|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics and bioavailability of selenium and zinc in soils in an area subjected to water and soil erosion : A case study of Changting County, Fujian Province |
TANG Zhi-Min1( ), ZHANG Xiao-Dong1( ), ZHANG Xiao-Dong1( ), MEI Li-Hui2, ZHAN Long1, CHEN Guo-Guang1, LIU Hong-Ying1, ZHOU Mo1, ZHANG Ming1, ZHANG Jie1 ), MEI Li-Hui2, ZHAN Long1, CHEN Guo-Guang1, LIU Hong-Ying1, ZHOU Mo1, ZHANG Ming1, ZHANG Jie1 |
1. Nanjing Center, China Geological Survey, Nanjing 210016, China
2. The First Geological Brigade of Jiangxi Geological Bureau, Nanchang 330200, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Water and soil erosion affects the distribution and partitioning of elements in soils. The distribution and partitioning patterns and bioavailability of trace beneficial elements such as selenium (Se) and zinc (Zn) in water and soil erosion areas serve as significant factors for measuring the ecological effects of water and soil erosion. Through the geochemical survey of soil and crops, this study investigated the geochemical characteristics and bioavailability of Se and Zn in the water and soil erosion area of Changting County, Fujian Province, obtaining the critical geochemical parameters of Se and Zn in soil and crops in the study area. The results are as follows: (1) The soil Se and Zn contents in the study area show median values of 0.43×10-6 and 46×10-6, respectively; (2) Se is enriched in the soil developed from metamorphic rocks, whereas Zn is enriched in the soil developed from metamorphic rocks and granites; (3) The soil Se and Zn contents are higher in bamboo forests compared to other land-use types; (4) The soil Se content shows a decreasing trend as the water and soil erosion intensifies; (5) The bio-concentration factors of Se and Zn are significantly positively correlated with w(Si)/w(Al) ratios, and negatively correlated with Se, Zn, and organic matter. As indicated by the results above, the distribution and partitioning of soil trace beneficial elements like Se and Zn in the study area are primarily subjected to metamorphic rocks and granites. The water and soil erosion is accompanied by a significant soil Se loss. The bioavailability of soil Se and Zn is reduced by the adsorption of clay minerals and organic matter. Additionally, there may be a large proportion of inactive Se and Zn in the soil of the water and soil erosion area.
|
|
Received: 28 July 2023
Published: 19 September 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
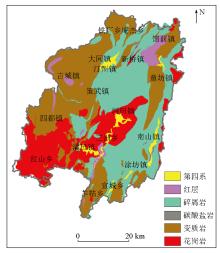
|
Rock formation types in the study area
|
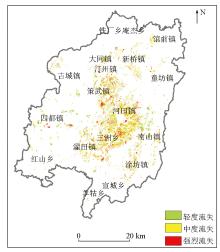
|
Distribution map of soil erosive area in Changting County
|
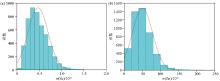
|
Histogram of soil selenium(a) and zinc(b) content in the study area
|

| 元素 | 平均值 | 中位数 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 全国土壤背景值[23] | 福建省土壤背景值[23] | | Se | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.05 | 1.06 | 0.20 | 44% | 0.22 | 0.32 | | Zn | 48 | 46 | 6 | 117 | 23 | 48% | 67 | 70 |
|
Descriptive statistical results of soil selenium and zinc content in the study area
|
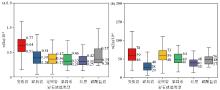
|
Box plot of selenium(a) and zinc(b) content in soils developed from different rock formations in the study area
|
|
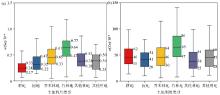
Box plot of soil selenium(a) and zinc(b) in different land use type
