|
|
|
| Sulfur-lead isotopes based tracing of the metal element anomalies identified in the total metal measurement of surface fine-grained soils: A case study of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type concealed gold deposit |
YUAN Yu-Ting1( ), LIU Xue-Min1( ), LIU Xue-Min1( ), WANG Xue-Qiu2, TAN Qin-Ping3 ), WANG Xue-Qiu2, TAN Qin-Ping3 |
1. Applied Nuclear Technology in Geosciences Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu 610059, China
2. Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, China
3. State Key Laboratory of Ore Deposit Geochemistry, Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guiyang 550081, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Exploring concealed deposits in covered areas is an important way to solve the current resource dilemma. Extensive experimental studies using the deep-penetration geochemical methods developed at home and abroad have been conducted targeting some known concealed deposits, yielding satisfactory results. However, these methods have yet to be widely employed for prospecting in unknown covered areas due to the failure in determining whether surface metal element anomalies are directly from deep ore bodies. Accordingly, it is urgent to develop a tracing technique for surface anomalies. The Shuiyindong gold deposit in Guizhou Province is a super-large fully-concealed Carlin-type gold deposit in China, and its ore-forming fluids are rich in elements such as S, Au, As, Sb, and Hg. This study sampled surface fine-grained soils in the Shuiyindong gold deposit for the concentration analysis of five trace elements (Au, As, Cu, Sb, and Hg), verifying the prospecting effect of the total metal measurement technique of fine-grained soils in this deposit. Moreover, the source of surface soil anomalies was identified using sulfur (S) and lead (Pb) isotopes. This study found that: ① The total metal measurement technique of fine-grained soils showed encouraging indicative effects, with the high Au-As-Sb-Hg anomalies obtained roughly consistent with the distribution of concealed ore bodies and faults, and Hg exhibited the best indication effect on concealed ore bodies. ② The δ34S values and the ratios of radiogenic w(207Pb)/w(204Pb) and w(206Pb)/w(204Pb) in the soil above concealed ore bodies and faults were significantly higher than those in the soil of the surrounding rock area, effectively indicating that the anomalies in the surface fine-grained soils were from deep concealed ore bodies. This study provides a theoretical basis for exploring concealed Carlin-type gold deposits in the same type of covered areas using the total metal measurement technique of fine-grained soils.
|
|
Received: 24 April 2022
Published: 11 October 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
20])
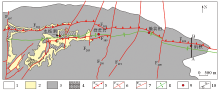
1—Yongningzhen formation;2—Changxing-Dalong formation;3—Yelang formation;4—Longtan formation;5—reverse fault and its No.;6—normal fault and its No.;7—unclassified faulti and its No.;8—anticlinal axis;9—deposit;10—A-B profile line
">
|
Geological sketch of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit(modified from reference[20])
1—Yongningzhen formation;2—Changxing-Dalong formation;3—Yelang formation;4—Longtan formation;5—reverse fault and its No.;6—normal fault and its No.;7—unclassified faulti and its No.;8—anticlinal axis;9—deposit;10—A-B profile line
|
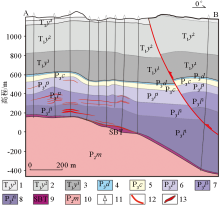
Fig.1)
1—the third unit of the Yelang formation;2—the second unit of the Yelang formation;3—the first unit of the Yelang formation;4—Dalong formation;5—Changxing formation;6—the third unit of the Longtan formation;7—the second unit of the Longtan formation;8—the first unit of the Longtan formation;9—unconformity(SBT);10—Maokou formation;11—drill hole;12—fault;13—orebody
">
|
Geological cross-section A-B through the Nayang section of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit (the position of A-B is shown in Fig.1)
1—the third unit of the Yelang formation;2—the second unit of the Yelang formation;3—the first unit of the Yelang formation;4—Dalong formation;5—Changxing formation;6—the third unit of the Longtan formation;7—the second unit of the Longtan formation;8—the first unit of the Longtan formation;9—unconformity(SBT);10—Maokou formation;11—drill hole;12—fault;13—orebody
|
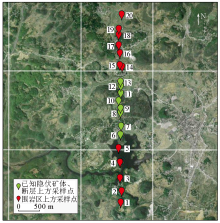
|
Distribution map of sampling sites in the Nayang section of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type deposit
(Ovi interactive map projection)
|

| 检测项目 | 检测依据 | 检测仪器 | 标准样品 | | Au | DZ/T 0279.4
—2016 | XSERIES2电感
耦合等离子
体质谱仪 | GAu-9、
GAu-11 | | Cu | GB/T 14506.30
—2010 | GSS-19、
GSS-23 | | As、Sb | DZ/T 0279.13
—2016 | AFS-8330双道
原子荧光
光度计 | | Hg | NY/T 1121.10
—2006 | | S同位素 | DZ/T 0184.15—
1997 | Deltavplus气体
同位素质谱计 | IAEA-SO-5、
IAEA-SO-6、
NBS-127 | | Pb同位素 | DZ/T 0184.12—
1997 | Phoenix热表面
电离质谱仪 | NBS981 |
|
Analytical methods, instruments and standards of elements
|

