|
|
|
| Practices and future research directions of geophysical exploration for normal-pressure shale gas in complex structural areas,southeastern Chongqing |
HE Xi-Peng1( ), LIU Ming2, XUE Ye2, LI Yan-Jing2, HE Gui-Song2, MENG Qing-Li2, ZHANG Yong2, LIU Hao-Juan2, LAN Jia-Da2, YANG Fan2 ), LIU Ming2, XUE Ye2, LI Yan-Jing2, HE Gui-Song2, MENG Qing-Li2, ZHANG Yong2, LIU Hao-Juan2, LAN Jia-Da2, YANG Fan2 |
1. East China Oil & Gas Company,SINOPEC,Nanjing 210019,China
2. Research Institute of Exploration and Development,East China Oil & Gas Company,SINOPEC,Nanjing 210019,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Southern China boasts great potential for normal-pressure shale gas resources,with distribution areas primarily including the peripheral complex structural areas and the extrabasinal fold belts of the Sichuan Basin.These areas exhibit intricate surface and subsurface geological conditions,leading to poor seismic acquisition quality,low imaging accuracy,and unclear varying patterns of sweet spot parameters.This study systematically summarized the research achievements and technical advances in the seismic acquisition,image processing,and reservoir prediction for normal-pressure shale gas in southeastern Chongqing,including:①The development of variable-density 3D observation system design technique and the seismic excitation and reception technique for complex mountains with limestone surfaces,ensuring sufficient sampling of the reflected wave field in complex subsurface structures and improving data quality and construction efficiency;②The optimization of prestack seismic preprocessing technique for complex mountains,imaging techniques for complex structures in basin-margin transition zones, and imaging techniques for synclinal structures in extrabasinal fold belts,achieving resulting profiles with high signal-to-noise ratios,wide effective frequency bands,and high structural imaging accuracy;③The quantitative prediction of the thickness,formation pressure coefficient,and brittleness of high-quality shales based on research on petrophysical characteristics;the quantitative prediction of the organic carbon content,gas content,and porosity of shales based on statistical petrophysics;the quantitative prediction of fractures formed due to the superimposed effect of multi-stage structural modifications based on the paleo-stress field evolution revealed using the finite element simulation technique;and the ascertainment of the distribution patterns of the current in-situ stress field using the current stress field prediction technique developed using the combined spring model.The above breakthroughs have effectively guided the sweet spot prediction,exploration,and production of normal-pressure shale gas,providing a basis for the discovery of the Nanchuan normal-pressure shale gas field.Subsequent research should focus on more scientific and reasonable seismic acquisition techniques based on seismic reception using 5G wireless nodes,high-precision automatic image processing technologies for high-steep structures in complex mountains,and integrated geology-engineering-economy seismic evaluation methods for sweet spots.
