|
|
|
| Elemental geochemical characteristics and genetic mechanisms of Se-rich soils in the Lixiahe area in Jiangsu Province |
LIAO Qi-Lin1,2( ), HUANG Shun-Sheng1,2( ), HUANG Shun-Sheng1,2( ), XU Wei-Wei1,2, CUI Xiao-Dan1,2, JIN Yang1,2, LIU Ling1,2, WANG Yuan-Yuan1,2, LI Wen-Bo1,2, ZHOU Qiang1,2 ), XU Wei-Wei1,2, CUI Xiao-Dan1,2, JIN Yang1,2, LIU Ling1,2, WANG Yuan-Yuan1,2, LI Wen-Bo1,2, ZHOU Qiang1,2 |
1. Technology Innovation Center for Ecological Monitoring & Restoration Project on Land (Arable), Ministry of Natural Resources, Nanjing 210018, China
2. Geological Survey of Jiangsu Province, Nanjing 210018, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Based on relevant eco-geochemical survey data collected fromthe Lixiahe plain area in Jiangsu Province,this study systematically explored the geochemical characteristics of elements in Se-rich soils and the genetic mechanism through elemental distribution contrast, correlation analysis, R-type cluster analysis, and principal component analysis. This study can be referenced for the rational production and utilization of Se-rich land resources of the Quaternary sedimentary type. Key findings are as follows: (1)Se-rich soilsin the Lixiahe area are typical Quaternary sediments, and the closed lagoon facies sedimentary environment characterized by rich organic matter and slightly reducing conditions plays a foundational role in the formation of local Se-rich soils;(2) Typical element association, Se-OM-N-K-Fe-Co, in Se-rich soils is primarily located within a depth of 30 cm from the surface, with Se content ranging mostly from 0.3×10-6 to 0.4×10-6 in a uniform distribution; (3) Significant positive correlations between Se and some other elements can be observed in the soils, with the correlation coefficients (r)between Se and OM,and Se and CEC being 0.74 and 0.66, respectively.In contrast, Se exhibits a significant negative correlation with pH, with a correlation coefficient of -0.35; (4) The formation of Se-rich soilsmight have experienced three Se enrichment stages: the initial enrichment in soil parent materials, the re-enrichment during soil formation, and the supergene enrichment after soil formation, accompanied by interference from non-lagoon facies sediments (such as marine sediments). Organic matter adsorption, colloid adsorption, and biogeochemistry constitute the main causes of Se enrichment in the soils; (5) The Se-rich soils are also relatively enriched in heavy metal elements like Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni, Co, and V, which are within the national limit standards.
|
|
Received: 25 August 2024
Published: 19 September 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
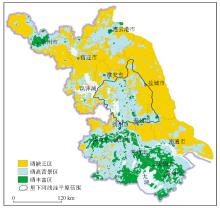
|
