|
|
|
| A method for seismic data denoising based on the neural network with a retractable attention mechanism |
ZHANG Min1,2( ), XU Yi-Zhuo1,2, YI Ji-Dong1,2 ), XU Yi-Zhuo1,2, YI Ji-Dong1,2 |
1. School of Geosciences,China University of Petroleum(East China),Qingdao 266580,China
2. Key Laboratory of Deep Oil and Gas,Qingdao 266580,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Random noise in seismic data impairs the quality of the data,thus affecting the accuracy of subsequent processing and interpretation.Conventional denoising methods,constrained by prior conditions,exhibit low efficiency.Neural networks possess a strong feature extraction ability,which can make up for these shortcomings.However,the limitations of convolution kernels in conventional neural networks may lead to the loss of global information.Hence,this study introduced a retractable attention mechanism to the convolutional neural network (CNN).This mechanism presents both dense and sparse self-attention modules in the CNN.The alternate use of the two self-attention modules can significantly enhance the performance of the CNN and expand the receptive field.The shallow and deep features of seismic data were extracted using the convolutional layer and self-attention modules.Combined with CNN's local modeling ability and Transformer's global modeling ability,they contributed to enhancing CNN's global interaction and ability to reduce noise and deal with details.As indicated by the experimental results of synthetic and field data,the method used in this study can more effectively suppress noise and retain effective information of seismic data compared to Unet and DnCNN,significantly improving the signal-to-noise ratio and thus assisting in the processing and interpretation of seismic data.
|
|
Received: 20 September 2023
Published: 19 September 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
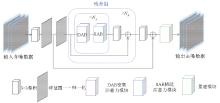
|
STCNN network model
|
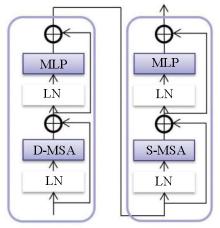
|
Residual group
|
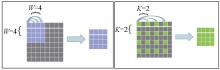
|
Dense attention and sparse attention
a—dense attention;b—sparse attention
|
|
Partial training samples of synthetic seismic data
|
|
Partial training samples of real seismic data
|
|
Synthetic seismic data(a) and noisy seismic data(b)
|
|
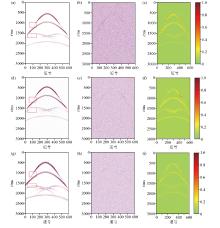
Results of three denoising methods in synthetic seismic data
a—DnCNN denoising result;b—noise data removed by DnCNN;c—similarity map between panels fig.a and fig.b;d—Unet denoising result;e—noise data removed by Unet;f—similarity map between panels fig.d and fig.e;g—STCNN denoising result;h—noise data removed by STCNN;i—similarity map between panels fig.g and fig.h
|
|
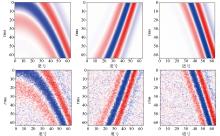
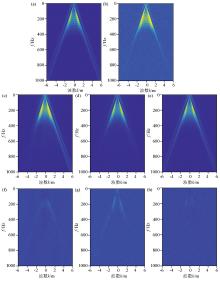
Comparison of the f-k spectrum of three denoising results in synthetic seismic data testing
a—f-k spectra of clean seismic data;b—f-k spectra of noisy seismic data;c—f-k spectra of DnCNN denoising result;d—f-k spectra of Unet denoising result;e—f-k spectra of STCNN denoising result;f—f-k spectra of noise data removed by DnCNN;g—f-k spectra of noise data removed by Unet;h—f-k spectra of f-k spectra of noise data removed by STCNN
|

| 加入噪声水平 | 去噪算法 | 去噪后PSNR/dB | 去噪后SSIM | σ= 10%
PSNR:18.45 | DnCNN
Unet
STCNN | 32.91
34.73
35.15 | 0.9712
0.9837
0.9901 | σ= 20%
PSNR:12.57 | DnCNN
Unet
STCNN | 28.31
29.62
31.12 | 0.9015
0.9286
0.9474 | σ= 50%
PSNR:5.36 | DnCNN
Unet
STCNN | 13.64
14.12
19.54 | 0.6845
0.6926
0.7687 |
|
Comparison of denoising effect indexes at different noise levels
|
|
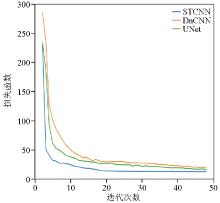
Loss function curves of the three networks
|

| 去噪方法 | DnCNN | Unet | STCNN | | 训练时间/h | 1.45 | 3.36 | 2.87 |
|
Comparison of the running time of the three methods
|
|
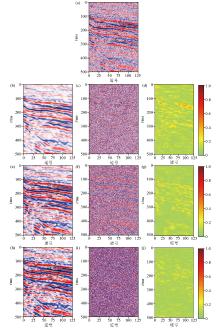
Field seismic signal denoising results
a—field seismic data;b—DnCNN denoising result;c—noise data removed by DnCNN;d—similarity map between panels fig.b and fig.c;e—Unet denoising result;f—noise data removed by Unet;g—similarity map between panels fig.e and fig.f;h—STCNN denoising result;i—noise data removed by STCNN;j—similarity map between panels fig.h and fig.i
|
| [1] |
Li J, Wu X, Hu Z. Deep learning for simultaneous seismic image super-resolution and denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60(1):1-11.
