|
|
|
| An exploration method for the radiation of ion adsorption-type rare earth element deposits based on multi-channel gamma-ray spectrometry: A case study of the Dechang area in the Panzhihua-Xichang region |
LI Huai-Yuan1,2( ), NIE Fei1( ), NIE Fei1( ), JIANG Shou-Jin1, HU Jun-Feng1, ZOU Jia-Zuo1, GUO Jin-Chen1 ), JIANG Shou-Jin1, HU Jun-Feng1, ZOU Jia-Zuo1, GUO Jin-Chen1 |
1. Civil-Military Integration Center of Geological Survey, China Geological Survey, Chengdu 610000,China
2. School of Geophysics, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu 610000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Mianning-Dechang rare earth element (REE) metallogenic belt exhibits considerable resource potential. Previous prospecting was oriented to hard-rock REE deposits associated with Himalayan alkaline complexes, with ion adsorption-type REE deposits under-studied. To explore the mineralization prospect of granite weathering crusts widespread in the metallogenic belt, this study investigated the Shizishan area through multi-channel gamma-ray spectrometry, soil profile survey, and shallow drilling. One ion adsorption-type REE ore occurrence was identified in the granite weathering crust at Mosuoying. This study analyzed the radioactive response of the geological, geophysical, and geochemical profiles and ore contents, finding that the elemental contents of thorium (Th) and potassium (K) were highly indicative of REE and rare metal mineralization. Highly mineralized, industrial-scale ion adsorption-type REE deposits will likely occur when 6.25<w(Th)/w(K)<10, w(eTh)>37×10-6, and w(eK)>4.2%. As revealed by the analysis of the response of radioactive anomalies to supergene weathering, thorium anomaly halos can effectively indicate granitic plutons while potassium anomaly halos can well delineate the extent of granite weathering crusts.
|
|
Received: 26 September 2023
Published: 21 October 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
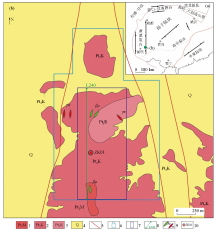
Tectonic map (a) and geological map (b) of the study area
1—fine-grained dolomitic diorite of Maoping unit; 2—coarse-medium-grained black dolomitic diorite of Kelang unit; 3—fine-grained porphyritic dolomitic diorite of Ranfangou unit; 4—Quaternary system; 5—measured faults; 6—extent of gamma-energetic spectral profiles; 7—extent of soil profiles; 8-Physical and chemical composite profiles; 9—phyllic dyke veins, granitic porphyritic veins; 10—drill holes
|

| 代号 | 铀含量/10-6 | 钍含量/10-6 | 钾含量/10-6 | 异常上限/10-6 | 频数 | | | S | CV | | S | CV | | S | CV | U | Th | K | | Q | 4.98 | 1.88 | 0.38 | 18.85 | 9.02 | 0.48 | 2.12 | 1.04 | 0.49 | 7.35 | 26.39 | 3.63 | 41 | | Pt2R | 7.90 | 2.47 | 0.31 | 28.64 | 10.87 | 0.38 | 3.81 | 1.31 | 0.34 | 7.90 | 64.47 | 6.64 | 243 | | Pt2K | 7.45 | 2.31 | 0.31 | 30.64 | 10.44 | 0.34 | 3.71 | 1.24 | 0.33 | 16.91 | 68.33 | 7.37 | 1159 | | Pt2M | 11.07 | 2.49 | 0.23 | 34.01 | 11.69 | 0.34 | 5.98 | 1.37 | 0.23 | 11.07 | 60.06 | 5.98 | 15 | | Q | 7.09 | 2.12 | 0.29 | 24.7 | 7.98 | 0.32 | 3.29 | 0.98 | 0.29 | 16.58 | 65.98 | 6.25 | 755 | | 平均值 | 7.28 | 2.33 | 0.32 | 28.01 | 10.47 | 0.37 | 3.56 | 1.25 | 0.35 | | | | |