| 元素 | 位置 | 最小值 | 中位数 | 最大值 | 算术平均值 | 几何平均值 | 标准偏差 | 变异系数/% | | Au | 总矿段 | 0.93 | 2.61 | 5.55 | 2.84 | 2.60 | 1.24 | 44 | | 围岩区上方 | 0.93 | 2.20 | 3.15 | 2.21 | 2.11 | 0.67 | 30 | | 矿体上方 | 1.80 | 3.81 | 5.55 | 3.79 | 3.56 | 1.33 | 35 | | 矿体/围岩区上方 | | 1.73 | | 1.71 | 1.69 | | | | Cu | 总矿段 | 31.96 | 74.66 | 103.00 | 72.29 | 69.07 | 19.91 | 28 | | 围岩区上方 | 58.87 | 82.47 | 103.00 | 80.46 | 79.18 | 14.70 | 18 | | 矿体上方 | 31.96 | 69.25 | 85.06 | 60.04 | 56.27 | 21.22 | 35 | | 矿体/围岩区上方 | | 0.84 | | 0.75 | 0.71 | | | | As | 总矿段 | 8.10 | 49.21 | 325.09 | 83.13 | 49.54 | 93.21 | 112 | | 围岩区上方 | 8.10 | 29.01 | 224.00 | 47.94 | 30.28 | 59.53 | 124 | | 矿体上方 | 42.46 | 84.32 | 325.09 | 135.92 | 103.63 | 112.71 | 83 | | 矿体/围岩区上方 | | 2.91 | | 2.84 | 3.42 | | | | Sb | 总矿段 | 0.75 | 11.41 | 98.90 | 16.94 | 7.78 | 23.30 | 138 | | 围岩区上方 | 0.75 | 2.91 | 50.27 | 10.13 | 4.20 | 15.25 | 151 | | 矿体上方 | 11.33 | 14.84 | 98.90 | 27.15 | 19.60 | 30.15 | 111 | | 矿体/围岩区上方 | | 5.11 | | 2.68 | 4.66 | | | | Hg | 总矿段 | 0.217 | 1.157 | 11.884 | 2.483 | 1.247 | 3.372 | 136 | | 围岩区上方 | 0.217 | 0.820 | 2.656 | 0.891 | 0.626 | 0.761 | 85 | | 矿体上方 | 1.189 | 3.292 | 11.884 | 4.872 | 3.505 | 4.369 | 90 | | 矿体/围岩区上方 | | 4.01 | | 5.47 | 5.60 | | |
|
Statistical parameters of five trace elements in fine-grained soils in the Nayang section of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type deposit
|

| 元素 | Cu | As | Sb | Hg | | Au | -0.254 | 0.654** | 0.477* | 0.720** | | Cu | | 0.018 | 0.004 | -0.014 | | As | | | 0.562** | 0.890** | | Sb | | | | 0.577** |
|
Correlation analysis of five trace elements in fine-grained soils in the Nayang section of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type deposit
|
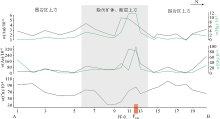
|
Change trends of five trace elements in fine-grained soils along the exploration line in the Nayang section of the Shuiyindong gold deposit
|

| 硫、铅同位素组成 | 最小值 | 中位数 | 最大值 | 算术平均值 | 几何平均值 | 标准偏差 | 变异系数/% | | δ34S/‰ | 总矿段 | -3.2 | 4.6 | 12.5 | 4.2 | | 3.8 | 89.5 | | 围岩区上方 | -3.2 | 1.7 | 6.2 | 2.0 | | 2.6 | 130.9 | | 矿体上方 | 4.5 | 7.5 | 12.5 | 7.5 | 7.2 | 2.6 | 34.6 | | 矿体/围岩区上方 | | 4.5 | | 3.8 | | | | w(206Pb)/
w(204Pb) | 总矿段 | 18.860 | 19.904 | 21.438 | 19.969 | 19.951 | 0.869 | 4.35 | | 围岩区上方 | 18.860 | 19.176 | 20.692 | 19.398 | 19.391 | 0.573 | 2.95 | | 矿体上方 | 20.220 | 20.850 | 21.438 | 20.826 | 20.823 | 0.368 | 1.77 | | 矿体/围岩区上方 | | 1.087 | | 1.074 | 1.074 | | | w(207Pb)/
w(204Pb) | 总矿段 | 15.622 | 15.719 | 15.834 | 15.724 | 15.724 | 0.065 | 0.41 | | 围岩区上方 | 15.622 | 15.685 | 15.779 | 15.684 | 15.684 | 0.049 | 0.31 | | 矿体上方 | 15.740 | 15.784 | 15.834 | 15.783 | 15.783 | 0.031 | 0.20 | | 矿体/围岩区上方 | | 1.006 | | 1.006 | 1.006 | | | w(208Pb)/
w(204Pb) | 总矿段 | 38.888 | 39.034 | 39.276 | 39.048 | 39.048 | 0.096 | 0.25 | | 围岩区上方 | 39.011 | 39.095 | 39.276 | 39.100 | 39.100 | 0.082 | 0.21 | | 矿体上方 | 38.888 | 38.962 | 39.046 | 38.969 | 38.969 | 0.050 | 0.13 | | 矿体/围岩区上方 | | 0.997 | | 0.997 | 0.997 | | |
|
Statistical parameters of S and Pb isotopic compositions of fine-grained soils in the Nayang section of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit
|
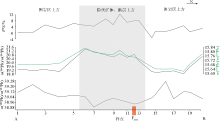
|
Change trends of S and Pb isotopic compositions of fine-grained soils in the Nayang section of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit
|
|
|
Sulfur isotopic data of ore and wall rock samples in the Shuiyindong Carlin-type deposit
|
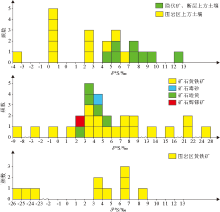
|
Sulfur isotopic composition of soils, ores and surrounding rocks in the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit
|