|
| [2] |
曹静杰, 杨志权, 杨勇, 等. 一种基于曲波变换的自适应地震随机噪声消除方法[J]. 石油物探, 2018, 57(1):72-78.
|
| [2] |
Cao J J, Yang Z Q, Yang Y, et al. An adaptive seismic random noise elimination method based on Curvelet transform[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2018, 57(1):72-78.
|
| [3] |
吴招才, 刘天佑. 地震数据去噪中的小波方法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2008, 23(2):493-499.
|
| [3] |
Wu Z C, Liu T Y. Wavelet method in seismic data attenuation[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2008, 23(2):493-499.
|
| [4] |
张恒磊, 张云翠, 宋双, 等. 基于Curvelet域的叠前地震资料去噪方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2008, 43(5):508-513.
|
| [4] |
Zhang H L, Zhang Y C, Song S, et al. Curvelet domain-based prestack seismic data denoise method[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2008, 43(5):508-513.
|
| [5] |
孙苗苗, 李振春, 曲英铭, 等. 基于曲波域稀疏约束的OVT域地震数据去噪方法研究[J]. 石油物探, 2019, 58(2):208-218.
|
| [5] |
Sun M M, Li Z C, Qu Y M, et al. A seismic denoising method based on Curvelet transform with constraint in OVT domain[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019, 58(2):208-218.
|
| [6] |
薛昭, 董良国, 单联瑜. Radon变换去噪方法的保幅性理论分析[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2012, 47(6):858-867.
|
| [6] |
Xue Z, Dong L G, Shang L Y. Amplitude preservation theoretical analysis of Radon transforms denoising method[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2012, 47(6):858-867.
|
| [7] |
Liu C, Liu Y, Yang B J, et al. A 2D multistage median filter to reduce random seismic noise[J]. Geophysics, 2006, 71(5):V105-V110.
|
| [8] |
国胧予, 刘财, 刘洋, 等. 基于f-x域流式预测滤波器的地震随机噪声衰减方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63(1):329-338.
|
| [8] |
Guo L Y, Liu C, Liu Y, et al. Seismic random noise attenuation based on streaming prediction filter in the f-x domain[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(1):329-338.
|
| [9] |
Naghizadeh M, Sacchi M. Multicomponent f-x seismic random noise attenuation via vector autoregressive operators[J]. Geophysics, 2012, 77(2):V91-V99.
|
| [10] |
Witten B, Shragge J. Extended wave-equation imaging conditions for passive seismic data[J]. Geophysics, 2015, 80(6):WC61-WC72.
|
| [11] |
张良, 韩立国, 方金伟, 等. 双稀疏字典和FISTA的地震数据去噪[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(7):2071-2683.
|
| [11] |
Zhang L, Han L G, Fang J W, et al. Seismic data denoising via double sparsity dictionary and fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(7):2071-2683.
|
| [12] |
唐杰, 孟涛, 张文征, 等. 利用基于深度学习的过完备字典信号稀疏表示算法压制地震随机噪声[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2020, 55(6):1202-1209,1160.
|
| [12] |
Tang J, Meng T, Zhang W Z, et al. Suppression of seismic random noise with overcomplete dictionary signal sparse representation algorithm based on deep learning[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2020, 55(6):1202-1209,1160.
