|
|
|
| Feasibility of the transient electromagnetic method in the exploration of double-layer waterlogged goafs with different layer spacings in coal mines |
ZHANG Fan1,2,3,4,5( ), FENG Guo-Rui1,2,3,4,5, QI Ting-Ye1,2,3,4,5( ), FENG Guo-Rui1,2,3,4,5, QI Ting-Ye1,2,3,4,5( ), YU Chuan-Tao1, ZHANG Xin-Jun1, WANG Chao-Yu1,2,3,4,5, DU Sun-Wen1,2,3,4,5, ZHAO De-Kang1,2,3,4,5 ), YU Chuan-Tao1, ZHANG Xin-Jun1, WANG Chao-Yu1,2,3,4,5, DU Sun-Wen1,2,3,4,5, ZHAO De-Kang1,2,3,4,5 |
1. College of Mining Engineering,Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024,China
2. Key Laboratory of Shanxi Province for Mine Rock Strata Control and Disaster Prevention,Taiyuan 030024,China
3. Shanxi Province Coal-based Resources Green and Efficiency Development Engineering Center,Taiyuan 030024,China
4. Shanxi Province Research Center of Green Mining Engineering Technology,Taiyuan 030024,China
5. Shanxi Zhejiang University Institute of New Materials and Chemical Engineering,Taiyuan 030024,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract It is difficult to explore the overlapping double-layer waterlogged goafs using the transient electromagnetic method. The reason is that upper waterlogged goafs will hinder the propagation of the electromagnetic field, thus prolonging the observation of the lower waterlogged goafs and reducing the signal-to-noise ratio. Besides, the burial depths and layer spacings of double-layer waterlogged goafs affect the signal-to-noise ratio and the observation time of transient electromagnetic signals. By building a double-layer waterlogged goaf model based on the Majiayan coal mine in Shanxi, this study analyzed the electromagnetic field propagation under layer spacings of 25 m, 50 m, 75 m, and 100 m,and calculated the observation time of waterlogged goafs with different layer spacings. Furthermore, it quantitatively characterized the differences between induced voltages in the double-layer waterlogged goafs with different layer spacings using root mean square errors. Additionally, this study proposed the identification criteria for explorable lower waterlogged goafs based on the record errors and noise levels during the observation. The results of physical simulation experiments are as follows: The differences between the induced voltages of double-layered waterlogged goafs with different layer spacings occur mainly in the late stage; the differences between induced voltages gradually decrease as the layer spacing and the burial depth of upper waterlogged goafs increases; the difference between induced voltages is close to the noise level when the layer spacing is greater than 75 m. The actual detection of the double layer waterlogged goaf with a spacing of 75 meters was conducted in Majiayan Coal Mine, and the results showed that the lower waterlogged goaf was not effectively identified.Therefore, It is difficult to effectively explore the lower waterlogged goafs when the layer spacing is greater than 75 m.
|
|
Received: 27 October 2022
Published: 27 October 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
QI Ting-Ye
E-mail: zf320425736@163.com;qty198402@163.com
|
|
|
|