Spatial distribution of the main Se-enriched soil in Jiangsu Province and studied area location
|

| 指标 | | | | CV | | Sa | | | | CVa | 里下河土
壤均值 | 江苏省土
壤均值[19] | 石嘴山富硒
土壤均值 | | Se | 0.26 | 0.7 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.30 | 1179 | 0.26 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.34 | | OM | 1.46 | 10.84 | 4.33 | 0.24 | 4.20 | 1268 | 1.95 | 6.54 | 4.25 | 0.22 | 2.28 | 1.88 | 1.89 | | N | 404 | 5035 | 2335 | 0.23 | 2274 | 1275 | 1142 | 3474 | 2314 | 0.20 | 1431 | 1252 | 978 | | P | 359 | 3688 | 1024 | 0.32 | 983 | 1219 | 474 | 1466 | 962 | 0.21 | 703 | 791 | 983 | | K | 1.43 | 2.54 | 1.99 | 0.08 | 1.98 | 1236 | 1.68 | 2.32 | 2.00 | 0.06 | 1.91 | 1.82 | 1.35 | | Ca | 0.61 | 3.77 | 0.98 | 0.43 | 0.92 | 1052 | 0.61 | 1.03 | 0.82 | 0.10 | 1.33 | 2.13 | 4.97 | | Mg | 0.58 | 1.60 | 1.01 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 1160 | 0.78 | 1.18 | 0.98 | 0.08 | 0.97 | 1.01 | 1.53 | | Fe | 1.93 | 5.47 | 3.48 | 0.14 | 3.44 | 1201 | 2.58 | 4.39 | 3.48 | 0.10 | 3.57 | 3.35 | 3.19 | | Mn | 216 | 2944 | 493 | 0.29 | 478 | 1194 | 264 | 667 | 465 | 0.17 | 583 | 629 | 645 | | Mo | 0.19 | 17.40 | 0.77 | 1.25 | 0.64 | 1094 | 0.26 | 0.86 | 0.56 | 0.22 | 0.48 | 0.55 | 60 | | B | 26.3 | 145.0 | 57.0 | 0.15 | 56.0 | 1158 | 47.0 | 70.0 | 58.0 | 0.08 | 57 | 56 | 0.82 | | F | 265 | 986 | 603 | 0.16 | 595 | 1249 | 403 | 799 | 599 | 0.14 | 573 | 546 | 660 | | Cl | 37.4 | 1031 | 138 | 0.58 | 122 | 1180 | 37 | 227 | 118 | 0.37 | 100 | 209 | - | | As | 3.29 | 17.50 | 7.81 | 0.22 | 7.62 | 1223 | 4.45 | 10.90 | 7.69 | 0.17 | 8.7 | 9.4 | 12.91 | | Cd | 0.11 | 0.59 | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 1173 | 0.12 | 0.30 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.133 | 0.151 | 0.21 | | Hg | 0.037 | 0.440 | 0.095 | 0.39 | 0.089 | 1197 | 0.037 | 0.140 | 0.086 | 0.26 | 0.062 | 0.082 | 0.038 | | Sb | 0.38 | 15.70 | 0.86 | 0.54 | 0.83 | 1180 | 0.46 | 1.14 | 0.80 | 0.17 | 0.83 | 0.96 | - | | Cu | 11.3 | 354.0 | 31.0 | 0.38 | 30.0 | 1156 | 19.0 | 41.2 | 30.0 | 0.15 | 27 | 26 | 24 | | Pb | 18.4 | 48.2 | 28.0 | 0.14 | 28.0 | 1233 | 20.0 | 35.6 | 28.0 | 0.11 | 25.9 | 26.8 | 23 | | Zn | 55.2 | 368.0 | 97.0 | 0.23 | 95.0 | 1134 | 67.0 | 116.0 | 92.0 | 0.11 | 74 | 73 | 72 | | Cr | 54.2 | 210.0 | 87.0 | 0.16 | 86.0 | 1217 | 66.0 | 106.0 | 86.0 | 0.09 | 81 | 76 | 66 | | Ni | 16.5 | 445.0 | 37.0 | 0.39 | 36.0 | 1213 | 25.0 | 48.6 | 37.0 | 0.13 | 34.6 | 32.9 | 32 | | Co | 6.21 | 21.20 | 14.00 | 0.15 | 14.00 | 1189 | 10.00 | 17.50 | 14.00 | 0.11 | 13.6 | 13.7 | 13 | | V | 48.2 | 142.0 | 95.0 | 0.15 | 94.0 | 1272 | 62.0 | 128.0 | 95.0 | 0.14 | 92 | 88 | - | | CEC | 86 | 333 | 199 | 0.20 | 195 | 1289 | 105 | 290 | 198 | 0.19 | - | - | - | | pH | 4.46 | 8.47 | 6.54 | 0.13 | 6.49 | 1311 | 4.63 | 8.47 | 6.54 | 0.13 | 7.19 | 7.33 | 8.51 |
