|
|
|
| A data decoupling analysis of different devices in time-domain IP sounding |
LI Zhong-Ping1,2( ), HAO Feng-Yun3, WU Hong-Fei4, ZHANG Rui-Fang5, ZHU Zhao-Ming2, JIA Quan-Shan5, LIU Shuang1 ), HAO Feng-Yun3, WU Hong-Fei4, ZHANG Rui-Fang5, ZHU Zhao-Ming2, JIA Quan-Shan5, LIU Shuang1 |
1. School of Geophysics and Spatial Information, China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), Wuhan 430074, China
2. Shandong Zhengyuan Geological Exploration Institute, China General Administration of Metallurgical Geology, Jinan 250014, China
3. Habahe Jinba Mining Co. Ltd., Aertai 836700, China
4. Aertai Zhengyuan International Mining Co. Ltd., Aertai 836700, China
5. 273 Geological Brigade of Shandong Nuclear Industry, Yantai 264000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study aims to eliminate the electromagnetic coupling interference in IP sounding. Based on the theory that frequency-and time-domain data can be mutually converted, this study achieved rapid decoupling while retaining the IP information to the greatest extent by using decoupling methods including static IP inversion, the full waveform IP inversion of Cole-Cole parameters, and delay inversion. This study investigated a gold deposit in Yinan County, Shandong Province and conducted the inversion of time-domain IP sounding data before and after decoupling. The results are as follows. The electromagnetic coupling effect of symmetrical quadrupole devices and unconventional electrode array increases with an increase in the distance between adjacent electrodes, and its influencing depth is mostly less than 150 m in the inversion results of time-domain IP sounding; the electromagnetic coupling interference produced by the unconventional electrode array that adopts a collinear device of dislocation multipoles (tripoles, quadrupoles, and dipoles) is apparently greater than that of symmetrical quadrupole devices and monopole-dipole devices; noncollinear monopole-dipole devices generate slight electromagnetic coupling effect in the process of time-domain IP sounding.
|
|
Received: 05 July 2021
Published: 21 June 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|
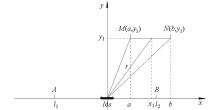
|
Schematic diagram of transmitting dipole AB and receiving dipole MN on uniform half space
|

| 矿区 | 装置类型 | 最大供电极距/m | 电极排列方式 | | 金场 | 对称四极 | AB=1 200 | 共线 | | 对称四极 | AB=1800 | 共线 | | 对称四极 | AB=4000 | 共线 | | 非常规电极排列 | AB=4000 | 共线 | | 夏家沟 | 单极—偶极 | 隔离系数n=19,
MN=50 | 不共线 |
|
Device type, maximum power supply pole distance and electrode arrangement
|
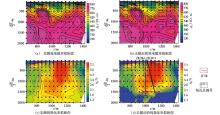
|
Results after decoupling of measured data of time domain IP sounding of symmetrical quadrupole device (ABmax=4 000 m) in section 28 of Jinchang mining area of Yinan Gold Mine
|
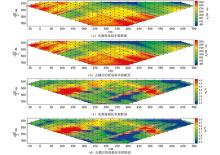
|
Results after decoupling of measured data of time domain IP sounding of monopole dipole device in Section 7 of copper mine in Xiajiagou area
|
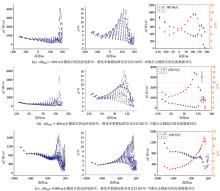
|
Comparison of standard deviation of inversion results before and after different AB decoupling in symmetrical quadrupole IP sounding of section 28
|
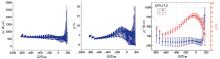
|
Comparison of standard deviations of inversion results before and after decoupling of unconventional electrode IP soundings on section 28 and point 1079.47
|

|
Comparison of the standard deviation of the inversion results before and after the decoupling of the monopole-dipole IP sounding on section 7 and point -20
|