| 指标 | As | Sb | Hg | δ34S | w(206Pb)/w(204Pb) | w(207Pb)/w(204Pb) | w(208Pb)/w(204Pb) | | Au | 0.653** | 0.476* | 0.719** | 0.652** | 0.711** | 0.689** | -0.438 | | As | | 0.562** | 0.890** | 0.359 | 0.503* | 0.39 | -0.417 | | Sb | | | 0.578** | 0.35 | 0.391 | 0.29 | -0.316 | | Hg | | | | 0.464* | 0.522* | 0.406 | -0.487* | | δ34S | | | | | 0.679** | 0.655** | -0.508* | | w(206Pb)/w(204Pb) | | | | | | 0.966** | -0.652** | | w(207Pb)/w(204Pb) | | | | | | | -0.595** |
|
Correlation analysis of four trace elements in fine-grained soils with sulfur and lead isotopes in the Nayang section of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type deposit
|

| 样品 | w(206Pb)/
w(204Pb) | w(207Pb)/
w(204Pb) | w(208Pb)/
w(204Pb) | 参考文献 | | IIe | 18.361 | 15.56 | 38.452 | [25] | | IIf | 18.383 | 15.642 | 38.729 | | IIIa | 18.304 | 15.54 | 38.501 | | IIIb-1 | 18.452 | 15.532 | 38.332 | | IIIb-2 | 17.942 | 15.56 | 38.158 | | IIIb-3 | 18.145 | 15.551 | 38.382 | | SYD-11 | 18.648 | 15.612 | 38.712 | [39] | | SYD-3 | 18.213 | 15.628 | 38.496 | | SYD-20 | 18.459 | 15.608 | 38.508 | | 分布范围 | 17.942~
18.648 | 15.532~
15.642 | 38.158~
38.729 | | | 平均值 | 18.323 | 15.581 | 38.474 | |
|
Lead isotopic composition of pyrite in the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit
|
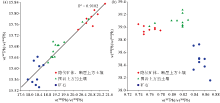
|
w(207Pb)/w(204Pb)-w(206Pb)/w(204Pb)(a)、w(208Pb)/w(204Pb)-w(207Pb)/w(206Pb)(b) diagram of the surface soil and ore pyrite in the Nayang section of Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit
|
| [1] |
龚敏. 非常规化探方法在地质勘查中的应用浅析[J]. 科技资讯, 2012(34):86-87.
|
| [1] |
Gong M. Application of unconventional geochemical exploration methods in geological exploration[J]. Science and Technology Information, 2012(34):86-87.
|
| [2] |
Kristiansson K, Malmqvist L. Evidence for nondiffusive transport of ${ }_{86}^{222} \mathrm{Rn}$ in the ground and a new physical model for the transport[J]. Geophysics, 1982, 47(10):1444-1452.

|
| [3] |
Clark J R. Enzyme-induced leaching of B-horizon soils for mineral exploration in areas of glacial overburden[J]. Transactions of the Institution of Mining and Metallurgy Section B-Applied Earth Science, 1993, 102:B19-B29.
|
| [4] |
Mann A W, Birrell R D, Mann A T, et al. Application of the mobile metal ion technique to routine geochemical exploration[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1998, 61(1/13):87-102.

|
| [5] |
Wang X Q. Leaching of mobile forms of metals in overburden:Development and application[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1998, 61(1/3):39-55.

|
| [6] |
Antropova L V, Goldberg I S, Voroshilov N A, et al. New methods of regional exploration for blind mineralization: Application in the USSR[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1992, 43(2):157-166.