|
Geochemical parameters of elements of selenium-enriched soil in Lixiahe area
|
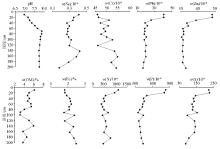
|
Variation of Se and other elements in typical soil sedimentary profile in the Lixiahe Se-rich area
|

| 指标 | Se | pH | CEC | OM | N | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | F | Cd | Cu | Pb | Zn | Ni | Co | | Se | 1.0** | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Mo | 0.34** | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | pH | -0.35** | 1.0** | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | CEC | 0.66** | -0.46** | 1.0** | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | OM | 0.74** | -0.49** | 0.62** | 1.0** | | | | | | | | | | | | | | N | 0.73** | -0.45** | 0.59** | 0.94** | 1.0** | | | | | | | | | | | | | P | 0.02* | 0.00* | -0.31** | 0.21** | 0.24** | | | | | | | | | | | | | K | 0.55** | -0.17** | 0.65** | 0.38** | 0.41** | 1.0** | | | | | | | | | | | | Ca | -0.23** | 0.68** | -0.45** | -0.36** | -0.33** | -0.02** | 1.0** | | | | | | | | | | | Mg | 0.25** | 0.37** | 0.22** | 0.04* | 0.10** | 0.71** | 0.58** | 1.0** | | | | | | | | | | Fe | 0.58** | -0.18** | 0.72** | 0.40** | 0.44** | 0.93** | -0.00* | 0.74** | 1.0** | | | | | | | | | Mn | 0.08** | 0.18** | 0.06** | -0.08** | -0.05* | 0.22** | 0.26* | 0.35** | 0.35** | | | | | | | | | F | 0.53** | -0.23** | 0.63** | 0.41** | 0.44** | 0.79** | -0.05* | 0.59** | 0.84** | 1.0** | | | | | | | | Cl | 0.23** | -0.18** | 0.09** | 0.39** | 0.40** | 0.06** | -0.01* | 0.02* | 0.07** | 0.15** | | | | | | | | As | 0.15** | 0.08** | 0.12** | 0.06** | 0.10** | 0.38** | 0.05* | 0.36** | 0.37** | 0.26** | | | | | | | | Cd | 0.49** | 0.12** | 0.17** | 0.39** | 0.44** | 0.45** | 0.28* | 0.55** | 0.48** | 0.39** | 1.0** | | | | | | | Hg | 0.05* | -0.14** | 0.01** | 0.20** | 0.19** | -0.15** | -0.17** | -0.18** | -0.10** | -0.07** | 0.06** | | | | | | | Sb | 0.42** | -0.11** | 0.30** | 0.29** | 0.30** | 0.33** | -0.02* | 0.28** | 0.40** | 0.39** | 0.36** | | | | | | | Cu | 0.57** | -0.17** | 0.60** | 0.46** | 0.46** | 0.69** | -0.02* | 0.52** | 0.75** | 0.65** | 0.46** | 1.0** | | | | | | Pb | 0.57** | -0.22** | 0.41** | 0.53** | 0.54** | 0.51** | -0.05* | 0.36** | 0.55** | 0.46** | 0.55** | 0.52** | 1.0** | | | | | Zn | 0.55** | -0.11** | 0.43** | 0.45** | 0.47** | 0.56** | 0.05* | 0.49** | 0.66** | 0.53** | 0.60** | 0.59** | 0.60** | 1.0** | | | | Cr | 0.16** | -0.03* | 0.14** | 0.08** | 0.08** | 0.11** | 0.03* | 0.11** | 0.24** | 0.15** | 0.16** | 0.19** | 0.13** | 0.52** | | | | Ni | 0.54** | -0.18** | 0.66** | 0.41** | 0.41** | 0.76** | -0.05* | 0.56** | 0.81** | 0.68** | 0.37** | 0.95** | 0.46** | 0.57** | 1.0** | | | Co | 0.55** | -0.14** | 0.69** | 0.35** | 0.39** | 0.92** | 0.01* | 0.74** | 0.97** | 0.82** | 0.46** | 0.72** | 0.50** | 0.60** | 0.79** | 1.0** | | V | 0.52** | -0.05* | 0.48** | 0.36** | 0.37** | 0.66** | 0.12* | 0.64** | 0.76** | 0.58** | 0.52** | 0.59** | 0.61** | 0.64** | 0.63** | 0.72** |
