|
|
|
| Staining algorithm-based reverse time migration imaging for pre-salt structures |
ZHAO Guo-Yong1( ), ZHANG Jian1, LIU Chang2,3, REN Yi2,3, XING Bo-Shen2,3, LI Zi-Zheng2,3, QU Ying-Ming2,3( ), ZHANG Jian1, LIU Chang2,3, REN Yi2,3, XING Bo-Shen2,3, LI Zi-Zheng2,3, QU Ying-Ming2,3( ) ) |
1. R&D Center of Science and Technology,Sinopec Geophysical Corporation,Nanjing 210005,China
2. Key Laboratory of Deep Oil and Gas,China University of Petroleum(East China),Qingdao 266580,China
3. School of Geosciences,China University of Petroleum(East China),Qingdao 266580,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The reverse time migration (RTM) technique can accurately simulate the propagation of seismic waves in subsurface media and image subsurface structures.However,seismic waves can be reflected,refracted,or scattered in weakly illuminated areas,leading to locally reduced signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) in RTM imaging results.The staining algorithm can achieve the tracking and imaging of known geobodies by generalizing the wave equation to the complex domain.It requires a conventional real velocity and an imaginary velocity field as inputs.A conventional staining algorithm requires known real subsurface structures,which is impractical in this study.Hence,this study put forward regional staining to promote the practical development of the staining algorithm.Focusing on subsalt imaging,this study proposed a staining algorithm-based RTM imaging method for subsalt structures.The salt dome model demonstrated that the method proposed in this study can significantly improve the imaging SNRs and resolution of self-selected target regions.
|
|
Received: 20 July 2023
Published: 19 September 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
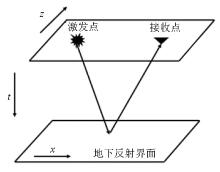
|
RTM imaging principle
|
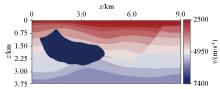
|
Salt velocity model
|
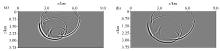
|
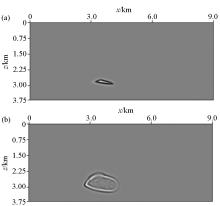
Snapshot of the wavefield of the salt
a—snapshot of the wavefield at the time 1 200 ms; b—snapshot of the wavefield at the time 1 400 ms
|
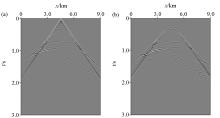
|
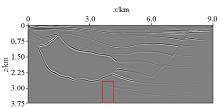
Salt shot record
a—shot record with direct wave; b—shot record without direct wave
|
|
Salt RTM imaging result
|
|
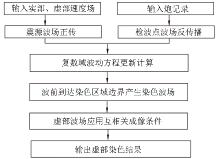
Staining algorithm RTM flowchart
|

|
Salt complex domain velocity model
|
|
Snapshot of the wavefield of complex domain
a—snapshot of the wavefield at the time 1 200 ms;b—snapshot of the wavefield at the time 1 400 ms
|
|
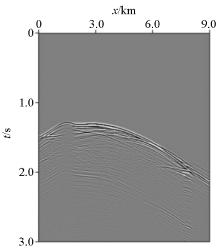
Salt complex domain shot record
|

|
Salt staining RTM imaging result
|
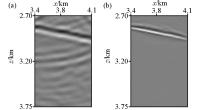
fig. 5 and fig. 10 local enlargement
a—figure 5 localized enlargment;b—figure 10 localized enlargment
">
|
Comparison of fig. 5 and fig. 10 local enlargement
a—figure 5 localized enlargment;b—figure 10 localized enlargment
|
|
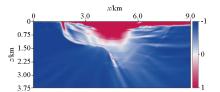
Salt model illumination
|
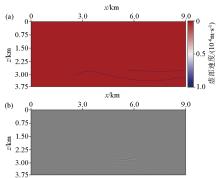
|
Salt model
a—enlarged salt complex domain velocity model;b—enlarged salt staining RTM imaging result
|
|
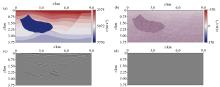
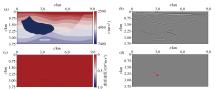
Random error analysis
a—migration velocity field with ±5% random error;b—difference between the velocity field after introducing random errors and the true velocity field;c—RTM based on random error migration velocity field; d—stained RTM based on random error migration velocity
|
|
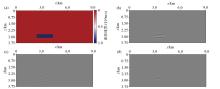
Analysis of anomalies
a—new salt model containing thin layer;b—RTM of new salt model containing thin layer;c—complex domain velocity of precision staining;d—RTM based on precision staining
|
|
Constrained area staining imaging
a—complex domain velocity of area staining;b—RTM based on area staining;c—RTM based on constrained area staining;d—time-limited absorption boundary condition RTM
|
| [1] |
Hemon C. Equations d'onde et modeles[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 1978, 26(4):790-821.
