|
|
|
| Distributions of the total concentration, bioavailability, and speciation of selenium in soils in Luoyang City, Henan Province, China |
TIAN Qiang-Guo1( ), HOU Jin-Kai1, YANG Zai-Wei2,3, LI Li-Yuan2,3( ), HOU Jin-Kai1, YANG Zai-Wei2,3, LI Li-Yuan2,3( ) ) |
1. Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources Survey, Henan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Development, Luoyang 471023, China
2. School of Environment and Natural Resources, Zhejiang University of Science and Technology, Hangzhou 310023, China
3. Key Laboratory of Recycling and Eco-Treatment of Waste Biomass of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou 310023, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Targeting the selenium resource in soils of Luoyang City, Henan Province, this study analyzed the distribution of total selenium concentration under different geological settings, soil types, land use types, acidity and alkalinity, and organic matter. Furthermore, it determined the bioavailability and speciation distribution of selenium in the soils. The results indicate that: (1) The soils in Luoyang City have total selenium concentrations of (0.03~5.67)×10-6, with an average of 0.30×10-6, and the area of soils with moderate and rich selenium accounts for 94.73%; (2) The average selenium concentration is the highest in soils of the Jixian Yunmengshan formation and the lowest in soils of the Cambrian Xinji Formation; (3) The average total selenium concentration is the highest in lime concretion black soil and the lowest in paddy soil; (4) Regarding land use types, the average total selenium concentration is relatively high in soils of paddy land and woodland; (5) Soils with high acidity and high organic matter concentrations are favorable for selenium enrichment; (6) In terms of soil types, the average concentration of bioavailable selenium is the highest in fluvo-aquic soils and the lowest in red clays; (7) The average concentration of bioavailable selenium is higher in alkaline soils than in neutral and acidic soils; (8) Selenium in soils primarily occurs in residue, strong organic bound, and humic acidic bound forms, with the highest average concentration of bioavailable selenium occurring in alkaline soils and red clays. The selenium resource in the soils in Luoyang City has high utilization potential, and it is feasible to conduct targeted development and planning of the selenium-rich industry according to the distribution of total selenium concentration in the study area.
|
|
Received: 25 September 2022
Published: 27 October 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
LI Li-Yuan
E-mail: 527013743@qq.com;llyuan@zust.edu.cn
|
|
|
|

| 编号 | 形态 | 提取剂 | 操作步骤 | | F1 | 水溶态 | 蒸馏水 | 25 mL,摇匀,振荡30 min,离心20 min,过滤 | | F2 | 离子交换态 | 1 mol/L氯化镁溶液 | 25 mL,摇匀,振荡30 min,离心20 min,过滤 | | F3 | 碳酸盐结合态 | 1 mol/L醋酸钠溶液 | 25 mL,摇匀,振荡1 h,放置2 h,离心20 min,过滤 | | F4 | 腐殖酸结合态 | 0.1 mol/L焦磷酸钠溶液 | 50 mL,摇匀,振荡40 min,离心20 min,过滤 | | F5 | 铁锰氧化态 | 0.25 mol/L盐酸羟胺—盐酸混合液 | 50 mL,摇匀,振荡1 h,离心20 min,过滤 | | F6 | 强有机结合态 | 30%过氧化氢、(1+1)硝酸溶液和