|
Correlation coefficients of elements content in the Se-enriched soils in Lixiahe area
|
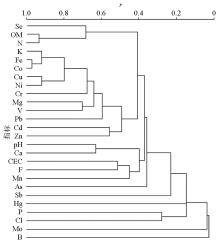
|
Dendrogram of Se and other elements or geochemical indicators of Se-rich soil in the Lixiahe area
|

| 指标 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | | Se | 0.506 | 0.621 | 0.251 | -0.153 | -0.238 | -0.126 | | OM | 0.142 | 0.871 | 0.208 | -0.249 | -0.113 | 0.009 | | pH | -0.080 | -0.214 | -0.193 | 0.862 | 0.025 | -0.002 | | CEC | 0.414 | 0.758 | 0.149 | -0.067 | -0.091 | -0.152 | | N | 0.100 | 0.874 | 0.175 | -0.205 | -0.097 | 0.058 | | P | -0.464 | 0.464 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.082 | 0.524 | | K | 0.947 | 0.027 | 0.019 | -0.150 | -0.013 | -0.003 | | Ca | -0.355 | -0.077 | -0.152 | 0.774 | -0.079 | 0.115 | | Mg | 0.826 | -0.061 | -0.049 | 0.364 | -0.025 | 0.105 | | Fe | 0.960 | 0.048 | 0.154 | -0.097 | 0.069 | -0.025 | | Mn | 0.389 | -0.106 | 0.226 | 0.520 | 0.365 | 0.177 | | Mo | 0.164 | 0.141 | 0.216 | -0.166 | 0.094 | 0.541 | | B | -0.150 | -0.111 | 0.049 | 0.088 | 0.840 | -0.064 | | F | 0.575 | 0.129 | 0.003 | -0.239 | 0.620 | 0.000 | | Cl | -0.245 | -0.136 | -0.145 | 0.050 | 0.238 | 0.648 | | Cd | 0.186 | 0.598 | 0.302 | 0.050 | -0.026 | 0.424 | | As | -0.058 | -0.171 | 0.723 | -0.213 | -0.018 | 0.248 | | Hg | -0.413 | 0.182 | 0.559 | 0.032 | 0.137 | -0.185 | | Sb | 0.267 | 0.143 | 0.685 | -0.170 | 0.123 | 0.042 | | Cu | 0.778 | 0.311 | 0.244 | -0.071 | -0.009 | 0.104 | | Pb | 0.392 | 0.135 | 0.763 | -0.163 | -0.166 | -0.049 | | Zn | 0.354 | 0.298 | 0.380 | -0.024 | 0.043 | 0.493 | | Cr | 0.730 | 0.105 | 0.230 | -0.048 | 0.100 | -0.228 | | Ni | 0.951 | 0.096 | 0.152 | -0.096 | -0.014 | -0.094 | | Co | 0.959 | 0.032 | 0.082 | -0.078 | 0.092 | -0.032 | | V | 0.837 | -0.016 | 0.259 | -0.068 | -0.157 | -0.068 | | 特征值 | 9.042 | 3.499 | 2.178 | 2.135 | 1.502 | 1.290 | | 方差贡献率/% | 34.775 | 13.459 | 8.377 | 8.213 | 5.776 | 4.960 | | 累积方差贡献率/% | 34.775 | 48.235 | 56.611 | 64.824 | 70.600 | 75.560 |
|
Rotated component matrix of elements distribution in Se-rich soil from the Lixiahe area
|

| 硒富集过程 | 主要控制因素 | 地球化学证据 | 富硒效果及其机制 | 成因类型 | | 初始富硒(Se首次聚集) | 相对封闭的第四纪潟湖相沉积环境和碱性偏还原的富含有机质的先天含Se沉积物 | Se与铁族元素(Fe、Ni、Co、V等)之间呈现显著正相关性,主成分分析结果中Se载荷因子为正 | 通过有机质吸附等将第四纪沉积物携带的Se汇聚到潟湖相,但未达到富硒土壤标准 | 第四纪沉积成因,与先天富硒岩层无关,潟湖相是其最佳聚集部位,富硒土壤主要分布在30 cm以上深度, Se平均含量通常刚达标 | | 成土富硒(Se二次聚集) | 第四纪沉积成土期间不断聚集的有机质和沉积分选作用生成的细颗粒矿物(含胶体、黏土矿物等) | Se与OM、CEC之间呈现显著正相关性,主成分分析结果中Se载荷因子为正且具有最大值 | 通过沉积分选和胶体吸附等将Se进一步汇聚到黏土矿物,部分达到富硒土壤标准 | | 表生富硒(Se三次聚集) | 成土后的生物活动及表土中相对更富集的有机质和相对酸化的土壤质地或环境 | Se与OM呈最显著正相关性、与pH呈较显著负相关性,Se-OM-N为其最具代表性元素组合,主成分分析显示Se载荷因子为正 | 通过生物富集作用(含pH降低等)将黏土矿物中的Se进一步汇聚到地表,形成富硒土壤 | | 伴随第四纪沉积的干扰作用 | 潟湖相之外的第四纪沉积物(如海相沉积物的混入) | 富硒土壤中B、Cl、P等与所有元素相关性均不密切,主成分分析显示Se载荷因子为负 | 对富硒土壤生成无贡献,只会干扰富硒土壤的形成或质量 |