|
| [13] |
宋辉, 高洋, 陈伟, 等. 基于卷积降噪自编码器的地震数据去噪[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2020, 55(6):1210-1219,1160-1161.
|
| [13] |
Song H, Gao Y, Chen W, et al. Seismic noise suppression based on convolutional denoising autoencoder[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2020, 55(6):1210-1219,1160-1161.
|
| [14] |
Wang Y Q, Lu W K, Liu J L, et al. Random seismic noise attenuation bas ed on data augmentation and CNN[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(1):421-433.
|
| [15] |
高好天, 孙宁娜, 孙可奕, 等. DnCNN和U-Net对地震随机噪声压制的对比分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(6):2441-2453.
|
| [15] |
Gao H T, Sun N N, Sun K Y, et al. Comparative analysis of DnCNN and U-Net on suppression of seismic random doise[J]. The Journal of China Universities of Posts and Telecommunications, 2021, 36(6):2441-2453.
|
| [16] |
Wang F, Chen S. Residual learning of deep convolutional neural network for seismic random noise attenuation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(8):1314-1318.
|
| [17] |
陈天, 易远元. 基于深度卷积神经网络的地震数据随机噪声压制[J]. 地震学报, 2021, 43(4):474-482,533.
|
| [17] |
Chen T, Yi Y Y. Random noise suppression of seismic data based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 2021, 43(4):474-482,533.
|
| [18] |
Si X, Yuan Y, Si T, et al. Attenuation of Random noise using denoising convolutional neural networks[J]. Interpretation, 2019, 7(3):SE269-SE280.
|
| [19] |
王钰清, 陆文凯, 刘金林, 等. 基于数据增广和CNN的地震随机噪声压制[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(1):421-433.
|
| [19] |
Wang Y Q, Lu W K, Liu J L, et al. Random seismic noise attention based on data augmentation and CNN[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(1):421-433.
|
| [20] |
罗仁泽, 李阳阳. 一种基于RUnet卷积神经网络的地震资料随机噪声压制方法[J]. 石油物探, 2020, 59(1):51-59.
|
| [20] |
Luo R Z, Li Y Y. Random seismic noise attenuation based on RUnet convolutional neural network[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2020, 59(1):51-59.
|
| [21] |
Yang L, Chen W, Wang H, et al. Deep learning seismic random noise attenuation via improved residual convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(9):7968-7981.
|
| [22] |
杨翠倩, 周亚同, 何昊, 等. 基于全局上下文和注意力机制深度卷积神经网络的地震数据去噪[J]. 石油物探, 2021, 60(5):751-762,855.
|
| [22] |
Yang C Q, Zhou Y T, He H, et al. Global context and attention-based deep convolutional neural network for seismic data denoising[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2021, 60(5):751-762,855.
|
| [23] |
周文辉, 石敏, 朱登明, 等. 基于残差注意力网络的地震数据超分辨率方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(8):24-31.
|
| [23] |
Zhou W H, Shi M, Zhu D M, et al. Seismic data super-resolution method based on residual attention network[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(8):24-31.
|
| [24] |
Liu Z, Lin Y T, Cao Y, et al. Swin transformer:Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]// Montreal:2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision(ICCV), 2021:9992-10002.
|
| [25] |
Cao H, Wang Y Y, Chen J, et al. Swin-Unet:Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation[J]. Image and Video Processing, 2021.
|
| [26] |
Fan C M, Liu T J, Liu K H. SUNet:Swin transformer UNet for image denoising[C]// Austin:2022 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems(ISCAS), 2022:2333-2337.
|
| [27] |
Zhang K, Li Y, Liang J, et al. Practical blind image denoising via swin-conv-UNet and data synthesis[J]. Machine Inteligence Research, 2023, 20(6):822-836.
|
| [1] |
ZHENG Xiao-Cheng, ZHANG Ming-Hua, REN-Wei . Application of convolution neural networks in gold exploration and prediction in Shandong Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1433-1440. |
| [2] |
WANG Kang, LIU Cai-Yun, XIONG Jie, WANG Yong-Chang, HU Huan-Fa, KANG Jia-Shuai. Seismic wave impedance inversion based on the fully convolutional residual shrinkage network[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1538-1546. |
|
|
|
|

