|
|
|
| A study of deep metallogenic prediction and metallogenic mechanism of the Dachang deposit in Guangxi |
LIU Cheng-Gong1,2, JING Jian-En1,3( ), JIN Sheng1,3, WEI Wen-Bo1,3 ), JIN Sheng1,3, WEI Wen-Bo1,3 |
1. School of Geophysics and Information Technology, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China
2. China National Petroleum Pipeline Engineering Corporation, Langfang 065000, China
3. State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract As one of the large tin-polymetallic deposits in the world, the Dachang deposit has complicated metallogenic mechanism and rich hidden mineral resources. In order to detect the distribution and study mineralization mechanism of the concealed deposits around the cage and cover rock in the Dachang ore district, the authors finely processed the audio magnetoelectromagnetic data covering the Dachang ore district, and obtained a two-dimensional electrical structure model within the depth of 3 km. According to the results of resistivity model, the location of concealed granite and orebody was determined. Granite is characterized by high resistance and is buried at a depth of about 1.5 km, with the formation of ridge uplift along the fault structure. The low-resistivity orebody is located in the middle Devonian strata at the top of granite, so it is inferred that the orebody was developed from the granite at the bottom, which indicates that granite has an obvious ore-controlling effect. According to the zonal characteristics of copper in the near place and tin in the distant place as well as anomalies of metallic elements in the Dachang ore district, it is most possible to find skarn type Zn-Cu deposits and Sb-W deposits. The research shows that, in the late Cretaceous period, the magmatic hydrothermal fluids of the middle and lower crust together with a small amount of upper mantle rose to the shallow Devonian strata of the crust along the basement fault in the NW direction, and then formed mineralization with surrounding rocks through crystallization differentiation.
|
|
Received: 11 August 2020
Published: 29 April 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
JING Jian-En
E-mail: jje2008@cugb.edu.cn
|
|
|
|
12])
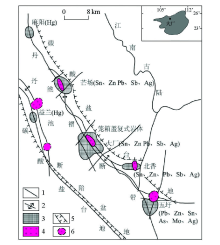
1—fracture; 2—anticline; 3—ore field; 4—granite;5—basin boundary; 6—speculative granite
">
|
Structure and mineral distribution map of The Danchi metallogenic belt (modified by Xu Xinhuang et al[12])
1—fracture; 2—anticline; 3—ore field; 4—granite;5—basin boundary; 6—speculative granite
|
16])
">
|
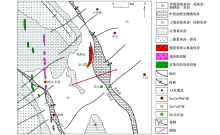
Geological structure and mineral distribution map of the large factory ore field (modified by Cai Minghai et al[16])
|

|
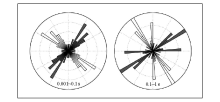
Apparent resistivity and phase diagram of some measuring points
|
|
Strike analysis results for the specific corresponding frequency band
|
|
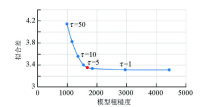
Model roughness and fitting difference curve of inversion by different regularization factors
|
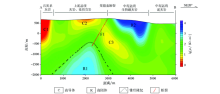
|
Resistivity map of Dachang deposit
|
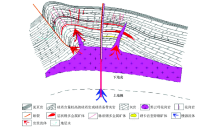
|
Metallogenic model diagram of Dachang deposit(modified by data of the 215 geological team,Guangxi province)
|
| [1] |
朱裕生, 梅燕雄, 吕志诚, 等. 隐(盲)矿床的预测找矿和深部勘探[J]. 中国地质, 2007,34(1):43-48.
|
| [1] |
Zhu Y S, Mei Y X, Lyu Z C, et al. Predictive prospecting and deep exploration of hidden (blind) deposits[J]. Geology of China, 2007,34(1):43-48.
|
| [2] |
滕吉文, 杨立强, 姚敬金, 等. 金属矿产资源的深部找矿、勘探与成矿的深层动力过程[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007,22(2):317-334. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.02.001.