|
|
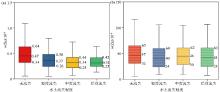
Box plot of soil selenium(a) and zinc(b) content in soil erosive area with different extent
|

|
Geochemical map of soil selenium(a) and zinc(b) in the study area
|

| 指标 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | | pH值 | -0.201 | 0.154 | 0.794 | -0.352 | | S | 0.644 | -0.449 | 0.331 | 0.182 | | Se | 0.779 | -0.313 | -0.132 | 0.122 | | Zn | 0.663 | 0.361 | 0.255 | -0.199 | | SiO2 | -0.886 | -0.331 | 0.162 | 0.163 | | Al2O3 | 0.479 | 0.626 | -0.289 | -0.353 | | TFe2O3 | 0.853 | -0.155 | -0.045 | -0.258 | | MgO | 0.654 | -0.150 | 0.168 | -0.083 | | CaO | -0.010 | 0.092 | 0.864 | -0.014 | | Na2O | 0.050 | 0.633 | 0.176 | 0.594 | | K2O | 0.164 | 0.815 | -0.008 | 0.304 | | 有机质 | 0.687 | -0.296 | 0.133 | 0.521 | | 方差的百分比/% | 34.8 | 18.0 | 14.7 | 9.6 | | 累积百分比/% | 34.8 | 52.8 | 67.5 | 77.1 |
|
Results of principal component analysis
|
|
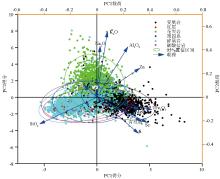
Soil element loading of the principal component
|

| 指标 | Zn-R | Se-R | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | TFe2O3 | K2O | MgO | Na2O | pH | S | 有机质 | Se-T | Zn-T | BCFSe | BCFZn | w(Si)/
w(Al) | CIA | w(Fe)/
w(Mg) | | Zn-R | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Se-R | 0.346* | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | SiO2 | 0.007 | -0.503** | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Al2O3 | 0.051 | 0.506** | -0.963** | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | CaO | -0.122 | 0.387** | -0.526** | 0.416** | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | TFe2O3 | 0.052 | 0.563** | -0.733** | 0.576** | 0.600** | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | K2O | -0.295* | -0.163 | -0.494** | 0.455** | 0.169 | 0.135 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | MgO | -0.106 | 0.158 | -0.268 | 0.039 | 0.545** | 0.710** | 0.134 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | Na2O | -0.310* | -0.216 | -0.179 | 0.098 | 0.272 | 0.061 | 0.765** | 0.281 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | pH | -0.140 | -0.230 | 0.426** | -0.539** | 0.335* | -0.037 | -0.172 | 0.396** | 0.183 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | S | -0.019 | 0.055 | -0.351* | 0.447** | 0.187 | -0.163 | 0.119 | -.388** | -0.104 | -.368** | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | 有机质 | 0.049 | 0.258 | -0.597** | 0.620** | 0.466** | 0.215 | 0.180 | -0.040 | -0.020 | -.297* | 0.774** | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | Se-T | 0.042 | 0.649** | -0.739** | 0.661** | 0.700** | 0.788** | 0.035 | 0.386** | -0.036 | -0.058 | 0.189 | 0.575** | 1.000 | | | | | | | | Zn-T | -0.147 | 0.290* | -0.719** | 0.582** | 0.661** | 0.732** | 0.541** | 0.631** | 0.494** | 0.069 | -0.035 | 0.349* | 0.633** | 1.000 | | | | | | | BCFSe | 0.289* | 0.005 | 0.613** | -0.513** | -0.556** | -0.582** | -0.238 | -0.379** | -0.140 | -0.027 | -0.216 | -0.520** | -0.729** | -0.611** | 1.000 | | | | | | BCFZn | 0.533** | -0.055 | 0.649** | -0.511** | -0.573** | -0.576** | -0.613** | -0.540** | -0.544** | -0.041 | -0.056 | -0.346* | -0.495** | -0.839** | 0.664** | 1.000 | | | | w(Si)/
w(Al) | 0.096 | -0.349* | 0.939** | -0.909** | -0.466** | -0.606** | -0.637** | -0.236 | -0.327* | 0.412** | -0.315* | -0.547** | -0.617** | -0.679** | 0.605** | 0.696** | 1.000 | | | | CIA | 0.281 | 0.615** | -0.532** | 0.618** | 0.166 | 0.416** | -0.370** | -0.141 | -0.611** | -.455** | 0.315* | 0.414** | 0.588** | 0.069 | -0.307* | 0.060 | -0.392** | 1.000 | | w(Fe)/