3.2 mol/L醋酸铵—硝酸混合液 | 3 mL浓硝酸, 5 mL过氧化氢,摇匀,83 ℃恒温水浴1.5 h,补3 mL过
氧化氢,恒温水浴70 min,加入2.5 mL醋酸铵—硝酸溶液,稀释至
25 mL,放置10 h,离心20min,过滤 | | F7 | 残渣态 | 浓硝酸—高氯酸溶液 | 取F6残渣加15 mL浓硝酸和3 mL高氯酸消煮 |
|
Analytical steps for determining the chemical fraction of Se in soil
|
|
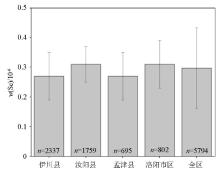
Distribution characteristics of soil total Se concentrations in different administrative regions
note: the column height is the arithmetic average, the error line is the calibration error, n is the sample number; the same below
|
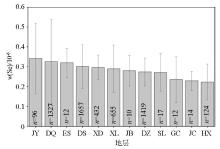
|
Distribution characteristics of total Se concentrations in soils from different parent materials
JY—Yunmengshan formation of Jixian system; DQ—Holocene series; ES—Shihezi formation of Permian system; DS—upper Pleistocene series; XD—Daan formation of Neogene system; XL—Luoyang formation of Neogene system; JB—Beidajian formation of Jixian system; DZ—middle Pleistocene series; SL—Liujiagou formation of Triassic system; GC—Chenzhaigou formation of Paleogene system; JC—Baicaoping formation of Jixian system; HX—Xinji formation of Cambrian system
|
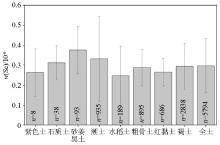
|
Distribution characteristics of total Se concentrations in different types of soils
|
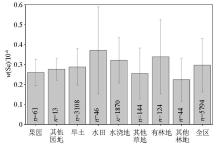
|
Distribution characteristics of total Se concentrations in soil under different land use patterns
|
|
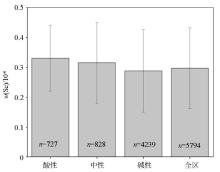
Distribution characteristics of total Se concentrations in acidic and alkaline soils
|

| 丰缺等级 | 有机质/% | 样本数 | 最小值/10-6 | 最大值/10-6 | 平均值/10-6 | 标准差/10-6 | | 极高 | >4.00 | 51 | 0.311 | 5.670 | 0.802 | 0.789 | | 高 | 3.01~4.00 | 168 | 0.253 | 1.660 | 0.489 | 0.188 | | 中上 | 2.01~3.00 | 1963 | 0.171 | 1.333 | 0.350 | 0.088 | | 中 | 1.01~2.00 | 3204 | 0.066 | 1.166 | 0.269 | 0.062 | | 低 | 0.60~1.00 | 279 | 0.058 | 0.443 | 0.138 | 0.046 | | 极低 | <0.60 | 129 | 0.033 | 0.207 | 0.083 | 0.033 |
|
Distribution characteristics of Se concentrations in soils with different organic matter contents
|
|
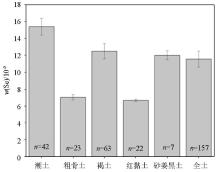
Distribution characteristics of bioavailable Se concentrations in different types of soils
|
|
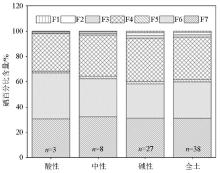
Fractions of Se in acidic and alkaline soils
|
|
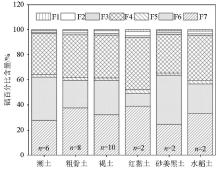
Fractions of Se in different types of soils
|
| [1] |
Mao J, Pop V J, Bath S C, et al. Effect of low-dose selenium on thyroid autoimmunity and thyroid function in UK pregnant women with mild-to-moderate iodine deficiency[J]. European Journal of Nutrition, 2016, 55 (1):55-61.
|
| [2] |
Li Z, Liang D L, Peng Q, et al. Interaction between selenium and soil organic matter and its impact on soil selenium bioavailability:A review[J]. Geoderma, 2017, 295:69-79.

|
| [3] |
Schwarz K, Foltzs C M. Selenium as an integral part of factor 3 against dietary necrotic liver degeneration[J]. Nutrition, 2002, 79(12):3292-3293.
|
| [4] |
Shi Z M, Pan P J, Feng Y W, et al. Environmental water chemistry and possible correlation with Kaschin-Beck Disease (KBD) in northwestern Sichuan,China[J]. Environment International, 2017, 99:282-292.