|
| [2] |
Teng J W, Yang L Q, Yao J J, et al. Deep disscover ore,exploration and exploitation for metal mineral resocrces and its deep dynamical process of formation[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007,22(2):317-334. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.02.001.
|
| [3] |
吕庆田, 史大年, 汤井田, 等. 长江中下游成矿带及典型矿集区深部结构探Sino-Probe-03年度进展综述[J]. 地球学报, 2011,32(3):257-268. http://doi.org/10.3975/cagsb.2011.03.01.
|
| [3] |
Lyu Q T, Shi D N, Tang J T, et al. Probing on deep structure of middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze metallogenic belt and typical ore concentration area:a review of annual progress of Sino-Probe-03[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2011,32(3):257-268. http://doi.org/10.3975/cagsb.2011.03.01.
|
| [4] |
陈毓川, 黄民智, 徐珏, 等. 大厂锡石——硫化物多金属矿带地质特征及成矿系列[J]. 地质学报, 1985,59(3):228-240.
|
| [4] |
Chen Y C, Huang M Z, Xu J, et al. Geological characteristics of the Dachang cassiterite sulphide deposits and metallogenetic series[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1985,59(3):228-240.
|
| [5] |
陈毓川, 李光岑, 黄民智, 等. 大厂锡矿地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993.
|
| [5] |
Chen Y C, Li G C, Huang M Z, et al. Tin Deposits of Dachang [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1993.
|
| [6] |
韩发, 赵汝松, 沈建忠, 等. 大厂锡多金属矿床地质及成因[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997.
|
| [6] |
Han F, Zhao R S, Shen J Z, et al. Geology and origin of ores in the Dachang tin-polymetallic ore field[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1997.
|
| [7] |
范森葵. 广西大厂锡多金属矿田地质特征、矿床模式与成矿预测[D]. 长沙:中南大学, 2011.
|
| [7] |
Fan S K. The geological characteristics, genesis and metallogenic prediction of Dachang tin-polymetallic ore field,Guangxi[D]. Changsha:Central South University, 2011.
|
| [8] |
李春平, 吴德成, 蔡明海. 大厂矿田长坡矿床深部区叠瓦状构造控矿特征及找矿前景分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2006,20(6):623-627. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2006.06.009.
|
| [8] |
Li C P, Wu D C, Cai M H. Control of mineralization of imbricate structure and prospecting perspective in deep part in the Changpo deposit of Dachang ore filed[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2006,20(6):623-627. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2006.06.009.
|
| [9] |
唐龙飞, 谭泽模, 黄敦杰, 等. 大厂矿田硫同位素特征及找矿预测[J]. 有色金属(矿山部分), 2014,66(6):30-35.10. http://doi.org/3969/j.issn.1671-4172.2014.06.008.
|
| [9] |
Tang L F, Tan Z M, Huang D J, et al. Sulfur isotope characteristics and prospecting prediction of Dachang tin-polymetallic ore field[J]. Nonferrous Metals(Mine Section), 2014,66(6):30-35. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-4172.2014.06.008.
|
| [10] |
Farquharson C G, Craven J A. Three-dimensional inversion of magnetotelluric data for mineral exploration:An example from the McArthur River uranium deposit,Saskatchewan,Canada [J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2009,68:450-458. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2008.02.002.
|
| [11] |
邓居智, 陈辉, 殷长春, 等. 九瑞矿集区三维电性结构研究及找矿意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015,58(12):4465-4477. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:DQWX.0.2015-12-012.
|
| [11] |
Deng J Z, Chen H, Yin C C, et al. Three-dimensional electrical structures and significance for mineral exploration in the Jiujiang-Ruichang District[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015,58(12):4465-4477. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:DQWX.0.2015-12-012.
|
| [12] |
徐新煌, 蔡建明, 陈洪德, 等. 广西丹池矿带锡多金属矿床地质地球化学特征及成矿作用[J]. 成都地质学院学报, 1991,18(4):12-25.
