|
|
|
| Factors influencing the Se content in tea leaves and rhizosphere soils of the Liubao tea in Wuzhou City, Guangxi |
PENG Xue-Rui( ), CHEN Xiang, ZHOU Si-Yu ), CHEN Xiang, ZHOU Si-Yu |
| No. 270 Geological Team of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Liuzhou 545005, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study aims to investigate the characteristics and influencing factors of selenium (Se) content in the tea leaf-rhizosphere soil system of the Liubao tea in Wuzhou, Guangxi. With the main tea gardens in Liubao and Shizhai towns, the core production areas of the Liubao tea, as study areas, this study conducted statistical analysis of the Se content in the tea leaves, rhizosphere soils, and tea leachate samples of the Liubao tea. The results show that: ① The Se content in soils of the study areas ranged from (0.40~1.98)×10-6, averaging 1.08×10-6; ② The Se content in Liubao tea leaves was between (0.03~0.25)×10-6, averaging 0.07×10-6, with a Se enrichment rate of 68%; ③ The leaching rates of Se in tea leachate ranged from 0~23.95%; ④ The Se content in the rhizosphere soils of tea gardens principally depended on soil parent materials and silica-sesquioxide ratios; ⑤ The P and N elements in soils can facilitate the absorption of soil Se by tea leaves, while the iron and aluminum oxides in acidified soils hinder the full utilization of soil Se by the Liubao tea. Hence, appropriate biochemical and agronomic measures are recommended for acidified soil amelioration to enhance the Se enrichment ability of the Liubao tea.
|
|
Received: 20 January 2023
Published: 16 April 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sampling points in study area
|

| 指标 | 标准偏差 | 变异系数 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 浓集系数(K) | | Al2O3 | 2.74 | 0.16 | 23.03 | 10.96 | 16.84 | 1.34 | | CaO | 0.02 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.054 | 0.08 | 0.03 | | Corg | 0.29 | 0.21 | 2.17 | 0.87 | 1.39 | 3.97 | | Fe2O3 | 1.51 | 0.24 | 9.51 | 2.93 | 6.36 | 1.35 | | K2O | 0.34 | 0.17 | 2.80 | 1.29 | 2.07 | 0.83 | | MgO | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.86 | 0.47 | 0.65 | 0.36 | | SiO2 | 5.61 | 0.09 | 77.57 | 51.53 | 63.66 | 0.98 | | As | 13.25 | 0.56 | 72.50 | 7.07 | 23.60 | 2.36 | | B | 13.32 | 0.32 | 78.70 | 9.93 | 41.49 | 1.04 | | Cd | 0.07 | 1.06 | 0.50 | 0.013 | 0.07 | 0.78 | | Cr | 20.59 | 0.21 | 150.00 | 58.90 | 95.81 | 1.47 | | Cu | 4.62 | 0.18 | 39.10 | 19.20 | 26.30 | 1.10 | | Ge | 0.20 | 0.14 | 1.74 | 0.70 | 1.38 | 1.06 | | Hg | 0.04 | 0.38 | 0.27 | 0.061 | 0.11 | 2.75 | | Mn | 95.57 | 0.65 | 488.00 | 56.50 | 147.19 | 0.25 | | Mo | 1.44 | 0.76 | 7.60 | 0.50 | 1.90 | 2.38 | | N | 243.68 | 0.19 | 2092.00 | 872.00 | 1283.66 | 2.01 | | Ni | 4.55 | 0.20 | 37.90 | 11.20 | 22.87 | 0.88 | | P | 105.47 | 0.27 | 700.00 | 235.00 | 389.08 | 0.75 | | Pb | 6.21 | 0.21 | 51.10 | 20.30 | 28.92 | 1.26 | | S | 69.14 | 0.24 | 472.00 | 157.00 | 288.00 | 1.92 | | Se | 0.44 | 0.41 | 1.98 | 0.40 | 1.08 | 5.40 | | Ti | 635.45 | 0.12 | 7213.00 | 4071.00 | 5094.82 | 1.18 | | Zn | 10.92 | 0.27 | 68.00 | 22.00 | 40.21 | 0.59 | | pH值 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 5.12 | 3.96 | 4.41 | | | Saf | 0.85 | 0.29 | 5.58 | 1.58 | 2.89 | 0.41 |
|
Characteristics of parameter contents in rhizosphere soils of Liubao tea of the study area(n=50)
|

