|
|
|
| 3D simulations of geological structures in coastal cities using a electrical resistivity method |
LIU Hong-Hua1,2( ), ZHANG Hui1,2, WANG Ru-Jie1,2, YU Peng1,2,3( ), ZHANG Hui1,2, WANG Ru-Jie1,2, YU Peng1,2,3( ), QIN Sheng-Qiang1,2, LI Wen-Yu4, CHE Rong-Qi4 ), QIN Sheng-Qiang1,2, LI Wen-Yu4, CHE Rong-Qi4 |
1. Key Laboratory of Geological Safety of Coastal Urban Underground Space, Ministry of Natural Resources, Qingdao 266100, China
2. Qingdao Geo-Engineering Surveying Institute (Qingdao Geological Exploration Development Bureau), Qingdao 266100, China
3. Key Laboratory of Coupling Process and Effect of Natural Resources Elements,Beijing 100055, China
4. School of Resource and Geosciences, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou 221116, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract For the underground construction of coastal cities in China, there is an urgent need to accurately position unfavorable geobodies such as faults and boulders. Based on the geological characteristics of coastal cities, this study conducted 3D numerical simulations using a high-density resistivity method, determining the effects of the electrical properties and thickness of the overburden on the survey results, as well as the DC electric field characteristics varying with the sizes and burial depths of detection targets. The results show that the resistivity difference between the overburden and the targets serves as a critical factor in determining the influence of the overburden. For low-resistivity fracture zones, a higher resistivity of the overburden signifies more prominent responses from the fracture zone. Under middle- to high-resistivity overburden conditions, shallowly buried boulders can be easily found, and larger boulders exhibit more significant high-resistivity characteristics. In the exploration along the Qingdao metro line 5, the high-density resistivity method played a vital role in exploring fracture zones and boulders, verifying the effective application effects of the method. The results of this study provide a basis for selecting engineering exploration methods and determining operating parameters in coastal cities.
|
|
Received: 11 August 2023
Published: 19 September 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
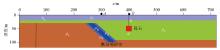
Geoelectric model for numerical simulation
|

| 序号 | 描述 | 参数 | 电阻率等参数数值 | | 1 | 第一层介质,素填土、粉质粘土、淤泥质粉质
粘土、含淤泥粉细砂、中细砂 | ρ1 | 10、50、100、200、500 W×m | | h1 | 5、10、15、20 m | | 2 | 第二层介质,强风化花岗岩、强风化煌斑岩 | ρ2 | 300 W×m | | h2 | (30~h1)m | | 3 | 第三层介质,中微风化花岗岩、中微风化煌斑岩 | ρ3 | 1000 W×m | | h3 | 90 m | | 4 | 断裂 | ρf1 | 50 W×m | | 5 | 构造破碎带 | ρf2 | 100 W×m | | 6 | 孤石 | ρr | 5000 W×m | | h | 0、10、30、50 m | | d | 10、20、30、40 m |
|
Model parameters
|
|
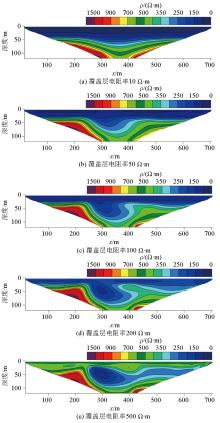
Inversed resistivity sections for different overburden resistivity
|
|
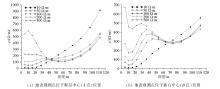
Resistivity curves of different overburden resistivity
|
|
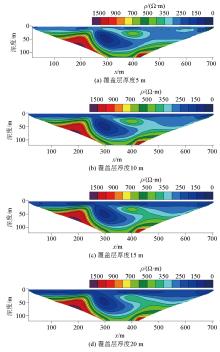
Inversed resistivity sections for different overburden thicks
|
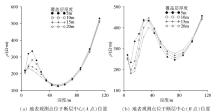
|
Resistivity curves with different thickness of covering layer
|
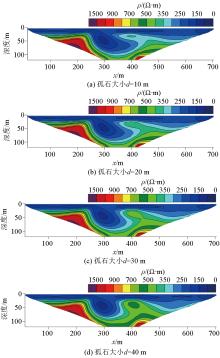
|
Inversed resistivity sections for different boulder sizes
|
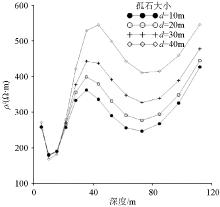
|
Resistivity curves of different sizes of boulders
|
|
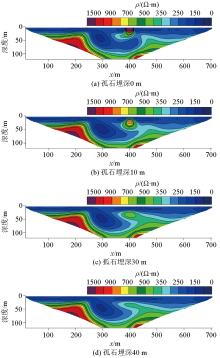
Inversed resistivity sections for different boulder depth
|
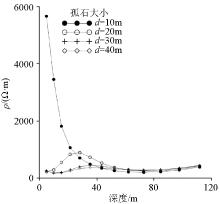
|
Resistivity curves of boulders with different buried depths
|
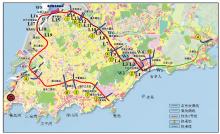
|
Lines layout for resistivity measurement
|
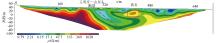
|
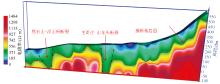
Inversed resistivity section for Line 5
|
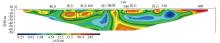
|
Inversed resistivity section for Line 16
|
|
Resistivity model
|
| [1] |
蔡洪美. 盾构地铁隧道孤石探测方法及研究展望[J]. 工程与试验, 2022, 62(4):7-10,58.
