|
|
|
| Application of the multi-dimensional study of geochemical anomalies in deep metallogenic prediction of the Zhexiang gold deposit in southwestern Guizhou, China |
TAI Wen-Xing1( ), YANG Cheng-Fu1( ), YANG Cheng-Fu1( ), JIN Xiao-Ye2, SHAO Yun-Bin1, LIU Guang-Fu1, ZHAO Ping1, WANG Ze-Peng1, TAN Li-Jin1 ), JIN Xiao-Ye2, SHAO Yun-Bin1, LIU Guang-Fu1, ZHAO Ping1, WANG Ze-Peng1, TAN Li-Jin1 |
1. No. 105 Geological Team, Guizhou Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development, Guiyang 550018, China
2. School of Earth Resources, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), Wuhan 430074, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Due to the lack of effective deep exploration techniques, it has become a key and difficult task to expand the scale of prospecting by obtaining the mineralization information in the deep and peripheral areas of the proven typical deposits of the Huijiabao anticline in southwestern Guizhou. To truly reflect the characteristics of deep geological anomalies, this study investigated the deep ore-bearing Longtan Formation of the Zhexiang gold deposit in the eastern Huijiabao anticline. The information on deep Au anomalies was extracted through geochemical exploration in boreholes of any azimuth according to the profiles, longitudinal profiles, and deep 3D planes of survey lines. Then this study summarized the distribution patterns of geochemical anomalies and evaluated the deep metallogenic potential of the Zhexiang gold deposit. The geochemical data obtained from deep boreholes were processed using the iterative histogram method and the sample length weighted average grade method, respectively. The results show that the Longtan Formation in the mining area had Au anomaly background values of (0.04~0.12)×10-6 and an anomaly threshold of about 0.24×10-6. As revealed by the anomaly contour maps generated from the processed data using the above two methods, the distribution characteristics of Au anomalies are in high agreement with those of deep ore bodies, and the distribution ranges of high Au anomalies in all profiles are highly consistent with the morphologies of the proved ore-bearing zones (bodies). Moreover, the large-scale and unclosed high Au anomalies follow the dip direction of fault F20 in the first member of the Longtan Formation. The 3D distribution of Au anomalies shows that the nearly EW-directed high anomaly zone in the central mining area is consistent with the axial region of the Huijiapu anticline. As indicated by the analysis of the multi-dimensional geochemical anomalies and the geological characteristics of the study area, fault F20 is the main ore transmitting and controlling fault in the mining area, and the northern and eastern deep parts around the mining area have great metallogenic and prospecting potential. In addition, two prospecting targets were delineated, needing further engineering verification. This study plays an important demonstration role in guiding the exploration of other mining areas in the Huijiabao anticline. The feasible study methods can be referenced for the study of geochemical anomalies in other mining areas.
|
|
Received: 03 July 2022