w(Mg) | 0.180 | 0.516** | -0.575** | 0.676** | 0.092 | 0.345* | -0.026 | -0.384** | -0.251 | -.553** | 0.264 | 0.304* | 0.505** | 0.088 | -0.269 | -0.019 | -0.478** | 0.735** | 1.000 |
|
Correlation coefficient between rice selenium and zinc contents and root soil indexes
|
|
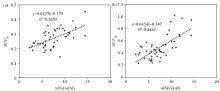
Scatter plot of rice BCFSe (a)、BCFZn (b) vs soil w(Si)/w(Al) values in the study area
|
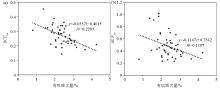
|
Scatter plot of rice BCFSe (a)、BCFZn (b) vs soil organic matter in the study area
|
|
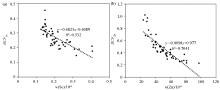
Scatter plot of rice BCFSe (a)、BCFZn (b) vs soil selenium、zinc in the study area
|
| [1] |
李智广, 曹炜, 刘秉正, 等. 我国水土流失状况与发展趋势研究[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2008, 6(1):57-62.
|
| [1] |
Li Z G, Cao W, Liu B Z, et al. Current status and developing trend of soil erosion in China[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 6(1):57-62.
|
| [2] |
史德明. 土壤侵蚀对生态环境与自然灾害的影响[J]. 地球科学进展, 1990, 5(4):41-44.
|
| [2] |
Shi D M. Influence of soil erosion on ecological environment and natural disasters[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1990, 5(4):41-44.
|
| [3] |
刘国华, 傅伯杰, 陈利顶, 等. 中国生态退化的主要类型、特征及分布[J]. 生态学报, 2000, 20(1):1-7.
|
| [3] |
Liu G H, Fu B J, Chen L D, et al. Main types,characteristics and distribution of ecological degradation in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2000, 20(1):1-7.
|
| [4] |
史志华, 刘前进, 张含玉, 等. 近十年土壤侵蚀与水土保持研究进展与展望[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(5):1117-1127.
|
| [4] |
Shi Z H, Liu Q J, Zhang H Y, et al. Study on soil erosion and conservation in the past 10 years:Progress and prospects[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(5):1117-1127.
|
| [5] |
Shi P, Schulin R. Erosion-induced losses of carbon,nitrogen,phosphorus and heavy metals from agricultural soils of contrasting organic matter management[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 618:210-218.
|
| [6] |
Berhe A A, Barnes R T, Six J, et al. Role of soil erosion in biogeochemical cycling of essential elements:Carbon,nitrogen,and phosphorus[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2018, 46:521-548.
|
| [7] |
宁嘉丽, 黄艳荟, 李桂芳, 等. 自然降雨下蔬菜地土壤侵蚀及氮素流失特征[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(1):293-302.
|
| [7] |
Ning J L, Huang Y H, Li G F, et al. Characteristics of soil erosion and nitrogen loss in vegetable field under natural rainfall[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(1):293-302.
|
| [8] |
Liu M D, Zhang Q R, Ge S D, et al. Rapid increase in the lateral transport of trace elements induced by soil erosion in major Karst regions in China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(8):4206-4214.
|
| [9] |
谭见安. 环境生命元素与克山病:生态化学地理研究[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 1996.
|
| [9] |
Tan J A. Environmental life elements and Keshan disease[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 1996.
|
| [10] |
李继云, 陈代中, 任尚学, 等. 影响人体硒低的环境因素——陕西渭北高塬大骨节病区的调查[J]. 环境科学, 1992, 13(6):16-22,84-85.
|
| [10] |
Li J Y, Chen D Z, Ren S X, et al. Environmental factors causing the low levei of Se in human body—A survey on the kaschin beck disease region in Loess Plateau,Shanxi Provice[J]. Environmental Science, 1992, 13(6):16-22,84-85.