|
| [5] |
周越, 吴文良, 孟凡乔, 等. 土壤中硒含量、形态及有效性分析[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2014, 31(6):527-532.
|
| [5] |
Zhou Y, Wu W L, Meng F Q, et al. Review on the content,specification of selenium and its availability in soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2014, 31(6):527-532.
|
| [6] |
Preedy V R. Selenium:Chemistry,Analysis, Function and Effects[M]. London: Royal Society of Chemistry, 2015.
|
| [7] |
邢润华. 安徽省宣城市土壤硒地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(3):750-760.
|
| [7] |
Xing R H. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of selenium in soil in Xuancheng City,Anhui Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3):750-760.
|
| [8] |
Tan L C, Nancharaiah Y V, Hullebusch E V, et al. Selenium:Environmental significance,pollution,and biological treatment technologies[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2016, 34(5):886-907

|
| [9] |
Panchal S K, Wanyonyi S, Brown L. Selenium,vanadium,and chromium as micronutrients to improve metabolic syndrome[J]. Current Hypertension Reports, 2017, 19(3):10.
|
| [10] |
彭晓敏, 高愈希. 自然界中的硒及其生物学效应[J]. 化学教育, 2019, 40(17):1-8.
|
| [10] |
Peng X M, Gao Y X. Selenium in nature and its biological effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Education, 2019, 40(17):1-8.
|
| [11] |
周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3):319-336.
|
| [11] |
Zhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3):319-336.
|
| [12] |
Wang J, Li H R, Yang L S, et al. Distribution and translocation of selenium from soil to highland barley in the Tibetan Plateau Kashin-Beck disease area[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2017, 39(1):221-229.
|
| [13] |
Ullah H, Liu G, Yousaf B, et al. Developmental selenium exposure and health risk in daily foodstuffs:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 149,291-306.

|
| [14] |
谢薇, 杨耀栋, 侯佳渝, 等. 天津市蓟州区土壤硒的有效性及影响因素[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(10):2306-2316.
|
| [14] |
Xie W, Yang Y D, Hou J Y, et al. Bioavailability of selenium and its influencing factors in soil of Jizhou District,Tianjin[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(10):2306-2316.
|
| [15] |
唐世琪, 刘秀金, 杨珂, 等. 典型碳酸盐岩区耕地土壤剖面重金属形态迁移转化特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(8):3913-3923.
|
| [15] |
Tang S Q, Liu X J, Yang K, et al. Migration,transformation characteristics,and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metal fractions in cultivated soil profiles in a typical carbonate-covered area[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(8):3913-3923.
|
| [16] |
侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛, 等. 中国土壤地球化学参数[M]. 北京.地质出版社, 2020:26-41,17.
|
| [16] |
Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, Yu T, et al. Soil geochemical parameters in China[M]. Beijing.Geological Press, 2020:26-41,17
|
| [17] |
Donald J L. Trace metals in soils,plants and animals[J]. Advances in Agronomy, 1972, 24:267-325.
|
| [18] |
Forgyce F M. Selenium deficiency and toxicity in the environment[J]. Essentials of Medical Geology, 2013, 5:375-416.
|
| [19] |
杨琼, 侯青叶, 顾秋蓓, 等. 广西武鸣县典型土壤剖面Se的地球化学特性及其影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(2):455-462.
|
| [19] |
Yang Q, Hou Q Y, Gu Q B, et al. Study of geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of soil selenium in the typical soil profiles in Wuming county of Guangxi[J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(2):455-462.
|
| [20] |
张春来, 杨慧, 黄芬, 等. 广西马山县岩溶区土壤硒含量分布及影响因素研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(6):1497-1503.
