|
|
|
| Ecological risk assessment of cultivated land in typical areas with high heavy metal background values in Guizhou Province |
WANG Hui-Yan1,2,3( ), PENG Min1,2,3, MA Hong-Hong1,2,3, ZHANG Fu-Gui1,2,3 ), PENG Min1,2,3, MA Hong-Hong1,2,3, ZHANG Fu-Gui1,2,3 |
1. Institute of Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, China
2. Research Center of Geochemical Survey and Assessment on Land Quality, China Geological Survey, Langfang 065000,China
3. Key Laboratory of Geochemical Cycling of Carbon and Mercury in the Earth's Critical Zone, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The heavy metal pollution in cultivated land is a hot and key issue, and the pollution status and mechanisms can be accurately grasped through small-scale ecological risk surveys of heavy metals in soil. In this study, the heavy metal ecological risk survey of cultivated land and major crops was carried out in Yancang and Lushan towns, Weining County, Guizhou Province. Meanwhile, the pollution status and ecological risks of heavy metals in soil were assessed using the geoaccumulation index and the potential ecological risk index proposed by Hakanson. The results are as follows. The compound pollution of heavy metals exists in the soil of the cultivated land, with Cd showing the highest pollution level and ecological risks. Meanwhile, Cd exceeds the standard in some potato and maize samples, which is closely related towater-soluble and exchangeable Cd. Therefore, more attention should be paid to the studies on the pollution and speciation of heavy metals in the monitoring and remediation of soil pollution in cultivated land in the future.
|
|
Received: 11 March 2021
Published: 11 October 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geolocation of the study area and sampling locations
|

| 序号 | 指标 | 分析方法 | 检出限/10-3 | 重复性检验合格率/% | 报出率/% | | 1 | As | 原子荧光光谱法AFS | 1 | 91.67 | 99.48 | | 2 | Cd | 等离子体质谱法ICP-MS | 0.03 | 100 | 100 | | 3 | Cu | X射线荧光光谱法XRF | 1 | 100 | 100 | | 4 | Pb | X射线荧光光谱法XRF | 2 | 100 | 100 | | 5 | Zn | X射线荧光光谱法XRF | 4 | 100 | 100 | | 6 | 有机碳 | 容量法VOL | 0.01 | 100 | 100 |
|
Analytical methods and quality control
|

| 元素 | 分析质量 | 土壤 | | 全量 | 水溶态 | 离子交
换态 | 碳酸盐
结合态 | 腐殖酸
结合态 | 铁锰结
合态 | 强有机
结合态 | 残渣态 |
As | RE/% | 3.33 | 5.56 | -3.87 | 9.85 | 7.67 | -4.41 | 10.71 | -7.74 | | RSD/% | 5.15 | 9.12 | 3.34 | 10.26 | 4.61 | 7.93 | 9.73 | 5.43 |
Cd | RE/% | 2.48 | -6.52 | 5.63 | -2.42 | -1.59 | 4.64 | -3.45 | 6.63 | | RSD/% | 7.60 | 4.02 | 3.65 | 3.29 | 0.81 | 1.79 | 5.38 | 5.18 |
Cu | RE/% | 6.42 | 0.104 | 2.833 | -5.75 | -3.056 | 2.875 | 2.458 | -1.786 | | RSD/% | 1.53 | 4.14 | 5.24 | 28.16 | 3.67 | 2.45 | 2.98 | 3.01 |
Pb | RE/% | 4.38 | -0.737 | -2.024 | -5.621 | 5.536 | 2.639 | -9.574 | 0.067 | | RSD/% | 3.16 | 3.41 | 3.86 | 3.47 | 4.15 | 3.68 | 8.83 | 2.17 |
Zn | RE/% | 3.82 | 3.1 | -5.96 | 2.57 | 3.83 | -4.06 | 5.07 | 3.17 | | RSD/% | 1.22 | 6.84 | 6.67 | 3.59 | 5.32 | 4.86 | 3.29 | 5.11 |
|
Statistical of the elements analytical quality
|

|
Characteristic value of the heavy metal content of soil in the study area
|
|
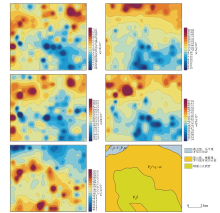
The geochemical maps of five heavy metals
|
|
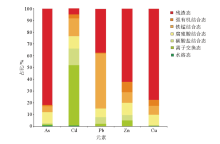
Chemical fractions of heavy metals in the siol samples
|

