|
|
|
| Prospecting for concealed skarn iron deposits using the high-precision gravity-magnetic survey method |
DONG Jian1,2( ), LI Xiao-Peng1,2( ), LI Xiao-Peng1,2( ), FU Chao3, DANG Zhi-Cai3, ZHAO Xiao-Bo4, ZENG Qing-Bin1,2, HU Xue-Ping1,2, WANG Jin-Hui1,2 ), FU Chao3, DANG Zhi-Cai3, ZHAO Xiao-Bo4, ZENG Qing-Bin1,2, HU Xue-Ping1,2, WANG Jin-Hui1,2 |
1. Shandong Institute of Geological Survey, Jinan 250013, China
2. Shandong Technology Research Center of Land Quality Geochemistry and Pollution Prevention Engineering, Jinan 250013, China
3. Tianjin Center of China Geological Survey, Tianjin 300170, China
4. Geological Exploration Institute of Shandong Zhengyuan, China Metallurgical Geology Bureau, Jinan 250013, China |
|
|
|
|
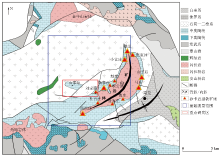
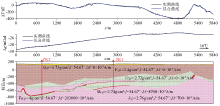
Abstract The Laiwu area in central Shandong Province, situated in the eastern North China Craton, is a significant production area of skarn iron-rich ores. Its ore deposits occur primarily in the contact zone between the mining rock mass and the Middle Ordovician carbonate formation. Based on the latest areal gravity and magnetic survey results, this study thoroughly investigated the characteristics of gravity and magnetic anomalies along the Shijiaquan-Liujiamiao area in the western periphery of the mine rock mass. Then, this study delineated the deep prospecting target combining the characteristics of gravity and magnetic fields of the known iron deposits in the Laiwu area. Large-scale gravity and magnetic profiles were arranged in the favorable mineralization area. With the known boreholes as constraints, the gravity and magnetic anomalies were qualitatively and quantitatively interpreted using the 2.5D gravity-magnetic joint inversion technique. The interpretation results provide a basis for the location and depth of the borehole to be placed, which revealed a 15.8 m-thick iron-rich ore deposit, suggesting remarkable prospecting effects. This study holds critical indicative significance for further exploration of skarn iron ore deposits in this area.
|
|
Received: 06 February 2023
Published: 26 February 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geological map of Laiwu area
|

| 岩层 | 密度σ
/(103kg
· ) | 磁化率κ
/(10-6
·4πSI) | 剩磁Jr
/(10-3A
·m-1) | 物性特征 | | 第四系(黏土) | 1.73 | | | 低密度、无磁性 | | 石炭—二叠系(砂岩) | 2.40 | | | 中等密度、无磁性 | | 寒武—奥陶系(灰岩) | 2.72 | | | 高密度、无磁性 | 中生代侵入岩
(闪长岩) | 2.76 | 4400 | 700 | 高密度、中等磁性 | | 矽卡岩 | 2.74 | 5346 | 8708 | 高密度、高磁性 | | 磁铁矿 | 4.0 | 500000 | 213000 | 高密度、强磁性 |
|
Physical characteristics of rocks (minerals) in the study area
|
|
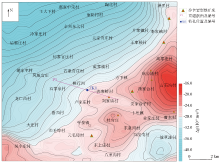
Bouguer gravity anomly in Laiwu area
|
|
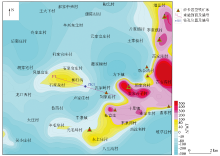
Aeromagnetic pole anomaly in Laiwu area
|
|
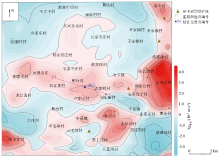
Residual Bouguer gravity anomly in Laiwu area
|
|
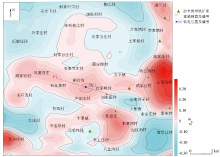
Vertical second derivative of Bouguer gravity in Laiwu area
|
|
The 2.5D combined granity and magnetic inversion inference of the Shijiaquan-Liujiamiao profile
|
| [1] |
赵一鸣. 中国主要富铁矿床类型及地质特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(4):686-705.
|
| [1] |
Zhao Y M. Main genetic types and geological characteristics of iron-rich ore deposits in China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(4):686-705.
|
| [2] |
张招崇, 李厚民, 李建威, 等. 我国铁矿成矿背景与富铁矿成矿机制[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2021, 51(6):827-852.
|
| [2] |
Zhang Z C, Li H M, Li J W, et al. Geological settings and metallogenesis of high-grade iron deposits in China[J]. Scientia Sinica:Terrae, 2021, 51(6):827-852.

|
| [3] |
段壮. 山东莱芜地区矽卡岩型铁矿床成矿作用与成矿机制研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2019:8-13.
|
| [3] |
Duan Z. The mineralization and mechanism of the iron skarn deposits in Laiwu district,Shandong Province[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2019:8-13.
|
| [4] |
费详惠, 张招崇, 韩鎏. 山东张家洼矽卡岩型铁矿矿物学特征及其对成矿环境的指示意义[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(6):1873-1896.
|
| [4] |
Fei X H, Zhang Z C, Han L. Mineralogy of the Zhangjiawa skarn iron deposit in Shandong Province and its implications for metallogenic environment[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(6):1873-1896.
|
| [5] |
郝兴中, 王巧云. 鲁中隆起区中北部矽卡岩型铁矿成矿预测[J]. 地质学刊, 2016, 40(3):443-449.
|
| [5] |
Hao X Z, Wang Q Y. Metallogenic prediction of skarn iron deposits in the central and northern Luzhong uplift,East China[J]. Journal of Geology, 2016, 40(3):443-449.