Published: 11 October 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
3])
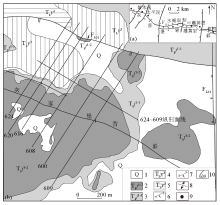
1—Quaternary floating soil;2—clay rocks of the second sub-member of the first member of Jialingjiang formation of Triassic system;3—dolomite limestone of the first sub-member of the first member of Jialingjiang formation of Triassic system;4—calcareous clay rocks of the third member of the Yelang formation of Triassic system;5—bioclastic limestone of the second member of the Yelang formation of Triassic system;6—normal fault;7—thrust fault;8—anticline;9—gold deposit;10—line of survey
">
|
Distribution of Huijiapu anticline ore field (a) and geology of Zhexiang gold deposit (b) in southwest of Guizhou Province(revised according to reference [3])
1—Quaternary floating soil;2—clay rocks of the second sub-member of the first member of Jialingjiang formation of Triassic system;3—dolomite limestone of the first sub-member of the first member of Jialingjiang formation of Triassic system;4—calcareous clay rocks of the third member of the Yelang formation of Triassic system;5—bioclastic limestone of the second member of the Yelang formation of Triassic system;6—normal fault;7—thrust fault;8—anticline;9—gold deposit;10—line of survey
|
|
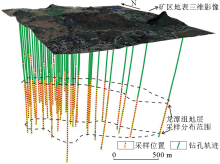
3D distribution map of borehole sampling with Longtan formation in Zhexiang gold deposit
|
|
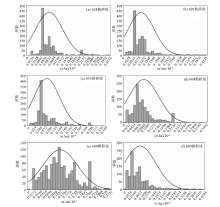
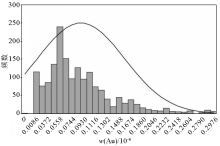
Normal distribution-histogram of Au element anomaly background values of the six exploration lines
|

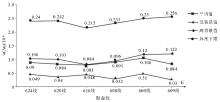
| 勘查线 | 624线 | 620线 | 616线 | 608线 | 600线 | 609线 | | 迭代次数 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | | 标准离差/10-6 | 0.075 | 0.079 | 0.067 | 0.071 | 0.072 | 0.086 | | 平均值/10-6 | 0.090 | 0.084 | 0.081 | 0.091 | 0.106 | 0.084 | | 背景值/10-6 | 0.049~0.106 | 0.040~0.103 | 0.048~0.084 | 0.032~0.096 | 0.051~0.120 | 0.030~0.123 | | 异常下限/10-6 | 0.240 | 0.242 | 0.215 | 0.233 | 0.250 | 0.256 |
|
Background values and lower limits of geochemical anomalies of the six exploration lines
|
|
The variation rule of Au anomaly background value and anomaly lower limit of the six exploration lines in Zhexiang gold depodit
|
|
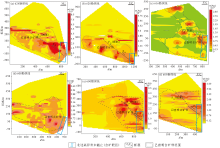
Au element anomaly map of six lines in Zhexiang gold deposit
|
3])
1—drilling holes;2—ore body and its number;3—line of omission;4—geological boundary line;5—the (presumed) fracture;6—Permian Maokou formation;7—structural erosion variant;8—Permian Longtan formation;9—Permian Changxing formation and Dalong formation;10—Triassic Yelang formation;11—Triassic Jialingjiang formation
">
|
Ore distribution map of Lontan formation in Zhexiang gold deposit(revised according to reference [3])
1—drilling holes;2—ore body and its number;3—line of omission;4—geological boundary line;5—the (presumed) fracture;6—Permian Maokou formation;7—structural erosion variant;8—Permian Longtan formation;9—Permian Changxing formation and Dalong formation;10—Triassic Yelang formation;11—Triassic Jialingjiang formation
|
|
Normal distribution-histogram of Au element anomaly background values in profile line 624 and 625
|
|