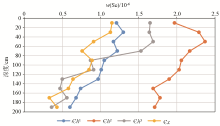
| 洞口组一
段($\epsilon$h1) | 洞口组二
段($\epsilon$h2) | 黄洞口组
三段($\epsilon$h3) | 小内冲组
($\epsilon$x) | | τ | 1.18 | 0.40 | 0.23 | 5.16 |
|
Statistics of mass transfer coefficient of selenium in different geological background(n=40)
|
|
Contents of selenium along vertical soil profiles of different geological backgrounds
|

| 指标 | r | | 指标 | r | | 指标 | r | | 指标 | r | | Cr | 0.884** | | As | 0.313* | | Corg | 0.016 | | N | -0.148 | | Ti | 0.793** | | Cu | 0.307* | | K2O | -0.015 | | Pb | -0.158 | | Mo | 0.560** | | Saf | -0.785** | | B | -0.018 | | Zn | 0.161 | | Ni | 0.499** | | P | -0.370** | | Cd | -0.124 | | pH | -0.022 | | Ge | 0.460** | | S | -0.327* | | Hg | -0.150 | | | | | MgO | 0.428** | | CaO | -0.042 | | Mn | -0.106 | | | |
|
Correlation coefficients of selenium contents and other physicochemical parameters of rhizosphere soils (n=50)
|

| 样品序号 | 茶叶中Se
含量/10-6 | 浸出液中Se
浓度/(mg·L-1) | 浸出率/% | | 1 | 0.074 | 0.0005 | 13.51 | | 2 | 0.130 | 0.001 | 15.38 | | 3 | 0.248 | 0.001 | 8.06 | | 4 | 0.084 | 0.001 | 23.95 | | 5 | 0.062 | 0 | 0 | | 6 | 0.082 | 0 | 0 |
|
Dissovled rate of selenium in tea
|

| 指标 | r | 指标 | r | 指标 | r | | Saf | 0.734** | Se | -0.686** | Ge | -0.317* | | P | 0.546** | Cr | -0.596** | pH | 0.035 | | N | 0.501** | As | -0.478** | Corg | 0.228 | | S | 0.349* | Ti | -0.461** | | | | Hg | 0.292* | MgO | -0.341* | | |
|
Correlation coefficients between the bioconcentration factors of selenium in tea leaves and contents of other elements in soils(n=50)
|