|
| [7] |
谢学锦. 用新观念与新技术寻找巨型矿床[J]. 科学中国人, 1995(5):15-16.
|
| [7] |
Xie X J. Searching for giant deposits with new ideas and new technologies[J]. Scientific Chinese, 1995(5):15-16.
|
| [8] |
王学求, 刘占元, 白金峰, 等. 深穿透地球化学对比研究两例[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2005, 27(3):250-255,183.
|
| [8] |
Wang X Q, Liu Z Y, Bai J F, et al. Deep-enetration geochemistry-comparison studies of two concealed deposis.[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2005, 27(3):250-255,183.
|
| [9] |
李建亭, 刘雪敏, 王学求, 等. 地表土壤微细粒测量中微量元素和同位素对福建罗卜岭隐伏铜钼矿床的示踪与判别[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(1):32-45.
|
| [9] |
Li J T, Liu X M, Wang X Q, et al. Tracing and identification of concealed Luoboling copper-molybdenum deposit in Fujian Province using trace elements and isotopes in fine-grained surface soils[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1):32-45.
|
| [10] |
刘雪敏, 陈岳龙, 王学求. 深穿透地球化学异常源同位素识别研究:以新疆金窝子金矿床、内蒙古拜仁达坝—维拉斯托多金属矿床为例[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5):1104-1116.
|
| [10] |
Liu X M, Chen Y L, Wang X Q. Research on isotope identification for anomalous sources of deep-penetration geochemistry:Two cases of Jinwozi Au deposit,Xinjiang and Bairendaba-Weilasituo Polymetallic deposit,Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5):1104-1116.
|
| [11] |
徐洋, 汪明启, 高玉岩, 等. 利用铅同位素研究山东邹平王家庄铜矿地气物质来源[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(1):23-27.
|
| [11] |
Xu Y, Wang M Q, Gao Y Y, et al. Tracing the source of geogas materiala with the lead isotope method in the Wangjiazhuang Copper Ore Deposit of Zouping,Shandong Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(1):23-27.
|
| [12] |
R·W博伊尔. 金的地球化学及金矿床[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1984.
|
| [12] |
Boyle R W. Gold geochemistry and gold deposits[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1984.
|
| [13] |
Radtke A S. Geology of the Carlin gold deposit, Nevada[G]// U.S.Geological Survey Professional Paper,Geological Survey(U.S.), 1985.
|
| [14] |
蒲含科. 板其金矿矿物岩石特征及矿床成因讨论[J]. 贵州地质, 1987(2):151-161.
|
| [14] |
Pu H K. Mineral and rock charscteristics and ore genesis of Banqi gold ore[J]. Geology of Guizhou, 1987(2):151-161.
|
| [15] |
陈潭钧. 册亨板其金矿矿床地质特征及成因初探[J]. 贵州地质, 1986, 13(4):325-339.
|
| [15] |
Chen T J. A preliminary discussion on geological features and origin of Banqi Au-ore deposit in Ceheng[J]. Geology of Guizhou, 1986, 13(4):325-339.
|
| [16] |
谭运金. 滇黔桂地区微细粒浸染型金矿床的矿床地球化学类型[J]. 矿床地质, 1994, 13(4):308-321.
|
| [16] |
Tan Y J. Geochemical types of the micro-and fine-grained disseminated gold deposits in Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi region[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1994, 13(4):308-321.
|
| [17] |
刘建中, 邓一明, 邱林, 等. 中国第一个Ⅰ类型卡林型金矿床— —水银洞金矿地质[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(S1):175-178.
|
| [17] |
Liu J Z, Deng Y M, Qiu L, et al. Geological characteristic of the Shuiyindong gold deposit,the first Ⅰ-type Carlin-type gold deposit in China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2006, 25(S1):175-178.
|
| [18] |
刘建中, 李建威, 周宗桂, 等. 贵州贞丰—普安金矿整装勘查区找矿与研究新进展[J]. 贵州地质, 2017, 34(4):244-254.
|
| [18] |
Liu J Z, Li J W, Zhou Z G, et al. New progress of exploration and research of Zhenfeng-Puan gold fully equipped exploration area.[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2017, 34(4):244-254.
|
| [19] |
陈发恩, 刘建中, 杨成富, 等. 贵州省贞丰县水银洞超大型金矿床地质特征及构造控矿分析[J]. 贵州地质, 2019, 36(1):18-27.
|
| [19] |
Chen F E, Liu J Z, Yang C F, et al. Geological characteristics and structural ore control analysis of Shuiyindong super large gold deposit in Zhenfeng County, Guizhou Province[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2019, 36(1):18-27.
|
| [20] |
谭亲平, 夏勇, 谢卓君, 等. 黔西南水银洞卡林型金矿构造地球化学及对隐伏矿找矿的指示[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(6):886-898.
|
| [20] |
Tan Q P, Xia Y, Xie Z J, et al. Tectono-geochemistry and cocealed ores prospecting in the Shuiyindong gold deposit of Southwestern Guizhou[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2020, 41(6):886-898.
|
| [21] |
林鲁军, 庞振山, 薛建玲, 等. 水银洞金矿矿床地质特征、成因及找矿标志[J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(S1):1017-1018.
|
| [21] |
Lin L J, Pang Z S, Xue J L, et al. Geological characteristics, genesis and prospecting signs of the Shuiyindong gold deposit[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2015, 35(S1):1017-1018.
