|
|
|
| Fast inversion of short-offset transient electromagnetic (SOTEM) data based on the supervised descent method |
RAO Li-Ting1,2,3,4( ), WU Xin2,3,4( ), WU Xin2,3,4( ), GUO Rui5, DANG Bo1, DANG Rui-Rong1 ), GUO Rui5, DANG Bo1, DANG Rui-Rong1 |
1. School of Electronic Engineering, Xi’an Shiyou University, Xi’an 710065, China
2. Key Laboratory of Mineral Resources, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029, China
3. College of Earth and Planetary Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4. Innovation Academy of Earth Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029, China
5. Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The short-offset transient electromagnetic (SOTEM) data are typically processed using conventional inversion methods based on physical modeling, manifesting relatively low efficiency and difficulty in integrating priori information. In contrast, the data-driven inversion methods can enhance the inversion accuracy and efficiency but fail to ensure the generalization capability. To achieve high inversion accuracy and efficiency for SOTEM data and a reliable generalization capability, this study proposed an inversion method that integrates physical modeling with the data-driven approach, introducing the supervised descent method in machine learning into SOTEM data inversion. The proposed inversion method involves the offline training and online prediction stages. In the offline training stage, the prior information is flexibly integrated into the model training through a reasonable training dataset to obtain the average descent directions with implicit model features. In the online prediction stage, the physical modeling functions and the descent directions are employed to reconstruct the model parameters under the conventional inversion framework. In this study, the layered geodetic model was applied to design the training and test datasets for the 1D inversion of SOTEM data based on the supervised descent method. The inversion results were compared with those obtained using Occam's inversion algorithm, demonstrating that the proposed inversion method shows significantly enhanced inversion efficiency, higher inversion accuracy, and higher generalization capability.
|
|
Received: 03 January 2023
Published: 21 October 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
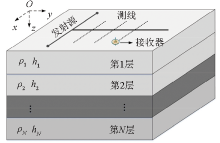
|
The SOTEM system configuration over the layered earth model
|

| 线下训练 | 线上预测 | 1)生成L个先验模型 及其仿真数据 (i=1,2,…,L),重新排列
形成先验模型矩阵 和先验数据矩阵 ;
2)设定 为初始模型;
3) for j=1,2,…,J
4) ;
5) ;
6) ;
7) ;
8) ;
9) end | 1)设定m0为固定初始模型;
2) ;
3) for j=1,2,…,J
4) ;
5) 计算当前数据拟合差rms;
6) if rms<rms0
7) 迭代终止;
8) ;
9) end |
|
Implementation steps of the algorithm
|
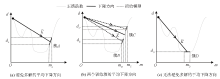
|
Diagram of descent directions for different training sets
|

| 参数 | 三层模型 | 四层模型 | 五层模型 | | ρ1/(Ω·m) | 100~300 | 80~120 | 100~400 | | ρ2/(Ω·m) | 20~100 | 300~500 | 20~80 | | ρ3/(Ω·m) | 200~500 | 50~150 | 200~400 | | ρ4/(Ω·m) | | 300~500 | 20~80 | | ρ5/(Ω·m) | | | 300~500 | | | 80~200 | 80~150 | 50~100 | | | 100~300 | 80~150 | 50~100 | | | 9999 | 150~300 | 100~200 | | | | 9999 | 150~300 | | | | | 9999 | | 个数 | 1024 | 1024 | 1024 |
|
Training sets of different geoelectric models
|

| 参数 | 训练集 | 测试集 | | ρ1/(Ω·m) | 300~600 | 300~500 | | ρ2/(Ω·m) | 30~200 | 50~150 | | ρ3/(Ω·m) | 300~600 | 400~600 | | | 100~300 | 100~250 | | | 100~300 | 100~250 | | 个数 | 1024 | 50 |
|
Parameter setting for training and testing set of three-layer model
|

| 参数 | 训练集 | 测试集 | | ρ1/(Ω·m) | 300~600 | 300~500 | | ρ2/(Ω·m) | 50~150 | 60~140 | | ρ3/(Ω·m) | 200~300 | 200~300 | | ρ4/(Ω·m) | 20~100 | 30~90 | | ρ5/(Ω·m) | 300~600 | 300~500 | | | 50~150 | 80~150 | | | 50~100 | 50~100 | | | 100~200 | 120~180 | | | 100~200 | 100~200 | | 个数 | 1024 | 50 |
|
Parameter setting for training and testing set of five-layer model
|
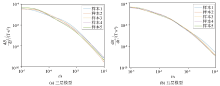
|
Simulation data of some test samples
|
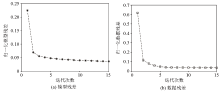
|
Convergence curve of offline training
|
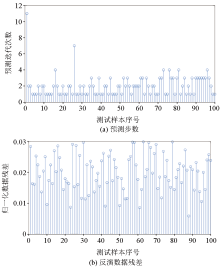
|
Predicting steps and data residual of online predicting
|
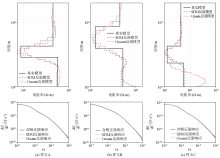
|
Real model response with noise and inversion model response of 3 samples for three-layer model
|
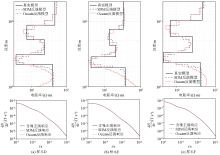
|
Real model response with noise and inversion model response of 3 samples for five-layer model
|
| [1] |
底青云, 朱日祥, 薛国强, 等. 我国深地资源电磁探测新技术研究进展[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(6):2128-2138.
