|
|
|
| An integrated data quality evaluation of Earth magnetic anomaly grid EMAG2v3 and global gravimetric database V29: A case study of the Aegir ridge in the Arctic |
ZHANG Mian1,2( ), ZHANG Chun-Guan1,2( ), ZHANG Chun-Guan1,2( ), ZHAO Min1,2, ZHONG Zhen-Hua2, YUAN Bing-Qiang1,2, ZHOU Lei1,2, HAN Mei1,2 ), ZHAO Min1,2, ZHONG Zhen-Hua2, YUAN Bing-Qiang1,2, ZHOU Lei1,2, HAN Mei1,2 |
1. School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Xi'an Shiyou University, Xi'an 710065, China
2. Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Petroleum Accumulation Geology, Xi'an Shiyou University, Xi'an 710065, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract To evaluate the qualities of the marine magnetic data in the Earth magnetic anomaly grid EMAG2v3 and the marine gravity data in global gravimetric database V29, this study selected the magnetic and gravity data of the Aegir axial rift and its adjacent areas within a range of about 150 km from EMAG2v3 and V29, respectively to conduct comparative research. This study systematically collected the anomaly data of the study area from EMAG2v3 and V29 for comparison with the measured gravity and magnetic data of the study area. First, this study gridded and whitened the EMAG2v3 data, V29 data, and measured gravity and magnetic anomaly data to obtain the corresponding images. Then, this study analyzed the correlations between the EMAG2v3 data and the shipborne magnetic data and between the V29 data and the shipborne gravity data, obtaining the magnetic and gravity correlation diagrams and corresponding correlation coefficients. By comparing the correlation coefficients and differences between the two kinds of magnetic data and the two kinds of gravity data, this study conducted an integrated evaluation of magnetic the gravity data of the study area from EMAG2v3 and V29, respectively. As indicated by the results, EMAG2v3 incorporates many shipborne magnetic data, with the shipborne magnetic anomaly data showing higher quality than the data from the EMAG2v3 for areas with dense survey lines. The results also show that the shipborne gravity anomalies showed roughly the same variations as those from V29, indicating the same lateral resolution of the two types of anomaly data.
|
|
Received: 22 November 2022
Published: 23 January 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
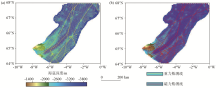
|
The seafloor topography and the distribution of gravity survey lines (a) and magnetic survey lines (b) in the Aegir axis rift
|
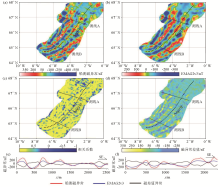
|
Aegir axis rift magnetic anomaly and data comparison
a—aeromagnetic anomaly; b—Earth magnetic anomaly grid(EMAG2v3); c—correlation coefficient between aeromagnetic anomaly and EMAG2v3; d—difference between aeromagnetic anomaly and EMAG2v3; e—line magnetic anomaly and difference of measurement A; f—line magnetic anomaly and difference of measurement B
|

| 相关系数 | 占总面积
比例/% | 磁异常差值
绝对值/nT | 占总面
积比例/% | | -1.0~0.3 | 9.94 | <10 | 16.07 | | 0.3~0.5 | 4.83 | 10~50 | 48.31 | | 0.5~0.8 | 16.32 | 50~100 | 24.27 | | >0.8 | 68.89 | >100 | 11.34 |
|
Correlation coefficient value and difference interval of magnetic force
|
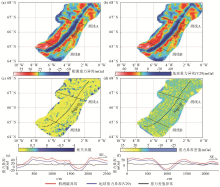
|
Aegir axis rift gravity anomaly and data comparison
a—ship-measured gravity anomaly; b—Earth gravity anomaly (V29); c—correlation coefficient between ship-measured gravity anomaly and Earth gravity anomaly (V29); d—difference between ship-measured gravity anomaly and Earth gravity anomaly (V29); e—line A gravity anomaly and difference; f—line B gravity anomaly and difference
|