|
Gamma-ray spectrum parameters of major geologic bodies in the study area
|

| 参数 | 偏高晕 | 高晕 | 异常晕 | +S≤
Q≤ +2S | +2S≤
Q≤ +3S | Q≥ +3S | | U | 9.51≤Q≤11.73 | 11.73≤Q≤13.94 | 13.94≤Q≤21.90 | | Th | 37.87≤Q≤47.87 | 47.87≤Q≤57.87 | 57.87≤Q≤83.61 | | K | 4.78≤Q≤6.03 | 6.03≤Q≤7.28 | 7.28≤Q≤10.63 |
|
Multichannel spectrum anomaly classification table
|
|
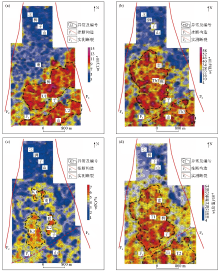
Plane contour map of the results of ground-based gamma spectrometry measurements at Shizishan
a—plane contour of uranium channel content;b—plane contour of thorium channel content;c—plane contour of potassium channel content;d—plane of total tract content
|

| 参数 | 土壤地球化学元素 | | 元素 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | Sc | Nb | Ta | | 最小值/10-6 | 15 | 35.8 | 3.99 | 15.7 | 4.67 | 0.24 | 4.41 | 0.88 | 5.9 | 1.23 | 3.49 | 0.54 | 3.29 | 0.51 | 32.6 | 5 | 6.88 | 0.73 | | 最大值/10-6 | 310 | 522 | 114 | 402 | 95.3 | 4.05 | 84.8 | 17.6 | 117 | 24.7 | 70.4 | 9.55 | 55.6 | 7.23 | 723 | 52.3 | 50.7 | 6.52 | | 平均值/10-6 | 81.7 | 185.4 | 23.3 | 83 | 20.2 | 1.2 | 17.3 | 3.5 | 23.3 | 4.9 | 14.1 | 2.2 | 13.6 | 2 | 139.6 | 16.8 | 28 | 3.1 | 藏北地台
丰度/10-6 | 16.4 | 30.8 | 3.69 | 17.8 | 2.85 | 0.68 | 2.7 | 0.44 | 2.4 | 0.46 | 1.4 | 0.21 | 1.4 | 0.21 | 11.3 | 9.8 | 18 | 2.3 | | 丰度系数 | 5 | 6 | 6.3 | 4.7 | 7.1 | 1.7 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 9.7 | 10.7 | 10.1 | 10.4 | 9.7 | 9.4 | 12.4 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.4 |
|
Characterization of measured content of soil profiles in the study area
|
|
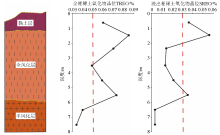
Shallow drill sampling grade map of Shizishan (red line is boundary grade)
|
|
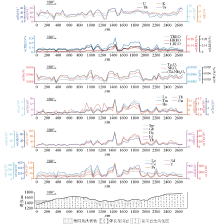
L240 comprehensive physico-chemical profile
|
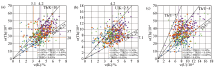
|
Scatter plot of the correlation between rare earth oxides and the content of each single element
a—Th,K element scatter plot;b—U,K element scatter plot;c—Th,U element scatter plot
|
| [1] |
王登红, 赵芝, 于扬, 等. 我国离子吸附型稀土矿产科学研究和调查评价新进展[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(3):317-325.
|
| [1] |
Wang D H, Zhao Z, Yu Y, et al. A review of the achievements in the survey and study of ion-absorption type REE deposits in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(3):317-325.
|
| [2] |
王登红, 王瑞江, 李建康, 等. 中国三稀矿产资源战略调查研究进展综述[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(2):361-370.
|
| [2] |
Wang D H, Wang R J, Li J K, et al. The progress in the strategic research and survey of rare earth,rare metal and rare-scattered elements mineral resources[J]. Geology in China, 2013, 40(2):361-370.
|
| [3] |
付小方, 郝雪峰, 阮林森, 等. 四川“三稀” 矿产资源的成矿特征及找矿勘查方向[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2023, 43(1):1-18.
|
| [3] |
Fu X F, Hao X F, Ruan L S, et al. Metallogenic characteristics and exploration prospecting of the 3R mineral resources in Sichuan,China[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2023, 43(1):1-18.
