|
|
|
| Critical factors in microtremor-based exploration at a depth of thousands of meters |
QI Juan-Juan( ) ) |
| Institute of Geophysical Prospecting of Beijing,Beijing 100027,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract To explore the critical factors influencing the results of microtremor-based exploration at a depth of thousands of meters,this study conducted experiments using triangular arrays based on spatial autocorrelation(SPAC) and extended SPAC(ESPAC).Focusing on factors such as array size,acquisition unit frequency,and acquisition duration,this study explored the frequency band ranges corresponding to different array sizes,the arrangement of arrays in kilometer-depth exploration for obtaining both deep and shallow data,and the improvement in deep resolution.Based on the analysis and discussion results,this study established a parameter-setting system to improve the accuracy of exploration at a depth of thousands of meters.
|
|
Received: 31 August 2023
Published: 27 June 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
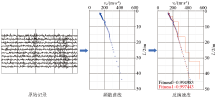
|
Basic principle of microtremor
|
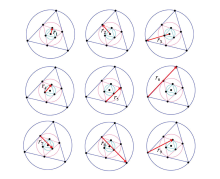
|
Groups of acquisition unit spacing combination
|
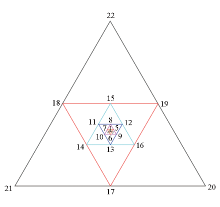
|
Diagram of 7-embedded triangular array
|

| 台阵说明 | 采集单元
个数n/个 | 最大边长
zmax/m | 最小边长
zmin/m | | 7重三角形 | 22 | 640 | 10 | | 6重三角形 | 19 | 640 | 20 | | 5重三角形 | 16 | 640 | 40 | | 4重三角形 | 13 | 640 | 80 | | 3重三角形 | 10 | 640 | 160 | | 2重三角形 | 7 | 640 | 320 | | 1重三角形 | 4 | 640 | - |
|
Description of embedded triangular array scale
|
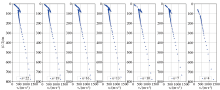
|
Dispersion curves obtained with different numbers of acquisition units
|
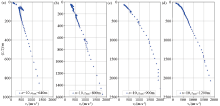
|
Examples of kilometer deep exploration
|
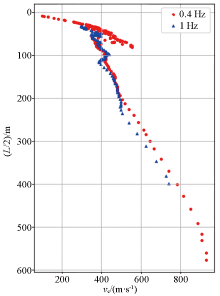
|
Comparison of dispersion curves obtained by different frequency acquisition units
|
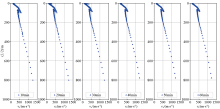
|
Dispersion curves obtained with different acquisition duration
|
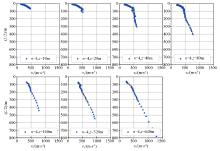
|
Dispersion curves obtained with different array sizes
|

| 道数 | 台阵边
长/m | 频率
范围/Hz | 速度/(m·s-1) | 深度范围/m | | 1,2,3,4 | 10 | 3.71~25.00 | 134.68~481.93 | 2.97~64.93 | | 1,5,6,7 | 20 | 2.32~16.89 | 137.46~512.82 | 4.55~110.55 | | 1,8,9,10 | 40 | 1.00~9.47 | 163.27~606.06 | 8.64~302.73 | | 1,11,12,13 | 80 | 0.95~7.42 | 203.05~769.23 | 13.82~403.94 | | 1,14,15,16 | 160 | 0.88~2.49 | 310.08~769.23 | 62.26~437.61 | | 1,17,18,19 | 320 | 0.85~2.44 | 341.88~930.23 | 72.18~544.32 | | 1,20,21,22 | 640 | 0.78~2.05 | 231.21~1481.4 | 56.7~948.15 |
|
Statistics of frequency range corresponding to different array sizes
|
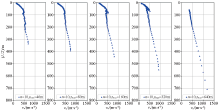
|
Dispersion curves obtained with different embedded triangular array sizes
|
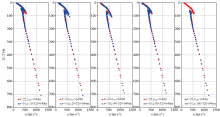
|
Comparison of dispersion curves obtained by different minimum side length array and 7-embedded triangular array
|
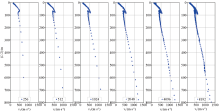
|
Dispersion curves obtained with different iteration sample number
|
| [1] |
王振东. 微动的空间自相关法及其实用技术[J]. 物探与化探, 1986, 10(2):123-133.