|
| [22] |
齐少烽, 陈发恩, 冯琳, 等. 贵州省水银洞金矿地质特征及成因浅析[J]. 中国地质调查, 2015, 2(6):53-58.
|
| [22] |
Qi S F, Chen F E, Feng L, et al. Geological characteristic and genesis of the Shuiyindong gold deposit,Guizhou[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2015, 2(6):53-58.
|
| [23] |
刘建中, 夏勇, 邓一明, 等. 贵州水银洞超大型金矿床金的赋存状态再研究[J]. 贵州地质, 2007, 24(3):165-169.
|
| [23] |
Liu J Z, Xia Y, Deng Y M, et al. Restudy on modes of gold occurrence in the Shuiyindong super-large-sized gold deposit[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2007, 24(3):165-169.
|
| [24] |
谭亲平, 夏勇, 王学求, 等. 黔西南灰家堡金矿田成矿构造模式及构造地球化学研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017, 41(2):291-304.
|
| [24] |
Tan Q P, Xia Y, Wang X Q, et al. Tectonic model and tectonic-geochemistry characteristic of the Huijiabao gold orefield,SW Guizhou Province[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2017, 41(2):291-304.
|
| [25] |
夏勇, 张瑜, 苏文超, 等. 黔西南水银洞层控超大型卡林型金矿床成矿模式及成矿预测研究[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(10):1473-1482.
|
| [25] |
Xia Y, Zhang Y, Su W C, et al. Metallogenic model and prognosis of the Shuiyindong super-large stratabound carlin-type gold deposit,Sourthwestern Guizhou Province,China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(10):1473-1482.
|
| [26] |
郭振春. 黔西南灰家堡金矿田“两层楼”模式及找矿意义[J]. 黄金地质, 2002, 8(4):18-23.
|
| [26] |
Guo Z C. The two-stairs model of the Huijiapu gold field in south-western Guizhou and its prospecting significance[J]. Gold Geology, 2002, 8(4):18-23.
|
| [27] |
刘建中, 杨成富, 王泽鹏, 等. 贵州省贞丰县水银洞金矿床地质研究[J]. 中国地质调查, 2017, 4(2):32-41.
|
| [27] |
Liu J Z, Yang C F, Wang Z P, et al. Geological research of Shuiyindong gold deposit in Zhenfeng Country,Guizhou Province[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2017, 4(2):32-41.
|
| [28] |
刘世川. 水银洞金矿成矿构造特征再认识与找矿思路[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2021, 33(1):88-91.
|
| [28] |
Liu S C. Reunderstanding of metallogenic tectonic characteristics of Shuiyindong gold deposit and ideas for prospecting[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2021, 33(1):88-91.
|
| [29] |
周正均. 水银洞金矿区矿床地质特征分析[J]. 世界有色金属, 2017, 483(15):117,119.
|
| [29] |
Zhou Z J. Analysis of geological characteristic of gold deposit in mercury cave gold mine[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 483(15):117,119.
|
| [30] |
王崇予. 贵州贞丰水银洞金矿床矿石矿相学特征[J]. 新疆有色金属, 2018, 41(5):58-59.
|
| [30] |
Wang C Y. Mineral facies characteristics of ore deposits in Shuyindong gold deposit, Zhenfeng, Guizhou[J]. Xinjiang Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 41(5):58-59.
|
| [31] |
刘建中, 陈景河, 邓一明, 等. 贵州水银洞超大型金矿勘查实践及灰家堡矿集区勘查新进展[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2009, 32(2):138-143.
|
| [31] |
Liu J Z, Chen J H, Deng Y M, et al. Exploration of the Shuiyindong super-scale gold deposit and the evolution of exploration for metallogenic belt of the Huijiabao Anticline in Guizhou Province[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2009, 32(2):138-143.
|
| [32] |
苏信明. 太平洞金矿矿床成因及找矿标志[J]. 建材与装饰, 2016, 419(15):192-193.
|
| [32] |
Su X M. Genesis and prospecting signs of Taipingdong gold deposit[J]. Construction Materials & Decoration, 2016, 419(15):192-193.
|
| [33] |
赵静, 梁金龙, 李军, 等. 贵州贞丰水银洞金矿矿床成因与成矿模式:来自载金黄铁矿NanoSIMS多元素Mapping及原位微区硫同位素的证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(1):157-167.
|
| [33] |
Zhao J, Liang J L, Li J, et al. Genesis and metallogenic model of the Shuiyindong gold deposit,Guizhou Province:Evidences from high-resolution multi-element mapping and in situ sulfur isotopes of Au-carrying pyrites by NanoSIMS[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(1):157-167.
|
| [34] |
郑禄林, 杨瑞东, 刘建中, 等. 黔西南泥堡金矿床大型隐伏金矿体地质特征研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2014, 50(4):689-699.
|
| [34] |
Zheng L L, Yang R D, Liu J Z, et al. Geological features of a large concealed gold orebody in the Nibao gold deposit,Southwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2014, 50(4):689-699.
|
| [35] |
靳晓野. 黔西南泥堡、水银洞和丫他金矿床的成矿作用特征与矿床成因研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2017.
|
| [35] |
Jin X Y. Geology,mineralization and genesis of the Nibao,Shuivindong and Yata gold deposits in SW Guizhou Province,China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2017.