| 装置类型 | 最大供电极距/m | 去耦前反演结果相对去耦后反演结果标准偏差与二者平均值的百分比/% | | | | | 对称四极 | AB=1200 | 0.01 | 16.16 | 3.89 | 0 | 141.4 | 3.29 | | 对称四极 | AB=1800 | 0.19 | 18.49 | 4.53 | 0 | 141.5 | 3.72 | | 对称四极 | AB=4000 | 0 | 29.75 | 4.11 | 0 | 141.5 | 4.25 | | 非常规 | AB=4000 | 0.03 | 28.42 | 5.49 | 0 | 141.5 | 17.79 | | 单极—偶极 | 隔离系数n=19,MN=50 m | 0.04 | 9.59 | 3.43 | 0 | 13.99 | 0.87 |
|
Comparison of inversion results before decoupling and after decoupling standard deviation fluctuation statistics
|
| [1] |
李水平, 司建涛, 程华, 等. 时间域激电测深在坦桑尼亚金矿床勘查中的应用例析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(2):588-595.
|
| [1] |
Li S P, Si J T, Cheng H, et al. Application of time domain IP sounding in the exploration of gold deposits in Tanzania[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(2): 588-595.
|
| [2] |
王振武, 吴运军, 高顺宝, 等. 综合物探在西藏仲巴县帮布勒地区找矿中的应用和意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(6):202-210.
|
| [2] |
Wang Z W, Wu Y J, Gao S B, et al. Application and significance of comprehensive geophysical prospecting in bangbule area, Zhongba County, Tibet[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(6): 202-210.
|
| [3] |
孙仁斌, 汪洋, 楚丽霞, 等. 关于时间域激发极化法中视极化率负值的判别和应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(1):273-278.
|
| [3] |
Sun R B, Wang Y, Chu L X, et al. Discrimination and application of negative apparent polarizability in time domain induced polarization method[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(1): 273-278.
|
| [4] |
曹金华, 李桐林, 刘永亮, 等. 激电和电磁效应对三维复电阻率正演结果的影响研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(2):579-583.
|
| [4] |
Cao J H, Li T L, Liu Y L, et al. Study on the influence of IP and EM effects on forward modeling results of 3D complex resistivity[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(2): 579-583.
|
| [5] |
肖都, 郭鹏, 林品荣, 等. 相位激电法在强干扰区的应用试验[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2016, 38(5):593-597.
|
| [5] |
Xiao D, Guo P, Lin P R, et al. Application test of phase induced polarization method in strong interference area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration Calculation Technology, 2016, 38(5): 593-597.
|
| [6] |
李栋, 杨帆, 高鹏举. 相位激电法电磁耦合效应的校正[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(2):316-320.
|
| [6] |
Li D, Yang F, Gao P J. Correction of electromagnetic coupling effect in phase induced polarization method[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2019, 10(2): 316-320.
|
| [7] |
刘卫强, 吕庆田, 林品荣, 等. 多周期全波形激电抗干扰数据处理方法及在大规模探测中的应用分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(10):3934-3949.
|
| [7] |
Liu W Q, Lyu Q T, Lin P R, et al. Multi period full waveform IP anti-jamming data processing method and its application in large-scale exploration[J]. Chinese J.Geophys., 2019, 62(10): 3934-3949.
|
| [8] |
王书民, 雷达. 相位激电法(偶极—偶极)单频电磁耦合校正方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2002, 26(1):57-59,63.
|
| [8] |
Wang S M, Lei D. Single frequency electromagnetic coupling correction method of phase induced polarization method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2002, 26(1): 57-59,63.
|
| [9] |
郭鹏, 肖都, 石福升, 等. 相位激电和时间域激电对激电效应响应关系研究[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2014, 36(6):679-683.
|
| [9] |
Guo P, Xiao D, Shi F S, et al. Study on the response of phase induced polarization and time domain induced polarization to induced polarization effect[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration Calculation Technology, 2014, 36(6): 679-683.
|
| [10] |
钟湘琴, 付国红, 程辉, 等. 直接消除电磁耦合的发送端去耦方法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(2):848-854.
|
| [10] |
Zhong X Q, Fu G H, Cheng H, et al. The decoupling method of transmitter for direct elimination of electromagnetic coupling[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(2): 848-854.
|
| [11] |
孙仁斌, 楚丽霞, 王宁, 等. 时间域激电测深二维反演在内蒙古兴和盆地贫水区找水勘查中若干案例研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(1):387-394.
|
| [11] |
Sun R B, Chu L X, Wang N, et al. Several case studies of two-dimensional inversion of time domain IP sounding in water exploration in water poor area of Xinghe basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(1): 387-394.
|
| [12] |
李忠平. 非常规电极排列在大功率激电测深中的应用[J]. 长春工程学院学报:自然科学版, 2009, 10(1):84-86.
|
| [12] |
Li Z P. Application of unconventional electrode array in high power IP sounding[J]. Journal of Changchun Institute of Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2009, 10(1): 84-86.
|
| [13] |
柳建新, 唐冬梅. 激电中梯装置感应耦合的自适应抑制方法[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 47(12):4122-4131.
|
| [13] |
Liu J X, Tang D M. Adaptive suppression method for inductive coupling of induced polarization intermediate ladder device[J]. Journal of Central South University:Natural Science Edition, 2016, 47(12): 4122-4131.
|
| [14] |
潘剑伟, 占嘉诚, 洪涛, 等. 地面核磁共振方法和高密度电阻率法联合找水[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(3):253-262.
|
| [14] |
Pan J W, Zhan J C, Hong T, et al. Combined water exploration by surface nuclear magnetic resonance and high density resistivity method[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(3): 253-262.
|
| [15] |
曹平华, 罗润林. 时间域激电数据进行频谱参数的反演方法及应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(5):1008-1011.
|
| [15] |
Cao P H, Luo R L. Inversion method and application of spectral parameters using time domain IP data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(5): 1008-1011.
|
| [16] |
Dey A, Morrison H F. Electromagnetic coupling in frequency and time domain induced polarization surveys over multilayered earth[J]. Geophysics, 1973, 38(2): 380-405.