|
| [4] |
邹佳作, 聂飞, 郭金承. 四川冕宁—德昌地区发现离子吸附型稀土矿点[J]. 中国地质, 2023, 50(2):648-649.
|
| [4] |
Zou J Z, Nie F, Guo J C. New discovery of ion-absorption type REE mineral occurrence in the Mianning-Dechang area,Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China, 2023, 50(2):648-649.
|
| [5] |
夏小洪, 刘图强, 尹川, 等. 四川攀枝花—西昌地区离子吸附型(中—重)稀土矿床的首次发现及其重要意义[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(4):1540-1543.
|
| [5] |
Xia X H, Liu T Q, Yin C, et al. First discovery of ion adsorption-type (medium-heavy) REE depositin the Panzhihua-Xichang area,Sichuan Province,and its significance[J]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(4):1540-1543.
|
| [6] |
池汝安, 田君, 罗仙平, 等. 风化壳淋积型稀土矿的基础研究[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2012, 3(4):1-13.
|
| [6] |
Chi R A, Tian J, Luo X P, et al. The basic research on the weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2012, 3(4):1-13.
|
| [7] |
王登红, 赵芝, 于扬, 等. 离子吸附型稀土资源研究进展、存在问题及今后研究方向[J]. 岩矿测试, 2013, 32(5):796-802.
|
| [7] |
Wang D H, Zhao Z, Yu Y, et al. Progress, problems and research orientation of ion-adsorption type rare earth resources[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(5):796-802.
|
| [8] |
王登红, 郑绵平, 王成辉, 等. 大宗急缺矿产和战略性新兴产业矿产调查工程进展与主要成果[J]. 中国地质调查, 2019, 6(6):1-11.
|
| [8] |
Wang D H, Zheng M P, Wang C H, et al. Progresses and main achievements on bulk lacking minerals and strategic emerging industry minerals survey project[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2019, 6(6):1-11.
|
| [9] |
王成辉, 王登红, 刘善宝, 等. 战略新兴矿产调查工程进展与主要成果[J]. 中国地质调查, 2022, 9(5):1-14.
|
| [9] |
Wang C H, Wang D H, Liu S B, et al. Progresses and main achievements on strategic emerging minerals survey project[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2022, 9(5):1-14.
|
| [10] |
范国强, 秦宇龙, 詹涵钰, 等. 四川攀西地区稀土资源成矿规律及找矿靶区[J]. 中国地质调查, 2022, 9(1):23-31.
|
| [10] |
Fan G Q, Qin Y L, Zhan H Y, et al. Metallization regularity and prospecting target area in Panzhihua-Xichang area of Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2022, 9(1):23-31.
|
| [11] |
华荣洲, 刘彝筠, 石柏慎. 伽马法在地质找矿工作中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 1980, 4(6):46-51.
|
| [11] |
Hua R Z, Liu Y Y, Shi B S. Application of gamma method in geological prospecting[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1980, 4(6):46-51.
|
| [12] |
刘菁华, 王祝文, 田钢, 等. 地面伽马能谱测量在浅覆盖区地质填图中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2003, 39(2):61-64.
|
| [12] |
Liu J H, Wang Z W, Tian G, et al. Application of ground gamma-spectrometry in geological mapping in shallow overburden areas[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2003, 39(2):61-64.
|
| [13] |
朱卫平, 刘诗华, 朱宏伟, 等. 常用地球物理方法勘探深度研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(6):2608-2618.
|
| [13] |
Zhu W P, Liu S H, Zhu H W, et al. Study on the exploration depth of geophysical methods commonly used[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(6):2608-2618.
|
| [14] |
侯增谦, 田世洪, 谢玉玲, 等. 川西冕宁—德昌喜马拉雅期稀土元素成矿带:矿床地质特征与区域成矿模型[J]. 矿床地质, 2008, 27(2):145-176.
|
| [14] |
Hou Z Q, Tian S H, Xie Y L, et al. Mianning-Dechang Himalayan REE belt associated with carbonatite-alkalic complex in eastern Indo-Asian collision zone,Southwest China:Geological characteristics of REE deposits and a possible metallogenic model[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2008, 27(2):145-176.