|
| [36] |
夏勇. 贵州贞丰县水银洞金矿床成矿特征和金的超常富集机制研究[D]. 贵阳: 中国科学院研究生院地球化学研究所, 2005.
|
| [36] |
Xia Y. Characteristics and model for Shuiyindong gold deposit in southwestern Guizhou,China[D]. Guiyang: Institute of Geochemistry,Chinese Academy of Sciences Guiyang, China, 2005.
|
| [37] |
宋发治. 贵州水银洞金矿床地质特征及成因研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2009.
|
| [37] |
Song F Z. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Shuiyindong gold deposit,Guizhou,China[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2009.
|
| [38] |
谭代卫, 刘建中. 贵州水银洞金矿簸箕田1矿段940-1060 m标高地质与生产勘探的矿体特征分析[C]// 中国地球物理学会, 2021.
|
| [38] |
Tan D W, Liu J Z. Analysis of the orebody characteristics of 940-1060 m elevation geology and production exploration in the 1st mining section of Fujitian,Shuiyindong Gold Mine,Guizhou[C]// Chinese Geophysical Society, 2021.
|
| [39] |
林鲁军. 贵州省贞丰县水银洞金矿床地质地球化学特征和成因[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.
|
| [39] |
Lin L J. Geological and geochemical characteristics and genesis of the Shuiyindong gold deposit,Zhenfeng County,Guizhou Provmce[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2017.
|
| [40] |
成杭新, 李括, 李敏, 等. 中国城市土壤化学元素的背景值与基准值[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(3):265-306.
|
| [40] |
Cheng H X, Li K, Li M, et al. Geochemical background and baseline value of chemical elements in urban soil in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(3):265-306.
|
| [41] |
鲁美, 叶荣, 张必敏, 等. 覆盖区地球化学勘查进展[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(6):1408-1411.
|
| [41] |
Lu M, Ye R, Zhang B M, et al. Progress in geochemical exploration of covered areas[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(6):1408-1411.
|
| [42] |
唐金荣, 吴传璧, 施俊法. 深穿透地球化学迁移机理与方法技术研究新进展[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(12):1579-1590.
|
| [42] |
Tang J R, Wu C B, Shi J F. Recent progress in the study of the deep-penetrating geochemical migration mechanisms and methods[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2007, 26(12):1579-1590.
|
| [43] |
王学求, 刘占元, 叶荣, 等. 新疆金窝子矿区深穿透地球化学对比研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2003, 27(4):247-250,254.
|
| [43] |
Wang X Q, Liu Z Y, Ye R, et al. Deep-penetrating geochemistry:A comparative study in the Jinwozi gold ore district,Xinjiang[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2003, 27(4):247-250,254.
|
| [44] |
张必敏, 王学求, 贺灵, 等. 内蒙古半干旱草原区隐伏矿地球化学勘查方法试验[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(5):804-810.
|
| [44] |
Zhang B M, Wang X Q, He L, et al. Geochemical exploration for concealed deposits on semi-arid grasslands of Inner Mongolia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(5):804-810.
|
| [45] |
刘汉粮, 王学求, 张必敏, 等. 沙泉子隐伏铜镍矿地球化学勘查方法试验[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2014, 36(6):763-770.
|
| [45] |
Liu H L, Wang X Q, Zhang B M, et al. Geochemical exploration for concealed Cu-Ni deposit,Shaquanzi,Xinjiang[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 36(6):763-770.
|
| [46] |
刘汉粮, 张必敏, 刘东盛, 等. 土壤微细粒全量测量在甘肃花牛山矿区的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(1):33-39.
|
| [46] |
Liu H L, Zhang B M, Liu D S, et al. The application of soil geochemical measurement method to the Huaniushan Pb-Zn deposit,Gansu Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(1):33-39.
|
| [47] |
张必敏, 王学求, 叶荣, 等. 土壤微细粒分离测量技术在黄土覆盖区隐伏金矿勘查中的应用及异常成因探讨[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2019, 39(2):301-310.
|
| [47] |
Zhang B M, Wang X Q, Ye R, et al. Fine-grained soil prospecting method for mineral exploration in loess covered areas and discussion on the origin of geochemical anomalies[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2019, 39(2):301-310.
|
| [48] |
常华进, 储雪蕾, 黄晶, 等. 沉积环境细菌作用下的硫同位素分馏[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(6):807-813.
|
| [48] |
Chang H J, Chu X L, H J, et al. Sulfur isotope fractionation accompanying bacterial action under sedimentary condition[J]. Geological Review, 2007, 53(6):807-813.
|
| [49] |
Bin L, Shao Y J. Genesis of the giant Zijinshan epithermal Cu-Au and Luoboling porphyry Cu-Mo deposits in the Zijinshan ore district, Fujian Province, SE China: A multi-isotope and trace element investigation[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 88:753-767.