|
|
Received: 15 May 2023
Published: 16 April 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
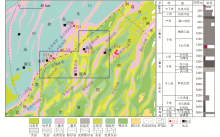
|
Tectonic division and stratigraphic column of southeastern Chongqing
|

| 构造位置 | 盆缘过渡带 | 盆外褶皱区 | | 地震地质条件分区 | 砂岩地表向斜构造 | 灰岩地表斜坡构造 | 灰岩地表高陡构造 | 灰岩地表 | | 向斜构造 | | 主要出露地层岩性 | 侏罗系及上三
叠统砂岩 | 中下三叠统及二
叠系灰岩 | 中下三叠统及二
叠系灰岩 | 中下三叠统及二
叠系灰岩 | | 地下构造 | 页岩埋深 | 4 000~6 000 m | 1 000~4 000 m | 2 000~4 000 m | 1 000~4 000 m | | 地层倾角 | 10°~20° | 20°~40° | 30°~60° | 10°~30° | | 构造宽度 | >10 km | 4.2~9.1 km | 1.5~4.5 km | >15 km | | 断裂密度 | < 0.01条/km2 | 0.10条/km2 | 0.15条/km2 | < 0.01条/km2 | | 断裂断距 | <100 m | 50~200 m | 50~1 900 m | 50~1 500 m | | 断裂长度 | 1~8 km | 0.5~12 km | 1~30 km | 1~26 km | | 地震反射波场 | 简单 | 较简单 | 复杂 | 简单 | | 地震激发接收效果 | 单炮主频 | 28~35 Hz | 23~38 Hz | 20~36 Hz | 23~38 Hz | | 单炮有效频宽(-24 dB) | 50~60 Hz | 40~48 Hz | 38~45 Hz | 40~48 Hz | | 单炮信噪比 | 1.3~1.7 | 0.7~0.9 | 0.6~0.8 | 0.7~0.9 | | 评价 | 好 | 差 | 差 | 差 | | 观测系统参数 | 接收排列片 | 28线216道 | 28线216道 | 28线216道 | 20线216道 | | 道距 | 40 m | 40 m | 40 m | 40 m | | 线距 | 280 m | 280 m | 280 m | 240~280 m | | 排列长度 | 4 300 m | 4 300 m | 4 300 m | 4 300~4 480 m | | 最大偏移距 | 5 805 m | 5 805 m | 5 805 m | 4 914~5 186 m | | 最大非纵距 | 3 900 m | 3 900 m | 3 900 m | 2 380~2 900 m | | 横纵比 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.53~0.67 | | 炮点距 | 80 m | 40 m | 40 m | 80 m | | 炮线距 | 360 m | 360 m | 240 m | 240~360 m | | 炮点密度 | 34.72炮/km2 | 69.44炮/km2 | 104.17炮/km2 | 34.72~52.08炮/km2 | | 面元 | 20 m×20 m | 20 m×20 m | 20 m×20 m | 20 m×20 m | | 叠加次数 | 84 | 168 | 252 | 60~90 | | 炮道密度 | 21万道/km2 | 42万道/km2 | 63万道/km2 | 15~22.5万道/km2 | | 平均40.3万道/km2 | 平均20万道/km2 |
|
Comparison of seismic geological condition and acquisition observation system parameters in different regions of normal-pressure shale gas area
|

| 前期激发接收参数 | 优化后激发接收参数 | 激发
因素 | 侏罗系砂岩 | 井深16 m、药量10 kg | 井深21 m、药量14 kg | | 三叠系灰岩 | 井深16 m、药量12 kg | 井深23 m、药量16 kg | | 二叠系灰岩 | 井深18 m、药量10 kg | 井深25 m、药量18 kg | | 志留系砂岩 | 井深16 m、药量10 kg | 井深21 m、药量14 kg | | 接收因素 | DUS1单点数
字检波器 | 20DX-10 Hz模拟检波器 | 砂岩区1串/灰岩区
2串圆形埋置 |
|
Comparison before and after optimization of excitation and reception parameters
|
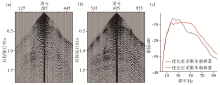
|
Comparison of single gun record and spectrum of seismic acquisition before and after optimization of excitation and reception parameters
a—single gun record of seismic acquisition before optimization of excitation and reception parameters;b—single gun record of seismic acquisition after optimization of excitation and reception parameters;c—single gun record spectrum comparison before and after parameter optimization
|
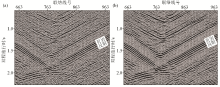
|
