|
|
|
| Application of broadband data-based extended elastic impedance inversion method in Paleogene lithology prediction of areas at a low exploration level in Lufeng 22 subsag |
XIAO Zhang-Bo( ), LEI Yong-Chang, YU Jun-Qing, WU Qiong-Ling, YANG Chao-Qun ), LEI Yong-Chang, YU Jun-Qing, WU Qiong-Ling, YANG Chao-Qun |
| Shenzhen Branch of CNOOC China Limited,Shenzhen 518054,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Areas at a low exploration level have drawn increasing attention as future contributors to reserves growth.However,they are facing many geophysical challenges.Lufeng 22 subsag is such an area due to few drilled wells and insufficient geological data.In this case,it is difficult to build an accurate low-frequency inversion model using traditional logging data or stacking velocity.Moreover,affected by ghost reflections,low- and high-frequency waves in marine seismic data are suppressed.As a result,the bandwidth of seismic data is decreased,thus reducing the authenticity and accuracy of inversion results.To address these problems,this paper firstly obtained seismic data with broader bandwidth using broadband processing technology.Then,it built a low-frequency model for areas without well control using colored inversion combined with a high-precision velocity field obtained through tomographic imaging.Based on this,this paper predicted the distribution of source rocks and reservoirs using the extended elastic impedance inversion method.This technology was applied to the Lufeng 22 subsag,enabling the successful prediction of the distribution of high-quality source rocks and favorable reservoir areas.Thick layers of middle-deep lacustrine-facies source rocks as well as oil and gas have been discovered during the drilling of the first exploration well in the subsag,which started the exploration in the new area.This study indicates that this technology effectively improves the reliability of seismic inversion of middle-deep layers using broadband data and can well identify lithology utilizing low-frequency information,thus serving as an effective technology for the lithology prediction of areas at a low exploration level.
|
|
Received: 12 March 2021
Published: 28 June 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|
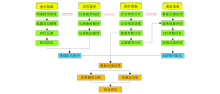
|
Technical flowchart of well-free broadband seismic inversion
|
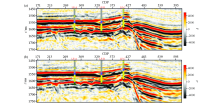
|
Comparison of seismic section processed by conventional(a) and broadband processing(b) methods
|
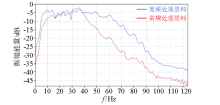
|
Comparison between amplitude spectrum of conventional seismic data and broadband seismic data
|
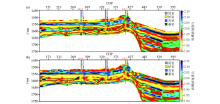
|
Comparison of seismic data inversion section processed by conventional(a) and broadband(b) processing methods
|
|
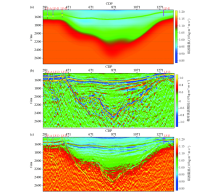
Construction flowchart of low frequency constraint model
a—initial low frequency constraint model;b—relative low frequency constraint model;c—final low frequency constraint model
|
|
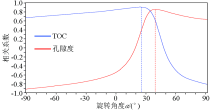
Analysis of the correlation between EEI and TOC,porosity at different rotation angles
|
|
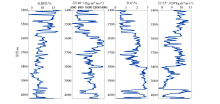
Comparison of EEI curve,TOC curve and porosity curve with different rotation angles
|
|
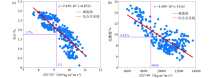
Extended elastic impedance EEI corresponding to TOC(a) and porosity(b)
|