|
| [50] |
陕亮, 郑有业, 许荣科, 等. 硫同位素示踪与热液成矿作用研究[J]. 地质与资源, 2009, 18(3):197-203.
|
| [50] |
Shan L, Zheng Y Y, Xu R K, et al. Review on sulfur isotopic tracing and hydrothermal metallogenesis[J]. Geology and Resources, 2009, 18(3):197-203.
|
| [51] |
曾键年, 范永香, 林卫兵. 江西金山金矿床成矿物质来源的铅和硫同位素示踪[J]. 现代地质, 2002, 16(2):170-176.
|
| [51] |
Zeng J N, Fan Y X, Lin W B. The lead and sulfur isotopic tracing of the source of ore-forming material in Jinshan gold deposit in Jiangxi Province[J]. Geoscience, 2002, 16(2):170-176.
|
| [52] |
席明杰, 马生明, 朱立新, 等. 硫同位素在地球化学异常成因研究中的应用[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(5):705-718.
|
| [52] |
Xi M J, Ma S M, Zhu L X, et al. The application of sulfur isotope in the cause of geochemical abnormality[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(5):705-718.
|
| [53] |
唐龙飞, 谭泽模, 黄敦杰, 等. 大厂矿田硫同位素特征及找矿预测[J]. 有色金属:矿山部分, 2014, 66(6):30-35.
|
| [53] |
Tang L F, Tan Z M, Huang D J, et al. Sulfur isotope characteristic and prospecting prediction of Dachang tinpolymetallic ore field[J]. Nonferrous Metals:Mining Section, 2014, 66(6):30-35.
|
| [54] |
王成辉, 王登红, 刘建中, 等. 贵州水银洞超大型卡林型金矿同位素地球化学特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(2):396-403.
|
| [54] |
Wang C H, Wang D H, Liu J Z, et al. Characteristics of isotope geochemistry of Shuiyindong super-large Carlin gold deposit in Guizhou[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(2):396-403.
|
| [55] |
朱赖民, 金景福, 何明友, 等. 黔西南微细浸染型金矿床深部物质来源的同位素地球化学研究[J]. 长春科技大学学报, 1998, 28(1):39-44.
|
| [55] |
Zhu L M, Jin J F, He M Y, et al. A study of isotopic geochemistry on plutonic material source for the fine-disseminated gold deposits in Southwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology, 1998, 28(1):39-44.
|
| [56] |
刘建中, 邓一明, 刘川勤, 等. 贵州省贞丰县水银洞层控特大型金矿成矿条件与成矿模式[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(1):169-177.
|
| [56] |
Liu J Z, Deng Y M, Liu C Q, et al. Metallogenic conditions and model of the superlarge Shuiyindong stratabound gold deposit in Zhenfeng County,Guizhou Province[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(1):169-177.
|
| [57] |
熊灿娟, 粟梅. 水银洞金矿区硫同位素地球化学研究[J]. 科技与创新, 2015(9):8-9.
|
| [57] |
Xiong C J, Su M. Shuiyindong goldfields sulfur isotope geochemistry[J]. Science and Technology & Innovation, 2015(9):8-9.
|
| [58] |
王泽鹏, 夏勇, 宋谢炎, 等. 黔西南灰家堡卡林型金矿田硫铅同位素组成及成矿物质来源研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(6):746-752.
|
| [58] |
Wang Z P, Xia Y, Song X Y, et al. Sulfur and lead isotopic composition of the Huijiabao carlin-type gold field and the ore-forming material sources in sources in southwest of Guizhou[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2013, 32(6):746-752.
|
| [59] |
汪明启. 铅同位素地球化学勘查方法及其应用[J]. 地质地球化学, 1991(6):37-40,43.
|
| [59] |
Wang M Q. Lead isotope geochemical prospecting method and its application[J]. Geogeochemistry, 1991(6):37-40,43.
|
| [60] |
汪明启, 高玉岩. 利用铅同位素研究金属矿床地气物质来源:甘肃蛟龙掌铅锌矿床研究实例[J]. 地球化学, 2007, 36(4):391-399.
|
| [60] |
Wang M Q, Gao Y Y. Tracing source of geogas with lead isotopes:A case study in Jiaolongzhang Pb-Zn deposit,Gansu Province[J]. Geochemistry, 2007, 36(4):391-399.
|
| [61] |
李中兰, 崔学军, 刘红英, 等. 铅同位素方法在隐伏矿深度与资源量定量预测中的应用研究——以北祁连西段寒山金矿为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2007, 31(4):441-451.
|
| [61] |
Li Z L, Cui X J, Liu H Y, et al. Application of Pb isotope for quantitative forecasting of blind ore deposits:A case study from the Hanshan gold deposit in the Northwestern Qilian Orogenic Belt[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2007, 31(4):441-451.
|
| [62] |
崔学军, 李中兰, 朱炳泉, 等. 铅同位素在矿产资源评价中的应用——以甘肃省鹰嘴山金矿区为例[J]. 矿床地质, 2008, 27(1):88-100.
|
| [62] |
Cui X J, Li Z L, Zhu B Q, et al. Application of Pb isotopes to evaluation of mineral resources:A case study of Yingzuishan gold deposit,Gansu Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2008, 27(1):88-100.
|
| [63] |
Zhang X C, Spiro B, Halls C, et al. Sediment-hosted disseminated gold deposits in Southwest Guizhou, PRC:Their geological setting and origin in relation to mineralogical, fluid inclusion, and stable-isotope characteristics[J]. International Geology Review, 2003, 45(5):407-470.