Profile comparison of before and after regularization of five-dimensional pre-stack data
a—profile before regularization of five-dimensional pre-stack data;b—profile after regularization of five-dimensional pre-stack data
|

| 序号 | 甜点参数 | 计算方法 | 工作原理 | 预测吻合率 | | 1 | 优质页岩厚度 | ①叠前反演求取纵横波速度比
②求取纵横波速度比≤1.65的地层厚度 | 优质页岩气层纵横波速度比(1.58~1.65)低于普通泥页岩(1.65~1.75) | ≥95% | | 2 | 压力系数 | ,
式中 为地层压力,MPa; 为上覆岩层压力,MPa; 、 为校正系数,针对渝东南常压页岩气储层,通过实际钻孔测试资料拟合求得A为0.068、B为6.64×10-4; 为孔隙接近于零时地层速度,近似基质速度,m/s; 为刚性接近于零时速度,近似孔隙流体速度,m/s; 为预测层段的层速度,m/s | ①钻探表明随页岩地层压力系数增大,地层速度降低
②在Fillippone法基础上引入校正系数 、 ,消除岩性、埋深、物性等其他诸多因素对速度影响 | ≥90% | | 3 | 脆性指数 | ,
式中 为构建的脆性指数; 、 分别为杨氏模量、泊松比,由叠前反演求取;c为常数,针对渝东南常压页岩气储层,实际数据拟合求得c为1.70 | 构建脆性指数 ,与实际矿物脆性指数相关性高 | ≥90% | | 4 | 有机碳含量 | ,
式中 为有机碳含量; 为密度值,由叠前反演求取 | 密度值与TOC负相关性良好,相关系数达0.86,由两者的拟合关系得到基于密度的有机碳含量计算模型 | ≥92% | | 5 | 含气量 | ,
式中 为含气量; 、 分别为拉梅常数值、纵波阻抗值,由叠前反演求取 | 密度、纵波阻抗、 和泊松比等弹性参数与含气量具有较好负相关性,建立页岩含气量预测多元回归模型 | ≥91% | | 6 | 孔隙度 | ①优选出叠后地震属性瞬时相位、瞬时频率,叠前AVO属性截距、梯度,以及弹性参数纵波阻抗、杨氏模量、密度、泊松比等共8种属性
②采用概率神经网络技术,建立上述8种属性与孔隙度间的映射关系,求取孔隙度 | 对叠后、叠前地震等属性以及叠前反演求取的弹性参数代入概率神经网络进行训练学习,利用实验分析、测井资料设定训练数据集、验证数据集,优选敏感属性并建立与孔隙度间的概率神经网络映射关系 | ≥90% |
|
Quantitative prediction methods for reservoir dessert parameters of normal-pressure shale gas
|
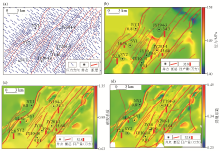
|
Prediction of ancient stress field and HFI in Nanchuan area
a—maximum principal stress direction in middle Yanshanian; b—maximum principal stress in middle Yanshanian; c—S1 in middle Yanshanian; d—HFI in middle Yanshanian
|
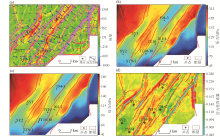
|
Stress field prediction maps of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation shale reservoir in Nanchuan area
a—direction of horizontal maximum principal stress;b—horizontal maximum principal stress;c—horizontal minimum principal stress;d—horizontal stress difference coefficient
|
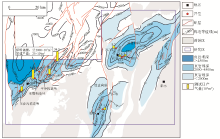
|
The exploration situation map of normal-pressure shale gas in complex structural area of southeastern Chongqing
|
| [1] |
邹才能, 赵群, 丛连铸, 等. 中国页岩气开发进展、潜力及前景[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(1):1-14.
|
| [1] |
Zou C N, Zhao Q, Cong L Z, et al. Development progress, potential and prospect of shale gas in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(1):1-14.
|
| [2] |
马永生, 蔡勋育, 赵培荣. 中国页岩气勘探开发理论认识与实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(4):561-574.
|
| [2] |
Ma Y S, Cai X Y, Zhao P R. China’s shale gas exploration and development:Understanding and practice[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(4):561-574.
|
| [3] |
聂海宽, 何治亮, 刘光祥, 等. 中国页岩气勘探开发现状与优选方向[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2020, 49(1):13-35.