| 形态 | 占比/% | | As | Cd | Pb | Zn | Cu | | 生物有效组分 | 水溶态+离子交换态+
碳酸盐结合态 | 2.76 | 66.07 | 7.51 | 9.58 | 1.11 | | 潜在生物有效组分 | 腐殖酸结合态+铁锰
结合态+强有机结合态 | 15.44 | 28.96 | 55.10 | 28.18 | 21.32 | | 残渣态 | 81.70 | 4.97 | 37.39 | 62.23 | 77.57 |
|
Proportion of different morphology occurrence of heavy metals
|

| 元素 | Igeo≤0 | 0<Igeo≤1 | 1<Igeo≤2 | 2<Igeo≤3 | 3<Igeo≤4 | 4<Igeo≤5 | Igeo>5 | | 无污染 | 无污染到中度污染 | 中度污染 | 中度污染到强污染 | 强污染 | 强污染到极强污染 | 极强污染 | | 样品数 | 比例/% | 样品数 | 比例/% | 样品数 | 比例/% | 样品数 | 比例/% | 样品数 | 比例/% | 样品数 | 比例/% | 样品数 | 比例/% | | As | 112 | 99.12 | 1 | 0.88 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cd | 0 | 0 | 7 | 6.19 | 49 | 43.36 | 55 | 48.67 | 2 | 1.77 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cu | 6 | 5.31 | 28 | 24.78 | 52 | 46.02 | 26 | 23.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Pb | 65 | 57.52 | 46 | 40.71 | 2 | 1.77 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Zn | 5 | 4.42 | 103 | 91.15 | 5 | 4.42 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
|
Statistics of Igeo for heavy metals in root soil
|

| 级别 | RI风险点位占比/% | Er风险点位占比/% | | As | Cd | Cu | Pb | Zn | | 轻度 | 20.35 | 100 | 0 | 91.15 | 100 | 100 | | 中度 | 65.49 | 0 | 3.54 | 8.85 | 0 | 0 | | 强度 | 14.16 | 0 | 35.40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | 很强 | 0 | 0 | 57.22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | 极强 | 0 | 0 | 3.54 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
|
Ststistics of the ecological risk index for heavy metals in root soil
|

| 指标 | As | Cd | Cu | Pb | Zn | Al | Corg | | As | 1 | | | | | | | | Cd | 0.420** | 1 | | | | | | | Cu | -0.590** | -0.148 | 1 | | | | | | Pb | 0.674** | 0.563** | -0.344** | 1 | | | | | Zn | 0.388** | 0.834** | -0.002 | 0.655** | 1 | | | | Al | -0.532** | -0.360** | 0.557** | -0.394** | -0.199* | 1 | | | Corg | 0.445** | 0.474** | -0.347** | 0.526** | 0.434** | -0.406** | 1 |
|
Correlation of heavy metals in soil
|

| 参数 | As | Cd | Cu | Pb | Zn | | 最大值/10-6 | 0.022 | 0.155 | 3.35 | 0.117 | 39.1 | | | 最小值/10-6 | 0.013 | 0.009 | 1.16 | <0.02 | 14.2 | | | 玉米(n=93) | 限量值/10-6 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 10 | 0.2 | 50 | | | 超标个数 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | | 最大值/10-6 | 0.006 | 0.300 | 2.211 | <0.02 | 7.703 | | | 最小值/10-6 | 0.002 | 0.056 | 0.337 | <0.02 | 3.079 | | | 马铃薯(n=20) | 限量值/10-6 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 6 | 0.2 | 15 | | | 超标个数 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
|
Characteristics of the heavy metal content in corn and potatoes
|

| 指标 | 马铃薯Cd | 总Cd | 水溶态 | 离子交换态 | 碳酸盐
结合态 | 腐殖酸
结合态 | 铁锰结合态 | 强有机
结合态 | 残渣态 | | 马铃薯Cd | 1 | | | | | | | | | | 总Cd | 0.023 | 1 | | | | | | | | | 水溶态 | 0.636** | -0.026 | 1 | | | | | | | | 离子交换态 | 0.473* | 0.824** | 0.235 | 1 | | | | | | | 碳酸盐结合态 | -0.253 | 0.820** | -0.239 | 0.458* | 1 | | | | | | 腐殖酸结合态 | -0.144 | 0.832** | -0.121 | 0.586** | 0.641** | 1 | | | | | 铁锰结合态 | -0.296 | 0.866** | -0.258 | 0.489* | 0.948** | 0.715** | 1 | | | | 强有机结合态 | -0.224 | 0.696** | -0.166 | 0.390 | 0.878** | 0.398 | 0.891** | 1 | | | 残渣态 | -0.333 | 0.840** | -0.216 | 0.452* | 0.801** | 0.749** | 0.898** | 0.708** | 1 |
|
Person correlation matrix for Cd in root soil and potato
|

