|
|
|
| Analysis of 3D ground-borehole TEM response characteristics and rapid positioning method for anomalous bodies |
ZHAO You-Chao1( ), ZHANG Jun1,2( ), ZHANG Jun1,2( ), FAN Tao3, YAO Wei-Hua3, YANG Yang1,4, SUN Huai-Feng1,4 ), FAN Tao3, YAO Wei-Hua3, YANG Yang1,4, SUN Huai-Feng1,4 |
1. Geotechnical and Structural Engineering Research Center, Shandong University, Jinan 250061, China
2. Shandong Provincial Communications Planning and Design Institute, Jinan 250031, China
3. Xi'an Research Institute of China Coal Technology & Engineering Group, Xi'an 710077, China
4. Advanced Exploration and Transparent City Innovation Center, Shandong Research Institute of Industrial Technology, Jinan 250061, China |
|
|
|
|
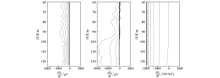
Abstract Through systematic forward modeling and analysis of a 3D geoelectric model containing anomalous bodies, this study proposed a rapid positioning method of anomalous bodies based on the ground-borehole transient electromagnetic (TEM) method. The analysis of the forward modeling response laws of the 3D geoelectric model containing anomalous bodies shows that the zero points of the X and Y component curves and the extreme points of the Z component curve of a pure anomaly field correspond well to the depths of the anomalous bodies; the morphologies of the X and Y component curves are basically unchanged when the sizes, resistivity, and burial depths of the anomalous bodies change but change when the orientations of anomalous bodies change. On this basis, this study proposed the following method to rapidly position anomalous bodies using the ground-borehole TEM method. First, determine the depths of anomalous bodies according to the zero points of the X and Y curves. Next, determine the quadrants (within 90°) of anomalous bodies according to the morphologies of the X and Y component curves. Finally, position anomalous bodies within 45° of boreholes according to the morphologies of the X+Y or X-Y component curves. Numerical experiments show that the positioning results of models of anomalous bodies with different orientations are consistent with those of the model designed in this study. As further verified using the ground-borehole TEM measured data of a mining area in northern Shaanxi, the inference that there is a water-filled goaf to the northwest of the borehole obtained using the method proposed in this study well agrees with the actual situation.
|
|
Received: 27 September 2021
Published: 28 June 2022
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
ZHANG Jun
E-mail: 201914579@mail.sdu.edu.cn;1035058515@qq.com
|
|
|
|
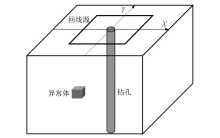
|
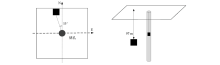
Schematic diagram of model
|

| 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | 模型4 | | 埋深/m | 50 | 50 | 50/100/150 | 50 | | ρ异常体/(Ω·m) | 10/50/100 | 10 | 10 | 10 | | 水平方位角/(°) | 45 | 45 | 45 | 45/135/225/315 | | 尺寸/m | 2 | 2/4/6 | 2 | 2 | | ρ围岩/(Ω·m) | 1 000 | 1 000 | 1 000 | 1 000 | 异常体与钻孔
水平间距/m | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
|
3-D model forward parameters
|
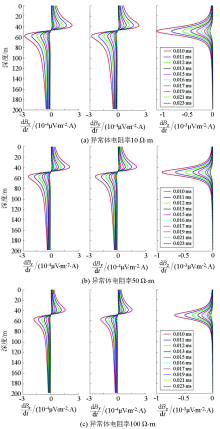
|
Response curves of different target resistivity models
|
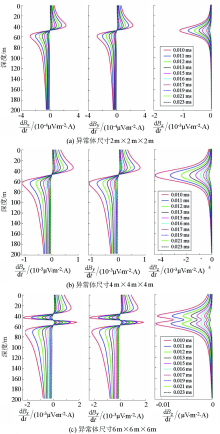
|
Response curves of different target size
|
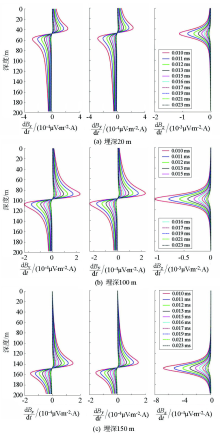
|
Response curves of different depth of target
|
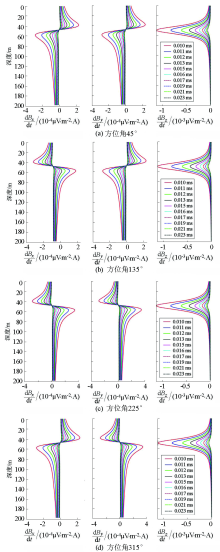
|
Response curves of different target azimuth
|
|
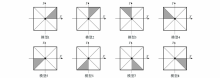
Schematic diagram of regional division
|