|
Genetic model of Se-enriched soil in the Lixiahe area
|
| [1] |
Rotruck J T, Pope A L, Ganther H E, et al. Selenium: Biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase[J]. Science, 1973, 179(4073):588-590.
|
| [2] |
Sun W X, Huang B, Zhao Y C, et al. Spatial variability of soil selenium as affected by geologic and pedogenic processes and its effect on ecosystem and human health[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2009, 43(4):217-225.
|
| [3] |
Dinh Q T, Cui Z W, Huang J, et al. Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health:A review[J]. Environment International, 2018, 112:294-309.
|
| [4] |
Cao Z H, Wang X C, Yao D H, et al. Selenium geochemistry of paddy soils in Yangtze River Delta[J]. Environment International, 2001, 26(5-6):335-339.
|
| [5] |
杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶, 等. 海南岛农田土壤Se的地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5):837-849.
|
| [5] |
Yang Z F, Yu T, Hou Q Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in farmland of Hainan Island[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5):837-849.
|
| [6] |
魏振山, 涂其军, 唐蜀虹, 等. 天山北坡乌鲁木齐至沙湾地区富硒土壤地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(5):893-898.
|
| [6] |
Wei Z S, Tu Q J, Tang S H, et al. A discussion on the geochemical features and origin of selenium-rich soil on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains from Urumqi to Shawan County[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(5):893-898.
|
| [7] |
黄子龙, 林清梅, 范汝海. 广西全州县富硒土壤地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(2):381-385.
|
| [7] |
Huang Z L, Lin Q M, Fan R H. Geochemical characteristics of selenium-rich soil in Quanzhou County of Guangxi[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(2):381-385.
|
| [8] |
刘才泽, 王永华, 曾琴琴, 等. 成渝典型地区土壤硒地球化学特征及其成因分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(6):1289-1295.
|
| [8] |
Liu C Z, Wang Y H, Zeng Q Q, et al. The distribution and source of soil selenium in typical areas of Chengdu-Chongqing region[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(6):1289-1295.
|
| [9] |
周墨, 陈国光, 张明, 等. 赣南地区土壤硒元素地球化学特征及其影响因素研究:以青塘—梅窖地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(6):1292-1301.
|
| [9] |
Zhou M, Chen G G, Zhang M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soils of South Jiangxi Province:A typical area of Qingtang-Meijiao[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(6):1292-1301.
|
| [10] |
王金达, 于君宝, 张学林. 黄土高原土壤中硒等元素的地球化学特征[J]. 地理科学, 2000, 20(5):469-473.