|
| [64] |
Hu R Z, Su W C, Bi X W, et al. Geology and geochemistry of Carlin-type gold deposits in China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2002, 37(3):378-392.

|
| [65] |
刘建中, 夏勇, 张兴春, 等. 层控卡林型金矿床矿床模型——贵州水银洞超大型金矿[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2008, 16(3):1-5.
|
| [65] |
Liu J Z, Xia Y, Zhang X C, et al. Model of strata karlin-type gold deposit:The shuiyindong super-scale gold deposit[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2008, 16(3):1-5.
|
| [66] |
Spycher N F, Reed M H. Evolution of a broadlands-type epithermal ore fluid along alternative P-T paths:Implications for the transport and deposition of base, precious, and volatile metals[J]. Economic Geology. 1989, 84(2):328-359.

|
| [67] |
Wang X Q, Cheng Z Z, Lu Y X, et al. Nanoscale metals in earthgas and mobile forms of metals in overburden in wide-spaced regional exploration for giant deposits in overburden terrains[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1997, 58(1):63-72.

|
| [68] |
Wang X Q, Xie X J, Ye S Y, et al. Concepts for geochemical gold exploration based on the abundance and distribution of ultrafine gold[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1995, 55(1/3):93-101.

|
| [69] |
苏航, 陈功新, 邢林啸, 等. 冀中坳陷典型地热田前缘晕元素特征及其对地热学意义[J]. 有色金属:矿山部分, 2021, 73(3):88-97.
|
| [69] |
Su H, Chen G X, Xing L X, et al. Characteristics of the front halo elements of typical geothermal fields in Jizhong depression and their geothermal significance[J]. Nonferrous Metals:Mining Section, 2021, 73(3):88-97.
|
| [70] |
王小春. 微细浸染型金矿中As Sb Hg Ti Ba元素的找矿指示意义[J]. 矿产与地质, 1992, 6(4):307-312.
|
| [70] |
Wang X C. Indicator signifcance of As,Sb,Hg,Ti and Ba for the micro-disseminated type gold deposits[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 1992, 6(4):307-312.
|
| [71] |
Schuster E. The behavior of mercury in the soil with special emphasis on complexation and adsorption processes-A review of the literature[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 1991, 56(1):667-680.

|
| [72] |
Yin Y J, Herbert E A, Huang P, et al. Adsorption/Desorption isotherms of Hg(II) by soil[J]. Soil Science, 1997, 162(1):35-45.

|
| [73] |
Li R H, Wang X Q, Yang L Q, et al. The characteristic of microstructural deformation of gold bearing pyrite in Jiaodong:The links between nanoscale gold enrichment and crystal distortion[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 122:103495

|
| [74] |
韩志轩, 张必敏, 乔宇, 等. 隐伏铜矿区土壤微细粒测量有效性实验——以江西通江岭铜矿为例[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(6):977-986.
|
| [74] |
Han Z X, Zhang B M, Qiao Y, et al. Validity experiments of fine-grained soil geochemical survey for exploring concealed copper deposits:A case study in the Tongjiangling copper deposit,Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2020, 41(6):977-986.
|
| [1] |
WAN Tai-Ping, ZHANG Li, LIU Han-Liang. Regional geochemical characteristics and metallogenic prospect area prediction of strategic mineral antimony in the Eerguna block, Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1179-1188. |
| [2] |
WANG Hui-Yan, PENG Min, MA Hong-Hong, ZHANG Fu-Gui. Ecological risk assessment of cultivated land in typical areas with high heavy metal background values in Guizhou Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 1109-1117. |
|
|
|
|