|
| [3] |
Nie H K, He Z L, Liu G X, et al. Status and direction of shale gas exploration and development in China[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2020, 49(1):13-35.
|
| [4] |
郭旭升, 胡德高, 舒志国, 等. 重庆涪陵国家级页岩气示范区勘探开发建设进展与展望[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(8):14-23.
|
| [4] |
Guo X S, Hu D G, Shu Z G, et al. Exploration,development and construction in the Fuling national shale gas demonstration area in Chongqing:Progress and prospect[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(8):14-23.
|
| [5] |
何骁, 吴建发, 雍锐, 等. 四川盆地长宁—威远区块海相页岩气田成藏条件及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(2):259-272.
|
| [5] |
He X, Wu J F, Yong R, et al. Accumulation conditions and key exploration and development technologies of marine shale gas field in Changning-Weiyuan Block,Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(2):259-272.
|
| [6] |
蔡勋育, 赵培荣, 高波, 等. 中国石化页岩气 “十三五” 发展成果与展望[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(1):16-27.
|
| [6] |
Cai X Y, Zhao P R, Gao B, et al. Sinopec's shale gas development achievements during the "Thirteenth Five-Year Plan" period and outlook for the future[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(1):16-27.
|
| [7] |
何希鹏, 何贵松, 高玉巧, 等. 常压页岩气勘探开发关键技术进展及攻关方向[J]. 天然气工业, 2023, 46(6):1-14.
|
| [7] |
He X P, He G S, Gao Y Q, et al. Progress and research direction of key technologies for normal pressure shale gas exploration and development[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2023, 46(6):1-14.
|
| [8] |
何希鹏, 张培先, 任建华, 等. 渝东南南川地区东胜构造带常压页岩气勘探开发实践[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(6):1057-1066.
|
| [8] |
He X P, Zhang P X, Ren J H, et al. Exploration and development practice of normal pressure shale gas in Dongsheng structural belt,Nanchuan area,southeast Chongqing[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2023, 45(6):1057-1066.
|
| [9] |
何希鹏. 四川盆地东部页岩气甜点评价体系与富集高产影响因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(1):59-71.
|
| [9] |
He X P. Sweet spot evaluation system and enrichment and high yield influential factors of shale gas in Nanchuan area of eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(1):59-71.
|
| [10] |
郭彤楼, 蒋恕, 张培先, 等. 四川盆地外围常压页岩气勘探开发进展与攻关方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5):837-845.
|
| [10] |
Guo T L, Jiang S, Zhang P X, et al. Progress and direction of exploration and development of normally-pressured shale gas from the periphery of Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5):837-845.
|
| [11] |
何希鹏, 王运海, 王彦祺, 等. 渝东南盆缘转换带常压页岩气勘探实践[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(1):126-136.
|
| [11] |
He X P, Wang Y H, Wang Y Q, et al. Exploration practices of normal-pressure shale gas in the marginal transition zone of the southeast Sichuan Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(1):126-136.
|
| [12] |
何希鹏, 高玉巧, 何贵松, 等. 渝东南南川页岩气田地质特征及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2021, 11(3):305-316.
|
| [12] |
He X P, Gao Y Q, He G S, et al. Geological characteristics and key technologies for exploration and development of Nanchuan Shale Gas Field in southeast Chongqing[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2021, 11(3):305-316.
|
| [13] |
薛野, 杨帆, 刘厚裕, 等. 彭水地区碳酸盐岩山地地表地震激发接收因素优选及效果[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(3):608-617.
|
| [13] |
Xue Y, Yang F, Liu H Y, et al. Determination of the optimal factors of seismic excitation and reception on the ground surface of carbonate mountainous areas in Pengshui area and its seismic acquisition effects[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3):608-617.
|
| [14] |
刘明, 孟庆利, 杜园, 等. 地震勘探技术在南川地区页岩气勘探开发中的应用[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2022, 12(3):407-416.