|
| [10] |
Wang J D, Yu J B, Zhang X L. Geochemical features of elements of selenium in soil of Loess Plateau[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2000, 20(5):469-473.
|
| [11] |
韩伟, 王乔林, 宋云涛, 等. 四川省沐川县北部土壤硒地球化学特征与成因探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(1):215-222.
|
| [11] |
Han W, Wang Q L, Song Y T, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of selenium in soil in northern Muchuan County,Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1):215-222.
|
| [12] |
王志强, 杨建锋, 魏丽馨, 等. 石嘴山地区碱性土壤硒地球化学特征及生物有效性[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(1):229-237.
|
| [12] |
Wang Z Q, Yang J F, Wei L X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and bioavailability of selenium in alkaline soil in Shizuishan Area,Ningxia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1):229-237.
|
| [13] |
赵辰, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 等. 四川昭觉县中部乡镇表层土壤硒地球化学特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(3):412-426.
|
| [13] |
Zhao C, Sun B B, He L, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in surface soil of central townships in Zhaojue County,Sichuan Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(3):412-426.
|
| [14] |
袁宏伟, 陈江均, 郭腾达, 等. 巴彦淖尔市临河区狼山镇和新华镇一带富硒土壤地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 地质与勘探, 2022, 58(5):1027-1041.
|
| [14] |
Yuan H W, Chen J J, Guo T D, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of Se-rich soils in Langshan and Xinhua towns,Linhe district,Bayannur City[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2022, 58(5):1027-1041.
|
| [15] |
曾庆良, 余涛, 王锐. 土壤硒含量影响因素及富硒土地资源区划研究——以湖北恩施沙地为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(1):105-112.
|
| [15] |
Zeng Q L, Yu T, Wang R. The influencing factors of selenium in soils and classifying the selenium-rich soil resources in the typical area of Enshi,Hubei[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(1):105-112.
|
| [16] |
朱建明, 梁小兵, 凌宏文, 等. 环境中硒存在形式的研究现状[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2003, 22(1):75-81.
|
| [16] |
Zhu J M, Liang X B, Ling H W, et al. Advances in studying occurrence modes of selenium in environment[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, 2003, 22(1):75-81.
|
| [17] |
郑翔, 钱汉东, 吴雪枚. 湖北恩施双河硒矿床地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 高校地质学报, 2006, 12(1):83-92.
|
| [17] |
Zheng X, Qian H D, Wu X M. Geochemical and genetic characteristics of selenium ore deposit in Shuanghe,Enshi,Hubei Province[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2006, 12(1):83-92.
|
| [18] |
蔡子华, 宋明义, 胡艳华, 等. 湖沼相富硒土壤的发现及其生态学意义[J]. 物探与化探, 2011, 35(2):248-253.
|
| [18] |
Cai Z H, Song M Y, Hu Y H, et al. The discovery of lake facies selenium-rich soil and its ecological significance[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 35(2):248-253.
|
| [19] |
廖启林, 华明, 冯金顺, 等. 苏南局部富硒土壤及其天然富硒茶叶初步研究[J]. 中国地质, 2007, 34(2):347-353.
|
| [19] |
Liao Q L, Hua M, Feng J S, et al. Natural Se-rich tea in local Se-rich soils in southern Jiangsu[J]. Geology in China, 2007, 34(2):347-353.
|
| [20] |
廖启林, 任静华, 许伟伟, 等. 江苏宜溧富硒稻米产区地质地球化学背景[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(5):1791-1802.
|
| [20] |
Liao Q L, Ren J H, Xu W W, et al. Geological and geochemical background of Se-rich rice production in Yili Area,Jiangsu Province[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(5):1791-1802.
|
| [21] |
廖启林, 崔晓丹, 黄顺生, 等. 江苏富硒土壤元素地球化学特征及主要来源[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6):1813-1825.
|
| [21] |
Liao Q L, Cui X D, Huang S S, et al. Element geochemistry of selenium-enriched soil and its main sources in Jiangsu Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6):1813-1825.