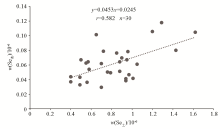
| n | Saf | Se土平均值 | Se茶平均值 | 相关系数 | | A组 | 30 | 1.58~2.92 | 1.32 | 0.064 | 0.121 | | B组 | 30 | 2.51~5.38 | 0.82 | 0.062 | 0.582** |
|
Characteristics of selenium contents in rhizosphere soils and tea leaves of group A and group B
|
|
Scattered plots of selenium contents in rhizosphere soils and tea leaves of group B
|
| [1] |
Roman M, Jitaru P, Barbante C. Selenium biochemistry and its role for human health[J]. Metallomics, 2014, 6(1):25-54.
|
| [2] |
吴永尧, 彭振坤, 陈建英, 等. 水稻对环境硒的富集和耐受能力研究[J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 1999, 16(4):42-44.
|
| [2] |
Wu Y Y, Peng Z K, Chen J Y, et al. Research on the capacity of rice accumulation and re-sistance Se in environment[J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 1999, 16(4):42-44.
|
| [3] |
王立平, 唐德剑, 沈亚美, 等. 硒的营养缺乏现状及补充方式[J]. 食品工业, 2020, 41(1):339-343.
|
| [3] |
Wang L P, Tang D J, Shen Y M, et al. The status quo of nutrient deficiency and suppleme-ntation methods of selenium[J]. The Food Industry, 2020, 41(1):339-343.
|
| [4] |
Navarro-Alarcon M, Cabrera-Vique C. Selenium in food and the human body:A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 400:115-141.
|
| [5] |
汤超华, 赵青余, 张凯, 等. 富硒农产品研究开发助力我国营养型农业发展[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(18):3122-3133.
|
| [5] |
Tang C H, Zhao Q Y, Zhang K, et al. Promoting the development of nutritionally guided agriculture in research and development of selenium-enriched agri-products in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(18):3122-3133.
|
| [6] |
陈永波, 吴一鸣, 刘源, 等. 浅议开阳富硒茶的发展现状与对策[J]. 耕作与栽培, 2010(6):9.
|
| [6] |
Chen Y B, Wu Y M, Liu Y, et al. Current situation and countermeasures of selenium-enriched tea in Kaiyang[J]. Tillage and Cultivation, 2010(6):9.
|
| [7] |
温立香, 郭雅玲. 富硒茶的研究进展[J]. 热带作物学报, 2013, 34(1):201-206.
|
| [7] |
Wen L X, Guo Y L. Research progress of selenium-enriched tea in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2013, 34(1):201-206.
|
| [8] |
彭赞文, 张立杰, 程道品, 等. 广西梧州六堡茶产区土壤硒含量及其与茶叶中硒的相关性分析[J]. 茶叶通讯, 2021, 48(3):430-434.
|
| [8] |
Peng Z W, Zhang L J, Cheng D P, et al. Correlation analysis of selenium content in soil and tea in Liubao tea producing area of Wuzhou,Guangxi[J]. Journal of Tea Communication, 2021, 48(3):430-434.
|
| [9] |
张豪杰, 郝心愿, 周超, 等. 富硒区茶树鲜叶中硒累积与土壤因子的相关性分析[J]. 茶叶科学, 2020, 40(4):465-477.
|
| [9] |
Zhang H J, Hao X Y, Zhou C, et al. Correlation analysis between selenium accumulation in tea leaves and soil factors in selenium-rich areas[J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2020, 40(4):465-477.
|
| [10] |
易桂花, 彭培好, 倪师军, 等. 四川蒙顶山茶叶含硒量与土壤的含硒量和pH值的关系[J]. 成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 37(5):566-569.
|
| [10] |
Yi G H, Peng P H, Ni S J, et al. Study on contents of tea selenium and the relationship of soil pH in Mengding tea gardens of Sichuan,China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology:Science & Technology Edition, 2010, 37(5):566-569.
|
| [11] |
叶飞, 龚自明, 高士伟, 等. 湖北恩施茶园土壤及茶叶硒元素调查研究[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2015, 33(3):275-278.
|
| [11] |
Ye F, Gong Z M, Gao S W, et al. Investigation of the selenium element in tea plantation of Enshi district,Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2015, 33(3):275-278.
|
| [12] |
中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T 0295—2016土地质量地球化学评价规范[S]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社有限责任公司, 2016.
|
| [12] |
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. DZ/T 0295—2016 Specification of land quality geochemical assessment[S]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2016
|
| [13] |
赵佐平, 付静, 岳思羽, 等. 陕南茶园茶叶品质分析及重金属含量现状评估[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(16):201-211.
|
| [13] |
Zhao Z P, Fu J, Yue S Y, et al. Analysis of tea quality and assessment of heavy metal content status in tea plantations of southern Shanxi Province,China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(16):201-211.
|
| [14] |
鄢明才, 顾铁新, 迟清华, 等. 中国土壤化学元素丰度与表生地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 1997, 21(3):161-167.
|
| [14] |
Yan M C, Gu T X, Chi Q H, et al. Abundance of chemical elements of soils in China and supergenesis geochemistry characteristics[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1997, 21(3):161-167.
|
| [15] |
Goldberg S, Lesch S M, Suarez D L. Predicting selenite adsorptionby soils using soil chemical parameters in the constant capacitance model[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(23):5750-5762.