| 钻井编号 | 深度/m | TOC/% | Ro/% | S1+S2/(mg·g-1) | Tmax/℃ | HI/(mg·g-1) | 母质类型 | 烃源岩质量 | | LF-B-1 | 3145~3227 | 1.93~7.75 | — | 7.51~28.82 | 434~440 | 302~606 | Ⅱ1-Ⅱ2 | 好—很好 | | LF-A-1 | 3651~3747 | 2.96~3.70 | 0.59~0.71 | 2.96~3.90 | 431~436 | 306~359 | Ⅰ-Ⅱ1 | 好—很好 | | LF-G-1 | 3798~3882 | 1.75~2.33 | 0.72~0.77 | 7.88~11.61 | 460~471 | 462~569 | Tmax过高 | 好 | | LF-T-1 | 3417~3576 | 1.70~2.45 | 0.58~0.66 | 7.40~20.60 | 437~441 | 408~557 | Ⅰ-Ⅱ1 | 中—好 |
|
Geochemical parameters of source rocks in WC4 of Lufeng sag
|
|
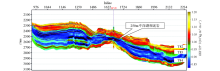
Extended elastic impedance EEI(25°) inversion section
|
|
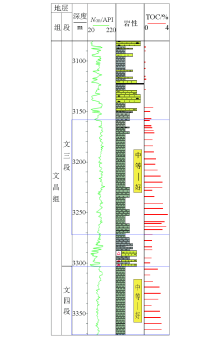
Geochemical logging map of LF-H well
|
|
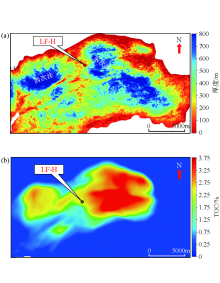
Distrbution map of source rock in WC3+WC4
a—source rock thickness map of WC3+WC4;b—TOC content distribution of source rocks in WC3+WC4
|
|
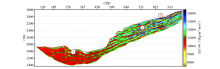
Extended elastic impedance EEI(40°) inversion section
|
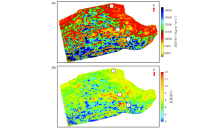
|
Plane distribution characteristics of sandstone
a—the root mean square attribute of sandstone;b—plane distribution of sandstone porosity
|
| [1] |
叶云飞, 刘春成, 刘志斌, 等. 海上宽频地震反演方法及其在南海深水区的应用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(2):65-70.
|
| [1] |
Ye Y F, Liu C C, Liu Z B, et al. Analysis of marine broadband seismic data inversion and application in deep water of South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(2):65-70.
|
| [2] |
李庆忠. 论地震约束反演的策略[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 1998, 33(4):423-438.
|
| [2] |
Li Q Z. On strategy of seismic restricted inversion[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 1998, 33(4):423-438.
|
| [3] |
乔凤远, 覃素华, 张宁, 等. 地震低频信息在反演中的作用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2018, 53(S2):266-271.
|
| [3] |
Qiao F Y, Qin S H, Zhang N, et al. Low-frequency seismic information applied in inversion[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2018, 53(S2):266-271.
|
| [4] |
张彬彬, 张军华, 吴永亭. 地震数据低频信号保护与拓频方法研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(3):1139-1144.
|
| [4] |
Zhang B B, Zhang J H, Wu Y T, et al. Research on protection and extension for seismic low frequencies[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(3):1139-1144.
|
| [5] |
叶云飞, 刘春成. 深水宽频地震资料反演及地震属性分析[J]. 海洋工程装备与技术, 2019, 6(S1):268-271.
|
| [5] |
Ye Y F, Liu C C. Advantage analysis and application of broadband seismic data in deep-water[J]. Ocean Engineering Equipment and Technology, 2019, 6(s1):268-271.
|
| [6] |
王艳冬, 王小六, 桑淑云, 等. 渤海海域水平拖缆数据宽频处理关键技术[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2020, 55(1):10-16.
|
| [6] |
Wang Y D, Wang X L, Sang S Y, et al. Key techniques for broadband processing of plane streamer data in Bohai Sea[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2020, 55(1):10-16.
|
| [7] |
Vitale G, Greco L, D’Alessandro A, et al. Bandwidth extension of a 4.5 Hz geophone for seismic monitoring purpose[C]// IEEE International Conference on Environmental Engineering, 2018:1-5.
|
| [8] |
王华忠, 郭颂, 周阳. “两宽一高”地震数据下的宽带波阻抗建模技术[J]. 石油物探, 2019, 58(1):1-8.
|
| [8] |
Wang H Z, Guo S, Zhuo Y. Broadband acoustic impedance model building for broadband, wide-azimuth, and high-density seismic data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019, 58(1):1-8.
|
| [9] |
马劲风, 王学军, 谢言光, 等. 波阻抗反演中低频分量构建的经验与技巧[J]. 石油物探, 2000, 39(1):27-34.
|
| [9] |
Ma J F, Wang X J, Xie Y G, et al. Experience and skill of constructing low frequency components in impedance inversion[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2000, 39(1):27-34.