|
| [2] |
Whitmore N D. Iterative depth migration by backward time propagation[C]// SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 1983,Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 1983:382-385.
|
| [3] |
Baysal E, Kosloff D D, Sherwood J W C. Reverse time migration[J]. Geophysics, 1983, 48(11):1514-1524.
|
| [4] |
Loewenthal D, Mufti I R. Reversed time migration in spatial frequency domain[J]. Geophysics, 1983, 48(5):627-635.
|
| [5] |
McMechan G A. Migration by extrapolation of time-dependent boundary values[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 1983, 31(3):413-420.
|
| [6] |
Levin S A. Principle of reverse-time migration[J]. Geophysics, 1984, 49(5):581-583.
|
| [7] |
Teng Y C, Dai T F. Finite-element prestack reverse-time migration for elastic waves[J]. Geophysics, 1989, 54(9):1204-1208.
|
| [8] |
Dong Z X, McMechan G A. 3-D prestack migration in anisotropic media[J]. Geophysics, 1993, 58(1):79-90.
|
| [9] |
Zhu J M, Lines L R. Comparison of Kirchhoff and reverse-time migration methods with applications to prestack depth imaging of complex structures[J]. Geophysics, 1998, 63(4):1166-1176.
|
| [10] |
Causse E, Ursin B. Viscoacoustic reverse-time migration[J]. Journal of Seismic Exploration, 2000, 9(2):165-183.
|
| [11] |
Zhang Y, Xu S, Bleistein N, et al. True-amplitude,angle-domain,common-image gathers from one-way wave-equation migrations[J]. Geophysics, 2007, 72(1):S49-S58.
|
| [12] |
Fletcher R P, Nichols D, Cavalca M. Wavepath-consistent effective Q estimation for Q-compensated reverse-time migration[C]// Copenhagen:74th EAGE Conference and Exhibition incorporating EUROPEC 2012,EAGE Publications BV,2012.
|
| [13] |
刘金朋, 王培培, 方中于, 等. 逆时偏移对棱柱波和回折波的成像效果分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(3):1396-1401.
|
| [13] |
Liu J P, Wang P P, Fang Z Y, et al. Imaging effect analysis of the prism waves and the diving waves based on reversetime migration[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(3):1396-1401.
|
| [14] |
邓文志, 李振春, 王延光, 等. 基于稳定逆时传播算子的黏声介质最小二乘逆时偏移[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(4):791-796.
|
| [14] |
Deng W Z, Li Z C, Wang Y G, et al. The least-squares reverse time migration for visco-acoustic medium based on a stable reverse-time propagator[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(4):791-796.
|
| [15] |
黄建平, 刘培君, 李庆洋, 等. 一种棱柱波逆时偏移方法及优化[J]. 石油物探, 2016, 55(5):719-727.
|
| [15] |
Huang J P, Liu P J, Li Q Y, et al. An optimized reverse time migration approach for the prism wave[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2016, 55(5):719-727.
|
| [16] |
Qu Y M, Huang J P, Li Z C, et al. Attenuation compensation in anisotropic least-squares reverse time migration[J]. Geophysics, 2017, 82(6):S411-S423.
|
| [17] |
Qu Y M, Li J L, Huang J P, et al. Elastic least-squares reverse time migration with velocities and density perturbation[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2018, 212(2):1033-1056.