| 地层名称 | 厚度/m | 岩性 | 视电阻率
/(Ω·m) | | 第四系
全新统 | 5~20 | 现代冲洪积物,以砂、砾为主,中间夹有透镜状黏土层 | 100 | 第四系中、
上更新统 | 0~70 | 棕红色含砂黏土、淡黄色亚砂土,含钙质结核,垂直节理发育 | 新近系
上新统 | 0~75 | 棕红色、浅紫红色黏土,亚黏土,内含砂质透镜体及钙质结核,底部为砂砾岩层 | 200 | | 二叠系上统
上石河子组 | 2~30 | 绿色、黄绿色中粗砂砾岩与绿色、兰灰色泥岩,砂质泥岩,间夹紫色泥岩 | 二叠系下统
下石河子组 | 33~124 | 下部岩性以灰色、灰绿色、灰黄色、灰白色、灰紫色泥岩,砂质泥岩,粉砂岩,铝质泥岩为主;上部以灰白、黄绿、灰绿色中细粒砂岩为主,间夹泥岩、砂质泥岩透镜体 | 100 | | 二叠系下统
山西组(含
4号煤层) | 34~60 | 灰色、灰黑色砂质泥岩,泥岩,粉、细砂岩,煤 | 50 | | 石炭系上统
太原组(含
9号煤层) | 110~130 | 灰色、灰黑色泥岩,砂质泥岩,粉砂岩,煤 | 50 | |
|
Stratigraphy of the study area
|
|
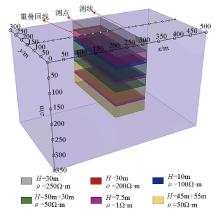
Numerical calculation model
|
|
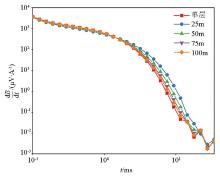
Induction voltage decay curve
|
|
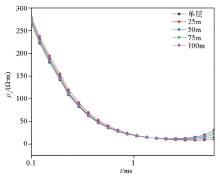
Apparent resistivity calculation results
|
|
Electromagnetic field depth
|
|
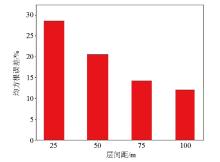
Root mean square error
|
|
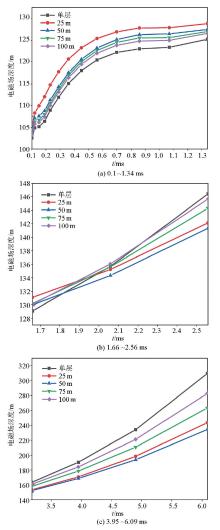
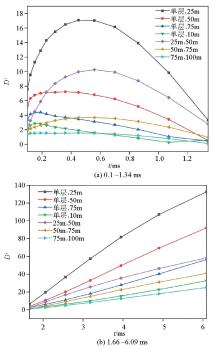
Di values for different time periods
|