|
| [11] |
陈雷. 大力推广长汀经验扎实做好水土流失治理工作[J]. 中国水土保持, 2012(6):1-3,29.
|
| [11] |
Chen L. Vigorously popularize Changting's experience and do a good job in soil erosion control[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2012(6):1-3,29.
|
| [12] |
张巧颖, 陈志强, 陈志彪, 等. 长汀县红壤侵蚀区土壤生态化学计量学特征[J]. 四川师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 40(5):699-702.
|
| [12] |
Zhang Q Y, Chen Z Q, Chen Z B, et al. Characteristics of soil ecological stoichiometry in red soil erosion area in Changting County[J]. Journal of Sichuan Normal University:Natural Science, 2017, 40(5):699-702.
|
| [13] |
李巍, 王成己, 谭丽婷, 等. 基于主成分分析的南方红壤水土流失区土壤肥力质量评价——以福建长汀、福州、武夷山为例[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2018, 24(9):58-60,100.
|
| [13] |
Li W, Wang C J, Tan L T, et al. The study of soil fertility quality evaluation in the red soil region of erosion area in South China based on principal component analysis—Taking Fujian Changting,Fuzhou and Wuyishan as examples[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2018, 24(9):58-60,100.
|
| [14] |
张克信, 潘桂棠, 何卫红, 等. 中国构造—地层大区划分新方案[J]. 地球科学, 2015, 40(2):206-233.
|
| [14] |
Zhang K X, Pan G T, He W H, et al. New division of tectonic-strata superregion in China[J]. Earth Science, 2015, 40(2):206-233.
|
| [15] |
严明书, 黄剑, 何忠庠, 等. 地质背景对土壤微量元素的影响——以渝北地区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(1):199-205,219.
|
| [15] |
Yan M S, Huang J, He Z X, et al. The influence of geological background on trace elements of soil:A case study of Yubei area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(1):199-205,219.
|
| [16] |
罗贤冬, 王伟, 安邦, 等. 安徽省潜山县地质背景、土壤类型对土壤有益微量元素含量的综合影响[J]. 华东地质, 2021, 42(2):210-216.
|
| [16] |
Luo X D, Wang W, An B, et al. Comprehensive influence of geological background and soil type on the content of soil beneficial trace elements in Qianshan County,Anhui Province[J]. East China Geology, 2021, 42(2):210-216.
|
| [17] |
李樋, 刘小念, 刘洪, 等. 基于地质建造的土壤营养元素空间分布特征研究——以大凉山区为例[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2021, 28(6):127-137.
|
| [17] |
Li T, Liu X N, Liu H, et al. Study on spatial distribution characteristics of soil nutrient elements based on geological construction—Take daliangshan region as an example[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2021, 28(6):127-137.
|
| [18] |
中国地质调查局南京地质调查中心. 长汀县水土流失综合地质调查报告[R]. 南京: 中国地质调查局南京地质调查中心, 2019.
|
| [18] |
Nanjing Center, China Geological Survey. Comprehensive geological survey report on soil erosion in Changting County[R]. Nanjing: Nanjing Center,China Geological Survey, 2019.
|
| [19] |
陈国光, 刘红樱, 陈进全, 等. 福建长汀县水土流失的地质影响因素及防治对策[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(6):26-35.
|
| [19] |
Chen G G, Liu H Y, Chen J Q, et al. Geological influence factors of soil erosion in Changting County,Fujian Province and the countermeasures to prevent and control[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(6):26-35.
|
| [20] |
中国地质调查局. DD2005-03生态地球化学评价样品分析技术要求(试行)[S]. 2005.
|
| [20] |
China Geological Survey. DD2005-03 Technical requirements for analysis of eco-geochemical evaluation samples (Trial)[S]. 2005.
|
| [21] |
Ahrens L H. A fundamental law of geochemistry[J]. Nature, 1953, 172:1148.
|
| [22] |
Reimann C, Filzmoser P. Normal and lognormal data distribution in geochemistry:Death of a myth.Consequences for the statistical treatment of geochemical and environmental data[J]. Environmental Geology, 2000, 39(9):1001-1014.