|
| [17] |
何继善, 熊彬, 鲍力知, 等. 激发极化观测中电磁耦合的时间特性[J]. 地球物理学报, 2008, 51(3):886-893.
|
| [17] |
He J S, Xiong B, Bao L Z, et al. Time characteristics of electromagnetic coupling in induced polarization observation[J]. Chinese J.Geophys., 2008, 51(3): 886-893.
|
| [18] |
何继善, 熊彬, 鲍力知, 等. 直接消除电磁耦合的斩波去耦方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2006, 49(6):1843-1850.
|
| [18] |
He J S, Xiong B, Bao L Z, et al. Chopper decoupling method for direct elimination of electromagnetic coupling[J]. Chinese J.Geophys., 2006, 49(6):1843-1850.
|
| [19] |
Fullagar P K, Zhou B Z, Bourne B. EM-coupling removal from time-domain_IP data[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 2000, 31(1/2): 134-139.

|
| [20] |
李建华, 林品荣, 何畏, 等. 基于全波形采样的激电多信息提取方法研究与应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(1):132-138.
|
| [20] |
Li J H, Lin P R, He W, et al. Research and application of IP multi information extraction method based on full waveform sampling[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020, 35(1): 132-138.
|
| [21] |
Kaufman A A, Keller G V. Frequency and transient soundings[M]. Elsevier Science Publ Co. Inc., 1983.
|
| [1] |
ZHANG Jing-Si, BIAN Li-En, WANG Jun, LIU Teng, YU Ya. The application of pre-stack hydrocarbon detection to Y structure of Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(5): 1215-1220. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Zhen-Yu, WANG Da-Yong, LEI Da, WANG Gang, YAO Da-Wei, ZHU Wei. Research on electromagnetic coupling effects in CSAMT receiving system[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(2): 376-382. |
|
|
|
|