|
Physical simulation experimental system (a) and front view (b) and top view (c) of the organic glass box
|
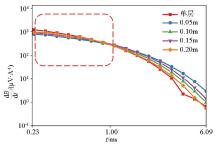
|
Physical simulation of induction voltage decay curve
|
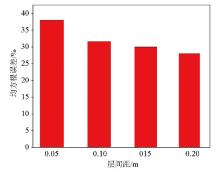
|
Physical simulation of root mean square error
|
|
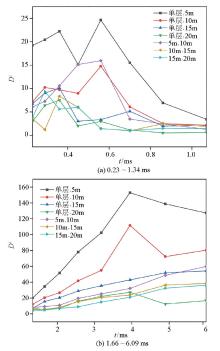
Physical simulation Di values for different time periods
|
|
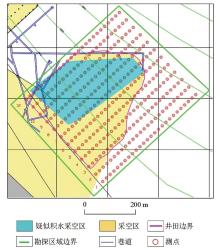
Survey network layout
|
|
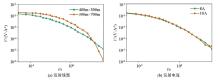
Comparison of experimental results with different parameter settings
|
|
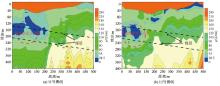
Inversion of resistivity cross-section by transient electrical sounding
|
| [1] |
袁亮. 深部采动响应与灾害防控研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报 2021, 46(3):716-725.
|
| [1] |
Yuan L. Research progress of mining response and disaster prevention and control in deep coal mines[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(3):716-725.
|
| [2] |
赵延林, 王卫军, 赵伏军, 等. 多层采空区隔离顶板安全性强度折减法[J]. 煤炭学报, 2010, 35(8):1257-1262.
|
| [2] |
Zhao Y L, Wang W J, Zhao F J, et al. Strength reduction method to study safety of multilayer goafs isolation roof[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2010, 35(8):1257-1262.
|
| [3] |
武强, 姚义, 赵颖旺, 等. 矿井突(透)水灾害过程中涉险人员危险性评价方法与应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(7) :2357-2366.
|
| [3] |
Wu Q, Yao Y, Zhao Y W, et al. An assessment of hazards to the risk-involved personnel in mine water disaster[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(7):2357-2366.
|
| [4] |
刘树才, 刘志新, 姜志海. 瞬变电磁法在煤矿采区水文勘探中的应用[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2005, 34(4):414-417.
|
| [4] |
Liu S C, Liu Z X, Jiang Z H. Application of TEM in hydrogeological prospecting of mining district[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2005, 34(4):414-417.
|
| [5] |
欧阳涛, 底青云, 薛国强, 等. 利用多通道瞬变电磁法识别深部矿体—以内蒙兴安盟铅锌银矿为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(5):1981-1990.
|
| [5] |
Ouyang T, Di Q Y, Xue G Q, et al. Identifying deep ore bodies using the Multi-channel transient electromagnetic method (MTEM): An example of a lead-zinc-silver mine in Inner Mongolia[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(5):1981-1990.
|
| [6] |
薛国强, 李海, 陈卫营, 等. 煤矿含水体瞬变电磁探测技术研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(1):77-85.
|
| [6] |
Xue G Q, Li H, Chen W Y, et al. Progress of transient electromagnetic detection technology for water-bearing bodies in coal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(1):77-85.
|
| [7] |
杨海燕, 刘志新, 张华, 等. 圆锥形场源瞬变电磁法试验研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(6):107-112.
|
| [7] |
Yang H Y, Liu Z X, Zhang H, et al. Experimental study on transient electromagnetic method with a conical source[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(6):107-112.
|
| [8] |
姚伟华, 王鹏, 李明星, 等. 三分量地—孔瞬变电磁法积水采空区探测试验[J]. 煤田地质与勘, 2019, 47(5):54-62.
|
| [8] |
Yao W H, Wang P, Li M X, et al. Experimental study of three-component down-hole TEM for detecting water-filled goaf[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2019, 47(5):54-62.
|
| [9] |
薛国强, 潘冬明, 于景邨. 煤矿采空区地球物理探测应用综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018, 33(5):427-43.
|
| [9] |
Xue G Q, Pan D M, Yu J C. Review the applications of geophysical methods for mapping coal-mine voids[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 33(5):427-432.
|
| [10] |
侯彦威, 姚伟华. 定源回线TEM 数据的约束反演方法及应用效果[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2019, 47(4):172-177.
|
| [10] |
Hou Y W, Yao W H. Constrained inversion method and application effect of TEM data of fixed source loop device[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2019, 47(4):172-177.
|
| [11] |
刘最亮, 王鹤宇, 冯兵, 等. 基于电性标志层识别的瞬变电磁精准处理技术[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(8):2346-2355.
|
| [11] |
Liu Z L, Wang H Y, Feng B, et al. TEM data accurate processing technology based on electrical marker layer[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(8):2346-2355.
|
| [12] |
郭嵩巍, 刘小畔, 郑凯, 等. 基于全区视电阻率的瞬变电磁一维Occam反演中雅克比矩阵的解析算法[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(3):559-567.
|
| [12] |
Guo S W, Liu X P, Zheng K, et al. Analytical algorithms of Jacobian matrix in one-dimensional Occam inversion of central loop transient electromagnetism based on all-time apparent resistivity[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(3):559-567.
|
| [13] |
Woods D V. A model study of the crone borehole pulse electromagnetic(PEM) system[D]. Kingston: Queen’s University, 1975.
|
| [14] |
Perry A E, Gerald W H. Influence of a conductive host on two-dimensional borehole transient electromagnetic responses[J]. Geophysics, 1984, 49(7):861-869.

|
| [15] |
West R, Ward S. Borehole transient electromagnetic response of a three-dimensional fracture zone in a conductive half-space[J]. Geophysics, 1988, 53(11):1469-1478.

|
| [16] |
Ryu J, Morrison H, Ward S. Electromagnetic fields about a loop source of current[J]. Geophysics, 1970, 35:862-896.

|
| [17] |
Goldman M, Stoyer C. Finite-difference calculations of the transient field of an axially symmetric earth for vertical magnetic dipole excitation[J]. Geophysics, 2012, 48(7):953-963.

|
| [18] |
King A. Cindered coal detection using transient electromagnetics methods[J]. Geoexploration, 1987, 24(4/5):367-379.