|
| [16] |
张亚丽, 张志敏, 张继军, 等. 安康西部农田土壤硒形态及农作物富硒特征[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(3):229-235.
|
| [16] |
Zhang Y L, Zhang Z M, Zhang J J, et al. Soil selenium speciation in cropland of western Ankang and the characterustics of corp selenium enrichment[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(3):229-235.
|
| [17] |
沈慧芳, 杨波, 方克明, 等. 江西浮梁茶园土壤硒与茶叶硒富集能力的研究[J]. 上海农业学报, 2015, 31(1):59-62.
|
| [17] |
Shen H F, Yang B, Fang K M, et al. Study on the selenium-enriching ability in tea and tea garden soil selenium in Fuliang,Jiangxi Provice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 2015, 31(1):59-62.
|
| [18] |
吴一群, 陈子聪, 颜明娟, 等. 福建省寿宁县茶园土壤硒状况及其有效性[J]. 茶叶学报, 2018, 59(3):131-134.
|
| [18] |
Wu Y Q, Chen Z C, Yan M J, et al. Status and availability of selenium in soil at tea plantations in Shouning County[J]. Acta Tea Sinica, 2018, 59(3):131-134.
|
| [19] |
宋志雪, 潘岩灵, 何华婷, 等. 都匀毛尖茶园土壤及茶叶锌硒含量的调查[J]. 茶叶, 2018, 44(4):191-193.
|
| [19] |
Song Z X, Pan Y L, He H T, et al. Investigation on zinc and selenium contents in soil and tea leaves of Duyun Maojian tea garden[J]. Journal of Tea, 2018, 44(4):191-193.
|
| [20] |
Zhu J M, Thomas M, Robert B, et al. The occurrence and origin of seleni-um minerals in Se-rich stone coals,spoils and their adjacent soils in Yutangba,China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012,330-331:27-38.
|
| [21] |
Chadwick O A, Brimhall G H, Hendricks D M. From a black toa gray box-A mass balance interpretation of pedogenesis[J]. Geomorphology, 1990: 3(3/4):369-390.

|
| [22] |
Babechuk M G, Widdowson M, Kamber B S. Quantifying chemical weathering intensity and trace element release from two contrasting basalt profiles,Deccan Traps,India[J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 363:56-75.

|
| [23] |
Oeser R A, Stroncik N, Moskwa L M, et al. Chemistry andmicrobiology of the Critical Zone along a steep climate andvegetation gradient in the Chilean Coastal Cordillera[J]. Catena, 2018, 170:183-203.

|
| [24] |
徐文波, 朱建明, 秦海波, 等. 铁/锰和铝氧化物吸附硒的行为研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2017, 37(3):357-365.
|
| [24] |
Xu W P, Zhu J M, Qin H B, et al. A study on selenium oxyanions adsorbed onto iron/mang-anese/aluminum oxides[J]. Acta Miner Alogicasinica, 2017, 37(3):357-365.
|
| [25] |
李永华, 王五一, 雒昆利, 等. 大巴山区土壤中的硒和氟[J]. 土壤学报, 2004, 41(1):61-67.
|
| [25] |
Li Y H, Wang W Y, Luo K L, et al. Distribution of selenium and fluorine in soils of daba mountains[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2004, 41(1):61-67.
|
| [26] |
Pezzarossa B, Piccotino D, Petruzzelli G. Sorption and desorption of selenium in different soils of the Mediterranean Area[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1999, 30(19/20):2669-2679.