|
| [18] |
吴玉, 符力耘, 陈高祥. 基于分数阶拉普拉斯算子解耦的黏声介质地震正演模拟与逆时偏移[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(4):1527-1537.
|
| [18] |
Wu Y, Fu L Y, Chen G X. Forward modeling and reverse time migration of viscoacoustic media using decoupled fractional Laplacians[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(4):1527-1537.
|
| [19] |
李金丽, 曲英铭, 刘建勋, 等. 三维黏声最小二乘逆时偏移方法模型研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(5):1013-1025.
|
| [19] |
Li J L, Qu Y M, Liu J X, et al. A model study of three-dimensional viscoacoustic least-squares reverse time migration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(5):1013-1025.
|
| [20] |
郭旭, 黄建平, 李振春, 等. 基于行波分离的VTI介质逆时偏移[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(1):100-109.
|
| [20] |
Guo X, Huang J P, Li Z C, et al. Reverse time migration in VTI media based on wavefield decomposition[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(1):100-109.
|
| [21] |
许璐, 张永生, 李博, 等. 逆时偏移波场分解成像条件研究及应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(4):1541-1547.
|
| [21] |
Xu L, Zhang Y S, Li B, et al. Research and application of reverse time migration using wavefield decomposition imaging condition[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(4):1541-1547.
|
| [22] |
段沛然, 谷丙洛, 李振春. 基于优化算子边界存储策略的高效逆时偏移方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2019, 54(1):93-101.
|
| [22] |
Duan P R, Gu B L, Li Z C. An efficient reverse time migration in the vertical time domain based on optimal operator boundary storage strategy[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2019, 54(1):93-101.
|
| [23] |
曲英铭, 魏哲枫, 刘畅, 等. 面向高陡构造的黏声棱柱波逆时偏移[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2020, 55(4):793-803,701-702.
|
| [23] |
Qu Y M, Wei Z F, Liu C, et al. Viscoacoustic reverse time migration of prismatic wave for steeply dipped structures[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2020, 55(4):793-803,701-702.
|
| [24] |
杨宏伟, 王霁川, 孔庆丰, 等. 井中地震粘声逆时偏移成像影响因素分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(4):877-886.
|
| [24] |
Yang H W, Wang J C, Kong Q F, et al. An analysis of influencing factors of visco-acoustic reverse time migration imaging in borehole seismic[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(4):877-886.
|
| [25] |
徐雷良, 赵国勇, 张剑, 等. 绕射波与一次波联合黏声最小二乘逆时偏移[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(1):91-98.
|
| [25] |
Xu L L, Zhao G Y, Zhang J, et al. Joint Q-compensated least-squares reverse time migration using primary and diffracted waves[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1):91-98.
|
| [26] |
Chen B, Jia X F. Staining algorithm for seismic modeling and migration[J]. Geophysics, 2014, 79(4):S121-S129.
|
| [27] |
杨路. 染色算法在三维复杂介质微弱地震信号模拟和成像中的应用[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2017.
|
| [27] |
Yang L. Staining algorithm in 3D seismic modelling and imaging[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2017.
|
| [28] |
李启华. 基于微弱信号的高质量偏移成像方法研究及其应用[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2018.
|
| [28] |
Li Q H. Research and application of high-quality migration method for weak signal imaging[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2018.
|
| [29] |
刘玉敏. 粘弹性波最小二乘逆时偏移成像研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2020.
|
| [29] |
Liu Y M. Research on viscoelastic least-squares reverse time migration imaging[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2020.
|
| [1] |
XI Yu-He, WANG Hong-Hua, WANG Yu-Cheng, WU Qi-Ming. Application of the minimum entropy method based on a velocity-controlled moving window to the reverse time migration of ground-penetrating radars[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1250-1260. |
| [2] |
XU Lei-Liang, ZHAO Guo-Yong, ZHANG Jian, ZHONG Tian-Miao, GU Jia-Ying, YOU Jian, QU Ying-Ming. Joint Q-compensated least-squares reverse time migration using primary and diffracted waves[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1): 91-98. |
|
|
|
|