|
| [15] |
莫宣学, 路凤香, 沈上越, 等. 三江特提斯火山作用与成矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社,1993.
|
| [15] |
Mo X X, Lu F X, Shen S Y, et al. Sanjiang Tethys volcanism and mineralization[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House,1993.
|
| [16] |
侯增谦, 卢记仁, 林盛中. 峨眉地幔柱轴部的榴辉岩—地幔岩源区:主元素、痕量元素及Sr、Nd、Pb同位素证据[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(2):200-219.
|
| [16] |
Hou Z Q, Lu J R, Lin S Z. The axial zone consisting of pyrolite and eclogite in the Emei mantle plume:Major,trace element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotope evidence[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(2):200-219.
|
| [17] |
从柏林. 攀西古裂谷的形成与演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,1988.
|
| [17] |
Cong B L. Formation and evolution of Panxiancientrift[M]. Beijing: Science Press,1988.
|
| [18] |
胡瑞忠, 温汉捷, 叶霖, 等. 扬子地块西南部关键金属元素成矿作用[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(33):3700-3714.
|
| [18] |
Hu R Z, Wen H J, Ye L, et al. Metallogeny of critical metals in the southwestern Yangtze Block[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(33):3700-3714.
|
| [19] |
郭金承, 聂飞, 吴松洋, 等. 川西德昌馒头山离子吸附型重稀土矿床的发现及其地质意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2024, 44(1):86-99.
|
| [19] |
Guo J C, Nie F, Wu S Y, et al. The discovery and geological significance of the Mantoushan ion-adsorption type heavy rare earth deposit in Dechang,western Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2024, 44(1):86-99.
|
| [20] |
曹秋义, 山亚, 张恩, 等. 地面伽马能谱测量在铀矿找矿中的应用研究——以黑龙江省嘉荫县磨石山地区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(4):701-704.
|
| [20] |
Cao Q Y, Shan Y, Zhang E, et al. The application of ground gamma spectrometricmeasurementto uranium prospecting:A case study of Millstone Hill in Jiayin County,Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(4):701-704.
|
| [21] |
候万雄, 杨顺林, 钟长洪, 等. 1:50 000德昌县幅地质图说明书[R]. 四川省地质矿产勘查开发局攀西地质队区调一队, 2000.
|
| [21] |
Hou W X, Yang S L, Zhong C H, et al. 1:50,000 Geological map of Dechang County Description[R]. Sichuan Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development, Pansi Geological Team, District Investigation Team 1,2000.
|
| [22] |
程立群, 张文雨, 王凯, 等. 多道能谱测量在冀东花岗岩型稀有金属矿勘查中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(4):942-950.
|
| [22] |
Cheng L Q, Zhang W Y, Wang K, et al. The application of multi-channel energy spectrum survey to the exploration of granite type rare metal deposits in eastern Hebei[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4):942-950.
|
| [23] |
黎彤, 袁怀雨, 吴胜昔, 等. 中国大陆壳体的区域元素丰度[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 1999, 23(2):101-107.
|
| [23] |
Li T, Yuan H Y, Wu S X, et al. Regional element abundances of continental crustobodies in China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 1999, 23(2):101-107.
|
| [24] |
张民, 何显川, 谭伟, 等. 云南临沧花岗岩离子吸附型稀土矿床地球化学特征及其成因讨论[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(1):201-214.
|
| [24] |
Zhang M, He X C, Tan W, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of ion-adsorbed rare earth deposit in Lincang granite,Yunnan Province[J]. Geology of China, 2019, 49(1):201-214.
|
| [1] |
ZHONG Hui-Rong, YANG Cheng-Zhi, YANG Qing-Hua, XIN Chao, YANG Lei, WANG Wei. Application of the unmanned aerial vehicle-airborne gamma-ray spectrometry system to follow-up geochemical surveys in high-relief areas[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1268-1274. |
| [2] |
LI Jing-Min, MI Yao-Hui, LUO Yao. A review of NURE airborne program and suggestions on airborne gamma-ray spectrometry survey in the new era[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2): 394-402. |
|
|
|
|