|
| [22] |
范健, 任静华, 廖启林, 等. 苏南典型区农田土壤硒—镉拮抗作用研究[J]. 土壤, 2021, 53(5):1023-1032.
|
| [22] |
Fan J, Ren J H, Liao Q L, et al. Antagonism between Se and Cd in typical farmland soil in southern Jiangsu Province[J]. Soils, 2021, 53(5):1023-1032.
|
| [23] |
Eiche E. Microscale distribution and elemental associations of Se in seleniferous soils in Punjab,India[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2015, 22(7):5425-5436.
|
| [24] |
Song T J, Cui G, Su X S, et al. The origin of soil selenium in a typical agricultural area in Hamatong River Basin,Sanjiang Plain,China[J]. Catena, 2020, 185:104355.
|
| [25] |
Xie T Y, Shi Z M, Gao Y W, et al. Modeling analysis of the characteristics of selenium-rich soil in heavy metal high background area and its impact on main crops[J]. Ecological Informatics, 2021, 66:101420.
|
| [26] |
夏伟, 杨军, 项剑桥, 等. 江汉平原富硒土壤来源解析及其生物富集程度研究——以沙洋县东北部为例[J]. 地质学报, 2023, 97(5):1670-1682.
|
| [26] |
Xia W, Yang J, Xiang J Q, et al. Source analysis and bioenrichment of selenium-rich soil in the Jianghan Plain:A case study from the northeast of Shayang County[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2023, 97(5):1670-1682.
|
| [27] |
杨良策, 李明龙, 杨廷安, 等. 湖北省恩施市表层土壤硒含量分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2015, 29(6):825-829,848.
|
| [27] |
Yang L C, Li M L, Yang T A, et al. Study on distribution characteristics of selenium content of surface soil and its influencing factors in Enshi city,Hubei Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2015, 29(6):825-829,848.
|
| [28] |
谢薇, 杨耀栋, 侯佳渝, 等. 天津市蓟州区富硒土壤成因与土壤硒来源研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1373-1381.
|
| [28] |
Xie W, Yang Y D, Hou J Y, et al. Studies on causes and influential factors of selenium-enriched soils in Jizhou district of Tianjin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1373-1381.
|
| [29] |
梁红霞, 侯克斌, 陈富荣, 等. 安徽池州地区富硒土壤地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2022, 36(2):154-162.
|
| [29] |
Liang H X, Hou K B, Chen F R, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis analysis of selenium-rich soilsin Chizhou Area,Anhui Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2022, 36(2):154-162.
|
| [30] |
吴俊. 福建省寿宁县土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(6):1167-1176.
|
| [30] |
Wu J. The distribution of soil selenium in Shouning County of Fujian Province and its influencing factors[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(6):1167-1176.
|
| [31] |
刘道荣, 焦森. 天然富硒土壤成因分类研究及开发适宜性评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5):1157-1163.
|
| [31] |
Liu D R, Jiao S. Assessment of genetic classification and development suitability of natural selenium-rich soil[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5):1157-1163.
|
| [32] |
吴兴盛. 福建省武平县富硒土壤特征及成因分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(3):778-784.
|
| [32] |
Wu X S. Characteristics and genesis of selenium-rich soil in Wuping Area,Fujian Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3):778-784.
|
| [33] |
时章亮, 金立新, 廖超, 等. 四川雷波县重点耕地区土壤硒含量特征及其成因分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(5):1253-1260.
|
| [33] |
Shi Z L, Jin L X, Liao C, et al. Content characteristics and genesis of soil selenium in important cultivated areas of Leibo County,Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(5):1253-1260.
|
| [34] |
Sawyer E W. The influence of source of rock type,sorting on the geochemical weathering of clastic sediments from the Quatico matasedimentary belt,Superior Province,Canada[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986,(55):932-936
|
| [35] |
Johnsson L. Selenium uptake by plants as a function of soil type,organic matter content and pH[J]. Plant and Soil, 1991, 133(1):57-64.