|
| [19] |
石显新, 闫述, 陈明生. 瞬变电磁勘探中的低阻层屏蔽问题[J]. 煤炭学报, 2005, 30(2):160-163.
|
| [19] |
Shi X X, Yan S, Chen M S. Study on screening of conductive bed in transient electromagnetic prospecting[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2005, 30(2):160-163.
|
| [20] |
侯彦威. TEM探测低阻覆盖层下煤矿浅埋积水采空区[J]. 煤炭工程, 2020, 52(5):101-105.
|
| [20] |
Hou Y W. TEM detection of goaf with shallow water under low resistivity overburdens[J]. Coal Engineering, 2020, 52(5):101-105.
|
| [21] |
方刚, 高波. 榆横北区地面瞬变电磁法探查含水层特征应用[J]. 中国煤炭, 2018, 44(11):30-35.
|
| [21] |
Fang G, Gao B. Application of the ground transient electromagnetic method in detecting aquifer characteristics in northern Yuheng mining area[J]. China Coal, 2018, 44(11):30-35.
|
| [22] |
Yan S, Xue G Q, Qiu W Z, et al. Feasibility of central loop TEM method for prospecting multilayer water-filled goaf[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2016, 13(4):427-432.
|
| [23] |
Kaufman A, Keller G V. Frequency and transient[M]. New York: Elseviser Science Publishing Company Inc, 1983:213.
|
| [24] |
Hohmann G, Raiche A. Inversion of controlled source electromagnetic data[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1992:452-486.
|
| [25] |
Zhdanov M. Geophysical electromagnetic theory and methods[M]. New York: Elsevier Science Publishing Company Inc, 2009:153-231.
|
| [26] |
闫述, 陈明生, 傅君眉. 瞬变电磁场的直接时域数值分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2002, 45(2):275-284.
|
| [26] |
Yan S, Chen M S, Fu J M. Direct time-domain numerical analysis of transient electromagnetic fields[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2002, 45(2):275-284.
|
| [27] |
Spies B R. Depth of investigation in electromagnetic sounding method[J]. Geophysics, 1989, 54(7):872-888.

|
| [28] |
闫述, 石显新, 陈明生. 瞬变电磁法的探测深度问题[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(6):1583-1591.
|
| [28] |
Yan S, Shi X X, Chen M S. The probing depth of transient electromagnetic field method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(6):1583-1591.
|
| [29] |
Stratton J. Electromagnetic theory[D]. McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1941.
|
| [30] |
Li H, Xue G Q, Zhou N N, et al. Appraisal of an array TEM method in detecting in a mined-out area beneath a conductive layer[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2015, 172(10):2917-2929.

|
| [31] |
姜志海, 焦险峰. 矿井瞬变电磁超前探测物理实验[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(11):1852-1857.
|
| [31] |
Jiang Z H, Jiao X F. Physical experiment of mine transient electromagnetic advanced detection[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(11):1852-1857.
|
| [32] |
姜志海, 杨光. 浅埋特厚小窑采空区瞬变电磁探测技术研究及应用[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2014, 3(5):769-774.
|
| [32] |
Jiang Z H, Yang G. Research and application of TEM detection technology for small mine gob area in shallowly-buried and extremely thick seam[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2014, 3(5):769-774.
|
| [33] |
焦险峰, 刘志新. 瞬变电磁法浅层分辨物理模拟实验研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2014, 43(4):738-741.
|
| [33] |
Jiao X F, Liu Z X. Physical model and experimental research on shallow resolution of transient electromagnetic method[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2014, 43(4):738-741.
|
| [34] |
陈载林. 瞬变电磁法几种规则形体的物理模拟实验[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(6):1092-1095.
|
| [34] |
Chen Z L. Physical simulation experiments on several regular shapes of transient electromagnetic method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(6):1092-1095.
|
| [35] |
王欣. 曙光煤矿瞬变电磁超前探测物理模拟试验研究[J]. 机械管理开发, 2018, 33(7):143-144,147.
|
| [35] |
Wang X. Experimental study on physical simulation of Transient Electromagnetic advanced detection in Shuguang Coal Mine[J]. Mechanical Management and Development, 2018, 33(7):143-144,147.
|
| [36] |
许时昂, 孙松, 韩鹏飞, 等. 瞬变电磁重叠覆盖超前探水模拟测试研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2014, 11(1):40-43.
|
| [36] |
Xu S A, Sun S, Han P F, et al. Simulation and test study of the overlapping coverage of detecting water in advance by transient electromagnetic method[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2014, 11(1):40-43.
|
| [1] |
ZHOU Zhong-Hang, ZHANG Ying-Ying. Correction of the influence of mountains on grounded-source transient electromagnetic responses[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1236-1249. |
| [2] |
HE Sheng, WANG Wan-Ping, DONG Gao-Feng, NAN Xiu-Jia, WEI Feng-Feng, BAI Yong-Yong. Application of the opposing-coils transient electromagnetic method in urban geological surveys[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1379-1386. |
|
|
|
|