|
| [14] |
Liu M, Meng Q L, Du Y, et al. Application of seismic exploration technology in shale gas exploration and development in Nanchuan area[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2022, 12(3):407-416.
|
| [15] |
孟庆利, 任俊兴, 杨帆. 南川地区溶洞及采空区地震资料针对性处理方法[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(3):205-211.
|
| [15] |
Meng Q L, Ren J X, Yang F. Targeted processing method for seismic data of Karst caves and goafs in Nanchuan Area[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(3):205-211.
|
| [16] |
陈祖庆, 杨鸿飞, 王静波, 等. 页岩气高精度三维地震勘探技术的应用与探讨——以四川盆地焦石坝大型页岩气田勘探实践为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(2):9-20.
|
| [16] |
Chen Z Q, Yang H F, Wang J B, et al. Application of 3D high-precision seismic technology to shale gas exploration:A case study of the large Jiaoshiba shale gas field in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(2):9-20.
|
| [17] |
翟桐立, 张洪军, 祝文亮, 等. 全方位高密度单点接收地震采集技术[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(S2):56-63.
|
| [17] |
Zhai T L, Zhang H J, Zhu W L, et al. Full-azimuth high-density single-point receiving technology for seismic acquisition[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(S2): 56-63.
|
| [18] |
薛野, 任俊兴, 杨帆, 等. 南川复杂构造带常压页岩气变密度三维地震采集技术的实践与认识[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(29):12461-12469.
|
| [18] |
Xue Y, Ren J X, Yang F, et al. Practice and understanding of variable-density 3 D seismic exploration technology of normal pressure shale gas in Nanchuan complex structural belt[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(29):12461-12469.
|
| [19] |
薛野, 刘田田. 贵州织金浅煤层地震勘探技术的实践与认识[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(4):161-167.
|
| [19] |
Xue Y, Liu T T. The practice and understanding of seismic exploration technology of shallow coal seams in Zhijin area,Guizhou Province[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2018, 46(4):161-167.
|
| [20] |
杨勤勇, 郭恺, 李博, 等. TTI各向异性地震成像技术及其在页岩气勘探中的应用[J]. 石油物探, 2019, 58(6):882-889,897.
|
| [20] |
Yang Q Y, Guo K, Li B, et al. Application of TTI anisotropic seismic imaging in shale gas exploration[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019, 58(6):882-889,897.
|
| [21] |
杨帆, 蓝加达, 孟庆利, 等. 井约束旅行时恒定层析成像技术在南川地区的应用[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2021, 11(4):514-520.
|
| [21] |
Yang F, Lan J D, Meng Q L, et al. Application of well-constrained travel time preserving tomography technology in Nanchuan area[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2021, 11(4):514-520.
|
| [22] |
李彦婧, 张勇, 潘兰, 等. 基于叠前同时反演的地层压力预测及应用[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(20):70-76.
|
| [22] |
Li Y J, Zhang Y, Pan L, et al. Application of formation pressure prediction based on pre-stack simultaneous inversion[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(20):70-76.
|
| [23] |
胡华锋, 胡起, 林正良. 页岩气储层地层压力预测方法及其在四川盆地的应用[J]. 石油物探, 2018, 57(3):362-368.
|
| [23] |
Hu H F, Hu Q, Lin Z L. Pore pressure prediction for shale gas reservoirs and its application in the Sichuan Basin,China[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2018, 57(3):362-368.
|
| [24] |
张斗中, 汤济广, 蔡俊. 渝东南川地区龙马溪组地应力场特征[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2021, 11(2):190-196.
|
| [24] |
Zhang D Z, Tang J G, Cai J. Characteristics of geostress field of Longmaxi Formation in Nanchuan area,Eastern Chongqing[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2021, 11(2):190-196.
|
| [25] |
任启强, 金强, 冯振东, 等. 和田河气田奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层关键期构造裂缝预测[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 44(6):1-13.