|
| [1] |
Di Q Y, Zhu R X, Xue G Q, et al. New development of the Electromagnetic (EM) methods for deep exploration[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(6):2128-2138.
|
| [2] |
何继善, 薛国强. 短偏移距电磁探测技术概述[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(1):1-8.
|
| [2] |
He J S, Xue G Q. Review of the key techniques on short-offset electromagnetic detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(1):1-8.
|
| [3] |
卢云飞, 薛国强, 邱卫忠, 等. SOTEM研究及其在煤田采空区中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(2):354-359.
|
| [3] |
Lu Y F, Xue G Q, Qiu W Z, et al. The research on SOTEM and its application in mined-out area of coal mine[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(2):354-359.
|
| [4] |
Xue G Q, Chen W Y, Yan S. Research study on the short offset time-domain electromagnetic method for deep exploration[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2018,155:131-137.
|
| [5] |
Guo Z W, Xue G Q, Liu J X, et al. Electromagnetic methods for mineral exploration in China:A review[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020,118:103357.
|
| [6] |
陈大磊, 陈卫营, 郭朋, 等. SOTEM法在城镇强干扰环境下的应用——以坊子煤矿采空区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(5):1226-1232.
|
| [6] |
Chen D L, Chen W Y, Guo P, et al. The application of SOTEM method to populated areas:A case study of Fangzi coal mine goaf[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(5):1226-1232.
|
| [7] |
林君, 薛国强, 李貅. 半航空电磁探测方法技术创新思考[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(9):2995-3004.
|
| [7] |
Lin J, Xue G Q, Li X. Technological innovation of semi-airborne electromagnetic detection method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(9):2995-3004.
|
| [8] |
张莹莹. 电性源瞬变电磁法综述[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(4):809-823.
|
| [8] |
Zhang Y Y. Review on the study of grounded-source transient electromagnetic method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4):809-823.
|
| [9] |
陈卫营, 薛国强, 崔江伟, 等. SOTEM响应特性分析与最佳观测区域研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(2):739-748.
|
| [9] |
Chen W Y, Xue G Q, Cui J W, et al. Study on the response and optimal observation area for SOTEM[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(2):739-748.
|
| [10] |
薛俊杰, 陈卫营, 王贺元. 电性源短偏移瞬变电磁探测深度分析与应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(2):381-384.
|
| [10] |
Xue J J, Chen W Y, Wang H Y. Analysis and application of the detection depth of electrical source Short-offset TEM[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(2):381-384.
|
| [11] |
常江浩, 薛国强. 电性源短偏移距瞬变电磁场扩散规律三维数值模拟[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2020, 42(6):711-721.
|
| [11] |
Chang J H, Xue G Q. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of diffusion law of short-offset grounded-wire transient electromagnetic field[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2020, 42(6):711-721.
|
| [12] |
陈卫营, 李海, 薛国强, 等. SOTEM数据一维OCCAM反演及其应用于三维模型的效果[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(9):3667-3676.
|
| [12] |
Chen W Y, Li H, Xue G Q, et al. 1D OCCAM inversion of SOTEM data and its application to 3D models[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(9):3667-3676.
|
| [13] |
宋婉婷, 陈卫营. SOTEM数据拟二维反演研究与应用[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2022, 44(1):132-142.
|
| [13] |
Song W T, Chen W Y. Study on quasi-2D inversion for SOTEM data and its application[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2022, 44(1):132-142.
|
| [14] |
Guo R, Wu X, Liu L H, et al. Adaptive sharp boundary inversion for transient electromagnetic data[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research M, 2017,57:129-138.
|
| [15] |
Zhdanov M S. Marine electromagnetic methods[G]//Foundations of geophysical electromagnetic theory and methods. Amsterdam:Elsevier,2018:625-662.