|
| [12] |
Xu X H, Cai J M, Chen H D, et al. Geological and geochemical characteristics and mineralization of the tin-polymetallic deposit in the Danchi ore belt, Guangxi[J]. Journal of Chengdu Geology, 1991,18(4):12-25.
|
| [13] |
陈洪德, 曾允浮, 李孝全. 丹池晚古生代盆地的沉积和构造演化[J]. 沉积学报, 1989,7(4):85-96. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:CJXB.0.1989-04-006.
|
| [13] |
Chen H D, Zeng Y F, Li X Q. Sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the late Paleozoic danchi basin[J]. Acta Sedigenica Sinica, 1989,7(4):85-96. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:CJXB.0.1989-04-006.
|
| [14] |
韩发, Hutchinson R W. 大厂锡多金属矿床热液喷气沉积成因的证据——含矿建造及热液沉积岩[J]. 矿床地质, 1989,8(3):25-37. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:KCDZ.0.1989-02-003.
|
| [14] |
Han F, Hutchinson R W. Evidence for exhalative origin for rocks and ores of the Dachang tin polymetallic field: the ore-bearing formation and hydrothermal exhalative sedimentary rocks[J]. Mineral Deposits Beijing, 1989,8(3):25-37. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:KCDZ.0.1989-02-003.
|
| [15] |
高志斌. 广西丹池地区锡多金属成矿带控矿因素及成矿预测[J]. 地质与勘探, 1988(8):18-24. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:DZKT.0.1988-08-002.
|
| [15] |
Gao Z B. Ore-controlling factors and metallogenic prediction of tin polymetallic metallogenic belt in Danchi, Guangxi [J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1988(8):18-24. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:DZKT.0.1988-08-002.
|
| [16] |
蔡明海, 梁婷, 吴德成, 等. 广西丹池成矿带构造特征及其控矿作用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2004,40(6):5-10. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2004.06.002.
|
| [16] |
Cai M H, Liang T, Wu D C, et al. Structural characteristics and ore-controlling effect of the Danchi metallogenic belt, in Guangxi Province[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2004,40(6):5-10. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2004.06.002.
|
| [17] |
张小路, 王钟. 广西大厂隐伏岩体重力反演及其地质意义[J]. 桂林冶金地质学院学报, 1990,10(4):417-425. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:GLGX.0.1990-04-011.
|
| [17] |
Zhang X L, Wang Z. The gravity inversion and its geological significance for the hidden granite body in Dachang,Guangxi[J]. Journal of Guilin Institute of Technology, 1990,10(4):417-425. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:GLGX.0.1990-04-011.
|
| [18] |
张小路, 王钟. 大厂矿田地面磁测资料综合处理研究报告[R]. 桂林:桂林工学院, 2006.
|
| [18] |
Zhang X L, Wang Z. Research report on comprehensive processing of surface magnetic survey data in Dachang ore field [R]. Guilin:Guilin Institute of Technology, 2006.
|
| [19] |
孙德梅, 刘心铸, 彭聪, 等. 应用重磁资料研究广西芒场——大厂成矿带的地质构造及隐伏岩体预测[D]. 北京:中国地质科学院矿床地质研究所, 1994.
|
| [19] |
Sun D M, Liu X Z, Peng C, et al. Application of gravity and magnetic data to study the geological structure and hidden rock mass prediction of the Mangchang-Dachang metallogenic belt in Guangxi[D]. Beijing:Institute of Mineral Deposits, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1994.
|
| [20] |
蔡明海, 何龙清, 刘国庆, 等. 广西大厂锡矿田侵入岩SHRIMP锫石U-Pb年龄及其意义[J]. 地质论评, 2006,52(3):409-414. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:YSXB.0.2011-06-005.
|
| [20] |
Cai M H, He L Q, Liu G Q, et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of the intrusive rocks in the Dachang tin-polymetallic ore field, Guangxi and their geological significance[J]. Geological Review, 2006,52(3):409-414. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:YSXB.0.2011-06-005.