Comparison of Au element anomalies and orebody characteristics in 624 and 625 profile
|

| 钻孔 | 总样长/
m | 样品数 | 线金
属量 | Au加
权平均
品位/
10-6 | 钻孔 | 总样长/
m | 样品数 | 线金
属量 | Au加
权平均
品位/
10-6 | 钻孔 | 总样长/
m | 样品数 | 线金
属量 | Au加
权平均
品位/
10-6 | | ZK40764 | 229.45 | 210 | 929.53 | 0.41 | ZK60064 | 165.58 | 161 | 294.47 | 0.18 | ZK60801 | 208.56 | 204 | 122.45 | 0.06 | | ZK41924 | 244.45 | 226 | 596.89 | 0.24 | ZK60024 | 252.95 | 236 | 914.03 | 0.36 | ZK60824 | 184.50 | 175 | 466.04 | 0.25 | | ZK41916 | 197.72 | 188 | 259.01 | 0.13 | ZK43901 | 282.09 | 256 | 397.89 | 0.14 | ZK60832 | 252.88 | 249 | 533.41 | 0.21 | | ZK42308 | 261.40 | 248 | 589.34 | 0.23 | ZK60924 | 395.53 | 380 | 1156.56 | 0.29 | ZK60848 | 163.18 | 163 | 210.14 | 0.13 | | ZK42301 | 254.81 | 240 | 738.35 | 0.29 | ZK43916 | 287.45 | 269 | 559.61 | 0.20 | ZK60840 | 175.31 | 164 | 372.23 | 0.21 | | ZK42309 | 144.00 | 139 | 408.61 | 0.28 | ZK60940 | 295.15 | 286 | 694.79 | 0.24 | ZK43941 | 214.88 | 196 | 597.61 | 0.28 | | ZK42733 | 369.54 | 334 | 1229.94 | 0.33 | ZK60908 | 346.72 | 359 | 1147.11 | 0.33 | ZK42380 | 128.84 | 122 | 170.49 | 0.13 | | ZK40780 | 252.70 | 227 | 209.14 | 0.08 | ZK43932 | 219.44 | 205 | 508.39 | 0.23 | ZK60440 | 197.92 | 193 | 223.81 | 0.11 | | ZK41564 | 259.96 | 237 | 421.62 | 0.16 | ZK43948 | 211.29 | 199 | 486.53 | 0.23 | ZK60448 | 195.39 | 184 | 257.33 | 0.13 | | ZK42324 | 188.91 | 173 | 177.30 | 0.09 | ZK61708 | 241.26 | 230 | 326.99 | 0.14 | ZK60456 | 172.32 | 172 | 379.21 | 0.22 | | ZK42316 | 265.88 | 242 | 1199.16 | 0.45 | ZK45501 | 203.65 | 191 | 691.86 | 0.34 | ZK60432 | 270.21 | 259 | 380.15 | 0.14 | | ZK62016 | 196.87 | 189 | 409.46 | 0.21 | ZK62516 | 335.30 | 321 | 832.74 | 0.25 | ZK60424 | 246.10 | 239 | 1153.89 | 0.47 | | ZK62024 | 201.76 | 189 | 200.19 | 0.10 | ZK45516 | 189.12 | 177 | 459.33 | 0.24 | ZK42396 | 235.92 | 218 | 563.21 | 0.24 | | ZK45301 | 268.37 | 252 | 745.93 | 0.28 | ZK40708 | 176.52 | 169 | 272.65 | 0.15 | ZK43917 | 315.30 | 286 | 1468.45 | 0.47 | | ZK41580 | 271.83 | 255 | 323.68 | 0.12 | ZK40716 | 296.61 | 269 | 509.79 | 0.17 | ZK60001 | 395.31 | 365 | 684.65 | 0.17 | | ZK42332 | 244.74 | 235 | 82.53 | 0.03 | ZK40717 | 253.44 | 255 | 356.46 | 0.14 | ZK60048 | 175.49 | 167 | 268.81 | 0.15 | | ZK61601 | 311.69 | 305 | 561.75 | 0.18 | ZK40720 | 155.87 | 151 | 396.81 | 0.26 | ZK41132 | 200.35 | 182 | 294.94 | 0.15 | | ZK61616 | 194.82 | 181 | 243.22 | 0.13 | ZK40724 | 146.50 | 122 | 168.82 | 0.12 | ZK41140 | 130.80 | 123 | 203.31 | 0.16 | | ZK61624 | 234.21 | 230 | 729.29 | 0.31 | ZK40732 | 197.55 | 190 | 763.95 | 0.39 | ZK41501 | 336.71 | 308 | 363.42 | 0.11 | | ZK61632 | 166.74 | 158 | 611.43 | 0.37 | ZK40740 | 150.05 | 143 | 357.78 | 0.24 | ZK41508 | 99.76 | 92 | 266.52 | 0.27 | | ZK42348 | 329.20 | 281 | 840.39 | 0.26 | ZK40748 | 305.67 | 287 | 921.37 | 0.30 | ZK41516 | 274.65 | 247 | 633.97 | 0.23 | | ZK61216 | 254.63 | 241 | 367.28 | 0.14 | ZK41108 | 99.41 | 93 | 78.48 | 0.08 | ZK41520 | 114.39 | 110 | 815.82 | 0.71 | | ZK61224 | 205.88 | 197 | 429.88 | 0.21 | ZK41116 | 221.30 | 214 | 174.94 | 0.08 | ZK41524 | 186.61 | 174 | 914.88 | 0.49 | | ZK61240 | 238.77 | 249 | 437.91 | 0.18 | ZK41120 | 197.52 | 187 | 662.82 | 0.34 | ZK41532 | 248.35 | 230 | 404.43 | 0.16 | | ZK61232 | 247.55 | 240 | 634.79 | 0.26 | ZK41124 | 150.55 | 140 | 263.39 | 0.18 | ZK41548 | 155.85 | 255 | 392.24 | 0.25 | | ZK42364 | 270.69 | 250 | 821.25 | 0.30 | ZK41128 | 135.57 | 131 | 414.28 | 0.31 | ZK41901 | 218.79 | 213 | 291.80 | 0.13 | | ZK41904 | 197.55 | 255 | 448.63 | 0.23 | ZK41909 | 141.37 | 135 | 480.25 | 0.34 | | | | | | | ZK41908 | 269.65 | 254 | 836.51 | 0.31 | ZK42317 | 194.47 | 199 | 389.46 | 0.20 | | | | | |