|
| [20] |
Zhang C L, Yang H, Huang F, et al. Distribution and influencing factors of selenium content in soil in Karst areas in Mashan county,Guangxi,China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(6):1497-1503.
|
| [21] |
毛香菊, 刘璐, 程新涛, 等. 河南新密典型富硒区土壤Se元素地球化学特征及空间分布规律[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(10):1664-1670.
|
| [21] |
Mao X J, Liu L, Cheng X T, et al. Geochemical characteristics and spatial distribution of soil Se elements in typical Se-enriched areas in Xinmi,Henan[J]. Geological Bulletin, 2021, 40(10):1664-1670.
|
| [22] |
张建东, 王丽, 王浩东, 等. 紫阳县土壤硒的分布特征研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2017, 48(6):1404-1408.
|
| [22] |
Zhang J D, Wang L, Wang H D, et al. Study on the distribution characteristics of soil selenium in Ziyang County[J]. Soil Bulletin, 2017, 48(6):1404-1408.
|
| [23] |
龚仓, 王亮, 王顺祥, 等. 四川成都市唐昌镇土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2022, 41(3):473-450.
|
| [23] |
Gong C, Wang L, Wang S X, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of soil selenium distribution in Tangchang Town,Chengdu,Sichuan[J]. Soil Journal, 2022, 41(3):473-450.
|
| [24] |
戴慧敏, 宫传东, 董北, 等. 东北平原土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(6):1356-1364.
|
| [24] |
Dai H M, Gong C D, Dong B, et al. Distribution of soil selenium in the Northeast China plant and its influencing factors[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015, 52(6):1356-1364.
|
| [25] |
梁东丽, 彭琴, 崔泽玮, 等. 土壤中硒的形态转化及其对有效性的影响研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5):374-380.
|
| [25] |
Liang D L, Peng Q, Cui Z W, et al. Progress on selenium bioavailibility and influential factors in soil[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2017, 7(5):374-380.
|
| [26] |
王志强, 杨建锋, 魏丽馨, 等. 石嘴山地区碱性土壤硒地球化特征及生物有效性[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(1):229-237.
|
| [26] |
Wang Z Q, Yang J F, Wei L X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and bioavailability of selenium in alkaline soil in Shizuishan area,Ningxia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1):229-237.
|
| [27] |
杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶, 等. 海南岛农田土壤Se的地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5):837-849.
|
| [27] |
Yang Z F, Yu T, Hou Q Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in farmland of Hainan island[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5):837-849.
|
| [28] |
李永华, 王五一. 硒的土壤环境化学研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 2002, 33(3):230-233.
|
| [28] |
Li Y H, Wang W Y. Process on the study soil environmental chemistry of selenium[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2002, 33(3):230-233.
|
| [29] |
陈继平, 任蕊, 王晖, 等. 关中塿土地区土壤pH变化对硒形态及其有效性的影响[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(1):244-260.
|
| [29] |
Chen J P, Ren X, Wang H, et al. Effect of Lou soil pH change on selenium forms and availability[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(1):244-260.
|
| [30] |
瞿建国, 徐伯兴, 龚书椿. 上海不同地区土壤中硒的形态分布及其有效性研究[J]. 土壤学报, 1998(3):398-403.
|
| [30] |
Qu J G, Xu B X, Gong S C. Study on speciation distribution and availability of selenium in different soils of Shanghai[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1998(3):398-403.
|
| [1] |
XUE Dong-Xu, LIU Cheng, GUO Fa, WANG Jun, XU Duo-Xun, YANG Sheng-Fei, ZHANG Pei. Predicting the geothermal resources of the Tangyu geothermal field in Meixian County, Shaanxi Province, based on soil radon measurement and the controlled source audio magnetotelluric method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1169-1178. |
| [2] |
QUE Ze-Sheng, LI Guan-Chao, HU Ying, JIAN Rui-Min, LIU Bing. GIS-based assessment of the radioactivity levels and risks of soil environment[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1336-1347. |
|
|
|
|