| 指标 | 玉米Cd | 总Cd | 水溶态 | 离子交换态 | 碳酸盐
结合态 | 腐殖酸
结合态 | 铁锰结合态 | 强有机
结合态 | 残渣态 | | 玉米Cd | 1 | | | | | | | | | | 总Cd | -0.214* | 1 | | | | | | | | | 水溶态 | 0.482** | -0.285** | 1 | | | | | | | | 离子交换态 | 0.195 | 0.716** | 0.055 | 1 | | | | | | | 碳酸盐结合态 | -0.390** | 0.755** | -0.387** | 0.263* | 1 | | | | | | 腐殖酸结合态 | -0.389** | 0.639** | -0.358** | 0.337** | 0.640** | 1 | | | | | 铁锰结合态 | -0.348** | 0.641** | -0.341** | 0.068 | 0.537** | 0.332** | 1 | | | | 强有机结合态 | -0.289** | 0.581** | -0.307** | 0.135 | 0.626** | 0.077 | 0.658** | 1 | | | 残渣态 | -0.333** | 0.559** | -0.390** | 0.049 | 0.450** | 0.144 | 0.808** | 0.744** | 1 |
|
Person correlation matrix for Cd in root soil and corn
|

| 作物种类 | 自变量 | 回归方程 |
马铃薯 | 水溶态 | Y=4.2164x+0.0403,R2=0.8285,sig.=0 | | 离子交换态 | Y=0.0454x+0.0591,R2=0.2459,sig.=0.003 | | 玉米 | 水溶态 | Y=0.9730x+0.0290,R2=0.2163,sig.=0 |
|
The linear regression analysis of Cd in crop and root soil
|
| [1] |
Liu G N, Tao L, Liu X H, et al. Heavy metal speciation and pollution of agricultural soils along Jishui River in non-ferrous metal mine area in Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 132(3): 156-163.

|
| [2] |
张建, 杨瑞东, 陈蓉, 等. 贵州喀斯特地区土壤—辣椒体系重金属元素的生物迁移积累特征[J]. 食品科学, 2017, 38(21):175-181.
|
| [2] |
Zhang J, Yang R D, Chen R, et al. Bioconcentration of heavy metals in soil-capsicum annuum L. system in Karst areas of Guizhou Province[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(21): 175-181.
|
| [3] |
周亚龙, 郭志娟, 王成文, 等. 云南省镇雄县土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评估[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1358-1366.
|
| [3] |
Zhou Y L, Guo Z J, Wang C W, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of soils in Zhenxiong County, Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6): 1358-1366.
|
| [4] |
陈凤, 董泽琴, 王程程, 等. 锌冶炼区耕地土壤和农作物重金属污染状况及风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(10):4360-4369.
|
| [4] |
Chen F, Dong Z Q, Wang C C, et al. Heavy metal contamination of soils and crops near a zinc smelter[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(10): 4360-4369.
|
| [5] |
吴迪, 杨秀珍, 李存雄, 等. 贵州典型铅锌矿区水稻土壤和水稻中重金属含量及健康风险评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(10):1992-1998.
|
| [5] |
Wu D, Yang X Z, Li C X, et al. Concentrations and health risk assessments of heavy metals in soil and rice in zinc-lead mining area in Guizhou Province, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(10): 1992-1998.
|
| [6] |
杨刚, 沈飞, 钟贵江, 等. 西南山地铅锌矿区耕地土壤和谷类产品重金属含量及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(9):2014-2021.
|
| [6] |
Yang G, Shen F, Zhong G J, et al. Concentration and health risk of heavy metals in crops and soils in a zinc-lead mining area in southwest mountainous regions[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31(9): 2014-2021.
|
| [7] |
彭光寿. 贵州省乡镇企业发展与环境保护预测和对策[J]. 环境科学, 1989, 9(1):62-67.
|
| [7] |
Peng G S. Forecast and countermeasuresfor the development of township enterprises and environmental protection in Guizhou Province[J]. Environmental Science, 1989, 9(1): 62-67.