|
Weighted average grade value of each borehole sample length in deep Longtan formation of Zhexiang gold deposit
|
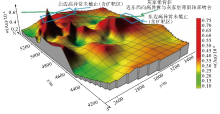
|
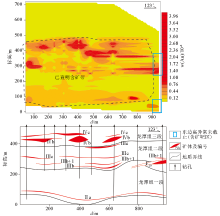
3D anomaly map of Au element of deep Longtan formation in Zhexiang gold deposit
|
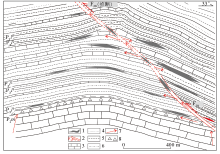
|
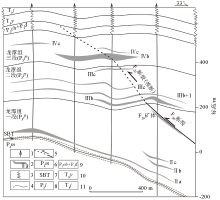
Deep structural ore-conttrolling model map in Zhexiang gold deposit
1—ore body;2—fracture;3—limestone;4—silted sandstone;5—clay rock;6—silty clay rock;7—direction of hydrothermal flow;8—variation of corrosion
|
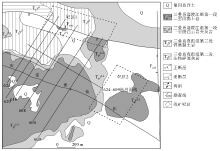
|
The map of prospecting target area in the periphery of Zhexiang gold deposit
|
| [1] |
张瑜, 夏勇, 王泽鹏, 等. 贵州簸箕田金矿单矿物稀土元素和同位素地球化学特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(2):385-395.
|
| [1] |
Zhang Y, Xia Y, Wang Z P, et al. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements and isotopes of single minerals in the Bojitian gold deposit,Guizhou Province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(2):385-395.
|
| [2] |
Jin X Y, Yang C F, Liu J Z, et al. Source and evolution of the ore-forming fluids of Carlin-type gold deposit in the Youjiang Basin,South China: Evidences from solute data of fluid inclusion extracts[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2021, 32(1):185-194.
|
| [3] |
邰文星, 周琦, 杨成富, 等. 黔西南者相金矿床三维地质可视化建模及应用[J/OL]. 武汉:地球科学: 2022[2022-07-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.p.20220407.1643.006.html.
|
| [3] |
Tai W X, Zhou Q, Yang C F, et al. Modeling and application of 3D geological visualization of gold deposits in Zhexiang gold deposit,Southwest Guizhou Province[J/OL]. Wuhan:Earth Science: 2022[2022-07-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.p.20220407.1643.006.html.
|
| [4] |
何金坪. 贵州省贞丰县者相二金矿勘探报告[R]. 贵州省地质矿产勘查开发局一0五地质大队, 2021.
|
| [4] |
He J P. Report on orebody in Zhexiang No.2 gold deposit,Zhenfeng County,Guizhou Province[R]. The 105 Geological Team of Guizhou Geological Mineral Exploration and Development Bureau, 2021.
|
| [5] |
何邵麟, 曾昭光, 罗明学, 等. 黔西南金矿勘查地球化学30年:回顾与展望[J]. 物探与化探, 2008, 32(5):461-464.
|
| [5] |
He S L, Zeng Z G, Luo M X, et al. Geochemistry of gold deposits in southwest Guizhou in the past 30 years: Retrospect and prospect[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2008, 32(5):461-464.
|
| [6] |
刘建中, 王泽鹏, 宋威方, 等. 中国南方卡林型金矿多层次构造滑脱成矿系统的构建[C]// 首届全国矿产勘查大会论文集, 2021:1061-1066.
|
| [6] |
Liu J Z, Wang Z P, Song W F, et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting potential of Carlin-gold deposit in South China[C]// Prospecting of the First National Mineral Exploration Conference, 2021:1061-1066.
|
| [7] |
阮天健. 鄂尔多斯盆地靖边新桥—横山麒麟沟地区油气地表地球化学勘探成果总结报告[R]. 中国地质大学(武汉), 2004.