| 区域 | 幅值 | 区域 | 幅值 | | 1 | |dBx/dt|>|dBy/dt| | 5 | |dBx/dt|>|dBy/dt| | | 2 | |dBx/dt|<|dBy/dt| | 6 | |dBx/dt|<|dBy/dt| | | 3 | |dBx/dt|<|dBy/dt| | 7 | |dBx/dt|<|dBy/dt| | | 4 | |dBx/dt|>|dBy/dt| | 8 | |dBx/dt|>|dBy/dt| |
|
Comparison of the amplitude of X and Y components
|

| 纯异常曲线形态 | 象限 | X-Y/X+Y曲线形态 | 区域 | | X:反“S”型,Y:反“S”型 | 第一 | X-Y:反“S”型 | 1 | | X:反“S”型,Y:反“S”型 | 第一 | X-Y:“S”型 | 2 | | X:“S”型,Y:反“S”型 | 第二 | X+Y:反“S”型 | 3 | | X:“S”型,Y:反“S”型 | 第二 | X+Y:“S”型 | 4 | | X:“S”型,Y:“S”型 | 第三 | X-Y:“S”型 | 5 | | X:“S”型,Y:“S”型 | 第三 | X-Y:反“S”型 | 6 | | X:反“S”型,Y:“S”型 | 第四 | X+Y:“S”型 | 7 | | X:反“S”型,Y:“S”型 | 第四 | X+Y:反“S”型 | 8 |
|
Regional positioning of target
|
|
Schematic diagram of target azimuth
|
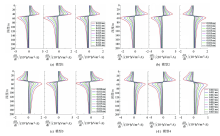
|
-1 Pure abnormal response curves of 8 models
|
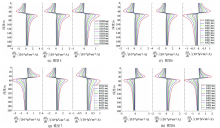
|
-2 Pure abnormal response curves of 8 models
|
|
The results of target positioning
|
|
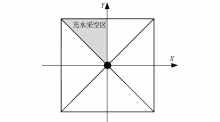
Schematic diagram of the location of the goaf
|
|
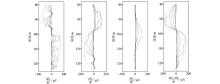
Total field response curve of measured data
|
|
Pure abnormal field response curve of the measured data
|
|
The results of water-filled goaf positioning
|
| [1] |
朴化荣. 电磁测深法原理[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990.
|
| [1] |
Piao H R. Principle of electromagnetic sounding[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1990.
|
| [2] |
Irvine R J. Drillhole TEM surveys at Thalanga, Queensland[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 1987, 18: 285-293.

|
| [3] |
Xue G Q, Qin K Z, Li X, et al. Discovery of a Large-scale porphyry molybdenum deposit in tibet through a modified TEM exploration method[J]. Journal of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, 2012, 17(1): 19-25.

|
| [4] |
Yang D, Oldenburg D W. Three-dimensional inversion of airborne time-domain electromagnetic data with applications to a porphyry deposit[J]. Geophysics, 2012, 77(2): B23-B34.
|
| [5] |
Ezersky M. TEM study of the geoelectrical structure and groundwater salinity of the Nahal Hever sinkhole site, Dead Sea shore, Israel[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2011, 75(1): 99-112.

|
| [6] |
Keydar S D. Application of seismic diffraction imaging for detecting near-surface inhomogeneities in the Dead Sea area[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2010, 71(2): 47-52.