|
| [1] |
Wang Z D. The micromotional spatial autocorrelation methodand its practical technique[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1986, 10(2):123-133.
|
| [2] |
冉伟彦, 王振东. 长波微动法及其新进展[J]. 物探与化探, 1994, 18(1):28-34.
|
| [2] |
Ran W Y, Wang Z D. The long-wave microtremors method and its advances[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1994, 18(1):28-34.
|
| [3] |
周超, 刘怡, 赵思为. 综合物探在城市地下空间地质调查隐伏断层探测中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2022, 19(1):64-70.
|
| [3] |
Zhou C, Liu Y, Zhao S W. Application of integrated geophysical methods in the detection of hidden faults in urban underground space investigation[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2022, 19(1):64-70.
|
| [4] |
石科, 杨富强, 李叶飞, 等. 利用微动探测研究城市地下空间结构[J]. 矿产与地质, 2020, 34(2):355-365.
|
| [4] |
Shi K, Yang F Q, Li Y F, et al. Study on urban underground space structure by micro motion exploration[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2020, 34(2):355-365.
|
| [5] |
徐佩芬, 李传金, 凌甦群, 等. 利用微动勘察方法探测煤矿陷落柱[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(7):1923-1930.
|
| [5] |
Xu P F, Li C J, Ling S Q, et al. Mapping collapsed columns in coal mines utilizing Microtremor Survey Methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(7):1923-1930.
|
| [6] |
董耀, 李光辉, 高鹏举, 等. 微动勘查技术在地热勘探中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(6):1345-1351.
|
| [6] |
Dong Y, Li G H, Gao P J, et al. The application of fretting exploration technology in the exploration of middle and deep clean energy[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(6):1345-1351.
|
| [7] |
何正勤, 丁志峰, 贾辉, 等. 用微动中的面波信息探测地壳浅部的速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2007, 50(2):492-498.
|
| [7] |
He Z Q, Ding Z F, Jia H, et al. To determine the velocity structure of shallow crust with surface wave information in microtremors[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2007, 50(2):492-498.
|
| [8] |
黄光明, 徐佩芬, 李长安, 等. 覆盖区岩溶溶洞的微动探测试验研究——以福建永安大湖盆地为例[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(2):536-544.
|
| [8] |
Huang G M, Xu P F, Li C A, et al. Application of 2D microtremor section survey method in covered Karst area,taking Yongan Dahu Basin,Fujian Province as example[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(2):536-544.
|
| [9] |
徐佩芬, 李世豪, 凌甦群, 等. 利用SPAC法估算地壳S波速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(11):3846-3854.
|
| [9] |
Xu P F, Li S H, Ling S Q, et al. Application of SPAC method to estimate the crustal S-wave velocity structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013, 56(11):3846-3854.
|
| [10] |
王振东. 面波勘探技术要点与最新进展[J]. 物探与化探, 2006, 30(1):1-6,12.
|
| [10] |
Wang Z D. Essentials and recent advances of the surface wave exploration technique[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2006, 30(1):1-6,12.
|
| [11] |
Aki K. Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves,with special reference to microtremors[J]. Bulletin,Earthquake Research Institute,1957:35.
|
| [12] |
Okada H, Suto K, Asten M W. The microtremor survey method[M].Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 2004.
|
| [13] |
Capon J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1969, 57(8):1408-1418.
|
| [14] |
刘云祯, 梅汝吾, 叶佩, 等. WD智能天然源面波数据采集处理系统及其应用试验[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(5):1007-1015.
|
| [14] |
Liu Y Z, Mei R W, Ye P, et al. Data acquisition and processing system of WD intelligent natural source surface wave and its application test[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(5):1007-1015.
|
| [1] |
SHI Jing-Tao, LIU Jun-Jian, ZHANG Jun-Chao, WANG Jiang-Yu-Long, JIANG Yu-Ge, WANG Mo, LI Heng-Fei, YANG Wen-Hao, YAN Xiang-Jin. Analysis of soil heavy metal influencing factors and sources in typical small watersheds in shallow mountainous area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3): 834-846. |
| [2] |
PENG Xue-Rui, CHEN Xiang, ZHOU Si-Yu. Factors influencing the Se content in tea leaves and rhizosphere soils of the Liubao tea in Wuzhou City, Guangxi[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(2): 545-554. |
|
|
|
|