|
| [7] |
Ruan T J. Summary report of oil and gas surface geochemical exploration results in Xinqiao-Hengshan Qilingou Area,Jingbian,Ordos Basin[R]. China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2004.
|
| [8] |
李惠, 张国义, 禹斌, 等. 构造叠加晕找盲矿法及其在矿山深部找矿效果[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(1):287-293.
|
| [8] |
Li H, Zhang G Y, Yu B, et al. Structual superimposed halo blind ore prospecting method and its prospecting effect in deep mine[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(1):287-293.
|
| [9] |
徐良易. 黔西南水银洞金矿床构造地球化学特征及其在隐伏矿床找矿中应用研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2016.
|
| [9] |
Xu L Y. Ectonic and geochemical characteristics of the Shuiyindong gold deposit in southwestern Guizhou Province and its application in prospecting for concealed deposits[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2016.
|
| [10] |
李惠, 禹斌, 李德亮, 等. 胶东石英脉型金矿床深部盲矿预测的构造叠加晕模型[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(S1):711-712.
|
| [10] |
Li H, Yu B, Li D L, et al. Structual superimposed halo model for blind ore prediction of deep quartz vein type gold deposit in Jiaodong[J]. Ore Deposit Geology, 2010, 29(S1):711-712.
|
| [11] |
代力. 四川夏塞银铅锌矿床I号矿体原生晕地球化学及深部预测[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.
|
| [11] |
Dai L. Primary halo geochemistry and deep prediction of No.1 orebody in Xiasai Ag-Pb-Zn deposit,Sichuan Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013.
|
| [12] |
韩扬. 云南芦子园Pb-Zn多金属矿床原生晕分带规律与深部成矿预测研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.
|
| [12] |
Han Y. Primary halo zoning and deep metallogenic prediction of Luziyuan Pb-Zn polymetallic deposit in Yunnan Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2016.
|
| [13] |
潘谋成, 胡凯, 曹剑, 等. 黔西南簸箕田卡林型金矿中含砷黄铁矿和毒砂的赋金特征研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2013, 19(2):293-306.
|
| [13] |
Pan M C, Hu K, Cao J, et al. Study on the gold-bearing characteristics of arsenic-bearing pyrite and arsenopyrite in the Bojitian Carlin-type gold deposit in Southwestern Guizhou[J]. Geological Journal of Universities, 2013, 19(2):293-306.
|
| [14] |
Di W, Luo G P. Application and effects of singularity analysis in evaluating the denudation degree of Carlin-type gold deposits in southwest Guizhou,China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 96:164-180.

|
| [15] |
林成贵, 程志中, 陈辉, 等. 四川省红泥坡铜矿原生晕特征及找矿方向[J/OL]. 北京:中国地质: 2021[2021-09-28]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.p.20200601.1747.018.html.
|
| [15] |
Lin C G, Cheng Z Z, Chen H, et al. Characteristics and prospecting direction of primary halo of Hongnipo copper deposit in Sichuan Province[J]. Peking:Geology in China: 2021[2021-09-28]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.p.20200601.1747.018.html.
|
| [16] |
李浩嵩. 滇东南都龙锡铟多金属矿床原生晕分带特征及深部矿体预测研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.
|
| [16] |
Li H S. Study on primary halo zoning and deep orebody prediction in Dulong Sn-Ln polymetallic deposit,southeast Yunnan[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2020.
|
| [17] |
张赞赞, 张舒, 吴明安, 等. 安徽庐枞盆地泥河玢岩型铁矿床地质—原生晕地球化学找矿模型[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(2):305-325.
|
| [17] |
Zhang Z Z, Zhang S, Wu M A, et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting potential of Nihe porphyrite type iron deposit in Luzong Basin,Anhui Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2020, 39(2):305-325.
|
| [1] |
CHEN Wei, TAN You, CAO Zheng-Duan, LIAO Zhi-Quan, ZHANG Ning-Fa, FU Hai-Hui. Application of tectonic primary halos in the exploration of deep concealed ore bodies: A case study of the Niuxingba plumbum-zinc-gold-silver deposit in Yinkeng, southern Jiangxi[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 892-905. |
| [2] |
WEI Cong-Ling, CHEN Jian-Li, GUO Peng. Metallogenic prediction of gold deposits in Laowan area, Henan Province using the weight of evidence model and MRAS[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3): 653-660. |
|
|
|
|