|
| [8] |
闭向阳. 西南土法炼锌导致的环境重金属污染研究[D]. 贵阳: 中国科学院地球化学研究所, 2007.
|
| [8] |
Bi X Y. Study on environmental heavy metal pollution caused by local zinc smelting activities in southwest China[D]. Guiyang: Institute of Geochemistry, CAS, 2007.
|
| [9] |
杨永忠. 贵州环境异常元素地球化学研究[J]. 贵州地质, 1999, 16(1):66-72.
|
| [9] |
Yang Y Z. The geochemistry of anomalous elements in the environment of Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 1999, 16(1): 66-72.
|
| [10] |
国土资源部中国地质调查局. 中国耕地地球化学调查报告(2015))[EB/OL]. http://www.cgs.gov.cn/upload/201506/20150626/gdbg.pdf, 2015-06-25.
|
| [10] |
China Geological Survey of Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. Geochemical survey for the cultivated land in China(2015)[EB/OL]. http://www.cgs.gov.cn/upload/201506/20150626/gdbg.pdf, 2015-06-25.
|
| [11] |
Tu C L, Wang Z G, Sun W X, et al. Effects of land use and parent materials on trace elements accumulation in topsoil[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2013, 42(1): 103-110.

|
| [12] |
DZ /T 0296—2016土地质量地球化学评价规范[S].
|
| [12] |
DZ/T 0296—2016 Specification of land quality geochemical assessment[S].
|
| [13] |
区域生态地球化学评价技术要求(试行)[S].
|
| [13] |
Technical requirements for regional ecological geochemical assessment (pilot)[S].
|
| [14] |
Muller G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River[J]. GeoJournal, 1969, 2(3): 108-118.
|
| [15] |
唐瑞玲, 王惠艳, 吕许朋, 等. 西南重金属高背景区农田系统土壤重金属生态风险评[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(5):917-927.
|
| [15] |
Tang R L, Wang H Y, Lyu X P, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland system from an area with high background of heavy metals, Southwestern China[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(5): 917-927.
|
| [16] |
Hakanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control:A sediment logical approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001.

|
| [17] |
GB 15618—2018土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)[S].
|
| [17] |
GB 15618—2018 Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land[S].
|
| [18] |
国家环境保护局. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
|
| [18] |
National Environmental Protection Agency. Soil background values in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990.
|
| [19] |
赵万伏, 宋垠先, 管东兴, 等. 典型黑色岩系分布区土壤重金属污染与生物有效性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(7):1332-1341.
|
| [19] |
Zhao W F, Song Y S, Guan D X, et al. Pollution status and bioavailability of heavy metals in soils of a typical black shale area[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(7): 1332-1341.
|
| [20] |
Liu G N, Wang J, Liu X, et al. Partitioning and geochemical fractions of heavy metals frogeogenic and anthropogenic sources in various soil partical size fractions[J]. Geoderma, 2018, 312: 104-113.

|
| [21] |
GB 2762—2017食品安全国家标准食品中污染物限量[S].
|
| [21] |
GB 2762—2017 National food safety standard Maximum levels of contaminants in foods[S].
|
| [22] |
NY 861—2004粮食(含谷物、豆类、薯类)及制品中Cu、Zn两种元素限量[S].
|
| [22] |
NY 861—2004 Limits of Cu Zn in cereals,legume,tubes and its products[S].
|
| [23] |
彭益书. 黔西北土法炼锌区炉渣、土壤与植物系统中重金属分布及迁移研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2018.
|
| [23] |
Peng Y S. Distribution and migration of heavy metal among system of the slg, soil and plant in the indigenous zinc smelting area of northwestern Guizhou Province, China[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2018.
|
| [24] |
Zhang Y, Wu Y, Yang A, et al. Assessment of cadmium content of potato grown in Weining County, Guizhou Province, China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2017, 189(5): 226.
|
| [1] |
FAN Hai-Yin, SONG Rui-Rui, YU Lin-Song, TENG Yong-Bo, WAN Fang, ZHANG Xiu-Wen, LI Sheng-Yu, ZHAO Chuang. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of groundwater in a typical chemical industry park in northwestern Shandong, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1326-1335. |
| [2] |
YANG Chan, WU Juan-Juan, CHE Xu-Xi, YUE Si-Yu, LIU Zhi-Feng, SONG Feng-Min. Pollution analysis and assessment of sediments in the upper reaches of the Hanjiang River[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1361-1370. |
|
|
|
|