| 相关系数 | 占总面积
比例/% | 磁异常差
值绝对值/nT | 占总面
积比例/% | | -1.0~0.3 | 6.03 | <10 | 10.65 | | 0.3~0.5 | 4.10 | 10~50 | 89.35 | | 0.5~0.8 | 16.40 | 50~100 | 0 | | >0.8 | 73.46 | >100 | 0 |
|
Correlation coefficient value and difference interval of gravity
|
| [1] |
张保军, 王泽民. 联合卫星重力、卫星测高和海洋资料研究全球海平面变化[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2015, 40(11):1453-1459.
|
| [1] |
Zhang B J, Wang Z M. Combined satellite gravity,satellite altimetry and oceanographic data to study global sea level change[J]. Journal of Wuhan University:Information Science Edition, 2015, 40(11):1453-1459.
|
| [2] |
Hinze W J, Aiken C, Brozena J, et al. New standards for reducing gravity data:The north American gravity database[J]. Geophysics, 2005, 70(4):J25-J32.
|
| [3] |
Olesen O B, Petersen N C. Stochastic data envelopment analysis—A review[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2016, 251(1):2-21

|
| [4] |
Parnell-Turner R, White N, Henstock T, et al. A continuous 55-million-year record of transient mantle plume activity beneath iceland[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2014, 7(12):914-919.
|
| [5] |
Hemant K, Maus S. Geological modeling of the new CHAMP magnetic anomaly maps using a geographical information system technique[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2005, 110(B12):103.
|
| [6] |
Maus S, Barckhausen U, Berkenbosch H, et al. EMAG2:A2-arc min resolution Earth magnetic anomaly grid compiled from satellite,airborne,and marine magnetic measurements[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2009, 10(8):Q08005.
|
| [7] |
Meyer B, Chulliat A, Saltus R. Derivation and error analysis of the earth magnetic anomaly grid at 2 arc min resolution version 3 (EMAG2v3)[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2017, 18(12):4522-4537.

|
| [8] |
Vervelidou F, Thébault E, Korte M. A high-resolution lithospheric magnetic field model over southern Africa based on a joint inversion of CHAMP,Swarm,WDMAM,and ground magnetic field data[J]. Solid Earth, 2018, 9(4):897-910.

|
| [9] |
Li C F, Lu Y, Wang J. A global reference model of Curie-point depths based on EMAG2[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1):45129.
|
| [10] |
Baykiev E, Guerri M, Fullea J. Integrating gravity and surface elevation with magnetic data:Mapping the curie temperature beneath the British Isles and surrounding areas[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2018, 6:165.

|
| [11] |
Acosta J D S, Hints R, Soesoo A. Insights on the tectonic styles across Estonia using satellite potential fields derived from WGM-2012 gravity data and EMAG2 magnetic data[R]. Copernicus Meetings, 2022.
|
| [12] |
Kumar S, Pal S K, Guha A, et al. New insights on Kimberlite emplacement around the Bundelkhand Craton using integrated satellite-based remote sensing,gravity and magnetic data[J]. Geocarto International, 2022, 37(4):999-1021.

|
| [13] |
Dickson W, Schiefelbein C F, Odegard M E, et al. Petroleum systems asymmetry across the South Atlantic equatorial margins[J]. Geological Society London,Special Publications, 2016, 431(1):219-233.

|
| [14] |
Maystrenko Y, Scheck-Wenderoth M. Density contrasts in the upper mantle and lower crust across the continent—Ocean transition:Constraints from 3D gravity modelling at the Norwegian margin[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2009, 179(1):536-548.