|
| [25] |
Ren Q Q, Jin Q, Feng Z D, et al. Prediction of key period fractures of Ordovician carbonate reservoir in Hetianhe gas field[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum:Edition of Natural Science, 2020, 44(6):1-13.
|
| [26] |
潘兰, 刘昊娟, 张勇, 等. 地应力地震预测方法在南川区块的应用[J]. 中国科技论文, 2021, 16(1):38-43.
|
| [26] |
Pan L, Liu H J, Zhang Y, et al. Application of in situ stress prediction technology based on seimic method in Nanchuan district[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2021, 16(1):38-43.
|
| [27] |
刘昊娟. 地应力地震预测及其在南川页岩气开发中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(3):560-568.
|
| [27] |
Liu H J. The application of in situ stress prediction based on seismic data to shale gas development:A case study of Nanchuan(south Sichuan)area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3):560-568.
|
| [28] |
张广智, 陈娇娇, 陈怀震, 等. 基于页岩岩石物理等效模型的地应力预测方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(6):2112-2122.
|
| [28] |
Zhang G Z, Chen J J, Chen H Z, et al. Prediction for in situ formation stress of shale based on rock physics equivalent model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(6):2112-2122.
|
| [29] |
王延光, 尚新民, 芮拥军. 单点高密度地震技术进展、实践与展望[J]. 石油物探, 2022, 61(4):571-590.
|
| [29] |
Wang Y G, Shan X M, Rui Y J. Progress, practice,and prospect of single-sensor high-density seismic technology[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2022, 61(4):571-590.
|
| [30] |
印兴耀, 马正乾, 宗兆云, 等. 地震岩石物理驱动的裂缝预测技术研究现状与进展(Ⅱ) ——五维地震裂缝预测技术[J]. 石油物探, 2022, 61(3):373-391.
|
| [30] |
Yin X Y, Ma Z Q, Zong Z Y, et al. Review of fracture prediction driven by the seismic rock physics theory (Ⅱ):Fracture prediction from five-dimensional seismic data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2022, 61(3):373-391.
|
| [31] |
郭旭升, 刘金连, 杨江峰, 等. 中国石化地球物理勘探实践与展望[J]. 石油物探, 2022, 61(1):1-14.
|
| [31] |
Guo X S, Liu J L, Yang J F, et al. Geophysical exploration practices and perspectives at Sinopec[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2022, 61(1):1-14.
|
| [32] |
曲寿利. 面向深层复杂地质体油气勘探的地震一体化技术[J]. 石油物探, 2021, 60(6):879-892.
|
| [32] |
Qu S L. An integrated seismic technology for oil and gas exploration in a deep complex geological body[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2021, 60(6):879-892.
|
| [33] |
赵邦六, 董世泰, 曾忠, 等. 中国石油 “十三五” 物探技术进展及 “十四五” 发展方向思考[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(1):108-120.
|
| [33] |
Zhao B L, Dong S T, Zeng Z, et al. Geophysical prospecting technology progress of PetroChina in the 13rd Five-Year Plan period and development direction consideration in the 14th Five-Year Plan period[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(1):108-120.
|
| [34] |
曲寿利. 物探新技术是降低油气勘探开发成本的重要利器[J]. 石油物探, 2019, 58(6):783-790.
|
| [34] |
Qu S L. New geophysical exploration technology:An important tool to reduce the cost of oil and gas exploration and development[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019, 58(6):783-790.
|
| [1] |
CAO Shao-He, REN Feng-Ru, WANG Xiao-Xiao. Critical techniques for sweet spot prediction for tight sandstone reservoirs in the Dongsheng gas field and their application effects[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4): 954-961. |
| [2] |
LI Lu-Lu, JIANG Guo-Yu, LIU Tao, HE Yan, ZHANG Yong-Bo. Geophysical identification of Cretaceous reservoirs in the Shinan area, Junggar Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(2): 334-341. |
|
|
|
|