|
| [1] |
Cai H M. Detection method and research prospect of boulder detection in shield subway tunnel[J]. Engineering & Test, 2022, 62(4):7-10,58.
|
| [2] |
徐佩芬, 侍文, 凌苏群, 等. 二维微动剖面探测“孤石”:以深圳地铁7号线为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(6):2120-2128.
|
| [2] |
Xu P F, Shi W, Ling S Q, et al. Mapping spherically weathered “Boulders” using 2D microtremor profiling method:A case study along subway line 7 in Shenzhen[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(6):2120-2128.
|
| [3] |
周超, 赵思为. 等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在轨道交通勘探中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2018, 15(1):60-64.
|
| [3] |
Zhou C, Zhao S W. The application of opposing coils transient electromagnetic method to exploration of rail transit[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2018, 15(1):60-64.
|
| [4] |
黄真萍, 周成峰, 曹洁梅. 温纳装置探测孤石深度影响因素及其数值模拟研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2012, 20(5):800-808.
|
| [4] |
Huang Z P, Zhou C F, Cao J M. Influencing factors and numerical simulation of wenner device for detecting boulder depth[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(5):800-808.
|
| [5] |
刘成禹, 林毅鹏, 林超群, 等. 球状孤石在探地雷达探测成果中的表现特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(4):860-866.
|
| [5] |
Liu C Y, Lin Y P, Lin C Q, et al. The performance characteristic of spherical boulder in the georadar detection[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(4):860-866.
|
| [6] |
李术才, 刘征宇, 刘斌, 等. 基于跨孔电阻率CT的地铁盾构区间孤石探测方法及物理模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(3):446-457.
|
| [6] |
Li S C, Liu Z Y, Liu B, et al. Boulder detection method for metro shield zones based on cross-hole resistivity tomography and its physical model tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(3):446-457.
|
| [7] |
徐佩芬, 李世豪, 杜建国, 等. 微动探测:地层分层和隐伏断裂构造探测的新方法[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(5):1841-1845.
|
| [7] |
Xu P F, Li S H, Du J G, et al. Microtremor survey method:A new geophysical method for dividing strata and detecting the buried fault structures[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(5):1841-1845.
|
| [8] |
朱红兵, 陈国光, 赵东东, 等. 微动探测技术在地层结构研究中的应用——以福州滨海新城核心区为例[J]. 华东地质, 2022, 43(3):297-305.
|
| [8] |
Zhu H B, Chen G G, Zhao D D, et al. Application of microtremor survey method in the study of stratum structure:A case study of Binhai New Town,Fuzhou City[J]. East China Geology, 2022, 43(3):297-305.
|
| [9] |
朱义坤, 赵景怀, 缪旭煌, 等. 综合物探方法在蚌埠隆起金多金属矿勘查中的应用——以怀远双沟勘查区为例[J]. 华东地质, 2023, 44(1):82-92.
|
| [9] |
Zhu Y K, Zhao J H, Miao X H, et al. Application of comprehensive geophysical survey in Bengbu uplift gold polymetallic ore exploration:a case study of Huaiyuan Shuanggou exploration area[J]. East China Geology, 2023, 44(1):82-92.
|
| [10] |
赵东东, 张宝松, 宗全兵, 等. 综合物探方法在地铁孤石探测中的应用研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(3):1360-1370.
|
| [10] |
Zhao D D, Zhang B S, Zong Q B, et al. Application of integrated geophysical method to detection of boulder in subway shield zone[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(3):1360-1370.
|
| [11] |
韦涛. 基于高密度电阻率法的浅覆盖型溶洞物探应用研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2021.
|
| [11] |
Wei T. Application of electrical resistivity imaging in geophysical prospecting of shallow covered Karst cave[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2021.
|
| [12] |
严波, 刘颖, 叶益信. 基于对偶加权后验误差估计的2.5维直流电阻率自适应有限元正演[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(1):145-150.
|
| [12] |
Yan B, Liu Y, Ye Y X. 2.5D direct current resistivity adaptive finite-element numerical modeling based on dual weighted posteriori error estimation[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(1):145-150.
|
| [13] |
孙大利, 李貅, 齐彦福, 等. 基于非结构网格三维有限元堤坝隐患时移特征分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(4):804-814.
|
| [13] |
Sun D L, Li X, Qi Y F, et al. Time-lapse characteristics analysis of hidden dangers of three-dimensional finite element levees based on unstructured grids[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(4):804-814.
|
| [14] |
饶荣富, 苏本玉. 直流电阻率法与工作面透明化[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(3):563-569.
|
| [14] |
Rao R F, Su B Y. Direct current resistivity method and the transparency of mining face[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3):563-569.
|
| [15] |
蒋鑫. 高密度电阻率法的正演数值模拟研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2013.
|
| [15] |
Jiang X. Forward modeling study of high-density resistivity method[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2013.
|
| [1] |
LIU Hong-Kai, GAO Lei, ZHANG Jie, HOU He-Sheng, XIE Min-Ying, LI Hong-Qiang. Bedrock surface and fault structures in the Rongcheng uplift revealed from reflection seismic profiles and their implications for the geothermal origin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4): 934-944. |
| [2] |
ZHU Jiang-Bo, WANG Qi-Nian, LIU Yu-Quan, GUAN Da-Wei, LI Tao, YOU Miao, ZHANG Jian. Electrical structure of the Bengbu-Huaibei area and its geological implications[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4): 971-978. |
|
|
|
|