|
| [6] |
耿安凯. 山东莱芜张家洼铁矿地质背景及矿床成因分析[J]. 世界有色金属, 2017(9):288-289.
|
| [6] |
Geng A K. Geological background and ore genesis analysis of the depression iron deposit in Laiwu,Shandong[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2017(9):288-289.
|
| [7] |
宗信德, 李卫, 赵宏生, 等. 山东莱芜接触交代—热液铁矿多因素成矿及特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2011, 20(5):370-375.
|
| [7] |
Zong X D, Li W, Zhao H S, et al. The contact metasomatic-hydrothermal iron deposit in Laiwu,Shandong Province:Multi-factor metallogenesis[J]. Geology and Resources, 2011, 20(5):370-375.
|
| [8] |
王云燕, 徐韶辉, 吴秉禄. 山东莱芜地区牛泉铁矿成矿地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 山东国土资源, 2021, 37(4):9-16.
|
| [8] |
Wang Y Y, Xu S H, Wu B L. Geological characteristics and origin of Niuquan iron deposit in Laiwu area in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2021, 37(4):9-16.
|
| [9] |
马明, 常洪华, 李亚东, 等. 淄博—莱芜地区矽卡岩型铁矿成矿规律和成矿模式探讨[J]. 山东国土资源, 2020, 36(7):9-15.
|
| [9] |
Ma M, Chang H H, Li Y D, et al. Study on metallogenic regularity and metallogenic model of skarn type iron deposit in zibo-Laiwu area[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2020, 36(7):9-15.
|
| [10] |
陈应华, 蓝廷广, 王洪, 等. 莱芜张家洼铁矿磁铁矿LA-ICP-MS微量元素特征及其对成矿过程的制约[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(4):32-49.
|
| [10] |
Chen Y H, Lan T G, Wang H, et al. LA-ICP-MS trace element characteristics of magnetite from the Zhangjiawa iron deposit,Laiwu and constraints on metallogenic processes[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(4):32-49.
|
| [11] |
宗信德, 徐建, 卢铁元, 等. 山东莱芜矿山矿田铁矿产出构造类型、矿体型式及大-大中型矿床赋存规律[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2010, 25(3):234-240.
|
| [11] |
Zong X D, Xu J, Lu T Y, et al. Stuctural types,ore body styles and occurrence pattern of large,large-medium iron deposits in Kuangshan iron ore field,Sandong Province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2010, 25(3):234-240.
|
| [12] |
王润生, 郝兴中, 刘洪波, 等. 鲁西齐河地区矽卡岩型铁矿重磁方法找矿规律研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(2):664-677.
|
| [12] |
Wang R S, Hao X Z, Liu H B, et al. Study on prospecting law of skarn type iron deposit by gravity and magnetic method in Qihe area of western Shandong[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(2):664-677.
|
| [13] |
宋豪, 张义蜜, 王万银. 河南内黄—浚县一带重磁异常与深部磁铁矿靶区预测研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1191-1204.
|
| [13] |
Song H, Zhang Y M, Wang W Y. The research on the prediction of gravity and magnetic anomalies and deep magnetite target areas in the Neihuang-Xunxian area of Henan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1191-1204.
|
| [14] |
施兴, 彭朝晖, 王德启, 等. 重力勘查在寻找铁矿上的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(2):159-162.
|
| [14] |
Shi X, Peng Z H, Wang D Q, et al. The application of gravity survey to iron deposit prospecting[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(2):159-162.
|
| [15] |
罗凡, 严加永, 付光明. 基于已知信息约束的重磁三维反演在深部磁铁矿勘查中的应用——以安徽泥河铁矿为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(1):50-60.
|
| [15] |
Luo F, Yan J Y, Fu G M. The application of gravity and magnetic three-dimensional inversion based on known information constraint in deep magnetite exploration:A case study of the Nihe iron deposit in Anhui Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(1):50-60.
|
| [16] |
邱光辉, 王海焦, 张海亮, 等. 重磁方法在程家村隐伏磁铁矿勘查中的应用[J]. 山东国土资源, 2016, 32(10):44-47,51.
|
| [16] |
Qiu G H, Wang H J, Zhang H L, et al. Application of gravity and magnetic methods in prospecting buried magnetite deposit in Chengjiacun[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2016, 32(10):44-47,51.
|
| [17] |
赵敏, 盛勇, 戚良刚. 高精度重磁测量在覆盖区找矿中的应用——以无为县蔚山铁铜矿预查为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1211-1216.
|
| [17] |
Zhao M, Sheng Y, Qi L G. The application of high precision gravity and magnetic survey to prospecting in coverage area:A case study of the reconnaissance of Weishan iron and copper deposit in Wuwei County[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1211-1216.
|
| [1] |
XU Xue-Yi, XIONG Sheng-Qing, YANG Xue, GAO Wei-Hong, FAN Zheng-Guo, JIA Zhi-Ye. Aerogeophysical anomalies and prospecting direction in the Fengtai ore concentration area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1157-1168. |
| [2] |
GAO Wei-Qiang, SHI Zhao-Yang, ZHANG Li-Ming, FENG Xu-Liang. Successive regression for determining the optimum terrain correction density in mountainous areas[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(6): 1530-1538. |
|
|
|
|

