68-73.
|
| [19] |
李凯. 面波勘探技术在工程勘察中的应用进展[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2011, 8(1):97-104.
|
| [19] |
Li K. Progress of surface wave exploration technology in engineering exploration[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2011, 8(1):97-104.
|
| [20] |
Okada H, Suto K. The microtremor survey method[M]. America: Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 2003.
|
| [21] |
鲁来玉. 基于平面波模型重访地震背景噪声互相关及空间自相关(SPAC)[J]. 地球与行星物理论评, 2021, 52(2):123-163.
|
| [21] |
Lu L Y. Revisiting the cross-correlation and SPatial AutoCorrelation (SPAC) of the seismic ambient noise based on the plane wave model[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 2021, 52(2):123-163.
|
| [22] |
徐宗博. 高频背景噪声波场模拟与面波成像[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2016.
|
| [22] |
Xu Z B. High-frequency background noise wave field simulation and surface wave imaging[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2016.
|
| [23] |
Park C B, Miller R D. Multichannel analysis of passive surface waves:Modeling and processing schemes[C]// Site Characterization and Modeling.Austin,Texas,USA.Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers,2005:23-26.
|
| [24] |
Lawrence J F, Denolle M, Seats K J, et al. A numeric evaluation of attenuation from ambient noise correlation functions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2013, 118(12):6134-6145.
|
| [25] |
范长丽, 贾慧涛, 蔡向阳. 微动在城区岩溶勘探中的效果研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2020, 17(5):652-657.
|
| [25] |
Fan C L, Jia H T, Cai X Y. Study on the effect of microtremor exploration in Karst exploration in urban area[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2020, 17(5):652-657.
|
| [26] |
于涵, 刘财, 王典, 等. 面波频散能量谱计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2022, 52(2):602-612.
|
| [26] |
Yu H, Liu C, Wang D, et al. Calculation method of surface wave dispersion energy spectrum[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2022, 52(2):602-612.
|
| [27] |
Ku T, Palanidoss S, Zhang Y H, et al. Practical configured microtremor array measurements(MAMs) for the geological investigation of underground space[J]. Underground Space, 2021, 6(3):240-251.
|
| [28] |
凡友华, 刘家琦, 肖柏勋. 计算瑞利波频散曲线的快速矢量传递算法[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版, 2002, 29(5):25-30.
|
| [28] |
Fan Y H, Liu J Q, Xiao B X. Fast vector-transfer algorithm for computation of Rayleigh wave dispersion curves[J]. Journal of Hunan University:Natural Science, 2002, 29(5):25-30.
|
| [29] |
韩飞. 高频瑞雷波法正反演研究及其在工程场地勘查中的应用[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017.
|
| [29] |
Han F. Forward and inversion research of high frequency Rayleigh wave method and its application in engineering site exploration[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017.
|
| [30] |
张莹莹, 王云专, 石颖, 等. 雷克子波频率研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(5):2162-2167.
|
| [30] |
Zhang Y Y, Wang Y Z, Shi Y, et al. Frequencies of the ricker wavelet[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(5):2162-2167.
|
| [31] |
程逢. 被动源面波勘探方法及其在城市地区的应用[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2018.
|
| [31] |
Cheng F. Passive source surface wave exploration method and its application in urban areas[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2018.
|
| [32] |
焦健. 基于空间自相关法的微动勘探技术的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012.
|
| [32] |
Jiao J. Research on microtremor exploration technology based on spatial autocorrelation method[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2012.
|
| [33] |
刘磊, 王斌战, 裴银, 等. SPAC方法在城市地热勘探中的应用[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2018, 32(3):447-452.
|
| [33] |
Liu L, Wang B Z, Pei Y, et al. Application of SPAC method in urban geothermal exploration[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018, 32(3):447-452.
|
| [34] |
王梦迟. 基于SPAC法天然源面波勘探技术研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018.
|
| [34] |
Wang M C. Research on natural source surface wave exploration technology based on SPAC method[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2018.
|
| [1] |
CHANG Jiang-Hao, XUE Jun-Jie, MENG Qing-Xin, ZHAO Peng. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of short-offset transient electromagnetic responses to water-rich bodies in coal mines[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1176-1184. |
| [2] |
JIA Bo, ZHANG Fu-Ming, ZHANG Li-Jun, LIU Hao-Hao, GUO Liang-Liang, SONG Wei, ZHANG Chao-Yang, HE Hai-Long, WANG Gang. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of grounded-source transient electromagnetic responses in roadways[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1185-1192. |
|
|
|
|