|
| [10] |
叶云飞, 崔维, 张益明, 等. 低频模型对波阻抗反演结果定量解释的影响[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(6):32-36.
|
| [10] |
Ye Y F, Cui W, Zhang Y M, et al. Impacts of low-frequency models on the quantitative interpretation of acoustic impedance inversion[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014, 26(6):32-36.
|
| [11] |
文晓涛, 杨吉鑫, 李雷豪, 等. 低频稀疏双约束宽频带地震阻抗反演[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(5):45-52.
|
| [11] |
Wen X T, Yang J X, Li L H, et al. Low-frequency sparse double-constrained broadband seismic impedance inversion[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(5):45-52.
|
| [12] |
Cambois G. AVO inversion and elastic impedance[J]. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 1949, 19(1):2484.
|
| [13] |
刘道理, 李坤, 杨登锋, 等. 基于频变AVO反演的深层储层含气性识别方法[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(1):48-54.
|
| [13] |
Liu D L, Li K, Yang D F, et al. A gas-bearing property identification method for deep reservoirs based on frequency-dependent AVO inversion[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(1):48-54.
|
| [14] |
李坤, 印兴耀, 宗兆云, 等. 频变黏弹性流体因子叠前地震F-AVA反演方法[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 43(1):23-32.
|
| [14] |
Li K, Yin X Y, Zong Z Y, et al. Estimating frequency-dependent viscoelastic fluid indicator from pre-stack F-AVA inversion[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum:Edition of Natural Science, 2019, 43(1):23-32.
|
| [15] |
Connolly P. Elastic impedance[J]. Leading Edge, 1999, 18(4):438-438.

|
| [16] |
宗兆云, 孙乾浩, 陈维涛, 等. 惠西南地区储层含油气性叠前地震固液解耦识别[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(4):56-64.
|
| [16] |
Zong Z Y, Sun Q H, Chen W T, et al. Pre-stack seismic solid-liquid decoupling identification for oil-gas reservoirs in southwestern Huizhou area[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(4):56-64.
|
| [17] |
Whitcombe D N. Elastic impedance normalization[J]. Geophysics, 2012, 67(1):60-62.

|
| [18] |
Whitcombe D N, Connolly P A, Reagan R L, et al. Extended elastic impedance forfluid and lithology prediction[J]. Geophysics, 2002, 67(1):63-67.

|
| [19] |
秦德海, 李德郁, 蔡纪琰, 等. 扩展弹性阻抗在低孔、低渗砂砾岩储层物性预测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018, 33(5):2148-2152.
|
| [19] |
Qin D H, Li D Y, Cai J Y, et al. Application of extended elastic impedance for physical property prediction of low porosity and low permeability glutenite reservoirs[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 33(5):2148-2152.
|
| [20] |
时磊, 刘俊州, 董宁, 等. 扩展弹性阻抗反演技术在致密砂岩薄储层含气性预测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(2):346-351.
|
| [20] |
Shi L, Liu J Z, Dong N, et al. Extended elastic impedance inversion technology and its application to the tight and thin sandstone reservoir[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(2):346-351.
|
| [21] |
刘晓晶, 印兴耀, 吴国忱, 等. 基于基追踪弹性阻抗反演的深部储层流体识别方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(1):277-286.
|
| [21] |
Liu X J, Yin X Y, Wu G C, et al. Identification of deep reservoir fluids based on basis pursuit inversion for elastic impedance[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(1):277-286.
|
| [22] |
宗兆云, 印兴耀, 张繁昌. 基于弹性阻抗贝叶斯反演的拉梅参数提取方法研究[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2011, 46(4):598-604,609.
|
| [22] |
Zong Z Y, Yin X Y, Zhang F C. Elastic impedance Bayesian inversion for lame parameters extracting[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2011, 46(4):598-604,609.
|
| [23] |
朱筱敏, 葛家旺, 吴陈冰洁, 等. 珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷深层砂岩储层特征及主控因素[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(s1):69-80.
|
| [23] |
Zhu X M, Ge J W, Wu C B J, et al. Reservoir characteristics and main controlling factors of deep sandstone in Lufeng sag,Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(s1):69-80.
|
|
|
|