|
| [16] |
苏扬, 殷长春, 刘云鹤, 等. 基于广义模型约束的时间域航空电磁反演研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(2):743-751.
|
| [16] |
Su Y, Yin C C, Liu Y H, et al. Inversions of time-domain airborne EM based on generalized model constraints[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(2):743-751.
|
| [17] |
孙怀凤, 张诺亚, 柳尚斌, 等. 基于L1范数的瞬变电磁非线性反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(12):4860-4873.
|
| [17] |
Sun H F, Zhang N Y, Liu S B, et al. L1-norm based nonlinear inversion of transient electromagnetic data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(12):4860-4873.
|
| [18] |
Rao L T, Wu X, Guo R, et al. A comparative study of different stabilizers for retrieving geoelectric structure based on a unified framework[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2020,175:104001.
|
| [19] |
Araya P M, Jennings J, Adler A, et al. Deep learning tomography[J]. The Leading Edge, 2018, 37(1):5866.
|
| [20] |
Tan C, Luy S H, Dong F, et al. Image reconstruction based on convolutional neural network for electrical resistance tomography[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(1):196-204.
|
| [21] |
Mandija S, Meliadò E F, Huttinga N R F, et al. Opening a new window on MR-based Electrical Properties Tomography with deep learning[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019,9:8895.
|
| [22] |
Li X Y, Zhou Y, Wang J M, et al. A novel deep neural network method for electrical impedance tomography[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2019, 41(14):4035-4049.
|
| [23] |
Wu Y, Lin Y Z. InversionNet:An efficient and accurate data-driven full waveform inversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020,6:419-433.
|
| [24] |
Ongie G, Jalal A, Metzler C A, et al. Deep learning techniques for inverse problems in imaging[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Information Theory, 2020, 1(1):39-56.
|
| [25] |
Raissi M, Perdikaris P, Karniadakis G E. Physics-informed neural networks:A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2019,378:686-707.
|
| [26] |
Jin Y C, Shen Q Y, Wu X Q, et al. A physics-driven deep-learning network for solving nonlinear inverse problems[J]. Petrophysics:The SPWLA Journal of Formation Evaluation and Reservoir Description, 2020, 61(1):86-98.
|
| [27] |
Guo R, Li M K, Yang F, et al. Application of supervised descent method for 2D magnetotelluric data inversion[J]. Geophysics, 2020, 85(4):WA53-WA65.
|
| [28] |
Colombo D, Turkoglu E, Li W C, et al. Physics-driven deep-learning inversion with application to transient electromagnetics[J]. Geophysics, 2021, 86(3):E209-E224.
|
| [29] |
Bang M, Oh S, Noh K, et al. Imaging subsurface orebodies with airborne electromagnetic data using a recurrent neural network[J]. Geophysics, 2021, 86(6):E407-E419.
|
| [30] |
Lu S, Liang B Y, Wang J W, et al. 1-D inversion of GREATEM data by supervised descent learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022,19:3053247.
|
| [31] |
Asif M R, Foged N, Maurya P K, et al. Integrating neural networks in least-squares inversion of airborne time-domain electromagnetic data[J]. Geophysics, 2022, 87(4):E177-E187.
|
| [32] |
Xiong X H, De la Torre F. Supervised descent method and its applications to face alignment[C]// 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2013:532-539.
|
| [33] |
Nabighian M N. 勘查地球物理电磁法:第1卷理论[M]. 赵经祥等,译. 北京: 地质出版社,1992.
|
| [33] |
Nabighian M N. Electromagnetic Methods in Applied Geophysics Volume 1,Theory[M].Translated by Zhao J X,et al. Beijing: Geology Press,1992.
|
| [34] |
Guptasarma D, Singh B. New digital linear filters for Hankel J0 and J1 transforms[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 1997, 45(5):745-762.
|
| [35] |
Knight J H. Transient electromagnetic calculations using the gaver-stehfest inverse laplace transform method[J]. Geophysics, 1982, 47(1):47.
|
| [1] |
HUANG Shi-Mao, YANG Guang, WANG Jun-Cheng, LUO Chuan-Gen, XU Ming-Zuan, ZHOU Nan-Nan, ZHAO Peng. Application cases of the short-offset transient electromagnetic method in detecting goafs with thick overburden in a coal mine[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1208-1214. |
| [2] |
SHANG Ya-Zhou, ZHANG Zhao-Hui, XU Duo-Nian, ZHAO Wen-Wen, CHEN Hua-Yong, HAN Hai-Bo. Log-based lithology identification of volcanic rocks using random forest method: A case study of Carboniferous strata in the Dixi area, Junggar Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4): 1025-1036. |
|
|
|
|