|
| [21] |
Cai M H, Mao J W, Liang T, et al. The origin of the tongkeng-changpo tin deposit, Dachang metal district,Guangxi,China:clues from fluid inclusions and He istope systematics[J]. Miner Deposit, 2007,42:613-626. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-007-0127-5.
|
| [22] |
黄启勋. 南盘江—右江成矿带广西境域深部找矿潜力分析[J]. 南方国土资源, 2015(9):30-32. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:GXDZ.0.2015-09-011.
|
| [22] |
Huang Q X. Analysis of deep prospecting potential in Guangxi region of Nanpanjiang-Youjiang metallogenic belt[J]. Southern Land Resources, 2015(9):30-32. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:GXDZ.0.2015-09-011.
|
| [23] |
Groom R W, Bailey R C. Decomposition of magnetotelluric impedance tensors in the presence of local three-dimensionalgalvanic distortion[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,1989,94(B2): 1913-1925. http://doi.org/10.1029/JB094iB02p01913.
|
| [24] |
蔡军涛, 陈小斌. 大地电磁资料精细处理和二维反演解释技术研究(二)——反演数据极化模式选择[J]. 地球物理学报, 2010,53(11):2703-2714. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:DQWX.0.2010-11-021.
|
| [24] |
Cai J T, Chen X B. Refined techniques for data processing and two-dimensional inversion in magnetotelluricⅡ:Which data polarization mode should be used in 2D inversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010,53(11):2703-2714. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:DQWX.0.2010-11-021.
|
| [25] |
Rodi W, Mackie R L. Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2D magnetotelluric inversion[J]. Geophysics, 2001,66(1):174-187. http://doi.org/10.1190/1.1444893.
|
| [26] |
Hansen P C. Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of the L-curve[J]. SIAM Review, 1992,34(4):561-580. http://doi.org/10.2307/2132628.
|
| [27] |
王钟, 张小路, 罗润林, 等. 大厂锡多金属矿区深边部找矿中的TEM异常特征[J]. 桂林工学院学报, 2009,29(3):303-309. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2009.03.005.
|
| [27] |
Wang Z, Zhang X L, Luo R L, et al. Abnormal characteristic of TEM response for prospecting depth and margin area of Tin-polymetallic deposit in Dachang[J]. Journal of Guilin Institute of Technology, 2009,29(3):303-309. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2009.03.005.
|
| [28] |
Fu M, Changkakoti A, Krouse H R, et al. An oxygen, hydrogen, sulfur, and carbon isotope study of carbonate-replacement skarn tin deposits of the Dachang tin field, China [J]. European Geological, 1991,86:1683-1703. http://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.86.8.1683.
|
| [29] |
Fu M, Kwak T A P, Mernagh T P, et al. Fluid inclusion studies of zoning in the Dachang tin-polymetallic ore field,People's Republic of China [J]. European Geological, 1993,88,283-300. http://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.88.2.283.
|
| [30] |
范森葵, 伍永田, 王明艳. 广西大厂矿田矿床分布规律与找矿方向[J]. 矿产与地质, 2008,22(6):520-524. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2008.06.009.
|
| [30] |
Fan S K, Wu Y T, Wang M Y. Distributing rules of deposits and prospecting direction in Dachang mining area,Guangxi[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2008,22(6):520-524. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2008.06.009.
|
| [31] |
邹锡青, 王思源. 广西芒场锡多金属矿田稳定同位素组成对矿床成因探讨[J]. 广西地质, 1993,6(2):63-69.
|
| [31] |
Zou X Q, Wang S Y. Discussion on the stable isotopic composition and genesis of Mengchang Tin-polymetallicore field ore deposit in Guangxi[J]. Geology of Guangxi, 1993,6(2):63-69.
|
| [32] |
秦德先, 陈健文, 田毓龙. 广西大厂长坡锡矿床地质及成因[J]. 有色金属矿产与勘查, 1998,7(3):146-151. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:YSJS.0.1998-03-003.