|
| [23] |
侯青叶. 中国土壤地球化学参数[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020.
|
| [23] |
Hou Q Y. Soil geochemical dataset of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020.
|
| [24] |
唐志敏, 张晓东, 张明, 等. 新安江流域土壤元素地球化学特征:来自岩石建造类型的约束[J]. 华东地质, 2023, 44(2):172-185.
|
| [24] |
Tang Z M, Zhang X D, Zhang M, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil elements in Xin'an River Basin:Constraints from rock formation types[J]. East China Geology, 2023, 44(2):172-185.
|
| [25] |
商靖敏, 罗维, 吴光红, 等. 洋河流域不同土地利用类型土壤硒(Se)分布及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(1):301-308.
|
| [25] |
Shang J M, Luo W, Wu G H, et al. Spatial distribution of Se in soils from different land use types and its influencing factors within the Yanghe watershed,China[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(1):301-308.
|
| [26] |
蒋勇军. 典型岩溶流域土地利用变化及其对土壤质量的影响——以云南小江流域为例[D]. 重庆: 西南师范大学, 2005.
|
| [26] |
Jiang Y J. Land use change in typical Karst watershed and its impact on soil quality— A case study of Xiaojiang watershed in Yunnan Province[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2005.
|
| [27] |
唐志敏, 白晓, 湛龙, 等. 福建省长汀县重点水土流失区土壤元素地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 华东地质, 2022. 43(3):324-335.
|
| [27] |
Tang Z M, Bai X, Zhan L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and its indicative significance of soil elements in key soil erosive areas of Changting County,Fujian Province[J]. East China Geology, 2022, 43(3):324-335.
|
| [28] |
国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 22499—2008富硒稻谷[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.
|
| [28] |
General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 22499—2008 Rich selenium paddy[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009.
|
| [29] |
方如康. 环境学词典[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003.
|
| [29] |
Fang R K. Dictionary of environmental science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003.
|
| [30] |
成杭新, 彭敏, 赵传冬, 等. 表生地球化学动力学与中国西南土壤中化学元素分布模式的驱动机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(6):159-191.
|
| [30] |
Cheng H X, Peng M, Zhao C D, et al. Epigenetic geochemical dynamics and driving mechanisms of distribution patterns of chemical elements in soil,Southwest China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(6):159-191.
|
| [31] |
Négrel P, Sadeghi M, Ladenberger A, et al. Geochemical fingerprinting and source discrimination of agricultural soils at continental scale[J]. Chemical Geology, 2015, 396:1-15.
|
| [32] |
王锐, 邓海, 贾中民, 等. 硒在土壤—农作物系统中的分布特征及富硒土壤阈值[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12):5571-5578.
|
| [32] |
Wang R, Deng H, Jia Z M, et al. Distribution characteristics of selenium in a soil-crop system and the threshold of selenium-rich soils[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(12):5571-5578.
|
| [33] |
成晓梦, 马荣荣, 彭敏, 等. 中国大宗农作物及根系土中硒的含量特征与富硒土壤标准建议[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1367-1372.
|
| [33] |
Cheng X M, Ma R R, Peng M, et al. Characteristics of selenium in crops and roots in China and recommendations for selenium-enriched soil standards[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1367-1372.
|
| [34] |
Hawrylak-Nowak B. Comparative effects of selenite and selenate on growth and selenium accumulation in lettuce plants under hydroponic conditions[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2013, 70(2):149-157.
|
| [35] |
Tolu J, Le Hécho I, Bueno M, et al. Selenium speciation analysis at trace level in soils[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2011, 684(1/2):126-133.
|
| [1] |
ZHAO Jun, RAN Qi, ZHU Bo-Hua, LI Yang, LIANG Shu-Yuan, CHANG Jian-Qiang. A method for identifying faults based on well-controlled multi-attribute fusion using a feedforward neural network[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4): 1045-1053. |
| [2] |
LI Qin, YANG Xiao-Ying, JIANG Xing-Yu, LI Jiang. Prediction of fractures in VTI media based on the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4): 1054-1064. |
|
|
|
|