|
| [7] |
李术才, 刘斌, 孙怀凤, 等. 隧道施工超前地质预报研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(6):1090-1113.
|
| [7] |
Li S C, Liu B, Sun H F, et al. State of ART and trends of advanced geological prediction in tunnel construction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(6): 1090-1113.
|
| [8] |
薛国强, 李貅. 瞬变电磁隧道超前预报成像技术[J]. 地球物理学报, 2008, 51(3):894-900.
|
| [8] |
Xue G Q, Li X. The technology of TEM tunnel prediction imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2008, 51(3): 894-900.
|
| [9] |
李术才, 孙怀凤, 李貅, 等. 隧道瞬变电磁超前预报平行磁场响应探测方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(7):1309-1318.
|
| [9] |
Li S C, Sun H F, Li X, et al. Advanced geology prediction with parallel transient electromagnetic detection in tunneling[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(7): 1309-1318.
|
| [10] |
李貅, 薛国强, 李术才, 等. 瞬变电磁隧道超前预报方法与应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013.
|
| [10] |
Li X, Xue G Q, Li S C, et al. The method and application of transient electromagnetic in tunnel prediction[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2013.
|
| [11] |
Dyck A V. Drill-hole electromagnetic methods[M]// Electromagnetic Methods in Applied Geophysics. Tulsa: Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 1991.
|
| [12] |
牛之链. 时间域电磁法原理[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2007.
|
| [12] |
Niu Z L. Principle of time domain electromagnetic[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2007
|
| [13] |
Woods D V. A model study of the Crone borehole pulse electromagnetic (PEM) system[R]. Ontario: Queen’s University, 1975.
|
| [14] |
Eaton P A, Hohmann G W. The influence of a conductive host on two-dimensional borehole transient electromagnetic responses[J]. Geophysics, 1984, 49(7): 861-869.

|
| [15] |
West R C, Ward S H. The borehole transient electromagnetic response of a three-dimensional fracture zone in a conductive half-space[J]. Geophysics, 1988, 53(11): 1469-1478.

|
| [16] |
Buselli G, Lee S K. Modelling of drill-hole TEM responses from multiple targets covered by a conductive overburden[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 1996, 27: 2-3, 141-153.
|
| [17] |
李建慧, 刘树才, 焦险峰, 等. 地—井瞬变电磁法三维正演研究[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2015, 50(3):556-564.
|
| [17] |
Li J H, Liu S C, Jiao X F, et al. Three-dimensional forward modeling for surfaceborehole transient electromagnetic method[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2015, 50(3): 556-564.
|
| [18] |
Dyck A V, West G F. The role of simple computer models in interpretations of wide-band, drill-hole electromagnetic surveys in mineral exploration[J]. Geophysics, 1984, 49(7): 957-980.

|
| [19] |
Bishop J R, Lewis J G, Macnae J C. Down-hole electromagnetic surveys at Renison Bell, Tasmania[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 1987, 18(3): 265-277.

|
| [20] |
孟庆鑫, 潘和平. 地—井瞬变电磁响应特征数值模拟分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(3):1046-1053.
|
| [20] |
Meng Q X, Pan H P. Numerical simulation analysis of surface-hole TEM responses[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 2012, 55(3): 1046-1053.
|
| [21] |
徐正玉, 杨海燕, 邓居智, 等. 回线源三维地—井瞬变电磁法FDTD数值模拟[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2015, 12(3):327-332.
|
| [21] |
Xu Z Y, Yang H Y, Deng J Z, et al. Three-dimensions FDTD numerical simulation on the down-hole TEM field with a loop source[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2015, 12(3): 327-332.
|
| [22] |
葛德彪, 闫玉波. 电磁波时域有限差分方法[M].2版. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2005.
|
| [22] |
Ge D B, Yan Y B. Finite-difference time-domain method for electromagnetic waves[M].2 ed. Xi'an: Xidian University Press, 2005.
|
| [23] |
孙怀凤, 李貅, 李术才, 等. 考虑关断时间的回线源激发TEM三维时域有限差分正演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(3):1049-1064.
|
| [23] |
Sun H F, Li X, Li S C, et al. Three-dimensional FDTD modeling of TEM excited by loop source considering ramp time[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 2013, 56(3): 1049-1064.
|
| [24] |
姚伟华, 王鹏, 李明星, 等. 三分量地—孔瞬变电磁法积水采空区探测试验[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2019, 47(5):54-62.
|
| [24] |
Yao W H, Wang P, Li M X, et al. Experimental study of three-component down-hole TEM for detecting water-filled goaf[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2019, 47(5): 54-62.
|
| [1] |
HE Shuai, YANG Bing-Nan, RUAN Shuai, LI Yong-Gang, HAN Yao-Fei, ZHU Da-Wei. Fine Interpretation of the exploration results of diamond-bearing rock masses in Maping area, Guizhou using the 3D AMT forward modeling and inversion technologies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3): 618-627. |
| [2] |
GUO Chu-Feng, ZHANG Shi-Hui, LIU Tian-You. 3D magnetic field forward modeling by finite-infinite element coupling method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3): 726-736. |
|
|
|
|