|
| [36] |
Liu Y L, Tian X L, Liu R, et al. Key driving factors of selenium-enriched soil in the low-Se geological belt:A case study in Red Beds of Sichuan Basin,China[J]. Catena, 2021, 196:104926.
|
| [37] |
余飞, 张风雷, 张永文, 等. 重庆典型农业区土壤硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4):830-838.
|
| [37] |
Yu F, Zhang F L, Zhang Y W, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influential factors of soil selenium in typical agricultural area,Chongqing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4):830-838.
|
| [38] |
牛雪, 何锦, 庞雅婕, 等. 三江平原西部土壤硒分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(1):223-229.
|
| [38] |
Niu X, He J, Pang Y J, et al. Distribution feature of soil selenium in West Sanjiang Plain and its influencing factors[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1):223-229.
|
| [39] |
张立, 刘国栋, 吕石佳, 等. 黑龙江省海伦市农耕区土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(5):1046-1054.
|
| [39] |
Zhang L, Liu G D, Lyu S J, et al. Distribution characteristics of selenium cultivated soil and its influencing factors in Hailun County of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(5):1046-1054.
|
| [40] |
李玉超, 王诚煜, 于成广. 辽宁丹东地区土壤Se元素地球化学特征及其影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2020, 50(6):1766-1775.
|
| [40] |
Li Y C, Wang C Y, Yu C G. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soil from Dandong Area,Liaoning Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2020, 50(6):1766-1775.
|
| [41] |
Li Y C, Wang C Y, Yu C G. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soil from Dandong area,Liaoning Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2020, 50(6):1766-1775.
|
| [42] |
史艳芙, 宗良纲, 张艳萍, 等. 茶树根际与非根际土壤硒特性及其影响因素分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(9):1903-1909.
|
| [42] |
Shi Y F, Zong L G, Zhang Y P, et al. Characteristic differences of selenium in the rhizospheric and non-rhizospheric soils of tea plantations,and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(9):1903-1909.
|
| [43] |
王志强, 杨建锋, 石天池. 宁夏石嘴山地区富硒土壤及其利用前景[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(1):228-237.
|
| [43] |
Wang Z Q, Yang J F, Shi T C. A preliminary study of Se-rich soil in the Shizuishan Area,Ningxia and its potential for application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1):228-237.
|
| [44] |
张亚峰, 苗国文, 马强, 等. 青海东部碱性土壤中硒的形态特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(5):1138-1144.
|
| [44] |
Zhang Y F, Miao G W, Ma Q, et al. Distribution characteristics of Se speciation of alkaline soil in eastern Qinghai[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(5):1138-1144.
|
| [45] |
魏然, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 等. 江西省鄱阳湖流域根系土硒形态分析及其迁移富集规律[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(1):109-113.
|
| [45] |
Wei R, Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, et al. An analysis of speciation of selenium as well as its transformation and enrichment in root soil of Poyang Lake basin,Jiangxi Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(1):109-113.
|
| [46] |
成晓梦, 马荣荣, 彭敏, 等. 中国大宗农作物及根系土中硒的含量特征与富硒土壤标准建议[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1367-1372.
|
| [46] |
Cheng X M, Ma R R, Peng M, et al. Characteristics of selenium in crops and roots in China and recommendations for selenium-enriched soil standards[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1367-1372.
|
| [47] |
Long Z D, Yuan L X, Hou Y Z, et al. Spatial variations in soil selenium and residential dietary selenium intake in a selenium-rich county,Shitai,Anhui,China[J]. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 2018, 50:111-116.
|
| [1] |
ZHANG Wen-Bin, ZHOU Xian-Jun, HOU Cui-Xia, WANG Ning-Zu, SUN Ping-Yuan, ZHAO Zhen-Guan, HE Bi. Geochemical characteristics of soils and prospecting potential of the northern Laojunmiao gold deposit in the Beishan area, Gansu Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4): 945-953. |
| [2] |
ZHOU Xue-Ni, CAO Ya-Ting, JI Yang. Element geochemical characteristics of weathering crust profiles of the Wenchuan section in the upper arid valley of the Minjiang River[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3): 597-608. |
|
|
|
|