|
| [32] |
Qin D X, Chen J W, Tian Y L. Geology and genesis of changpo tin deposit, Dachang, Guangxi[J]. Nonferrous Mineral Exploration, 1998,7(3):146-151. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:YSJS.0.1998-03-003.
|
| [33] |
成永生, 黄惠明. 广西大厂矿田泥盆系地层地球化学及其成矿指示[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013,23(9):2649-2658. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:ZYXZ.0.2013-09-037.
|
| [33] |
Cheng Y S, Huang H M. Geochemical characteristics and mineralization indication of Devonian strata in Dachang ore field, Guangxi[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013,23(9):2649-2658. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:ZYXZ.0.2013-09-037.
|
| [34] |
蔡明海, 梁婷, 吴德成. 广西大厂锡多金属矿田亢马矿床地质特征及成矿时代[J]. 地质学报, 2005,79(2):262-268. http://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.02.012.
|
| [34] |
Cai M H, Liang T, Wu D C. Geological characteristics and ore-forming time of the kangma deposit in the Dachang tin-polymetallic ore field, Guangxi[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005,79(2): 262-268. http://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.02.012.
|
| [35] |
刘成功. 南盘江盆地壳幔电性结构研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2020.
|
| [35] |
Liu C G. Studying on the electrical structure of the crust In the Nanpanjiang basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2020.
|
| [36] |
Guo J, Zhang R Q, Sun W D, et al. Genesis of tin-dominant polymetallic deposits in the Dachang district, South China:Insights from cassiterite U-Pb ages and trace element compositions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018,95:863-879. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.03.023.
|
| [37] |
梁婷, 王登红, 屈文俊, 等. 广西铜坑锡多金属矿黄铁矿的Re-0s同位素组成及成矿物质来源示踪[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2009,31(3):230-235. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2009.03.002.
|
| [37] |
Liang T, Wang D H, Qu W J, et al. Re-Os isotope composition and source of ore-forming material of pyrite in Tongkeng Tin-pollmetallic[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2009,31(3): 230-235. http://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2009.03.002.
|
| [38] |
梁婷, 王登红, 李华芹, 等. 广西大厂石榴石REE含量及Sm-Nd同位素定年[J]. 西北大学学报:自然科学版, 2011,41(4):676-681. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:XBDZ.0.2011-04-025.
|
| [38] |
Liang T, Wang D H, Li H Q, et al. REE geochemistry and Sm—Nd isotope age of garnet from the Dachang,Guangxi[J]. Journal of Northwest University:Natural Science Edition, 2011,41(4): 676-681. http://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:XBDZ.0.2011-04-025.
|
| [39] |
Jiang S Y, Han F, Shen J Z, et al. Chemical and Rb-Sr,Sm-Nd isotopic systematics of tourmaline from the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore deposit, Guangxi Province,P.R.China[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999,157(1-2):49-67. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-2541(98)00200-9.
|
| [40] |
Wang D H, Chen Y C, Chen W, et al. Dating of the Dachang superlarge tin-polymetallic deposit in Guangxi and its implication for the genesis of the No.100 orebody[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2004,78(2):452-458. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-6724.2004.tb00153.x.
|
| [41] |
Cheng Y S, Hu R Z. Lead isotope composition and constraints on origin of Dafulou ore deposit,Guangxi,China[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013,23(6):1766-1773. http://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62659-X.
|
| [1] |
YOU Xi-Ran, ZHANG Ji-Feng, SHI Yu. Artificial neural network-based transient electromagnetic imaging[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1206-1214. |
| [2] |
HE Sheng, WANG Wan-Ping, DONG Gao-Feng, NAN Xiu-Jia, WEI Feng-Feng, BAI Yong-Yong. Application of the opposing-coils transient electromagnetic method in urban geological surveys[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1379-1386. |
|
|
|
|