|
| [15] |
Blondes M S, Gans K D, Thordsen J J, et al. US Geological Survey National produced waters geochemical database v2.3 (PROVISIONAL)[R]. United States Geological Survey, 2016.
|
| [16] |
Christensen A N, Andersen O B. Comparison of satellite altimetric gravity and ship-borne gravity—Offshore western Australia[J]. ASEG Extended Abstracts, 2016, 2016(1):1-5.
|
| [17] |
刘善伟, 李家军, 万剑华, 等. 利用多代卫星测高数据计算中国近海及邻域重力异常[J]. 海洋科学, 2015, 39(12):130-134.
|
| [17] |
Liu S W, Li J J, Wan J H, et al. Calculation of gravity anomalies over China Sea and its vicinity based on multi-generation satellite altimetry data[J]. Marine Sciences, 2015, 39(12) :130-134.
|
| [18] |
管一鹤, 盛辉, 刘善伟, 等. 联合多代卫星测高资料反演中国南海重力异常[J]. 海洋测绘, 2016, 36 (1):11-14.
|
| [18] |
Guan Y H, Sheng H, Liu S W, et al. Inversion of the gravity anomalies by using multi-generation satellite altimeter data in the South China Sea[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2016, 36(1):11-14.
|
| [19] |
李随民, 姚书振, 韩玉丑. Surfer软件中利用趋势面方法圈定化探异常[J]. 地质与勘探, 2007, 43(2):72-75.
|
| [19] |
Li S M, Yao S Z, Han Y C. Delineation of geochemical anomalies by trend surface method in Surfer software[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2007, 43(2):72-75.
|
| [20] |
陆志波, 陆雍森. Surfer8.0在环境评价和规划中的应用[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2005, 33(2):191-195.
|
| [20] |
Lu Z B, Lu Y S. Application of Surfer8.0 to environmental assessment and planning[J]. Journal of Tongji University:Natural Science Edition, 2005, 33(2):191-195.
|
| [21] |
林伙海, 吴陈锋. 基于surfer8.0实现雨量图形可视化[J]. 气象, 2006, 32(7):115-118.
|
| [21] |
Lin H H, Wu C F. Realization of rainfall graphical visualization based on surfer8.0[J]. Meteorological, 2006, 32(7):115-118.
|
| [22] |
吴卫国. Surfer网格化与白化处理在数据扩边中的应用——以1∶5万水系沉积物测量成图为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(3):602-605.
|
| [22] |
Wu W G. The application of Surfer gridding and whitening in data edge expansion—Taking the measurement and mapping of 1∶50,000 river system sediments as an example[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(3):602-605.
|
| [23] |
Koptev A, Cloetingh S, Burov E, et al. Long-distance impact of Iceland plume on Norway’s rifted margin[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1):10408.
|
| [24] |
张春灌, 李想, 袁炳强, 等. 地球磁异常(EMAG2)数据中海域资料质量评估——以北极地区Kolbeinsey脊南段为例[J]. 地球科学进展, 2019, 34(3):288-294.
|
| [24] |
Zhang C G, Li X, Yuan B Q, et al. Quality evaluation of offshore data in the earth magnetic anomaly grid (2-arc-minute resolution):Taking the southern section of the kolbeinsey ridge in the Arctic region as an example[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2019, 34(3):288-294.
|
| [25] |
管志宁. 地磁场与磁力勘探[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005.
|
| [25] |
Guan Z N. Geomagnetic field and magnetic exploration[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2005.
|
| [26] |
胡毅, 王立明, 钟贵才, 等. 威德尔海的重磁场特征及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(11):1231-1238.
|
| [26] |
Hu Y, Wang L M, Zhong G C, et al. Gravity and magnetic field characteristics of the Weddell Sea and its tectonic significance[J]. Advances in Earth Sciences, 2015, 30(11):1231-1238.
|
| [27] |
张明华, 张家强. 现代卫星测高重力异常分辨能力分析及在海洋资源调查中应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2005, 29(4):295-298,303.
|
| [27] |
Zhang M H, Zhang J Q. Resolution of modern satellite altimetric gravity anomaly and its application to marine geological survey[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2005, 29(4):295-298,303.
|
| [28] |
张春灌, 袁炳强, 张国利. 最新全球重力数据库V23中陆域重力资料质量评估[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32(1):75-82.
|
| [28] |
Zhang C G, Yuan B Q, Zhang G L. Quality evaluation of land gravity data in the latest global gravity database V23[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32(1):75-82.
|
| [1] |
Cheng Zheng-Pu, Lian Sheng, Wei Qiang, Hu Wen-Guang, Lei Ming, Li Shu. Research on time-frequency electromagnetic method detection of Wumishan Formation thermal reservoir in deep Xiong’an New Area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1400-1409. |
| [2] |
LAN Jun, LI Zhao-Ling, ZHANG Peng, LI Zhi-Min, LI De-Jian, XING Nan, SUN Li, YANG Yun-Tao, XU Hong-Yan, WANG Jian, WANG Qiao-Yun. Research on the application of the integrated gravity-magnetic-radioactive geophysical exploration method in the exploration of rare earth deposit in Weishan, western Shandong[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1417-1424. |
|
|
|
|