|
| [27] |
肖高强, 宗庆霞, 向龙洲, 等. 云南省盈江县旧城—姐冒地区土壤和农产品硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(2):412-418.
|
| [27] |
Xiao G Q, Zong Q X, Xiang L Z, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soils and agricultural products in the Jiucheng-Jiemao area,Yingjiang County,Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(2):412-418.
|
| [28] |
李杰, 钟晓宇, 赖俊翔, 等. 广西典型岩溶地区硒在土壤—作物系统中累积特征及其影响因素[J]. 矿产与地质, 2022, 36(2):380-388.
|
| [28] |
Li J, Zhong X Y, Lai J X, et al. Accumulation characteristics and influencing factor of seleni-um in soil-crop system in typical karst area of Guangxi[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2022, 36(2):380-388.
|
| [29] |
杨如意, 杨程, 石晓菁, 等. 硒镉高背景区茶叶中硒和砷、汞、镉的积累与浸出特征研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(9):2023-2030.
|
| [29] |
Yang R Y, Yang C, Shi X J, et al. Selenium,arsenic,mercury and cadmium in tea leaves and infusion of a green tea grown in an area with a high geological background of selenium and cadmium[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(9):2023-2030.
|
| [30] |
郑宏彬, 张婉君, 穆青, 等. 恩施富硒茶硒和茶多酚的溶出特征及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2019, 38(1):103-111.
|
| [30] |
Zheng H B, Zhang W J, Mu Q, et al. Dissolution characteristics and antioxidant activity of selenium and tea polyphenols in Enshi Se-enriched tea[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2019, 38(1):103-111.
|
| [31] |
魏然, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 等. 江西省鄱阳湖流域根系土硒形态分析及其迁移富集规律[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(1):109-113.
|
| [31] |
Wei R, Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, et al. An analysis of speciation of selenium as well as its trans-formation and enrichment in root soil of Poyang Lake Basin,Jiangxi Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(1):109-113.
|
| [32] |
张立, 姜侠, 崔玉军, 等. 松嫩平原吕大火房垂直剖面中硒赋存形态及影响因素析[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6):603-608.
|
| [32] |
Zhang L, Jiang X, Cui Y J, et al. Analysis on the occurrenceforms of selenium and influencing factors in Ludahuofang vertical section of Songnen Plain[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6):603-608.
|
| [33] |
余飞, 张风雷, 张永文, 等. 重庆典型农业区土壤硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4):830-838.
|
| [33] |
Yu F, Zhang F L, Zhang Y W, et al. Geochemical characteristicsand influential factors of soil selenium in typical agricultural area,Chongqing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4):830-838.
|
| [34] |
严洪泽, 周国华, 孙彬彬, 等. 福建龙海杨梅产地元素地球化学特征[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(6):1155-1166.
|
| [34] |
Yan H Z, Zhou G H, Sun B B, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the bayberry producing area in Longhai,Fujian[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(6):1155-1166.
|
| [35] |
谢瑞芝, 董树亭, 胡昌浩, 等. 氮硫互作对玉米籽粒营养品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2003, 36(3):263-268.
|
| [35] |
Xie R Z, Dong S T, Hu C H, et al. Influence of nitrogen and sulfur interaction on grain quality of maize[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2003, 36(3):263-268.
|
| [36] |
吴军, 刘秀芳, 徐汉生. 硒在植物生命活动中的作用[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1999, 35(5):417-423.
|
| [36] |
Wu J, Liu X F, Xu H S. Functions of selenium in plants[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 1999, 35(5):417-423.
|
| [37] |
周鑫斌, 于淑慧, 谢德体. pH和三种阴离子对紫色土亚硒酸盐吸附—解吸的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(5):1069-1077.
|
| [37] |
Zhou X B, Yu S H, Xie D T. Effects of pH and threekinds of anions on selenium absorption and desorption in purple soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015, 52(5):1069-1077.
|
| [38] |
Kirkby E A, Mengel K. Ionic balance in different tissues of the tomato plant in relation to nitrate,urea,or ammonium nutrition[J]. Plant Physiology, 1967, 42(1):6-14.
|
| [39] |
Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan M H M B, Raza A, et al. Selenium in plants:Boon or bane?[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2020, 178:104-170.
|
| [40] |
Kämpf N, Curi N, Marques J J. Óxidos de alumínio, silício, manganês e titânio[C]// Química e mineralogia do solo, 2009:573-610.
|
| [41] |
Fontes M P F, Alleoni L R. Electrochemical attributes and availability of nutrients, toxic elements, and heavy metals in tropical soils[J]. Sci.Agr., 2006, 63:589-608.
|
| [42] |
Goh K H, Lim T T. Geochemistry of inorganic arsenic and selenium in a tropical soil:Effect of reaction time,pH,and competitive anions on arsenic and selenium adsorption[J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 55:849-859.

|
| [43] |
田育天, 李湘伟, 谢新乔, 等. 云南典型植烟土壤通气孔隙及其主控因素研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(6):1430-1438.
|
| [43] |
Tian Y T, Li X W, Xie X Q, et al. Soil aeration porosity in typical tobacco-planting soils and its main controlling factors in typical tobacco-planting soil in Yunnan Province, China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(6):1430-1438.
|
| [44] |
Fan J X, Zeng Y, Sun J X. The transformation and migration of selenium in soil under different Eh conditions[J]. Soil Sediment, 2018, 18:2935-2947.
|
| [45] |
马迅. 不同内源调控措施对江西丰城土壤中硒有效性的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2017.
|
| [45] |
Ma X. Selenium availability and its regulation in acidic selenium-rich soil[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017.
|
| [1] |
Duo-Ji-Wei-Se , Ci-Ren-Wang-Dui , Ni-Ma-Luo-Zhuo , ZHOU Peng, Ni-Ma-Ci-Ren . Characteristics and influencing factors of Se content in the farmland system in Bailang County, Tibet, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 1118-1126. |
| [2] |
HUANG Ping-An, WANG Xia-Qing, TANG Xiang-Ling, WANG Yu-Tang, LI Wei, LUO Zeng, Lyu Fei-Ya. Research progress in the influencing factors and correction methods of XRF-CS[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 726-738. |
|
|
|
|

